Some 3D Graphics (rgl) for Classification with Splines and Logistic Regression (from The Elements of Statistical Learning)(转)
This semester I'm teaching from Hastie, Tibshirani, and Friedman's book, The Elements of Statistical Learning, 2nd Edition. The authors provide aMixture Simulation data set that has two continuous predictors and a binary outcome. This data is used to demonstrate classification procedures by plotting classification boundaries in the two predictors. For example, the figure below is a reproduction of Figure 2.5 in the book:
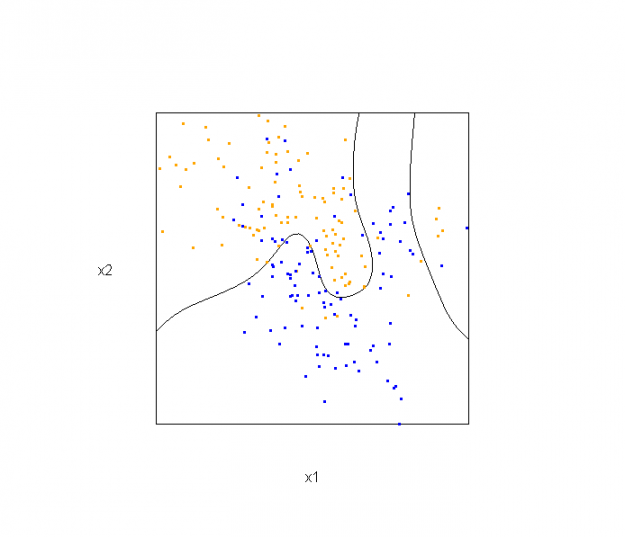
The solid line represents the Bayes decision boundary (i.e., {x: Pr("orange"|x) = 0.5}), which is computed from the model used to simulate these data. The Bayes decision boundary and other boundaries are determined by one or more surfaces (e.g., Pr("orange"|x)), which are generally omitted from the graphics. In class, we decided to use the R package rgl to create a 3D representation of this surface. Below is the code and graphic (well, a 2D projection) associated with the Bayes decision boundary:
library(rgl)
load(url("http://statweb.stanford.edu/~tibs/ElemStatLearn/datasets/ESL.mixture.rda"))
dat <- ESL.mixture ## create 3D graphic, rotate to view 2D x1/x2 projection
par3d(FOV=1,userMatrix=diag(4))
plot3d(dat$xnew[,1], dat$xnew[,2], dat$prob, type="n",
xlab="x1", ylab="x2", zlab="",
axes=FALSE, box=TRUE, aspect=1) ## plot points and bounding box
x1r <- range(dat$px1)
x2r <- range(dat$px2)
pts <- plot3d(dat$x[,1], dat$x[,2], 1,
type="p", radius=0.5, add=TRUE,
col=ifelse(dat$y, "orange", "blue"))
lns <- lines3d(x1r[c(1,2,2,1,1)], x2r[c(1,1,2,2,1)], 1) ## draw Bayes (True) decision boundary; provided by authors
dat$probm <- with(dat, matrix(prob, length(px1), length(px2)))
dat$cls <- with(dat, contourLines(px1, px2, probm, levels=0.5))
pls <- lapply(dat$cls, function(p) lines3d(p$x, p$y, z=1)) ## plot marginal (w.r.t mixture) probability surface and decision plane
sfc <- surface3d(dat$px1, dat$px2, dat$prob, alpha=1.0,
color="gray", specular="gray")
qds <- quads3d(x1r[c(1,2,2,1)], x2r[c(1,1,2,2)], 0.5, alpha=0.4,
color="gray", lit=FALSE)
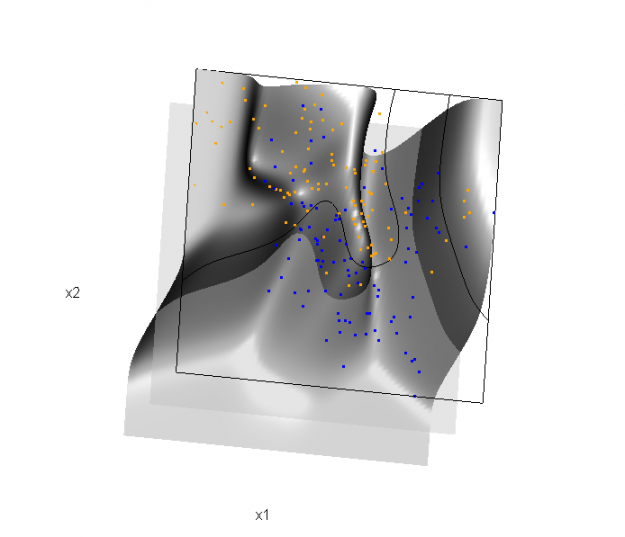
In the above graphic, the probability surface is represented in gray, and the Bayes decision boundary occurs where the plane f(x) = 0.5 (in light gray) intersects with the probability surface.
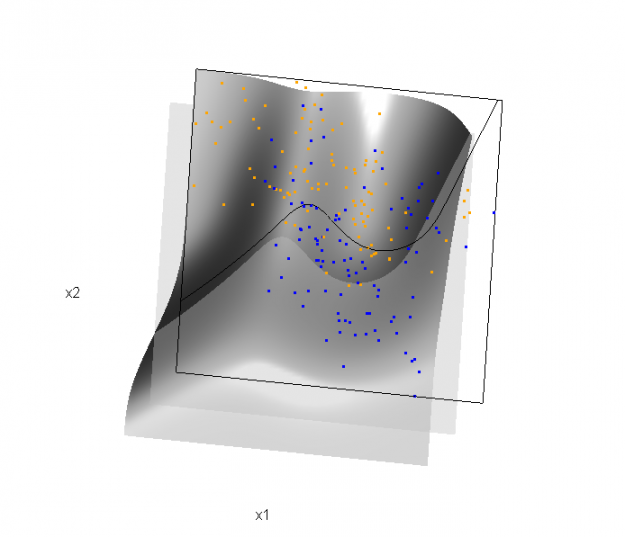
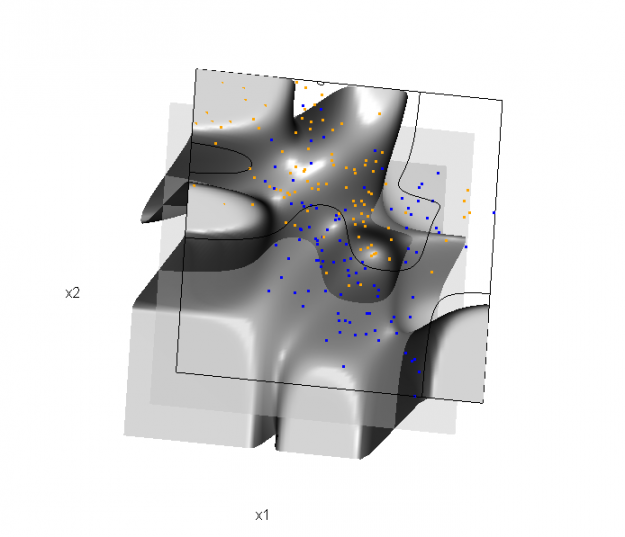
Of course, the classification task is to estimate a decision boundary given the data. Chapter 5 presents two multidimensional splines approaches, in conjunction with binary logistic regression, to estimate a decision boundary. The upper panel of Figure 5.11 in the book shows the decision boundary associated with additive natural cubic splines in x1 and x2 (4 df in each direction; 1+(4-1)+(4-1) = 7 parameters), and the lower panel shows the corresponding tensor product splines (4x4 = 16 parameters), which are much more flexible, of course. The code and graphics below reproduce the decision boundaries shown in Figure 5.11, and additionally illustrate the estimated probability surface (note: this code below should only be executed after the above code, since the 3D graphic is modified, rather than created anew):
Reproducing Figure 5.11 (top):
## clear the surface, decision plane, and decision boundary
par3d(userMatrix=diag(4)); pop3d(id=sfc); pop3d(id=qds)
for(pl in pls) pop3d(id=pl) ## fit additive natural cubic spline model
library(splines)
ddat <- data.frame(y=dat$y, x1=dat$x[,1], x2=dat$x[,2])
form.add <- y ~ ns(x1, df=3)+
ns(x2, df=3)
fit.add <- glm(form.add, data=ddat, family=binomial(link="logit")) ## compute probabilities, plot classification boundary
probs.add <- predict(fit.add, type="response",
newdata = data.frame(x1=dat$xnew[,1], x2=dat$xnew[,2]))
dat$probm.add <- with(dat, matrix(probs.add, length(px1), length(px2)))
dat$cls.add <- with(dat, contourLines(px1, px2, probm.add, levels=0.5))
pls <- lapply(dat$cls.add, function(p) lines3d(p$x, p$y, z=1)) ## plot probability surface and decision plane
sfc <- surface3d(dat$px1, dat$px2, probs.add, alpha=1.0,
color="gray", specular="gray")
qds <- quads3d(x1r[c(1,2,2,1)], x2r[c(1,1,2,2)], 0.5, alpha=0.4,
color="gray", lit=FALSE)
Reproducing Figure 5.11 (bottom)
## clear the surface, decision plane, and decision boundary
par3d(userMatrix=diag(4)); pop3d(id=sfc); pop3d(id=qds)
for(pl in pls) pop3d(id=pl) ## fit tensor product natural cubic spline model
form.tpr <- y ~ 0 + ns(x1, df=4, intercept=TRUE):
ns(x2, df=4, intercept=TRUE)
fit.tpr <- glm(form.tpr, data=ddat, family=binomial(link="logit")) ## compute probabilities, plot classification boundary
probs.tpr <- predict(fit.tpr, type="response",
newdata = data.frame(x1=dat$xnew[,1], x2=dat$xnew[,2]))
dat$probm.tpr <- with(dat, matrix(probs.tpr, length(px1), length(px2)))
dat$cls.tpr <- with(dat, contourLines(px1, px2, probm.tpr, levels=0.5))
pls <- lapply(dat$cls.tpr, function(p) lines3d(p$x, p$y, z=1)) ## plot probability surface and decision plane
sfc <- surface3d(dat$px1, dat$px2, probs.tpr, alpha=1.0,
color="gray", specular="gray")
qds <- quads3d(x1r[c(1,2,2,1)], x2r[c(1,1,2,2)], 0.5, alpha=0.4,
color="gray", lit=FALSE)
Although the graphics above are static, it is possible to embed an interactive 3D version within a web page (e.g., see the rgl vignette; best with Google Chrome), using the rgl function writeWebGL. I gave up on trying to embed such a graphic into this WordPress blog post, but I have created a separate page for the interactive 3D version of Figure 5.11b. Duncan Murdoch's work with this package is reall nice!
This entry was posted in Technical and tagged data, graphics, programming, R, statistics on February 1, 2015.
转自:http://biostatmatt.com/archives/2659
Some 3D Graphics (rgl) for Classification with Splines and Logistic Regression (from The Elements of Statistical Learning)(转)的更多相关文章
- More 3D Graphics (rgl) for Classification with Local Logistic Regression and Kernel Density Estimates (from The Elements of Statistical Learning)(转)
This post builds on a previous post, but can be read and understood independently. As part of my cou ...
- 机器学习理论基础学习3.3--- Linear classification 线性分类之logistic regression(基于经验风险最小化)
一.逻辑回归是什么? 1.逻辑回归 逻辑回归假设数据服从伯努利分布,通过极大化似然函数的方法,运用梯度下降来求解参数,来达到将数据二分类的目的. logistic回归也称为逻辑回归,与线性回归这样输出 ...
- 李宏毅机器学习笔记3:Classification、Logistic Regression
李宏毅老师的机器学习课程和吴恩达老师的机器学习课程都是都是ML和DL非常好的入门资料,在YouTube.网易云课堂.B站都能观看到相应的课程视频,接下来这一系列的博客我都将记录老师上课的笔记以及自己对 ...
- Logistic Regression Using Gradient Descent -- Binary Classification 代码实现
1. 原理 Cost function Theta 2. Python # -*- coding:utf8 -*- import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplo ...
- Classification week2: logistic regression classifier 笔记
华盛顿大学 machine learning: Classification 笔记. linear classifier 线性分类器 多项式: Logistic regression & 概率 ...
- Android Programming 3D Graphics with OpenGL ES (Including Nehe's Port)
https://www3.ntu.edu.sg/home/ehchua/programming/android/Android_3D.html
- Logistic Regression and Classification
分类(Classification)与回归都属于监督学习,两者的唯一区别在于,前者要预测的输出变量\(y\)只能取离散值,而后者的输出变量是连续的.这些离散的输出变量在分类问题中通常称之为标签(Lab ...
- Logistic Regression求解classification问题
classification问题和regression问题类似,区别在于y值是一个离散值,例如binary classification,y值只取0或1. 方法来自Andrew Ng的Machine ...
- 分类和逻辑回归(Classification and logistic regression)
分类问题和线性回归问题问题很像,只是在分类问题中,我们预测的y值包含在一个小的离散数据集里.首先,认识一下二元分类(binary classification),在二元分类中,y的取值只能是0和1.例 ...
随机推荐
- WCF和ASP.NET Web API在应用上的选择
小分享:我有几张阿里云优惠券,用券购买或者升级阿里云相应产品最多可以优惠五折!领券地址:https://promotion.aliyun.com/ntms/act/ambassador/shareto ...
- css3 loading动画 三个省略号
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8" ...
- asp.net SignalR 一对一聊天
<script src="~/Scripts/jquery-1.8.2.min.js"></script> <script src="~/S ...
- Android -- 从源码带你从EventBus2.0飚到EventBus3.0(一)
1,最近看了不少的面试题,不管是百度.网易.阿里的面试题,都会问到EventBus源码和RxJava源码,而自己只是在项目中使用过,却没有去用心的了解它底层是怎么实现的,所以今天就和大家一起来学习学习 ...
- ios sqlite3的简单使用
第一:创建表格 //创建表格 -(void)creatTab{ NSString*creatSQL=@"CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS PERSIONFO(ID INT ...
- 轻量级操作系统FreeRTOS的内存管理机制(一)
本文由嵌入式企鹅圈原创团队成员朱衡德(Hunter_Zhu)供稿. 近几年来,FreeRTOS在嵌入式操作系统排行榜中一直位居前列,作为开源的嵌入式操作系统之一,它支持许多不同架构的处理器以及多种编译 ...
- linux C/C++ 日志打印函数
//宏定义日志文件名 #define PROCESSNAME "log_filename" //当日志文件大于5M时,会删除该文件,该接口使用方法 参照printfvoid Wr ...
- unity 看到Sphere内部,通过Sphere播放全景视频时候遇到的问题
Unity创建一Sphere默认是看不到球体内部的,所以需要用 Cull Front 修改剔除的方向,这就会带来一个新的问题,所播放的视频是像镜子一样翻转着的,所以要改变它的UV坐标使其翻转过来 f ...
- C#网络程序设计(1)网络编程常识与C#常用特性
网络程序设计能够帮我们了解联网应用的底层通信原理! (1)网络编程常识: 1)什么是网络编程 只有主要实现进程(线程)相互通信和基本的网络应用原理性(协议)功能的程序,才能算是真正的网 ...
- jdk动态代理与cglib代理、spring aop代理实现原理解析
原创声明:本博客来源为本人原创作品,绝非他处摘取,转摘请联系博主 代理(proxy)的定义:为某对象提供代理服务,拥有操作代理对象的功能,在某些情况下,当客户不想或者不能直接引用另一个对象,而代理对象 ...
