kubeadm部署高可用版Kubernetes1.21[更新]
环境规划
| 主机名 | IP地址 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| k8s-master01 ~ 03 | 192.168.3.81 ~ 83 | master节点 * 3 |
| k8s-master-lb | 192.168.3.200 | keepalived虚拟IP |
| k8s-node01 ~ 02 | 192.168.3.84 ~ 85 | worker节点 * 2 |
| 配置信息 | 备注 |
|---|---|
| 系统版本 | CentOS 7.6 |
| Docker版本 | 19.03.x |
| Pod网段 | 172.16.0.0/12 |
| Service网段 | 192.168.0.0/16 |
基本环境配置
Kubeadm安装方式自1.14版本以后,安装方法几乎没有任何变化,此文档可以尝试安装最新的k8s集群,centos采用的是7.x版本
K8S官网:https://kubernetes.io/docs/setup/
最新版高可用安装:https://kubernetes.io/docs/setup/production-environment/tools/kubeadm/high-availability/
VIP(虚拟IP)不要和公司内网IP重复,首先去ping一下,不通才可用。VIP需要和主机在同一个局域网内!公有云上搭建VIP是公有云的负载均衡的IP,比如阿里云的内网SLB的地址,腾讯云内网ELB的地址。
服务器基础定义
配置在部署机执行
变量定义
#定义变量:
KUBE_MASTER=(192.168.3.81 192.168.3.82 192.168.3.83)
KUBE_NODE=(192.168.3.84 192.168.3.85)
VIP=192.168.3.200
hosts文件配置:
cat > /etc/hosts << EOF
${KUBE_MASTER[0]} k8s-master01
${KUBE_MASTER[1]} k8s-master02
${KUBE_MASTER[2]} k8s-master03
${KUBE_NODE[0]} k8s-node01
${KUBE_NODE[1]} k8s-node02
${VIP} k8s-vip
EOF
免密配置:
ssh-keygen -t rsa
for i in ${KUBE_MASTER[@]} ${KUBE_NODE[@]} ;do ssh-copy-id -i .ssh/id_rsa.pub $i;done
配置阿里云yum源,安装基本软件
rm -f /etc/yum.repos.d/*
curl -o /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo https://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo
yum install -y yum-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2
yum-config-manager --add-repo https://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
cat <<EOF > /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo
[kubernetes]
name=Kubernetes
baseurl=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64/
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
repo_gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg
EOF
sed -i -e '/mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/d' -e '/mirrors.aliyuncs.com/d' /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo
for ip in ${KUBE_MASTER[@]} ${KUBE_NODE[@]}; do
\scp -r /etc/yum.repos.d/* ${ip}:/etc/yum.repos.d/
yum clean all
yum install -y yum-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2
yum install wget jq psmisc vim net-tools telnet yum-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2 git -y
done
#阿里源:
wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo
wget -P /etc/yum.repos.d/ http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/epel-7.repo
修改主机名
cat >host.txt<<EOF
192.168.3.81,k8s-master01
192.168.3.82,k8s-master02
192.168.3.83,k8s-master03
192.168.3.84,k8s-node01
192.168.3.85,k8s-node02
EOF
for i in $(cat host.txt);do a=$(echo ${i} | awk -F, '{print $1}');b=$(echo ${i} | awk -F, '{print $2}');ssh $a "hostnamectl set-hostname $b";done
#for ip in ${KUBE_MASTER[@]} ${KUBE_NODE[@]}; do
# ssh ${ip} "hostnamectl set-hostname \$(grep \$(hostname -I) /etc/hosts | awk '{print \$2}')"
#done
关闭交换分区
for ip in ${KUBE_MASTER[@]} ${KUBE_NODE[@]}; do
ssh ${ip} "swapoff -a
sed -i '/swap.*swap/d' /etc/fstab
"
done
配置时间同步
for ip in ${KUBE_MASTER[@]} ${KUBE_NODE[@]}; do
ssh ${ip} "yum -y install chrony
sed -i 's/^server/#server/g' /etc/chrony.conf
sed -i '2aserver 2.cn.pool.ntp.org iburst' /etc/chrony.conf
sed -i '2aserver ntp1.aliyun.com iburst' /etc/chrony.conf
systemctl start chronyd
systemctl enable chronyd
"
done
内核配置:
for ip in ${KUBE_MASTER[@]} ${KUBE_NODE[@]}; do
cat > /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf << EOF
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
EOF
scp /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf ${ip}:/etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf
ssh ${ip} "sysctl --system
"
done
所有节点关闭防火墙、selinux、dnsmasq、swap服务器配置如下
for ip in ${KUBE_MASTER[@]} ${KUBE_NODE[@]}; do
systemctl disable --now firewalld
systemctl disable --now dnsmasq
systemctl disable --now NetworkManager
setenforce 0
sed -i 's#SELINUX=enforcing#SELINUX=disabled#g' /etc/sysconfig/selinux
sed -i 's#SELINUX=enforcing#SELINUX=disabled#g' /etc/selinux/config
swapoff -a && sysctl -w vm.swappiness=0
sed -ri '/^[^#]*swap/s@^@#@' /etc/fstab
done
安装ntpdate
for ip in ${KUBE_MASTER[@]} ${KUBE_NODE[@]}; do
rpm -ivh http://mirrors.wlnmp.com/centos/wlnmp-release-centos.noarch.rpm
yum install ntpdate -y
done
for ip in ${KUBE_MASTER[@]} ${KUBE_NODE[@]}; do
ulimit -SHn 65535
\scp /etc/security/limits.conf ${ip}:/etc/security/limits.conf
done
所有节点同步时间。时间同步配置如下:
# 配置时间同步,并加入到crontab
for ip in ${KUBE_MASTER[@]} ${KUBE_NODE[@]}; do
ln -sf /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai /etc/localtime
echo 'Asia/Shanghai' >/etc/timezone
ntpdate time2.aliyun.com
echo '*/5 * * * * /usr/sbin/ntpdate time2.aliyun.com' >/var/spool/cron/root
systemctl restart crond
done
所有节点配置limit
cat >>/etc/security/limits.conf<<EOF
# 末尾添加如下内容
* soft nofile 655360
* hard nofile 131072
* soft nproc 655350
* hard nproc 655350
* soft memlock unlimited
* hard memlock unlimited
EOF
for ip in ${KUBE_MASTER[@]} ${KUBE_NODE[@]}; do
ulimit -SHn 65535
\scp /etc/security/limits.conf ${ip}:/etc/security/limits.conf
done
下载源码文件
cd /root ; git clone https://gitee.com/dukuan/k8s-ha-install.git
升级内核
#CentOS7需要升级,CentOS8可以按需升级系统
#所有节点升级系统并重启,此处升级没有升级内核,下节会单独升级内核:
for ip in ${KUBE_MASTER[@]} ${KUBE_NODE[@]}; do
ssh ${ip} 'yum update -y --exclude=kernel* && reboot'
done
yum update -y --exclude=kernel* && reboot
配置内核
CentOS7 需要升级内核至4.18+,本地升级的版本为4.19:
cd /root
wget http://193.49.22.109/elrepo/kernel/el7/x86_64/RPMS/kernel-ml-devel-4.19.12-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64.rpm
wget http://193.49.22.109/elrepo/kernel/el7/x86_64/RPMS/kernel-ml-4.19.12-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64.rpm
#从master01节点传到其他节点:
cd /root
for i in ${KUBE_MASTER[@]} ${KUBE_NODE[@]};do
scp -r kernel-ml-4.19.12-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64.rpm kernel-ml-devel-4.19.12-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64.rpm $i:/root
done
#所有节点安装内核
for i in ${KUBE_MASTER[@]} ${KUBE_NODE[@]};do
ssh $i 'yum localinstall -y kernel-ml*'
done
#所有节点更改内核启动顺序
for i in ${KUBE_MASTER[@]} ${KUBE_NODE[@]};do
ssh $i '
grub2-set-default 0 && grub2-mkconfig -o /etc/grub2.cfg
grubby --args="user_namespace.enable=1" --update-kernel="$(grubby --default-kernel)"
'
done
#修改完成后检查现在的默认内核是否是4.19
for i in ${KUBE_MASTER[@]} ${KUBE_NODE[@]};do
ssh $i '
grubby --default-kernel
'
done
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# grubby --default-kernel
/boot/vmlinuz-4.19.12-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64
#通过uname -a 看到当前内核是 3.10 需要重启系统让新内核生效
#所有服务器重启,让新内核生效
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# uname -a
Linux k8s-master01 4.19.12-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64 #1 SMP Fri Dec 21 11:06:36 EST 2018 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux
ipvs配置[所有节点安装ipvsadm]
yum install ipvsadm ipset sysstat conntrack libseccomp -y
#所有节点配置ipvs模块,在内核4.19+版本nf_conntrack_ipv4已经改为nf_conntrack,4.18以下使用nf_conntrack_ipv4即可
modprobe -- ip_vs
modprobe -- ip_vs_rr
modprobe -- ip_vs_wrr
modprobe -- ip_vs_sh
modprobe -- nf_conntrack
#配置写入ipvs配置文件:
cat >/etc/modules-load.d/ipvs.conf <<EOF
ip_vs
ip_vs_lc
ip_vs_wlc
ip_vs_rr
ip_vs_wrr
ip_vs_lblc
ip_vs_lblcr
ip_vs_dh
ip_vs_sh
ip_vs_fo
ip_vs_nq
ip_vs_sed
ip_vs_ftp
ip_vs_sh
nf_conntrack
ip_tables
ip_set
xt_set
ipt_set
ipt_rpfilter
ipt_REJECT
ipip
EOF
systemctl enable --now systemd-modules-load.service
# shell
for i in ${KUBE_MASTER[@]} ${KUBE_NODE[@]};do
yum install ipvsadm ipset sysstat conntrack libseccomp -y
modprobe -- ip_vs
modprobe -- ip_vs_rr
modprobe -- ip_vs_wrr
modprobe -- ip_vs_sh
modprobe -- nf_conntrack
cat >/etc/modules-load.d/ipvs.conf <<EOF
ip_vs
ip_vs_lc
ip_vs_wlc
ip_vs_rr
ip_vs_wrr
ip_vs_lblc
ip_vs_lblcr
ip_vs_dh
ip_vs_sh
ip_vs_fo
ip_vs_nq
ip_vs_sed
ip_vs_ftp
ip_vs_sh
nf_conntrack
ip_tables
ip_set
xt_set
ipt_set
ipt_rpfilter
ipt_REJECT
ipip
EOF
systemctl enable --now systemd-modules-load.service
done
内核参数优化
#开启一些k8s集群中必须的内核参数,所有节点配置k8s内核:
for i in ${KUBE_MASTER[@]} ${KUBE_NODE[@]};do
ssh $i '
cat <<EOF > /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
fs.may_detach_mounts = 1
net.ipv4.conf.all.route_localnet = 1
vm.overcommit_memory=1
vm.panic_on_oom=0
fs.inotify.max_user_watches=89100
fs.file-max=52706963
fs.nr_open=52706963
net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_max=2310720
net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_time = 600
net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_probes = 3
net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_intvl =15
net.ipv4.tcp_max_tw_buckets = 36000
net.ipv4.tcp_tw_reuse = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_max_orphans = 327680
net.ipv4.tcp_orphan_retries = 3
net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_max_syn_backlog = 16384
net.ipv4.ip_conntrack_max = 65536
net.ipv4.tcp_max_syn_backlog = 16384
net.ipv4.tcp_timestamps = 0
net.core.somaxconn = 16384
EOF
sysctl --system
'
done
#所有节点配置完内核后,重启服务器,保证重启后内核依旧加载
for i in ${KUBE_MASTER[@]} ${KUBE_NODE[@]};do
ssh $i '
reboot
'
done
#所有服务器重启完成后检查
KUBE_MASTER=(192.168.3.81 192.168.3.82 192.168.3.83)
KUBE_NODE=(192.168.3.84 192.168.3.85)
for i in ${KUBE_MASTER[@]} ${KUBE_NODE[@]};do
ssh $i '
lsmod |& grep --color=auto -e ip_vs -e nf_conntrack
'
done
#重启前:
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# lsmod | grep --color=auto -e ip_vs -e nf_conntrack
ip_vs_sh 16384 0
ip_vs_wrr 16384 0
ip_vs_rr 16384 0
ip_vs 151552 6 ip_vs_rr,ip_vs_sh,ip_vs_wrr
nf_conntrack 143360 1 ip_vs
nf_defrag_ipv6 20480 1 nf_conntrack
nf_defrag_ipv4 16384 1 nf_conntrack
libcrc32c 16384 3 nf_conntrack,xfs,ip_vs
#重启后:
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# lsmod | grep --color=auto -e ip_vs -e nf_conntrack
ip_vs_ftp 16384 0
nf_nat 32768 1 ip_vs_ftp
ip_vs_sed 16384 0
ip_vs_nq 16384 0
ip_vs_fo 16384 0
ip_vs_sh 16384 0
ip_vs_dh 16384 0
ip_vs_lblcr 16384 0
ip_vs_lblc 16384 0
ip_vs_wrr 16384 0
ip_vs_rr 16384 0
ip_vs_wlc 16384 0
ip_vs_lc 16384 0
ip_vs 151552 24 ip_vs_wlc,ip_vs_rr,ip_vs_dh,ip_vs_lblcr,ip_vs_sh,ip_vs_fo,ip_vs_nq,ip_vs_lblc,ip_vs_wrr,ip_vs_lc,ip_vs_sed,ip_vs_ftp
nf_conntrack 143360 2 nf_nat,ip_vs
nf_defrag_ipv6 20480 1 nf_conntrack
nf_defrag_ipv4 16384 1 nf_conntrack
libcrc32c 16384 4 nf_conntrack,nf_nat,xfs,ip_vs
基本组件安装[所有节点]
docker安装和源配置
KUBE_MASTER=(192.168.3.81 192.168.3.82 192.168.3.83)
KUBE_NODE=(192.168.3.84 192.168.3.85)
for i in ${KUBE_MASTER[@]} ${KUBE_NODE[@]};do
ssh $i '
yum install docker-ce-20.10.* docker-cli-20.10.* -y
mkdir -p /etc/docker
cat > /etc/docker/daemon.json <<EOF
{
"registry-mirrors": ["https://ajvcw8qn.mirror.aliyuncs.com"],
"exec-opts": ["native.cgroupdriver=systemd"]
}
EOF
systemctl daemon-reload && systemctl enable --now docker
'
done
kubernetes组件安装
#所有节点安装kubeadm:
#yum install kubeadm-1.21* kubelet-1.21* kubectl-1.21* -y
# 默认配置的pause镜像使用gcr.io仓库,国内可能无法访问,所以这里配置Kubelet使用阿里云的pause镜像:
cat >/etc/sysconfig/kubelet<<EOF
KUBELET_EXTRA_ARGS="--pod-infra-container-image=registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/pause:3.4.1"
EOF
#设置Kubelet开机自启动:
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl enable --now kubelet
---------------------------------------------------
# 所有节点安装kubeadm
for i in ${KUBE_MASTER[@]} ${KUBE_NODE[@]};do
ssh $i '
#所有节点安装kubeadm:
yum install kubeadm-1.21* kubelet-1.21* kubectl-1.21* -y
# 默认配置的pause镜像使用gcr.io仓库,国内可能无法访问,所以这里配置Kubelet使用阿里云的pause镜像:
cat >/etc/sysconfig/kubelet<<EOF
KUBELET_EXTRA_ARGS="--pod-infra-container-image=registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/pause:3.4.1"
EOF
'
done
高可用组件部署
KUBE_MASTER=(192.168.3.81 192.168.3.82 192.168.3.83)
KUBE_NODE=(192.168.3.84 192.168.3.85)
VIP=192.168.3.200
for i in ${KUBE_MASTER[@]};do
#所有Master节点通过yum安装HAProxy和KeepAlived
ssh $i "
rm -f /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo* /etc/yum.repos.d/epel-7.repo*
wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo
wget -P /etc/yum.repos.d/ http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/epel-7.repo
yum clean all
yum install keepalived haproxy -y
mkdir -p /etc/haproxy
cat >/etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg<<EOF
global
maxconn 2000
ulimit-n 16384
log 127.0.0.1 local0 err
stats timeout 30s
defaults
log global
mode http
option httplog
timeout connect 5000
timeout client 50000
timeout server 50000
timeout http-request 15s
timeout http-keep-alive 15s
frontend monitor-in
bind *:33305
mode http
option httplog
monitor-uri /monitor
frontend k8s-master
bind 0.0.0.0:16443
bind 127.0.0.1:16443
mode tcp
option tcplog
tcp-request inspect-delay 5s
default_backend k8s-master
backend k8s-master
mode tcp
option tcplog
option tcp-check
balance roundrobin
default-server inter 10s downinter 5s rise 2 fall 2 slowstart 60s maxconn 250 maxqueue 256 weight 100
server k8s-master01 ${KUBE_MASTER[0]}:6443 check
server k8s-master02 ${KUBE_MASTER[1]}:6443 check
server k8s-master03 ${KUBE_MASTER[2]}:6443 check
EOF
"
done
keepalived部署:
#
KUBE_MASTER=(192.168.3.81 192.168.3.82 192.168.3.83)
KUBE_NODE=(192.168.3.84 192.168.3.85)
VIP=192.168.3.200
#所有Master节点配置KeepAlived,配置不一样,注意区分 ,注意每个节点的IP和网卡(interface参数)
mkdir /etc/keepalived
#传递到其他高可用服务器,并修改配置:
for i in ${KUBE_MASTER[@]};do
ssh $i '
VIP=192.168.3.200
mkdir -p /etc/keepalived
cat >/etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf<<EOF
! Configuration File for keepalived
global_defs {
router_id LVS_DEVEL
script_user root
enable_script_security
}
vrrp_script chk_apiserver {
script "/etc/keepalived/check_apiserver.sh"
interval 5
weight -5
fall 2
rise 1
}
vrrp_instance VI_1 {
state MASTER
interface eth0
mcast_src_ip 123456
virtual_router_id 51
priority 101
advert_int 2
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass K8SHA_KA_AUTH
}
virtual_ipaddress {
${VIP}
}
track_script {
chk_apiserver
}
}
EOF
'
done
for i in ${KUBE_MASTER[@]};do
ssh $i '
sed -i 's#123456#$(hostname -i|awk '{print $1}')#g' /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf
'
done
健康检查:
KUBE_MASTER=(192.168.3.81 192.168.3.82 192.168.3.83)
for i in ${KUBE_MASTER[@]};do
ssh $i '
cat >/etc/keepalived/check_apiserver.sh<<EOF
#!/bin/bash
err=0
for k in $(seq 1 3)
do
check_code=$(pgrep haproxy)
if [[ $check_code == "" ]]; then
err=$(expr $err + 1)
sleep 1
continue
else
err=0
break
fi
done
if [[ $err != "0" ]]; then
echo "systemctl stop keepalived"
/usr/bin/systemctl stop keepalived
exit 1
else
exit 0
fi
EOF
chmod +x /etc/keepalived/check_apiserver.sh
'
done
for i in ${KUBE_MASTER[@]};do
ssh $i '
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl enable --now haproxy
systemctl enable --now keepalived
'
done
#提示:
#如果ping不通且telnet没有出现 ] ,则认为VIP不可以,不可在继续往下执行,需要排查keepalived的问题,比如防火墙和selinux,haproxy和keepalived的状态,监听端口等
#所有节点查看防火墙状态必须为disable和inactive:systemctl status firewalld
#所有节点查看selinux状态,必须为disable:getenforce
#master节点查看haproxy和keepalived状态:systemctl status keepalived haproxy
#master节点查看监听端口:netstat -lntp
集群初始化:
#通过kubectl --version获取版本号:
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# kubectl version
Client Version: version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"21", GitVersion:"v1.21.2", GitCommit:"092fbfbf53427de67cac1e9fa54aaa09a28371d7", GitTreeState:"clean", BuildDate:"2021-06-16T12:59:11Z", GoVersion:"go1.16.5", Compiler:"gc", Platform:"linux/amd64"}
The connection to the server localhost:8080 was refused - did you specify the right host or port?
#版本号为: v1.21.2
vim kubeadm-config.yaml
#内容如下:
#------------------------------------------------------------------#
apiVersion: kubeadm.k8s.io/v1beta2
bootstrapTokens:
- groups:
- system:bootstrappers:kubeadm:default-node-token
token: 7t2weq.bjbawausm0jaxury
ttl: 24h0m0s
usages:
- signing
- authentication
kind: InitConfiguration
localAPIEndpoint:
advertiseAddress: 192.168.3.81
bindPort: 6443
nodeRegistration:
criSocket: /var/run/dockershim.sock
name: k8s-master01
taints:
- effect: NoSchedule
key: node-role.kubernetes.io/master
---
apiServer:
certSANs:
- 192.168.3.200
timeoutForControlPlane: 4m0s
apiVersion: kubeadm.k8s.io/v1beta2
certificatesDir: /etc/kubernetes/pki
clusterName: kubernetes
controlPlaneEndpoint: 192.168.3.200:16443
controllerManager: {}
dns:
type: CoreDNS
etcd:
local:
dataDir: /var/lib/etcd
imageRepository: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers
kind: ClusterConfiguration
kubernetesVersion: v1.20.0
networking:
dnsDomain: cluster.local
podSubnet: 172.16.0.0/12
serviceSubnet: 192.168.0.0/16
scheduler: {}
#------------------------------------------------------------------#
注意点:
kubernetesVersion: v1.20.0 这里的版本改为 v1.21.2
advertiseAddress: 192.168.3.81 改为master01 节点IP
#更新kubeadm文件:
kubeadm config migrate --old-config kubeadm-config.yaml --new-config new.yaml
#将new.yaml文件复制到其他master节点:
for i in k8s-master02 k8s-master03; do scp new.yaml $i:/root/; done
#之后所有Master节点提前下载镜像,可以节省初始化时间(其他节点不需要更改任何配置,包括IP地址也不需要更改):
kubeadm config images pull --config /root/new.yaml
#这很可能会下载失败,所以建议用下面的:
KUBE_MASTER=(192.168.3.81 192.168.3.82 192.168.3.83)
KUBE_NODE=(192.168.3.84 192.168.3.85)
#更新kubeadm-config.yaml
kubeadm config migrate --old-config kubeadm-config.yaml --new-config new.yaml
for i in ${KUBE_MASTER[@]} ${KUBE_NODE[@]};do ssh $i '
docker pull registry.cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/dotbalo/coredns:1.8.0
docker tag registry.cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/dotbalo/coredns:1.8.0 registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/coredns/coredns:v1.8.0
'; done
#由于kubelet还没初始化所以暂时不能直接启动,只需要设置开机启动即可
#配置kubelet开机启动 这个步骤时间比较长:
for i in ${KUBE_MASTER[@]} ${KUBE_NODE[@]};do
ssh $i '
systemctl enable --now kubelet
'
done
#Master01节点初始化,初始化以后会在/etc/kubernetes目录下生成对应的证书和配置文件,之后其他Master节点加入Master01即可:
kubeadm init --config /root/new.yaml --upload-certs
#初始化详细信息:
#初始化信息:
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# kubeadm init --config /root/new.yaml --upload-certs
[init] Using Kubernetes version: v1.21.2
[preflight] Running pre-flight checks
[preflight] Pulling images required for setting up a Kubernetes cluster
[preflight] This might take a minute or two, depending on the speed of your internet connection
[preflight] You can also perform this action in beforehand using 'kubeadm config images pull'
[certs] Using certificateDir folder "/etc/kubernetes/pki"
[certs] Generating "ca" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "apiserver" certificate and key
[certs] apiserver serving cert is signed for DNS names [k8s-master01 kubernetes kubernetes.default kubernetes.default.svc kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local] and IPs [192.168.0.1 192.168.3.81 192.168.3.200]
[certs] Generating "apiserver-kubelet-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "front-proxy-ca" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "front-proxy-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "etcd/ca" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "etcd/server" certificate and key
[certs] etcd/server serving cert is signed for DNS names [k8s-master01 localhost] and IPs [192.168.3.81 127.0.0.1 ::1]
[certs] Generating "etcd/peer" certificate and key
[certs] etcd/peer serving cert is signed for DNS names [k8s-master01 localhost] and IPs [192.168.3.81 127.0.0.1 ::1]
[certs] Generating "etcd/healthcheck-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "apiserver-etcd-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "sa" key and public key
[kubeconfig] Using kubeconfig folder "/etc/kubernetes"
[endpoint] WARNING: port specified in controlPlaneEndpoint overrides bindPort in the controlplane address
[kubeconfig] Writing "admin.conf" kubeconfig file
[endpoint] WARNING: port specified in controlPlaneEndpoint overrides bindPort in the controlplane address
[kubeconfig] Writing "kubelet.conf" kubeconfig file
[endpoint] WARNING: port specified in controlPlaneEndpoint overrides bindPort in the controlplane address
[kubeconfig] Writing "controller-manager.conf" kubeconfig file
[endpoint] WARNING: port specified in controlPlaneEndpoint overrides bindPort in the controlplane address
[kubeconfig] Writing "scheduler.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet environment file with flags to file "/var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env"
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet configuration to file "/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml"
[kubelet-start] Starting the kubelet
[control-plane] Using manifest folder "/etc/kubernetes/manifests"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-apiserver"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-controller-manager"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-scheduler"
[etcd] Creating static Pod manifest for local etcd in "/etc/kubernetes/manifests"
[wait-control-plane] Waiting for the kubelet to boot up the control plane as static Pods from directory "/etc/kubernetes/manifests". This can take up to 4m0s
[apiclient] All control plane components are healthy after 21.016274 seconds
[upload-config] Storing the configuration used in ConfigMap "kubeadm-config" in the "kube-system" Namespace
[kubelet] Creating a ConfigMap "kubelet-config-1.21" in namespace kube-system with the configuration for the kubelets in the cluster
[upload-certs] Storing the certificates in Secret "kubeadm-certs" in the "kube-system" Namespace
[upload-certs] Using certificate key:
0058686d77ca01df79db171e61746f7ca5cf0d8740a0e88bda2b3a63c9b6b692
[mark-control-plane] Marking the node k8s-master01 as control-plane by adding the labels: [node-role.kubernetes.io/master(deprecated) node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane node.kubernetes.io/exclude-from-external-load-balancers]
[mark-control-plane] Marking the node k8s-master01 as control-plane by adding the taints [node-role.kubernetes.io/master:NoSchedule]
[bootstrap-token] Using token: 7t2weq.bjbawausm0jaxury
[bootstrap-token] Configuring bootstrap tokens, cluster-info ConfigMap, RBAC Roles
[bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow Node Bootstrap tokens to get nodes
[bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow Node Bootstrap tokens to post CSRs in order for nodes to get long term certificate credentials
[bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow the csrapprover controller automatically approve CSRs from a Node Bootstrap Token
[bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow certificate rotation for all node client certificates in the cluster
[bootstrap-token] Creating the "cluster-info" ConfigMap in the "kube-public" namespace
[kubelet-finalize] Updating "/etc/kubernetes/kubelet.conf" to point to a rotatable kubelet client certificate and key
[addons] Applied essential addon: CoreDNS
[endpoint] WARNING: port specified in controlPlaneEndpoint overrides bindPort in the controlplane address
[addons] Applied essential addon: kube-proxy
Your Kubernetes control-plane has initialized successfully!
To start using your cluster, you need to run the following as a regular user:
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
Alternatively, if you are the root user, you can run:
export KUBECONFIG=/etc/kubernetes/admin.conf
You should now deploy a pod network to the cluster.
Run "kubectl apply -f [podnetwork].yaml" with one of the options listed at:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/cluster-administration/addons/
You can now join any number of the control-plane node running the following command on each as root:
kubeadm join 192.168.3.200:16443 --token 7t2weq.bjbawausm0jaxury \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:d2fab5e614dc53f1abfb5ab5820d63541bf45bf04a733feaef483764a5724d9d \
--control-plane --certificate-key 0058686d77ca01df79db171e61746f7ca5cf0d8740a0e88bda2b3a63c9b6b692
Please note that the certificate-key gives access to cluster sensitive data, keep it secret!
As a safeguard, uploaded-certs will be deleted in two hours; If necessary, you can use
"kubeadm init phase upload-certs --upload-certs" to reload certs afterward.
Then you can join any number of worker nodes by running the following on each as root:
kubeadm join 192.168.3.200:16443 --token 7t2weq.bjbawausm0jaxury \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:d2fab5e614dc53f1abfb5ab5820d63541bf45bf04a733feaef483764a5724d9d
master加入集群:
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
cat <<EOF >> /root/.bashrc
export KUBECONFIG=/etc/kubernetes/admin.conf
EOF
source /root/.bashrc
#master 加入集群:
kubeadm join 192.168.3.200:16443 --token 7t2weq.bjbawausm0jaxury \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:d2fab5e614dc53f1abfb5ab5820d63541bf45bf04a733feaef483764a5724d9d \
--control-plane --certificate-key 0058686d77ca01df79db171e61746f7ca5cf0d8740a0e88bda2b3a63c9b6b692
#node 加入集群:
kubeadm join 192.168.3.200:16443 --token 7t2weq.bjbawausm0jaxury \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:d2fab5e614dc53f1abfb5ab5820d63541bf45bf04a733feaef483764a5724d9d
calico网络配置
cd k8s-ha-install/
git checkout manual-installation-v1.21.x && cd calico/
[root@k8s-master01 calico]# ls
calico-etcd.yaml
KUBE_MASTER=(192.168.3.81 192.168.3.82 192.168.3.83)
sed -i 's#etcd_endpoints: "http://<ETCD_IP>:<ETCD_PORT>"#etcd_endpoints: "https://192.168.3.81:2379,https://192.168.3.82:2379,https://192.168.3.83:2379"#g' calico-etcd.yaml
ETCD_CA=`cat /etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/ca.crt | base64 | tr -d '\n'`
ETCD_CERT=`cat /etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.crt | base64 | tr -d '\n'`
ETCD_KEY=`cat /etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.key | base64 | tr -d '\n'`
sed -i "s@# etcd-key: null@etcd-key: ${ETCD_KEY}@g; s@# etcd-cert: null@etcd-cert: ${ETCD_CERT}@g; s@# etcd-ca: null@etcd-ca: ${ETCD_CA}@g" calico-etcd.yaml
sed -i 's#etcd_ca: ""#etcd_ca: "/calico-secrets/etcd-ca"#g; s#etcd_cert: ""#etcd_cert: "/calico-secrets/etcd-cert"#g; s#etcd_key: "" #etcd_key: "/calico-secrets/etcd-key" #g' calico-etcd.yaml
POD_SUBNET=`cat /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-controller-manager.yaml | grep cluster-cidr= | awk -F= '{print $NF}'`
# 注意下面的这个步骤是把calico-etcd.yaml文件里面的CALICO_IPV4POOL_CIDR下的网段改成自己的Pod网段,也就是把192.168.x.x/16改成自己的集群网段,并打开注释:
#所以更改的时候请确保这个步骤的这个网段没有被统一替换掉,如果被替换掉了,还请改回来:
#注意对齐,最好进去看一下:
sed -i 's@# - name: CALICO_IPV4POOL_CIDR@- name: CALICO_IPV4POOL_CIDR@g; s@# value: 172.16.0.0/12@ value: '"${POD_SUBNET}"'@g' calico-etcd.yaml
#修改完成,执行:
kubectl apply -f calico-etcd.yaml
#检查:
[root@k8s-master01 calico]# kubectl get pod -n kube-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
calico-kube-controllers-cdd5755b9-lhn8v 1/1 Running 0 10m
calico-node-4msfq 1/1 Running 0 10m
calico-node-jrnf9 1/1 Running 0 10m
calico-node-q4s4l 1/1 Running 5 10m
calico-node-wql4q 1/1 Running 0 10m
calico-node-zpnk4 1/1 Running 0 10m
coredns-6f6b8cc4f6-njzqt 1/1 Running 0 4h52m
coredns-6f6b8cc4f6-xhrrg 1/1 Running 0 4h52m
etcd-k8s-master01 1/1 Running 0 4h52m
etcd-k8s-master02 1/1 Running 0 4h
etcd-k8s-master03 1/1 Running 1 4h3m
kube-apiserver-k8s-master01 1/1 Running 0 4h52m
kube-apiserver-k8s-master02 1/1 Running 0 4h
kube-apiserver-k8s-master03 1/1 Running 1 4h3m
kube-controller-manager-k8s-master01 1/1 Running 2 4h52m
kube-controller-manager-k8s-master02 1/1 Running 0 4h
kube-controller-manager-k8s-master03 1/1 Running 1 4h3m
kube-proxy-9f7g9 1/1 Running 2 4h3m
kube-proxy-c4x9s 1/1 Running 0 4h52m
kube-proxy-gdkjp 1/1 Running 0 4h14m
kube-proxy-h5b4d 1/1 Running 0 4h45m
kube-proxy-vrb9j 1/1 Running 0 4h
kube-scheduler-k8s-master01 1/1 Running 2 4h52m
kube-scheduler-k8s-master02 1/1 Running 0 4h
kube-scheduler-k8s-master03 1/1 Running 2 4h3m
#必须要是都起来的状态
Metrics部署
#在新版的Kubernetes中系统资源的采集均使用Metrics-server,可以通过Metrics采集节点和Pod的内存、磁盘、CPU和网络的使用率
#将Master01节点的front-proxy-ca.crt复制到所有Node节点
KUBE_MASTER=(192.168.3.81 192.168.3.82 192.168.3.83)
KUBE_NODE=(192.168.3.84 192.168.3.85)
for i in ${KUBE_MASTER[1]} ${KUBE_MASTER[2]} ${KUBE_NODE[@]};do
\scp -r /etc/kubernetes/pki/front-proxy-ca.crt $i:/etc/kubernetes/pki/front-proxy-ca.crt;
done
cd /root/k8s-ha-install/metrics-server-0.4.x-kubeadm/
kubectl create -f comp.yaml
[root@k8s-master01 metrics-server-0.4.x-kubeadm]# kubectl top node --use-protocol-buffers
NAME CPU(cores) CPU% MEMORY(bytes) MEMORY%
k8s-master01 127m 1% 1839Mi 23%
k8s-master02 123m 1% 1488Mi 18%
k8s-master03 126m 1% 1755Mi 22%
k8s-node01 61m 0% 928Mi 11%
k8s-node02 67m 0% 956Mi 12%
[root@k8s-master01 metrics-server-0.4.x-kubeadm]# kubectl top pod --use-protocol-buffers -A
NAMESPACE NAME CPU(cores) MEMORY(bytes)
kube-system calico-kube-controllers-cdd5755b9-lhn8v 2m 22Mi
kube-system calico-node-4msfq 25m 73Mi
kube-system calico-node-jrnf9 19m 77Mi
kube-system calico-node-q4s4l 26m 73Mi
kube-system calico-node-wql4q 19m 72Mi
kube-system calico-node-zpnk4 20m 69Mi
kube-system coredns-6f6b8cc4f6-njzqt 2m 20Mi
kube-system coredns-6f6b8cc4f6-xhrrg 2m 17Mi
kube-system etcd-k8s-master01 22m 68Mi
kube-system etcd-k8s-master02 26m 66Mi
kube-system etcd-k8s-master03 22m 84Mi
kube-system kube-apiserver-k8s-master01 24m 460Mi
kube-system kube-apiserver-k8s-master02 32m 389Mi
kube-system kube-apiserver-k8s-master03 29m 419Mi
kube-system kube-controller-manager-k8s-master01 1m 26Mi
kube-system kube-controller-manager-k8s-master02 1m 30Mi
kube-system kube-controller-manager-k8s-master03 8m 72Mi
kube-system kube-proxy-9f7g9 1m 25Mi
kube-system kube-proxy-c4x9s 1m 23Mi
kube-system kube-proxy-gdkjp 1m 25Mi
kube-system kube-proxy-h5b4d 1m 27Mi
kube-system kube-proxy-vrb9j 1m 27Mi
kube-system kube-scheduler-k8s-master01 2m 26Mi
kube-system kube-scheduler-k8s-master02 2m 27Mi
kube-system kube-scheduler-k8s-master03 2m 30Mi
kube-system metrics-server-d6c46b546-jx6cp 3m 24Mi
dashboard 部署:
cd /root/k8s-ha-install/dashboard/
[root@k8s-master01 dashboard]# kubectl create -f .
serviceaccount/admin-user created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/admin-user created
namespace/kubernetes-dashboard created
serviceaccount/kubernetes-dashboard created
service/kubernetes-dashboard created
secret/kubernetes-dashboard-certs created
secret/kubernetes-dashboard-csrf created
secret/kubernetes-dashboard-key-holder created
configmap/kubernetes-dashboard-settings created
role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kubernetes-dashboard created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kubernetes-dashboard created
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kubernetes-dashboard created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kubernetes-dashboard created
deployment.apps/kubernetes-dashboard created
service/dashboard-metrics-scraper created
deployment.apps/dashboard-metrics-scraper created
#创建用户:
vim admin.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: admin-user
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: admin-user
annotations:
rbac.authorization.kubernetes.io/autoupdate: "true"
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: cluster-admin
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: admin-user
namespace: kube-system
#应用:
[root@k8s-master01 dashboard]# kubectl apply -f admin.yaml -n kube-system
serviceaccount/admin-user created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/admin-user created
#创建dashboard
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/dashboard/v2.0.3/aio/deploy/recommended.yaml
登录dashboard:
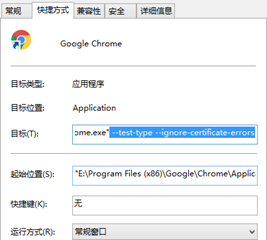
在谷歌浏览器(Chrome)启动文件中加入启动参数,用于解决无法访问Dashboard的问题
--test-type --ignore-certificate-errors
参考图:
#更改dashboard的svc为NodePort:
kubectl edit svc kubernetes-dashboard -n kubernetes-dashboard
找到: type: ClusterIP
改为: type: NodePort
#获取访问端口号:
kubectl get svc kubernetes-dashboard -n kubernetes-dashboard
[root@k8s-master01 dashboard]# kubectl get svc kubernetes-dashboard -n kubernetes-dashboard
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kubernetes-dashboard NodePort 192.168.157.22 <none> 443:31338/TCP 101s
# https://192.168.3.81:31338/#/login
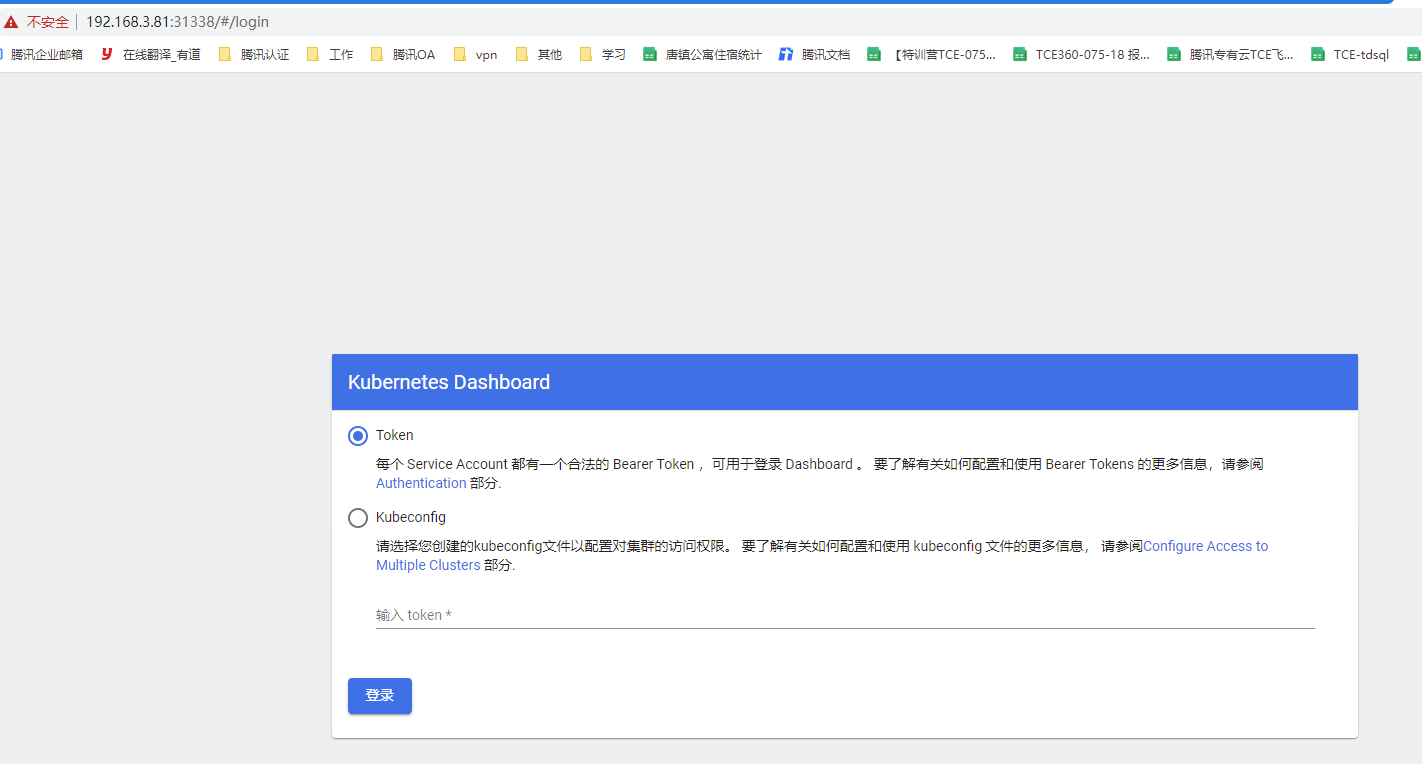
#获取登录token:
kubectl -n kube-system describe secret $(kubectl -n kube-system get secret | grep admin-user | awk '{print $1}')
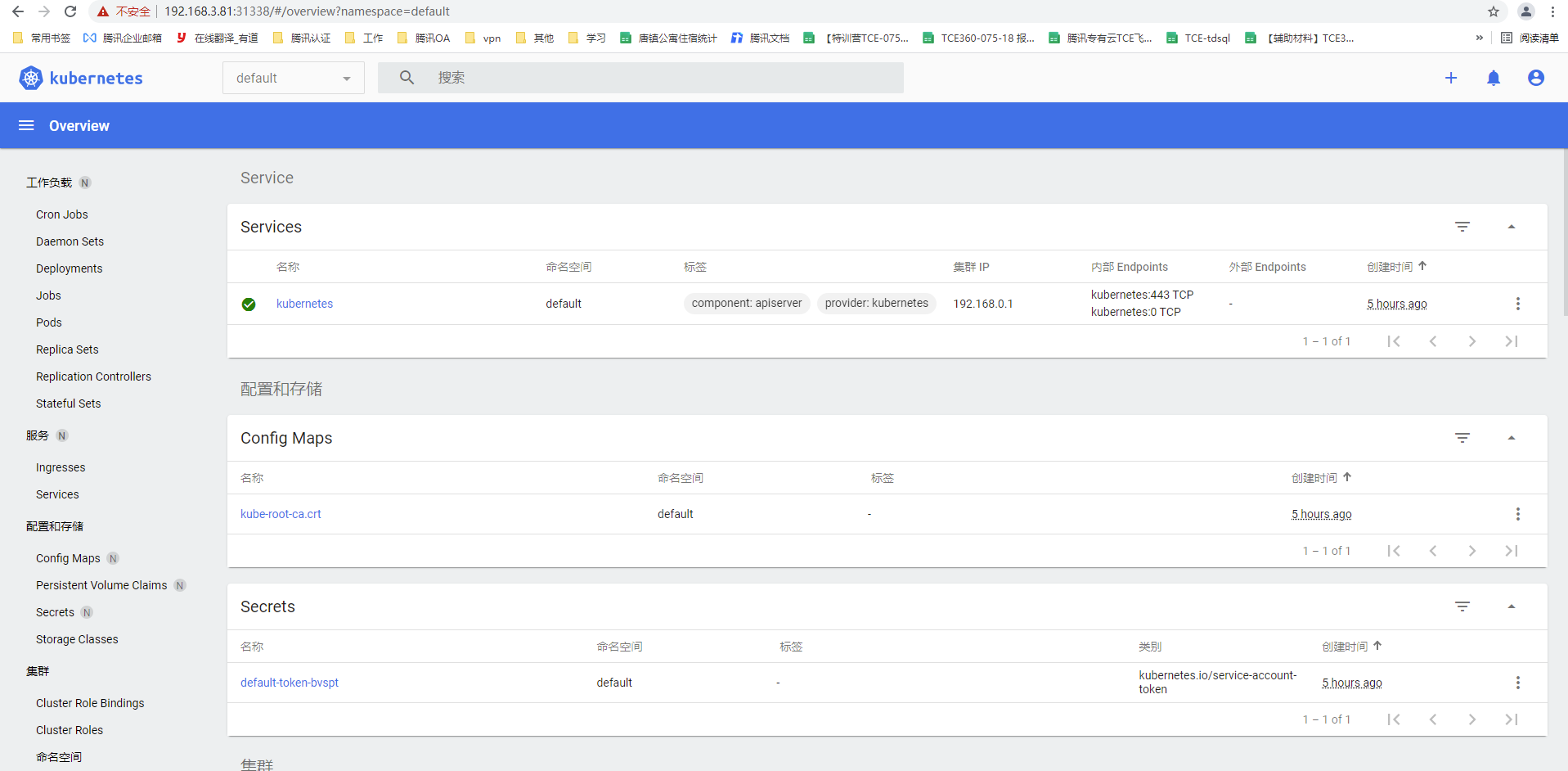
将Kube-proxy改为ipvs模式
在master01节点执行
kubectl edit cm kube-proxy -n kube-system
搜索: mode
找到: mode: ""
改为: mode: "ipvs"
#更新Kube-Proxy的Pod:
kubectl patch daemonset kube-proxy -p "{\"spec\":{\"template\":{\"metadata\":{\"annotations\":{\"date\":\"`date +'%s'`\"}}}}}" -n kube-system
#验证Kube-Proxy模式:
[root@k8s-master01 1.1.1]# curl 127.0.0.1:10249/proxyMode
ipvs
注意:
注意:kubeadm安装的集群,证书有效期默认是一年。master节点的kube-apiserver、kube-scheduler、kube-controller-manager、etcd都是以容器运行的。可以通过kubectl get po -n kube-system查看。
启动和二进制不同的是,
kubelet的配置文件在/etc/sysconfig/kubelet和/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml
其他组件的配置文件在/etc/Kubernetes/manifests目录下,比如kube-apiserver.yaml,该yaml文件更改后,kubelet会自动刷新配置,也就是会重启pod。不能再次创建该文件
Kubeadm安装后,master节点默认不允许部署pod,可以通过以下方式打开:
#查看Taints:
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# kubectl describe node -l node-role.kubernetes.io/master= | grep Taints
Taints: node-role.kubernetes.io/master:NoSchedule
Taints: node-role.kubernetes.io/master:NoSchedule
Taints: node-role.kubernetes.io/master:NoSchedule
删除Taint:
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# kubectl taint node -l node-role.kubernetes.io/master node-role.kubernetes.io/master:NoSchedule-
node/k8s-master01 untainted
node/k8s-master02 untainted
node/k8s-master03 untainted
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# kubectl describe node -l node-role.kubernetes.io/master= | grep Taints
Taints: <none>
Taints: <none>
Taints: <none>
kubeadm部署高可用版Kubernetes1.21[更新]的更多相关文章
- kubernetes kubeadm部署高可用集群
k8s kubeadm部署高可用集群 kubeadm是官方推出的部署工具,旨在降低kubernetes使用门槛与提高集群部署的便捷性. 同时越来越多的官方文档,围绕kubernetes容器化部署为环境 ...
- 附012.Kubeadm部署高可用Kubernetes
一 kubeadm介绍 1.1 概述 参考<附003.Kubeadm部署Kubernetes>. 1.2 kubeadm功能 参考<附003.Kubeadm部署Kubernetes& ...
- kubeadm部署高可用K8S集群(v1.14.2)
1. 简介 测试环境Kubernetes 1.14.2版本高可用搭建文档,搭建方式为kubeadm 2. 服务器版本和架构信息 系统版本:CentOS Linux release 7.6.1810 ( ...
- Kubeadm部署高可用K8S集群
一 基础环境 1.1 资源 节点名称 ip地址 VIP 192.168.12.150 master01 192.168.12.48 master02 192.168.12.242 master03 1 ...
- kubeadm部署高可用集群Kubernetes 1.14.1版本
Kubernetes高可用集群部署 部署架构: Master 组件: kube-apiserver Kubernetes API,集群的统一入口,各组件协调者,以HTTP API提供接口服务,所有对象 ...
- 企业运维实践-还不会部署高可用的kubernetes集群?使用kubeadm方式安装高可用k8s集群v1.23.7
关注「WeiyiGeek」公众号 设为「特别关注」每天带你玩转网络安全运维.应用开发.物联网IOT学习! 希望各位看友[关注.点赞.评论.收藏.投币],助力每一个梦想. 文章目录: 0x00 前言简述 ...
- Kubernetes 部署 1.9.7 高可用版
转载于https://codegreen.cn/2018/08/30/kubernetes-cluster-1.9.7/ 前言 在部署之前,首先感谢 手动搭建高可用的kubernetes 集群 博文的 ...
- kubernetes实战(二十五):kubeadm 安装 高可用 k8s v1.13.x
1.系统环境 使用kubeadm安装高可用k8s v.13.x较为简单,相比以往的版本省去了很多步骤. kubeadm安装高可用k8s v.11 和 v1.12 点我 主机信息 主机名 IP地址 说明 ...
- 容器云平台No.2~kubeadm创建高可用集群v1.19.1
通过kubernetes构建容器云平台第二篇,最近刚好官方发布了V1.19.0,本文就以最新版来介绍通过kubeadm安装高可用的kubernetes集群. 市面上安装k8s的工具很多,但是用于学习的 ...
随机推荐
- 关于ajax的数据传输类型,字符串传输
- str.isdigit()可以判断变量是否为数字
字符串.isdigit()可以判断变量是否为数字 是则输出True 不是则输出False 好像只能字符串
- Visual Studio/VS中任务列表的妙用
一.任务列表开启方法 首先说下开启的方法:视图-任务列表,即可打开任务列表. 快捷键Ctrl+'\'+T,熟练了可以快速开启.注意,'\'键是回车键上面的'',不要按成了'/' 二.任务列表标签设置 ...
- Excel导出数据Excel.Application组件权限设置方法
很多网络应用系统都会涉及到数据采用Excel方式导出的模块,部分朋友问我到底怎么弄,其实方式很多种,目前比较优秀的方式还是直接用Excel的Excel.Application方式比较合适. 采用Exc ...
- (Dubbo架构)基于MDC+Filter的跨应用分布式日志追踪解决方案
在单体应用中,日志追踪通常的解决方案是给日志添加 tranID(追踪ID),生成规则因系统而异,大致效果如下: 查询时只要使用 grep 命令进行追踪id筛选即可查到此次调用链中所有日志,但是在 du ...
- [bug] Hive:Caused by: MetaException(message:Hive Schema version 2.1.0 does not match metastore's schema version 1.2.0 Metastore is not upgraded or corrupt)
参考 https://www.cnblogs.com/liupuLearning/p/6610307.html 少了创建hive数据库一步
- 上,打开SSH服务的配置文件:/etc/ssh/sshd_config 加上如下两行: ClientAliveInterval 120 ClientAliveCountMax 720 第一行,表示每隔120秒向客户端
SSH的默认过一段时间会超时,有时候正在执行着脚本,出去一会回来就断开了,输出信息都看不到了... 禁止SSH自动超时最简单的办法就是,每隔一段时间在客户端和服务器之间发送一个"空包&quo ...
- k8s健康检查(9)
一.默认的健康检查 强大的自愈能力是 Kubernetes 这类容器编排引擎的一个重要特性.自愈的默认实现方式是自动重启发生故障的容器.除此之外,用户还可以利用 Liveness 和 Readines ...
- 043.Python线程基本介绍
一 线程的基本概念 1.1 进程和线程 进程是资源分配的最小单位 线程是计算机中调度的最小单位 进程池: 开启过多的进程并不一走提高你的效率, 如果cp负载任务过多,平均单个任务执行的效率就会低,反而 ...
- CentOS 7网络配置
修改配置文件 CentOS 7下的网络配置文件路径为:/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-interfacename 配置文件ifcfg-interface-na ...
