codeforces 732
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Polycarp urgently needs a shovel! He comes to the shop and chooses an appropriate one. The shovel that Policarp chooses is sold for kburles. Assume that there is an unlimited number of such shovels in the shop.
In his pocket Polycarp has an unlimited number of "10-burle coins" and exactly one coin of r burles (1 ≤ r ≤ 9).
What is the minimum number of shovels Polycarp has to buy so that he can pay for the purchase without any change? It is obvious that he can pay for 10 shovels without any change (by paying the requied amount of 10-burle coins and not using the coin of r burles). But perhaps he can buy fewer shovels and pay without any change. Note that Polycarp should buy at least one shovel.
The single line of input contains two integers k and r (1 ≤ k ≤ 1000, 1 ≤ r ≤ 9) — the price of one shovel and the denomination of the coin in Polycarp's pocket that is different from "10-burle coins".
Remember that he has an unlimited number of coins in the denomination of 10, that is, Polycarp has enough money to buy any number of shovels.
Print the required minimum number of shovels Polycarp has to buy so that he can pay for them without any change.
117 3
9
237 7
1
15 2
2
#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:102400000,102400000")
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <stack>
#include <map> using namespace std; #define For(i,j,n) for(int i=j;i<=n;i++)
#define mst(ss,b) memset(ss,b,sizeof(ss));
#define lson o<<1
#define rson o<<1|1 typedef long long LL;
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
template<class T> void read(T&num) {
char CH; bool F=false;
for(CH=getchar();CH<'0'||CH>'9';F= CH=='-',CH=getchar());
for(num=0;CH>='0'&&CH<='9';num=num*10+CH-'0',CH=getchar());
F && (num=-num);
}
int stk[70], tp;
template<class T> inline void print(T p) {
if(!p) { puts("0"); return; }
while(p) stk[++ tp] = p%10, p/=10;
while(tp) putchar(stk[tp--] + '0');
putchar('\n');
} const LL mod=1e9+7;
const double PI=acos(-1.0);
const int inf=1e9;
const int N=1e4+120;
const int maxn=3e5+200;
const double eps=1e-12; int main()
{
int k,r,ans=10;
read(k);read(r);
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++)
{
if(k*i%10==0||k*i%10==r){ans=i;break;}
}
cout<<ans;
return 0;
}
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Recently a dog was bought for Polycarp. The dog's name is Cormen. Now Polycarp has a lot of troubles. For example, Cormen likes going for a walk.
Empirically Polycarp learned that the dog needs at least k walks for any two consecutive days in order to feel good. For example, if k = 5and yesterday Polycarp went for a walk with Cormen 2 times, today he has to go for a walk at least 3 times.
Polycarp analysed all his affairs over the next n days and made a sequence of n integers a1, a2, ..., an, where ai is the number of times Polycarp will walk with the dog on the i-th day while doing all his affairs (for example, he has to go to a shop, throw out the trash, etc.).
Help Polycarp determine the minimum number of walks he needs to do additionaly in the next n days so that Cormen will feel good during all the n days. You can assume that on the day before the first day and on the day after the n-th day Polycarp will go for a walk with Cormen exactly k times.
Write a program that will find the minumum number of additional walks and the appropriate schedule — the sequence of integersb1, b2, ..., bn (bi ≥ ai), where bi means the total number of walks with the dog on the i-th day.
The first line contains two integers n and k (1 ≤ n, k ≤ 500) — the number of days and the minimum number of walks with Cormen for any two consecutive days.
The second line contains integers a1, a2, ..., an (0 ≤ ai ≤ 500) — the number of walks with Cormen on the i-th day which Polycarp has already planned.
In the first line print the smallest number of additional walks that Polycarp should do during the next n days so that Cormen will feel good during all days.
In the second line print n integers b1, b2, ..., bn, where bi — the total number of walks on the i-th day according to the found solutions (ai ≤ bi for all i from 1 to n). If there are multiple solutions, print any of them.
3 5
2 0 1
4
2 3 2
3 1
0 0 0
1
0 1 0
4 6
2 4 3 5
0
2 4 3 5
#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:102400000,102400000")
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <stack>
#include <map> using namespace std; #define For(i,j,n) for(int i=j;i<=n;i++)
#define mst(ss,b) memset(ss,b,sizeof(ss));
#define lson o<<1
#define rson o<<1|1 typedef long long LL;
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
template<class T> void read(T&num) {
char CH; bool F=false;
for(CH=getchar();CH<'0'||CH>'9';F= CH=='-',CH=getchar());
for(num=0;CH>='0'&&CH<='9';num=num*10+CH-'0',CH=getchar());
F && (num=-num);
}
int stk[70], tp;
template<class T> inline void print(T p) {
if(!p) { puts("0"); return; }
while(p) stk[++ tp] = p%10, p/=10;
while(tp) putchar(stk[tp--] + '0');
putchar('\n');
} const LL mod=1e9+7;
const double PI=acos(-1.0);
const int inf=1e9;
const int N=1e4+120;
const double eps=1e-12;
const int maxn=510;
int n,k,a[maxn];
int main()
{
read(n);read(k);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)read(a[i]);
int ans=0;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++)
{
if(a[i-1]+a[i]<k)
{
ans=ans+k-a[i-1]-a[i];
a[i]=k-a[i-1];
}
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)printf("%d ",a[i]);
return 0;
}
//贪心水题
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Vasiliy spent his vacation in a sanatorium, came back and found that he completely forgot details of his vacation!
Every day there was a breakfast, a dinner and a supper in a dining room of the sanatorium (of course, in this order). The only thing that Vasiliy has now is a card from the dining room contaning notes how many times he had a breakfast, a dinner and a supper (thus, the card contains three integers). Vasiliy could sometimes have missed some meal, for example, he could have had a breakfast and a supper, but a dinner, or, probably, at some days he haven't been at the dining room at all.
Vasiliy doesn't remember what was the time of the day when he arrived to sanatorium (before breakfast, before dinner, before supper or after supper), and the time when he left it (before breakfast, before dinner, before supper or after supper). So he considers any of these options. After Vasiliy arrived to the sanatorium, he was there all the time until he left. Please note, that it's possible that Vasiliy left the sanatorium on the same day he arrived.
According to the notes in the card, help Vasiliy determine the minimum number of meals in the dining room that he could have missed. We shouldn't count as missed meals on the arrival day before Vasiliy's arrival and meals on the departure day after he left.
The only line contains three integers b, d and s (0 ≤ b, d, s ≤ 1018, b + d + s ≥ 1) — the number of breakfasts, dinners and suppers which Vasiliy had during his vacation in the sanatorium.
Print single integer — the minimum possible number of meals which Vasiliy could have missed during his vacation.
3 2 1
1
1 0 0
0
1 1 1
0
1000000000000000000 0 1000000000000000000
999999999999999999
#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:102400000,102400000")
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <stack>
#include <map> using namespace std; #define For(i,j,n) for(int i=j;i<=n;i++)
#define mst(ss,b) memset(ss,b,sizeof(ss));
#define lson o<<1
#define rson o<<1|1 typedef long long LL;
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
template<class T> void read(T&num) {
char CH; bool F=false;
for(CH=getchar();CH<'0'||CH>'9';F= CH=='-',CH=getchar());
for(num=0;CH>='0'&&CH<='9';num=num*10+CH-'0',CH=getchar());
F && (num=-num);
}
int stk[70], tp;
template<class T> inline void print(T p) {
if(!p) { puts("0"); return; }
while(p) stk[++ tp] = p%10, p/=10;
while(tp) putchar(stk[tp--] + '0');
putchar('\n');
} const LL mod=1e9+7;
const double PI=acos(-1.0);
const int inf=1e9;
const int N=1e4+120;
const double eps=1e-12;
const int maxn=510;
LL a,b,c;
int main()
{
read(a);read(b);read(c);
LL mmax=max(a,max(b,c));
LL ans=0;
if(a>=b&&a>=c)
{
if(a==c)
{
if(b==a)ans=0;
else ans=a-b-1;
}
else
{
if(a==b)ans=a-c-1;
else ans=a-b-1+a-c-1;
}
}
else if(b>=a&&b>=c)
{
if(b==c)
{
if(a==b)ans=0;
else ans=b-a-1;
}
else ans=b-a-1+b-c-1;
}
else if(c>=a&&c>=b)
{
if(c==a)
{
if(b==c)ans=0;
else ans=c-b-1;
}
else ans=c-a-1+c-b-1;
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}
/*
题意:给出早中晚的吃饭的次数,随意什么时候来的和走的,问最少错过了多少顿饭
思路:分情况讨论贪心啊; */
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Vasiliy has an exam period which will continue for n days. He has to pass exams on m subjects. Subjects are numbered from 1 to m.
About every day we know exam for which one of m subjects can be passed on that day. Perhaps, some day you can't pass any exam. It is not allowed to pass more than one exam on any day.
On each day Vasiliy can either pass the exam of that day (it takes the whole day) or prepare all day for some exam or have a rest.
About each subject Vasiliy know a number ai — the number of days he should prepare to pass the exam number i. Vasiliy can switch subjects while preparing for exams, it is not necessary to prepare continuously during ai days for the exam number i. He can mix the order of preparation for exams in any way.
Your task is to determine the minimum number of days in which Vasiliy can pass all exams, or determine that it is impossible. Each exam should be passed exactly one time.
The first line contains two integers n and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 105) — the number of days in the exam period and the number of subjects.
The second line contains n integers d1, d2, ..., dn (0 ≤ di ≤ m), where di is the number of subject, the exam of which can be passed on the day number i. If di equals 0, it is not allowed to pass any exams on the day number i.
The third line contains m positive integers a1, a2, ..., am (1 ≤ ai ≤ 105), where ai is the number of days that are needed to prepare before passing the exam on the subject i.
Print one integer — the minimum number of days in which Vasiliy can pass all exams. If it is impossible, print -1.
7 2
0 1 0 2 1 0 2
2 1
5
10 3
0 0 1 2 3 0 2 0 1 2
1 1 4
9
5 1
1 1 1 1 1
5
-1
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int maxn=1e5+10;
int n,m,a[maxn],d[maxn],p[maxn];
int check(int x)
{
for(int i=1;i<=x;i++)if(d[i])p[d[i]]=i;
int sum=0,cnt=0;
for(int i=1;i<=x;i++)
{
if(d[i]==0){sum++;continue;}
if(p[d[i]]!=i)sum++;
else
{
if(sum<a[d[i]])return 0;
else
{
cnt++;
sum=sum-a[d[i]];
}
}
}
if(cnt==m)return 1;
return 0;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)scanf("%d",&d[i]);
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)scanf("%d",&a[i]);
if(m>n)printf("-1\n");
else
{
int l=1,r=n;
while(l<=r)
{
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
if(check(mid))r=mid-1;
else l=mid+1;
}
if(r==n&&check(r)==0)printf("-1\n");
else printf("%d\n",r+1);
}
return 0;
}
/*
题意:给出哪天哪课可以考试通过,和每科需要复习的天数,问最少需要多少天可以通过所有的科目; 思路:二分最少天数,然后贪心的check是否能通过所有考试
*/
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
The ICM ACPC World Finals is coming! Unfortunately, the organizers of the competition were so busy preparing tasks that totally missed an important technical point — the organization of electricity supplement for all the participants workstations.
There are n computers for participants, the i-th of which has power equal to positive integer pi. At the same time there are m sockets available, the j-th of which has power euqal to positive integer sj. It is possible to connect the i-th computer to the j-th socket if and only if their powers are the same: pi = sj. It is allowed to connect no more than one computer to one socket. Thus, if the powers of all computers and sockets are distinct, then no computer can be connected to any of the sockets.
In order to fix the situation professor Puch Williams urgently ordered a wagon of adapters — power splitters. Each adapter has one plug and one socket with a voltage divider between them. After plugging an adapter to a socket with power x, the power on the adapter's socket becomes equal to 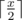 , it means that it is equal to the socket's power divided by two with rounding up, for example
, it means that it is equal to the socket's power divided by two with rounding up, for example 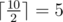 and
and 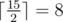 .
.
Each adapter can be used only once. It is possible to connect several adapters in a chain plugging the first to a socket. For example, if two adapters are plugged one after enother to a socket with power 10, it becomes possible to connect one computer with power 3 to this socket.
The organizers should install adapters so that it will be possible to supply with electricity the maximum number of computers c at the same time. If there are several possible connection configurations, they want to find the one that uses the minimum number of adaptersu to connect c computers.
Help organizers calculate the maximum number of connected computers c and the minimum number of adapters u needed for this.
The wagon of adapters contains enough of them to do the task. It is guaranteed that it's possible to connect at least one computer.
The first line contains two integers n and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 200 000) — the number of computers and the number of sockets.
The second line contains n integers p1, p2, ..., pn (1 ≤ pi ≤ 109) — the powers of the computers.
The third line contains m integers s1, s2, ..., sm (1 ≤ si ≤ 109) — the power of the sockets.
In the first line print two numbers c and u — the maximum number of computers which can at the same time be connected to electricity and the minimum number of adapters needed to connect c computers.
In the second line print m integers a1, a2, ..., am (0 ≤ ai ≤ 109), where ai equals the number of adapters orginizers need to plug into thei-th socket. The sum of all ai should be equal to u.
In third line print n integers b1, b2, ..., bn (0 ≤ bi ≤ m), where the bj-th equals the number of the socket which the j-th computer should be connected to. bj = 0 means that the j-th computer should not be connected to any socket. All bj that are different from 0 should be distinct. The power of the j-th computer should be equal to the power of the socket bj after plugging in abj adapters. The number of non-zero bj should be equal to c.
If there are multiple answers, print any of them.
2 2
1 1
2 2
2 2
1 1
1 2
2 1
2 100
99
1 6
6
1 0
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int maxn=2e5+10;
int n,m,a[maxn],b[maxn],num=0;
struct node
{
int id,p;
}po[maxn],pe[maxn],ha[maxn];
int cmp(node a,node b){return a.p<b.p;}
map<int,int>mp;
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&po[i].p);
po[i].id=i;
mp[po[i].p]++;
}
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&pe[i].p);
pe[i].id=i;
}
sort(po+1,po+n+1,cmp);
sort(pe+1,pe+m+1,cmp);
int c=0,u=0;
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
int flag=0,temp=pe[i].p,cnt=0;
while(temp>1)
{
if(mp[temp])
{
flag=1;
mp[temp]--;
break;
}
if(temp&1)temp=temp/2+1;
else temp=temp/2;
cnt++;
}
if(temp==1&&flag==0)
{
if(mp[1])flag=1,mp[1]--;
}
if(flag)
{
c++;u+=cnt;
a[pe[i].id]=cnt;
ha[num].p=temp;
ha[num++].id=pe[i].id;
}
}
printf("%d %d\n",c,u);
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)printf("%d ",a[i]);printf("\n");
sort(ha,ha+num,cmp);
int pos=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(ha[pos].p==po[i].p)
{
b[po[i].id]=ha[pos].id;
pos++;
}
else b[po[i].id]=0;
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)printf("%d ",b[i]);
return 0;
}
/*
题意:只有能量值相等才能相连,现在可以让一个插座的能量值/2向上取整;问最多可以连接多少个电脑,在这个状态下需要向下多少次
以及具体的连接情况可操作次数的情况;
思路:贪心就好,从小到大开始/2然后搞搞就好了;
*/
F:
题意:将无向边定向,使得最小的f(x)最大,f(x)表示x节点能到达的节点数目;
思路:可以发现当无向图中有f(x)最小的那个节点是最大的的那个边双连通分量里面的点,贪心可以知道先找边双连通分量,然后所有的点都指向这个边双连通分量;
AC代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=4e5+5;
int n,m,u[maxn],v[maxn],Vis[maxn],vis[maxn];
int low[maxn],pre[maxn],cnt,isbri[maxn],bcc_cnt=0,bcc[maxn];
struct Edge
{
int to,id;
};
vector<Edge>ve[maxn];
int dfs(int cur,int fa)
{
int tep=pre[cur]=++cnt;
int len=ve[cur].size();
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
{
int x=ve[cur][i].to,y=ve[cur][i].id;
if(x==fa)continue;
if(!pre[x])
{
int temp=dfs(x,cur);
tep=min(tep,temp);
if(temp>pre[cur])isbri[y]=1;
}
else tep=min(tep,pre[x]);
}
low[cur]=tep;
return tep;
}
void dfs1(int cur,int fa)
{
vis[cur]=1;
int len=ve[cur].size();
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
{
int x=ve[cur][i].to,y=ve[cur][i].id;
if(x==fa||isbri[y]||vis[x])continue;
bcc[bcc_cnt]++;
Vis[y]=1;
dfs1(x,cur);
}
}
pair<int,int> pa[maxn];
int flag[maxn];
void dfs2(int cur,int fa)
{
if(vis[cur])return ;
vis[cur]=1;
int len=ve[cur].size();
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
{
int x=ve[cur][i].to,y=ve[cur][i].id;
if(x==fa)continue;
if(!flag[y])
{
if(isbri[y])pa[y].first=x,pa[y].second=cur;
else pa[y].first=cur,pa[y].second=x;
flag[y]=1;
}
dfs2(x,cur);
}
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&u[i],&v[i]);
ve[u[i]].push_back((Edge){v[i],i});
ve[v[i]].push_back((Edge){u[i],i});
}
if(m==n-1)
{
printf("1\n");
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)printf("%d %d\n",u[i],v[i]);
return 0;
}
cnt=0;
dfs(1,0);
int ans=0,p;
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
if(isbri[i]||Vis[i])continue;
bcc[++bcc_cnt]=1;
dfs1(u[i],0);
if(bcc[bcc_cnt]>ans)
{
ans=bcc[bcc_cnt];
p=u[i];
}
}
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
dfs2(p,0);
printf("%d\n",ans);
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)printf("%d %d\n",pa[i].first,pa[i].second);
return 0;
}
codeforces 732的更多相关文章
- codeforces 732/D 二分
给出考试时间和考试需要准备的时间,问最早考完所有科目的时间 二分答案 NlogN 二分抄神犇的写法 感觉挺舒服的嘻嘻嘻 #include<bits/stdc++.h> using name ...
- Codeforces Round #732 (Div. 2)【ABCD】
比赛链接:https://codeforces.com/contest/1546 A. AquaMoon and Two Arrays 题意 给出两个大小为 \(n\) 的数组 \(a, b\) ,每 ...
- Codeforces Round #732 (Div.1) 题解
实在是打击人信心的一场比赛啊--一不注意就掉了 50+ 分,rating 没了啊/ll/dk/wq/kk A Weak pretest!!!!!11 /fn/fn/fn 一个很显然的注意点是在交换前后 ...
- CF1545X Codeforces Round #732
A. AquaMoon and Strange Sort 叉人题 如果数字各不相同,只需要统计每个数参与构成的逆序对总数,如果是奇数一定最终朝左,偶数朝右.无意义的数字交换对方向是没有影响的 继续考虑 ...
- codeforces 732E(贪心)
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/732/problem/E 题意:有n台计算机,m个插座,每台计算机有一个值a[i],每个插座有一个值b[i],每个插座最多只能对 ...
- codeforces 732D(二分)
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/732/problem/D 题意:有m门需要过的课程,n天的时间可以选择复习.考试(如果的d[i]为0则只能复习),一门课至少要复 ...
- Codeforces Round #377 (Div. 2)D(二分)
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/732/problem/D 题意: 在m天中要考k个课程, 数组a中有m个元素,表示第a[i]表示第i天可以进行哪门考试,若a[i ...
- Codeforces - 149D 不错的区间DP
题意:有一个字符串 s. 这个字符串是一个完全匹配的括号序列.在这个完全匹配的括号序列里,每个括号都有一个和它匹配的括号 你现在可以给这个匹配的括号序列中的括号染色,且有三个要求: 每个括号只有三种情 ...
- CodeForces - 616C(很有意思的bfs,set,map的使用)
传送门: http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/616/C C. The Labyrinth time limit per test 1 second me ...
随机推荐
- 20个免费的 JavaScript 游戏引擎分享给开发者
这篇文章收集了20个免费的 JavaScript 游戏引擎分享给开发者.这些游戏引擎能够帮助游戏开发人员更快速高效的开发出各种好玩的游戏. 使用 HTML5.CSS3 和 Javascript 可以帮 ...
- mysql整数字段 int bigint smallint tinyint
mysql中int.bigint.smallint和tinyint的区别与长度 未完待续...
- SQLServer ForXmlPath应用
SQLServer ForXmlPath应用 一:ForXmlPath介绍 forXmlPath 是SQL中的forXml语法的一部分,本文主要讲Path模式 ---SQL中FOR XML子句的 ...
- Wifite.py 修正版脚本代码
Kali2.0系统自带的WiFite脚本代码中有几行错误,以下是修正后的代码: #!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """ ...
- Ubuntu 安装WPS
1.到官网下载deb安装包 http://community.wps.cn/download/ 2.安装 sudo dpkg -i wps-office_10.1.0.5672~a21_amd64.d ...
- Android 手机卫士--解析json与消息机制发送不同类型消息
本文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/wuyudong/p/5900800.html,转载请注明源地址. 1.解析json数据 解析json的代码很简单 JSONObject jso ...
- jQuery和ExtJS的timeOut超时问题和event事件处理问题
对jQuery来说,超时可以直接设置timeout参数,并在error事件中捕获第二个参数,如果是“timeout”则表明捕获了超时事件,非常清楚. 例子: $.ajax({ type ...
- 解决Windows 8系统假死的方法
大部分半卡死的现象是因为Dynamic Tick的一个Bug.Dynamic Tick是NT 6.2内核的一个新功能(其实Linux早就有了),原理的话大概是在空闲的时候把CPU完全暂停,来节省电量. ...
- Winform读写App.config文件以及重启程序
//重启主程序 //System.Diagnostics.Process.Start(System.Reflection.Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly().Locatio ...
- yii2 GridView常见操作
作者:白狼 出处:http://www.manks.top/article/yii2_gridview 本文版权归作者,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接,否则 ...
