Java 多线程高并发编程 笔记(二)
1. 单例模式(在内存之中永远只有一个对象)
1.1 多线程安全单例模式——不使用同步锁
public class Singleton {
private static Singleton sin=new Singleton(); ///直接初始化一个实例对象
private Singleton(){ ///private类型的构造函数,保证其他类对象不能直接new一个该对象的实例
}
public static Singleton getSin(){ ///该类唯一的一个public方法
return sin;
}
}
上述代码中的一个缺点是该类加载的时候就会直接new 一个静态对象出来,当系统中这样的类较多时,会使得启动速度变慢 。现在流行的设计都是讲“延迟加载”,我们可以在第一次使用的时候才初始化第一个该类对象。所以这种适合在小系统。
1.2 多线程安全单例模式——使用同步方法
public class Singleton {
private static Singleton instance;
private Singleton (){
}
public static synchronized Singleton getInstance(){ //对获取实例的方法进行同步
if (instance == null)
instance = new Singleton();
return instance;
}
}
上述代码中的一次锁住了一个方法, 这个粒度有点大 ,改进就是只锁住其中的new语句就OK。就是所谓的“双重锁”机制。
1.3 多线程安全单例模式——使用双重同步锁
public class Singleton {
private static Singleton instance;
private Singleton (){
}
public static Singleton getInstance(){ //对获取实例的方法进行同步
if (instance == null){
synchronized(Singleton.class){
if (instance == null)
instance = new Singleton();
}
}
return instance;
}
}
1.4 多线程安全单例模式——使用内部类的单例模式
既不用加锁,也能实现懒加载
public class Singleton {
private Singleton(){
System.out.println("single");
}
private static class Inner{
private static Singleton s = new Singleton();
}
//无论有多少次,有多少个线程在调用getsingle的时候拿到的都是同一个对象
private static Singleton getSingle(){
return Inner.s;
}
public static void main(String[] agrs){
Thread[] ths = new Thread[200];
for(int i=0; i<ths.length;i++){
ths[i]=new Thread(()->{
Singleton.getSingle();
});
}
Arrays.asList(ths).forEach(o->o.start());
}
}
2. 高并发——容器
2.1 有N张火车票,每张票都有一个编号,同时有10个窗口对外售票,写一个模拟程序,分析可能会产生哪些问题?重复销售,超量销售;
public class TicketSeller1 {
static List<String> tickets = new ArrayList<>();
//初始化,放票
static{
for(int i=0; i<10000; i++)
tickets.add("票编号:"+i);
}
public static void main(String[] args){
//启动10个线程不断往外卖票
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
new Thread(()->{
while(tickets.size()>0){
System.out.println("销售了--"+tickets.remove(0));
}
}).start();
}
}
}
改成下面的代码还有问题吗?
public class TicketSeller2 {
//vector本身就是一个同步容器,它所有的方法都是加锁的
static Vector<String> tickets = new Vector<>();
static{
for(int i=0; i<10000; i++)
tickets.add("票编号:"+i);
}
public static void main(String[] args){
for(int i=0; i<10; i++){
new Thread(()->{
while(tickets.size()>0){
/*
try{
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);
}catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}*/
System.out.println("销售了--"+tickets.remove(0));
}
}).start();
}
}
}
仍有问题,判断与操作分离了(虽然在vector中size和remove方法都是原子的);
再改进:将判断和操作放到一个原子操作里面去
public class TicketSeller3 {
static List<String> tickets = new ArrayList<>();
static{
for(int i=0; i<10000; i++)
tickets.add("票编号:"+i);
}
public static void main(String[] args){
//启动10个线程不断往外卖票
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
new Thread(()->{
while(true){
synchronized (tickets){
if(tickets.size()<=0) break;
try{
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);
}catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("销售了--"+tickets.remove(0));
}
}
}).start();
}
}
}
加锁效率不高,尤其是每销售一张票都要把整个队列给锁定;
引入并发容器:
public class TicketSeller4 {
//并发容器
static Queue<String> tickets = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<>();
static{
for(int i=0; i<1000; i++){
tickets.add("票编号:"+i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
for(int i=0; i<10; i++){
new Thread(()->{
while(true){
//poll从头往外拿一个数据,是同步的
String s = tickets.poll();
if(s==null) break;
else System.out.println("销售了--"+s);
}
}).start();
}
}
}
if(s==null) break;虽然不是原子性的,但是我们判断以后没有对队列作修改操作,所以这里不会出错。 2.2 并发容器————ConcurrentMap
在多线程的情况下,什么样的容器效率比较高?
public class T_ConcurrentMap {
public static void main(String[] args){
//Map<String, String> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
//Map<String, String> map = new ConcurrentSkipListMap<>();
//HashTable 默认加锁,但是效率比较低
Map<String, String> map = new Hashtable<>();
//使用HashMap,自己往上加锁:Collection.synchronizedXXX
//Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
//Map<String, String> map = new TreeMap<>();
Random r = new Random();
Thread[] ths = new Thread[100];
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(ths.length);
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i=0; i<ths.length; i++){
ths[i] = new Thread(()->{
for(int j=0; j<10000; j++)
map.put("a"+r.nextInt(100000),"a"+r.nextInt(100000));
latch.countDown();
});
}
Arrays.asList(ths).forEach(o->o.start());
try{
latch.await();
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end-start);
}
}
HashTable:669;
ConcurrentHashMap:391;
why? HashTable 往里加任何一个数据的时候都是要锁定整个对象,而HashMap,ConcurrentHashMap默认把容器分成16段,每次往容器里插数据只锁定16段里面的一段(把锁细化),两个线程往里插不同的段的数据,那么这两个线程就能并发的插入;
ConcurrentSkipListMap:649 高并发并且排序
往里插数据效率低一些,因为要排序,查数据方便很多;
总结:
1. 对于map/set的选择使用
不加锁:hashmap;treemap;linkedhashmap;
加锁:hashtable;Collection.sychronizedXXX(传一个不加锁map,返回一个加了锁的map),在并发性不是特别高的情况下可以使用上面两种;如果并发性比较高,用concurrenthashmap,如果还需要排序,就用concurrentskiplistmap;
附:Collection.sychronizedXXX用法:
public class T_SynchronizedList {
public static void main(String[] args){
List<String> strs = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> strsSync = Collections.synchronizedList(strs);
}
}
2.3 并发容器——CopyOnWrite 写时复制容器
多线程环境下,写时效率低,读时效率高,适合写少读多的环境;
比较容器效率 :
public class T_CopyOnWrite {
public static void main(String[] args){
List<String> lists =
//new ArrayList<>();//这个会出并发问题
//new Vector<>();
new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
Random r = new Random();
Thread[] ths = new Thread[100];
for(int i=0; i<ths.length; i++){
Runnable task = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for(int j=0;j<1000;j++)
lists.add("a"+r.nextInt(10000));
}
};
ths[i] = new Thread(task);
}
runAndComputeTime(ths);
System.out.println(lists.size());
}
static void runAndComputeTime(Thread[] ths){
long s1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
Arrays.asList(ths).forEach(o->o.start());
Arrays.asList(ths).forEach(o->{
try{
o.join();
}catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
long s2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(s2-s1);
}
}
CopyOnWriteArrayList:4853 100000
Vector:114 100000
ArrayList:97 86864(有错)
2.4 并发容器——ConcurrentLinkedQueue
常用方法:
public class T_ConcurrentLinkedQueue {
public static void main(String[] args){
Queue<String> strs = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<>();
for(int i=0; i<10; i++){
//类似于add,有boolean返回值
strs.offer("a"+i);
}
System.out.println(strs);
System.out.println(strs.size());
System.out.println(strs.poll());//取值并删除
System.out.println(strs.size());
System.out.println(strs.peek());//只取值不删
System.out.println(strs.size());
}
}
2.5 并发容器——BlockingQueue
在高并发的情况下可以使用两种队列:
ConcurrentLinkedQueue:加锁式
BlockingQueue:阻塞式
LinkedBlockingQueue:
public class T_LinkedBlockingQueue {
static BlockingQueue<String> strs = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>();
static Random r = new Random();
public static void main(String[] args){
//生产者线程
new Thread(()->{
for(int i=0; i<100; i++){
try{
strs.put("a"+i);//使用put,如果满了,就会等待
}catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"p1").start();
//5个消费者线程
for(int i=0; i<5; i++){
new Thread(()->{
for(;;){
try{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"task-"+strs.take());//take如果空了,就会等待
}catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"c"+i).start();
}
}
}
ArrayBlockingQueue:
public class T_ArrayBlockingQueue {
//有界队列
static BlockingQueue<String> strs = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(10);
static Random r = new Random();
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
for(int i=0; i<10; i++){
strs.put("a"+i);
}
//strs.put("aaa");//满了就会等待,程序阻塞
//strs.add("aaa");//队列满了会报异常
strs.offer("aaa");//队列满了不会报异常,也加不进去
//strs.offer("aaa",1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);//隔一段时间之内加不进去就不往里面加了
System.out.println(strs);
}
}
DelayQueue:
public class T_DelayQueue {
//加入队列的元素只有等一定的时间之后才能被消费者拿走
//默认按等待时间排序
//DelayQueue 需要实现接口
static BlockingQueue<MyTask> tasks = new DelayQueue<>();
static Random r = new Random();
static class MyTask implements Delayed{
long runningTime;
MyTask(long rt){
this.runningTime = rt;
}
public int compareTo(Delayed o){
if(this.getDelay(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)<o.getDelay(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS))
return -1;
else if(this.getDelay(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)>o.getDelay(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS))
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
@Override
public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) {
return unit.convert(runningTime-System.currentTimeMillis(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
public String toString(){
return ""+runningTime;
}
}
public static void main(String[] agrs) throws InterruptedException{
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
MyTask t1 = new MyTask(now+1000);
MyTask t2 = new MyTask(now+2000);
MyTask t3 = new MyTask(now+1500);
MyTask t4 = new MyTask(now+2500);
MyTask t5 = new MyTask(now+500);
tasks.put(t1);
tasks.put(t2);
tasks.put(t3);
tasks.put(t4);
tasks.put(t5);
System.out.println(tasks);
for(int i=0; i<5; i++){
System.out.println(tasks.take());
}
}
}
[1558935218208, 1558935218708, 1558935219208, 1558935220208, 1558935219708]
1558935218208
1558935218708
1558935219208
1558935219708
1558935220208
可以用来做定时执行任务
TransferQueue:
public class T_TransferQueue {
public static void main(String[] agrs) throws InterruptedException{
LinkedTransferQueue<String> strs = new LinkedTransferQueue<>();
new Thread(()->{
try{
System.out.println(strs.take());
}catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
//先启动几个消费者线程,生产者生产出一个产品的时候不往队列里加,
//首先去找有没有消费者,有消费者直接给消费者消费,没有就阻塞
//用在更高并发的情况下
strs.transfer("aaa");
}
}
SynchronusQueue:
public class SynchronusQueue {//没有容量的队列
public static void main(String[] agrs) throws InterruptedException{
//同步队列是一种特殊的transferQueue
//
BlockingQueue<String> strs = new SynchronousQueue<>();
new Thread(()->{
try{
System.out.println(strs.take());
}catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
//strs.put("aaa");//不报错,阻塞等待消费者消费
strs.add("aaa");//报错queue full
System.out.println(strs.size);
}
}
3. 线程池
3.1 Executor
执行器,这是一个接口,内部维护了一个方法execute负责执行一项任务,参数为Runnable,方法具体实现有我们执行,如下面的代码,既可以使用单纯的方法调用也可以新砌一个新的线程去执行Runnable的run方法;
public class T_MyExecutor implements Executor {
public static void main(String[] agrs){
new T_MyExecutor().execute(()->System.out.println("hello executor"));
}
public void execute(Runnable commend){
commend.run();
//new Thread(commend).run();
}
}
3.2 ExecutorService
代表着启动一系列的线程为用户提供服务(本质上也是一个执行器),Java8官方文档就举了一个网络接受连接池的例子(代码如下)。
class NetworkService implements Runnable {
private final ServerSocket serverSocket;
private final ExecutorService pool;
public NetworkService(int port, int poolSize)
throws IOException {
serverSocket = new ServerSocket(port);
pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(poolSize);
}
public void run() { // run the service
try {
for (;;) {
pool.execute(new Handler(serverSocket.accept()));
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
pool.shutdown();
}
}
}
class Handler implements Runnable {
private final Socket socket;
Handler(Socket socket) { this.socket = socket; }
public void run() {
// read and service request on socket
}
}
在这里ExecutorService就代表着一个线程池对外提供接受网络请求的服务,同时它也是一系列线程池的接口,如,RorkJoinPool、ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor,、ThreadPoolExecutor等。同时,它可以提交Callable与Runnable的对象返回一个未来的执行结果对象Future。Callable是一个增强版的Runnable,它的call方法可以抛出异常可以有返回值,返回值放在Future对象中,我们可以使用Future对象的get方法来获得返回值。
除了以上方法来创建一个ExecutorService还可以使用Executors这个工具类来创建它,在这里我们可以把Executors理解为就像utils,collections的工具类,是操作Executor的一个工具类。
2.3 ThreadPool 线程池
public class T_ThreadPool {
public static void main(String[] agrs) throws InterruptedException{
//Executors有一些工厂方法,newFixedThreadPool创建一个个数为5的线程池
//ExecutorService接口是可以往里面扔任务(execute,submit)的,
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
for(int i=0; i<6;i++){
//5个线程,6个任务
service.execute(()->{
try{
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500);
}catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
}
System.out.println(service);
//ExecutorService 常用方法
service.shutdown();//所有任务执行完关闭
System.out.println(service.isTerminated());//所有任务是否执行完了
System.out.println(service.isShutdown());//关了并一定是执行完了,代表正在关闭的过程中
System.out.println(service);
}
}
执行结果:
java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor@7ba4f24f[Running, pool size = 5, active threads = 5, queued tasks = 1(排队的任务), completed tasks = 0]
false
true
java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor@7ba4f24f[Shutting down, pool size = 5, active threads = 5, queued tasks = 1, completed tasks = 0]
pool-1-thread-1
pool-1-thread-3
pool-1-thread-2
pool-1-thread-5
pool-1-thread-4
pool-1-thread-1
2.4 Future
public class T_Future {
public static void main(String[] agrs) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException{
//RunnableTask 不产生任何返回值
//new了个Callable对象并把它包装成FutureTask
FutureTask<Integer> task = new FutureTask<>(()->{
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500);
return 1000;
});//相当于创建一个匿名类:new Callable(){Integer call();}}
//启动一个线程
new Thread(task).start();
System.out.println(task.get());//阻塞,任务执行完了返回值
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
Future<Integer> f = service.submit(()->{
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500);
return 1;
});
System.out.println(f.get());
System.out.println(f.isDone());//任务执行完没有啊
System.out.println(f.get());
System.out.println(f.isDone());
}
}
2.5 线程池——newFixedThreadPool
小程序:计算1-200000之间的质数
比较一个线程和多个线程的效率:
public class T_ParallelComputing {
public static void main(String[] agrs) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
//计算1-200000之间所有的质数
List<Integer> resulrs = getPrime(1,200000);
//方法1:使用一个线程来计算
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end-start);
//方法2:使用线程池
final int cpuCoreNum = 4;
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(cpuCoreNum);
//创建4个任务,继承callable接口(有返回值)
MyTask t1 = new MyTask(1,80000);
MyTask t2 = new MyTask(80000,130000);
MyTask t3 = new MyTask(130000,170000);
MyTask t4 = new MyTask(170000,200000);
//将4个任务扔到线程池
Future<List<Integer>> f1 = service.submit(t1);
Future<List<Integer>> f2 = service.submit(t2);
Future<List<Integer>> f3 = service.submit(t3);
Future<List<Integer>> f4 = service.submit(t4);
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
f1.get();
f2.get();
f3.get();
f4.get();
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end-start);
}
static class MyTask implements Callable<List<Integer>> {
int startPos,endPos;
MyTask(int s,int e){
this.startPos = s;
this.endPos = e;
}
public List<Integer> call() throws Exception{
List<Integer> r = getPrime(startPos, endPos);
return r;
}
}
static boolean isPrime(int num){
for(int i=2;i<=num/2;i++){
if(num%i==0) return false;
}
return true;
}
static List<Integer> getPrime(int start,int end){
List<Integer> results = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=start;i<=end;i++){
if(isPrime(i)) results.add(i);
}
return results;
}
}
输出:
2513
786
2.6 线程池——CacheThreadPool
刚开始一个线程也没有,来一个任务起一个线程,如果来一个新的任务,线程池里刚好有一个线程空闲,直接让空闲线程执行任务,否则,起一个新线程;默认情况下,线程空闲超过60s自动销毁;
public class T_CacheThreadPool {
public static void main(String[] agrs) throws InterruptedException{
ExecutorService service = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
System.out.println(service);
for(int i=0;i<2;i++){
service.execute(()->{
try{
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500);
}catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
}
System.out.println(service);
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(80);
System.out.println(service);
}
}
运行结果:
java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor@1540e19d[Running, pool size = 0, active threads = 0, queued tasks = 0, completed tasks = 0]
java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor@1540e19d[Running, pool size = 2, active threads = 2, queued tasks = 0, completed tasks = 0]
pool-1-thread-2
pool-1-thread-1
java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor@1540e19d[Running, pool size = 0, active threads = 0, queued tasks = 0, completed tasks = 2]
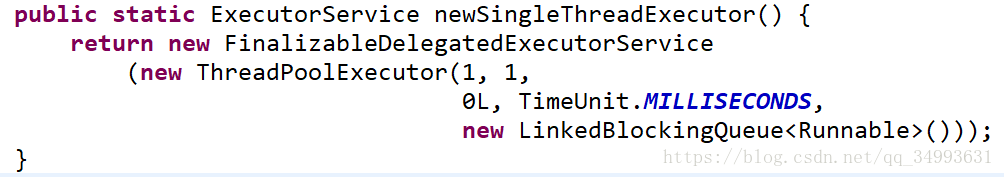
2.7 线程池——SingleThreadPool
线程池里就一个线程,保证任务顺序执行
public class SingleThreadPool {
public static void main(String[] agrs){
ExecutorService service = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
final int j = i;
service.execute(()->{
System.out.println(j+" "+Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
}
}
}
输出:
0 pool-1-thread-1
1 pool-1-thread-1
2 pool-1-thread-1
3 pool-1-thread-1
4 pool-1-thread-1
2.8 线程池——SchedulePool
与DelayQueue相对应,执行定时的任务,线程池里的线程可以复用
public class SchedulePool {
public static void main(String[] agrs){
ScheduledExecutorService service = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(4);
service.scheduleAtFixedRate(()->{
try{
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(new Random().nextInt(1000));
}catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
},0,500, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
}
2.9 线程池——WorkStealingPool
工作窃取:有一堆任务和一堆线程,每个线程都维护一个自己的任务队列,当一个线程执行完自己队列里的任务,会去别的线程队列中“偷”未执行的任务继续执行;
public class WorkStealPool {
public static void main(String[] agrs) throws IOException {
ExecutorService service = Executors.newWorkStealingPool();
//打印cup多少核
System.out.println(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());
service.execute(new R(1000));
service.execute(new R(2000));
service.execute(new R(2000));
service.execute(new R(2000));
service.execute(new R(2000));
//由于产生的是守护线程,主线程不阻塞看不到输出
System.in.read();
}
public static class R implements Runnable{
int time;
R(int t){
this.time = t;
}
public void run(){
try{
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(time);
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(time+" "+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
}
2.10 线程池——ForkJoinPool
如果有一项特别难以完成的大任务,可以把大任务切分成小的任务(Fork),最后合并小任务(Join);
public class ForkJoinPool2 {
static int[] nums = new int[1000000];
static final int MAX_NUM = 50000;
static Random r = new Random();
//求和
static {
for(int i=0; i<nums.length;i++){
nums[i]=r.nextInt(100);
}
System.out.println(Arrays.stream(nums).sum());
}
static class AddTask extends RecursiveAction{
int start,end;
AddTask(int s, int e){
start = s;
end = e;
}
protected void compute(){
if(end-start<=MAX_NUM){
long sum = 0L;
for(int i=start;i<end;i++){
sum+=nums[i];
}
System.out.println("from:"+start+"to:"+end+"="+sum);
}else{
int middle = start+(end-start)/2;
AddTask subTask1 = new AddTask(start,middle);
AddTask subTask2 = new AddTask(middle,end);
subTask1.fork();
subTask2.fork();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] agrs) throws IOException{
ForkJoinPool fjp = new ForkJoinPool();
AddTask task = new AddTask(0,nums.length);
fjp.execute(task);
System.in.read();
}
}
49508417
from:593750to:625000=1543717
from:468750to:500000=1548821
from:843750to:875000=1548865
from:968750to:1000000=1543900
from:718750to:750000=1539386
from:437500to:468750=1547593
from:812500to:843750=1538471
from:687500to:718750=1540626
from:562500to:593750=1545775
from:937500to:968750=1546144
from:406250to:437500=1550529
from:781250to:812500=1540313
from:218750to:250000=1556540
from:656250to:687500=1547825
from:93750to:125000=1545292
from:156250to:187500=1546528
from:531250to:562500=1544129
from:750000to:781250=1541918
from:500000to:531250=1551838
from:906250to:937500=1549404
from:625000to:656250=1550692
from:375000to:406250=1544616
from:62500to:93750=1554626
from:875000to:906250=1548556
from:343750to:375000=1554709
from:281250to:312500=1545881
from:125000to:156250=1550330
from:312500to:343750=1548005
from:250000to:281250=1552814
from:31250to:62500=1547229
from:187500to:218750=1545491
from:0to:31250=1547854
没有计算总的sun,因为RecursiveAction是没有返回值的,改为继承RecursiveTask,如下
public class ForkJoinPool2 {
static int[] nums = new int[1000000];
static final int MAX_NUM = 50000;
static Random r = new Random();
//求和
static {
for(int i=0; i<nums.length;i++){
nums[i]=r.nextInt(100);
}
System.out.println(Arrays.stream(nums).sum());
}
static class AddTask extends RecursiveTask<Long> {
int start,end;
AddTask(int s, int e){
start = s;
end = e;
}
protected Long compute(){
if(end-start<=MAX_NUM){
long sum = 0L;
for(int i=start;i<end;i++){
sum+=nums[i];
}
return sum;
}
int middle = start+(end-start)/2;
AddTask subTask1 = new AddTask(start,middle);
AddTask subTask2 = new AddTask(middle,end);
subTask1.fork();
subTask2.fork();
return subTask1.join()+subTask2.join();
}
}
public static void main(String[] agrs) throws IOException{
ForkJoinPool fjp = new ForkJoinPool();
AddTask task = new AddTask(0,nums.length);
fjp.execute(task);
long result = task.join();
System.out.println(result);
//System.in.read();
}
}
2.11 线程池——ThreadPoolExecutor
线程池的底层实现:

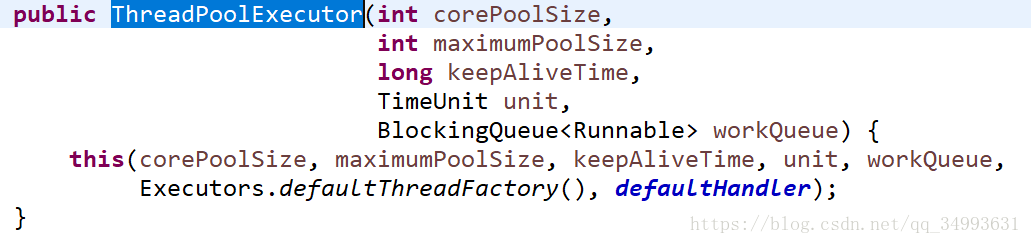
发现它们都基于ThreadPoolExector,WorkStealingPool与ForkJoinPool的底层都是ForkJoinPool。
2530
570
2.12——parallelStreamAPI
public class T_ParallelStreamAPI {
public static void main(String[] agrs){
List<Integer> nums = new ArrayList<>();
Random r = new Random();
for(int i=0;i<10000;i++){
nums.add(1000000+r.nextInt(1000000));
}
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
nums.forEach(v->isPrime(v));
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end-start);
//使用parallelStream api
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
//默认使用多线程
nums.parallelStream().forEach(T_ParallelStreamAPI::isPrime);
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end-start);
}
static boolean isPrime(int num){
for(int i=2;i<num/2;i++){
if(num%i==0)
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
2530
570
Java 多线程高并发编程 笔记(二)的更多相关文章
- Java 多线程高并发编程 笔记(一)
本篇文章主要是总结Java多线程/高并发编程的知识点,由浅入深,仅作自己的学习笔记,部分侵删. 一 . 基础知识点 1. 进程于线程的概念 2.线程创建的两种方式 注:public void run( ...
- Java多线程高并发学习笔记(二)——深入理解ReentrantLock与Condition
锁的概念 从jdk发行1.5版本之后,在原来synchronize的基础上,增加了重入锁ReentrantLock. 本文就不介绍synchronize了,有兴趣的同学可以去了解一下,本文重点介绍Re ...
- Java多线程高并发学习笔记——阻塞队列
在探讨可重入锁之后,接下来学习阻塞队列,这边篇文章也是断断续续的写了很久,因为最近开始学ssm框架,准备做一个自己的小网站,后续可能更新自己写网站的技术分享. 请尊重作者劳动成果,转载请标明原文链接: ...
- Java多线程高并发学习笔记(一)——Thread&Runnable
进程与线程 首先来看百度百科关于进程的介绍: 进程是一个具有独立功能的程序关于某个数据集合的一次运行活动.它可以申请和拥有系统资源,是一个动态的概念,是一个活动的实体.它不只是程序的代码,还包括当前的 ...
- JAVA多线程高并发学习笔记(三)——Callable、Future和FutureTask
为什么要是用Callable和Future Runnable的局限性 Executor采用Runnable作为基本的表达形式,虽然Runnable的run方法能够写入日志,写入文件,写入数据库等操作, ...
- Java多线程高并发学习笔记(三)——深入理解线程池
线程池最核心的一个类:ThreadPoolExecutor. 看一下该类的构造器: public ThreadPoolExecutor(int paramInt1, int paramInt2, lo ...
- 多线程高并发编程(3) -- ReentrantLock源码分析AQS
背景: AbstractQueuedSynchronizer(AQS) public abstract class AbstractQueuedSynchronizer extends Abstrac ...
- Java 多线程:并发编程的三大特性
Java 多线程:并发编程的三大特性 作者:Grey 原文地址: 博客园:Java 多线程:并发编程的三大特性 CSDN:Java 多线程:并发编程的三大特性 可见性 所谓线程数据的可见性,指的就是内 ...
- java线程高并发编程
java线程具体解释及高并发编程庖丁解牛 线程概述: 祖宗: 说起java高并发编程,就不得不提起一位老先生Doug Lea,这位老先生可不得了.看看百度百科对他的评价,一点也不为过: 假设IT的历史 ...
随机推荐
- BZOJ 4435 [Cerc2015]Juice Junctions 分治最小割+hash
分治最小割的题目,要求n2. 之前用的n3的方法自然不能用了. 于是用hash,设hash[i][j]表示在最小割为i的时候,j是否与S联通. 看懂这个需要理解一下最小割树的构造. 这种题建议用EK写 ...
- 20145239杜文超 《Java程序设计》第8周学习总结
20145239 <Java程序设计>第8周学习总结 教材学习内容总结 通用API 日志API 1.java.util.logging包提供了日志功能相关类与接口,使用日志的起点是logg ...
- Codeforces - 828C String Reconstruction —— 并查集find()函数
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/828/problem/C C. String Reconstruction time limit per test 2 seco ...
- 搭建LoadRunner中的场景(一) 创建场景
一.创建场景 1. 使用场景创建设置对话框 场景分类: 1. 人工场景:相比面向目标场景,人工场景在实际工作中的应用更为广泛. 2. 面向目标场景:预先定义了一个测试目标,LoadRunner将根据这 ...
- 【Codeforces】894E.Ralph and Mushrooms Tarjan缩点+DP
题意 给定$n$个点$m$条边有向图及边权$w$,第$i$次经过一条边边权为$w-1-2.-..-i$,$w\ge 0$给定起点$s$问从起点出发最多能够得到权和,某条边可重复经过 有向图能够重复经过 ...
- python 动态添加属性及方法及“__slots__的作用”
1.动态添加属性 class Person(object): def __init__(self, newName, newAge): self.name = newName self.age = n ...
- <十七>UML核心视图动态视图之时序图
一:时序图 --->时序图是用于描述按时间顺序排列的对象之间的交互模式. --->它按照参与交互的对象所具有的“生命线”和他们相互发送的消息来显示这些对象. --->时序图包含对象和 ...
- 【Opencv】Mat基础
1.Mat::imread() C++: Mat imread(const string& filename, int flags=1 ) filename – Name of file to ...
- BZOJ1878:[SDOI2009]HH的项链
浅谈树状数组与线段树:https://www.cnblogs.com/AKMer/p/9946944.html 题目传送门:https://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/prob ...
- WPF 使用MultiBinding ,TwoWay ,ValidationRule ,需要注意的事项
当wpf使用multibinding时, 其内部的validaterule的value 是其多个Binding的值, 要根据情况去验证, 还有就是在做IMultiConverter的ConvertBa ...
