python3笔记二十三:正则表达式之元字符
一:学习内容
- 匹配单个字符与数字:.、[]、^、\d、\D、\w、\W、\s、\S
- 匹配锚字符(边界字符):^、$、\A、\Z、\b、\B
- 匹配多个字符:(xyz) 、x?、x*、.*、x+、x{n}、x{n,}、x{n,m}、x|y
- 非贪婪匹配:*?、+?、??、{n,m}?
二:匹配单个字符与数字
1.点.:匹配除换行符以外的任意字符
2.[]:是字符集合,表示匹配方括号中所包含的任意一个字符
[0123456789] 表示匹配任意一个数字
[0-9] 表示匹配任意一个数字
[yml] 表示匹配'y','m','l'中任意一个字符
[a-z] 表示匹配任意一个小写字符
[A-Z] 表示匹配任意一个大写字符
[0-9a-zA-Z] 表示匹配任意一个数字和字母
[0-9a-zA-Z_] 表示匹配任意一个数字、字母和下划线
3.^:是脱字符,表示不匹配集合中的字符,注意^在[]中才表示不匹配,在其他位置意义不一样
[^test] 表示匹配除了test这几个字母以外的所有字符
[^0-9] 表示匹配所有的非数字字符
4.\d:匹配数字,效果同[0-9]
\d 表示匹配任意一个数字,这里可以不写[],直接使用\d
[^\d] 表示匹配所有的非数字字符,效果同[^0-9]
5.\D:匹配非数字字符,效果同[^0-9]
6.\w:匹配数字、字母和下划线,效果同[0-9a-zA-Z]
7.\W:匹配非数字、字母和下划线,效果同[^0-9a-zA-Z]
8.\s:匹配任意的空白符(空格、换行、回车、换页、制表符),效果同[ \f\n\r\t]
9.\S:匹配任意的非空白符(空格、换行、回车、换页、制表符),效果同[^ \f\n\r\t]
10.举例:
print(re.search(".","tester is a good girl!")) #.可以代表任意字符,所以匹配t,结果匹配一个t
print(re.search("[0123456789]","yml is a good gril 7")) #匹配结果为数字7
print(re.search("[tester]","tester is a good gril 7")) #匹配结果为一个t
print(re.search("[^tester]","tester is a good gril 7")) #匹配除tester之外的任意一个字符结果为空" "
print(re.search("[^0-9]","tester is a good gril 7")) #匹配一个非数字字符结果为t
print(re.search("\d","tester is a good gril 7")) #匹配结果为数字7
print(re.search("[^\d]","tester is a good gril 7")) #匹配结果为一个t
print(re.search("\D","tester is a good gril 7")) #匹配一个非数字字符结果为t
print(re.search("\w","tester is a good gril 7")) #匹配任意一个数字字母或下划线,结果为t
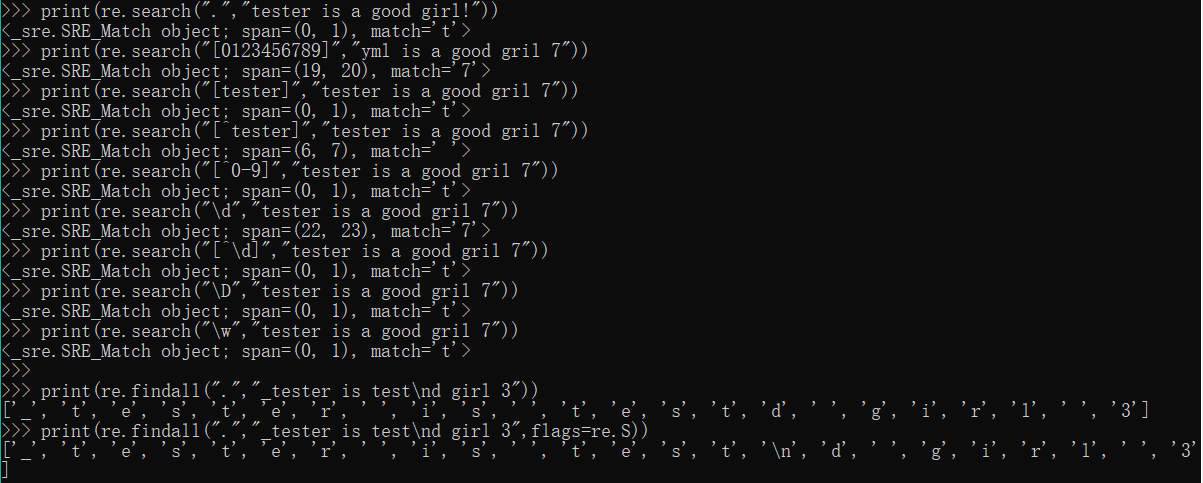
print(re.findall(".","_tester is test\nd girl 3")) #匹配除换行符以外的任意字符
print(re.findall(".","_tester is test\nd girl 3",flags=re.S)) #匹配包括换行符在内的任意字符
三:匹配锚字符(边界字符)
1.^:行首匹配,注意^在[]中才表示不匹配集合中的字符
2.$:行尾匹配
3.\A:匹配字符串开始,它和^区别是:
\A只匹配整个字符串的开头即使在re.M模式下,也不会匹配其他行的行首
^匹配的是每行的行首
4.\Z:匹配字符串结束,它和$区别是:
\Z只匹配整个字符串的结束即使在re.M模式下,也不会匹配其他行的行尾
$匹配的是每行的行尾
5.\b:匹配一个单词的边界,也就是指单词和空格间的位置
6.\B:匹配非单词的边界,也就是指单词和空格间的位置
7.举例:
print(re.search("^test","test is a good girl")) #表示行首必须要是test开头
print(re.search("girl$","test is a good girl")) #表示行尾必须要是girl结尾
print(re.search("\Atest","test is a good girl"))
print(re.findall("^test","test is a good girl\ntest is a good girl",flags=re.M))
print(re.findall("\Atest","test is a good girl\ntest is a good girl",flags=re.M))
print(re.findall("girl$","test is a good girl\ntest is a good girl",flags=re.M))
print(re.findall("girl\Z","test is a good girl\ntest is a good girl",flags=re.M))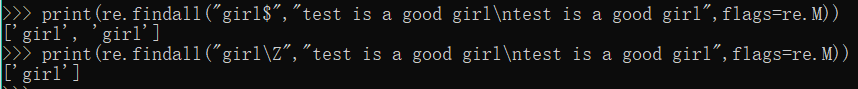
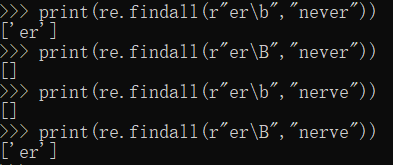
print(re.findall(r"er\b","never"))
print(re.findall(r"er\B","never"))
print(re.findall(r"er\b","nerve"))
print(re.findall(r"er\B","nerve"))
四:匹配多个字符
说明:下方的x、y、z均为假设的普通字符,n、m为非负整数,不是正则表达式的元字符
1.(xyz):匹配小括号内的内容,()内的内容xyz作为一个整体去匹配
2.x?:匹配0个或者1个x,非贪婪匹配(尽可能少的匹配)
3.x*:匹配0个或者任意多个x,贪婪匹配(尽可能多的匹配)
.*:表示匹配0个或任意多个字符(换行符除外)
4.x+:匹配至少一个x,贪婪匹配(尽可能多的匹配)
5.x{n}:匹配确定的n个x,n是一个非负整数
6.x{n,}:匹配至少n个x,n是一个非负整数
7.x{n,m}:匹配至少n个最多m个x,注意:n <= m
8.x|y:|表示或,匹配的是x或y
9.举例:
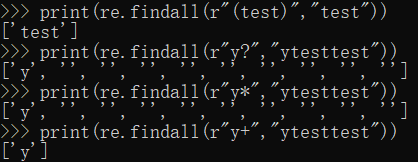
print(re.findall(r"(test)","test"))
print(re.findall(r"y?","ytesttest")) #匹配0个或1个
print(re.findall(r"y*","ytesttest")) #匹配0个或任意多个,贪婪匹配
print(re.findall(r"y+","ytesttest")) #匹配至少1个,贪婪匹配
print(re.findall(r"y{3}","ytestyyytest")) #匹配3个y
print(re.findall(r"y{3,}","yytestyyytest")) #匹配至少3个y
print(re.findall(r"y{3,6}","yytestyyytest")) #匹配至少3个y,最多6个y

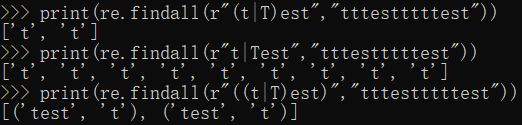
print(re.findall(r"(t|T)est","tttestttttest")) #匹配t或T
print(re.findall(r"t|Test","tttestttttest"))
print(re.findall(r"((t|T)est)","tttestttttest"))
#需求:提取tester......girl
str = "tester is a good girl!tester is a nice girl!tester is a very dddd girl"
print(re.findall(r"tester.*girl",str))
print(re.findall(r"tester.*?girl",str)) #非贪婪

五:非贪婪匹配
1. *?:前一个字符0次或无限次扩展,最小匹配
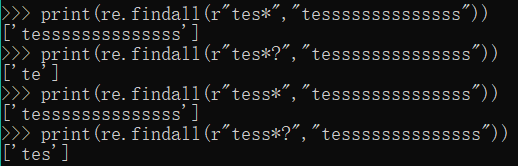
print(re.findall(r"tes*","tessssssssssssss"))
print(re.findall(r"tes*?","tessssssssssssss"))
print(re.findall(r"tess*","tessssssssssssss"))
print(re.findall(r"tess*?","tessssssssssssss"))
2. +?:前一个字符1次或无限次扩展,最小匹配
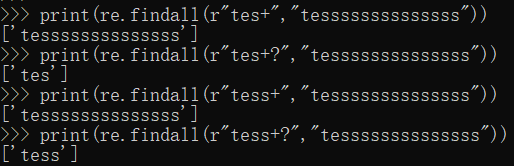
print(re.findall(r"tes+","tessssssssssssss"))
print(re.findall(r"tes+?","tessssssssssssss"))
print(re.findall(r"tess+","tessssssssssssss"))
print(re.findall(r"tess+?","tessssssssssssss"))
3. ??:前一个字符0次或1次扩展,最小匹配
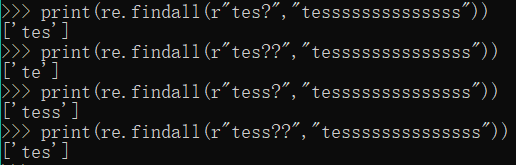
print(re.findall(r"tes?","tessssssssssssss"))
print(re.findall(r"tes??","tessssssssssssss"))
print(re.findall(r"tess?","tessssssssssssss"))
print(re.findall(r"tess??","tessssssssssssss"))
4. {n,m}?:扩展前一个字符n到m次,含m,最小匹配
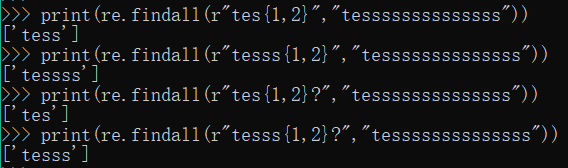
print(re.findall(r"tes{1,2}","tessssssssssssss"))
print(re.findall(r"tesss{1,2}","tessssssssssssss"))
print(re.findall(r"tes{1,2}?","tessssssssssssss"))
print(re.findall(r"tesss{1,2}?","tessssssssssssss"))
python3笔记二十三:正则表达式之元字符的更多相关文章
- python3笔记二十三:正则表达式之其他函数
一:学习内容 re.split函数 re.finditer函数 re.sub函数 group()分组 re.compile函数 二:字符串切割---re.split函数 需要导入包:import re ...
- python3.4学习笔记(二十三) Python调用淘宝IP库获取IP归属地返回省市运营商实例代码
python3.4学习笔记(二十三) Python调用淘宝IP库获取IP归属地返回省市运营商实例代码 淘宝IP地址库 http://ip.taobao.com/目前提供的服务包括:1. 根据用户提供的 ...
- (C/C++学习笔记) 二十三. 运行时类型识别
二十三. 运行时类型识别 ● 定义 运行时类型识别(Run-time Type Identification, RTTI) 通过RTTI, 程序能够使用基类的指针或引用来检查(check)这些指针或引 ...
- python3笔记二十二:正则表达式之函数
一:学习内容 re.match函数 re.search函数 re.findall函数 二:re.match函数 需要导入包:import re 1.格式:match(pattern,string,fl ...
- 【Python3 爬虫】08_正则表达式(元字符与语法)
元字符表 符号 说明 示例 . 表示任意字符 'abc' >>>'a.c' >>>结果为:'abc' ^ 表示字符开头 'abc' >>> ...
- Java基础学习笔记二十三 Java核心语法之反射
类加载器 类的加载 当程序要使用某个类时,如果该类还未被加载到内存中,则系统会通过加载,链接,初始化三步来实现对这个类进行初始化. 加载就是指将class文件读入内存,并为之创建一个Class对象.任 ...
- angular学习笔记(二十三)-$http(1)-api
之前说到的$http.get和$http.post,都是基于$http的快捷方式.下面来说说完整的$http: $http(config) $http接受一个json格式的参数config: conf ...
- python3笔记二十四:Mysql数据库操作命令
一:学习内容 Mysql操作命令:启动服务.停止服务.连接数据库.退出数据库.查看版本.显示当前时间.远程连接 数据库操作命令:创建数据库.删除数据库.切换数据库.查看当前选择的数据库 表操作命令:查 ...
- python3笔记二十一:时间操作datetime和calendar
一:学习内容 datetime calendar 二:datetime 1.模块说明:可以理解为datetime基于time进行了封装,提供了各种使用的函数,datetime模块的接口更直接,更容易调 ...
随机推荐
- CentOS7安装Docker-CE并部署项目
前言 这是我第一次使用dokcer部署项目,现学现卖.成功之后把所有用到的安装及部署和操作命令做一个总结.如有不足,请指教. 使用的是阿里云服务器.CentOS7版本. Dokcer安装 1.Cent ...
- SQL中 left join 的底层原理
介绍 left join的实现效果就是保留左表的全部信息,将右表往左表上拼接,如果拼不上则为NULL. 除了left join以外,还有inner join.outer join.right join ...
- jeesite表字段太多导致不能自动生成那张表的代码——————jetty 之 form too large | form too many keys 异常
看了Jetty的源码才发现,jetty限制了Form提交数据的大小,该源码类来自jetty lib库下的jetty-server-7.6.16.v20140903.jar包下的 org.eclipse ...
- SQLplus命令中删除键和翻页键不能用的问题
问题现象: 在进入连接数据库后,如何写错命令,删除键不好使,总是出现^H^H [oracle@master2 ~]$ sqlplus / as sysdba SQL*Plus: Release 12. ...
- Webmin代码执行漏洞复现
0x00 前言之前由于hw,没得时间分析.这个webmin相信大家很多次都在内网扫到过.也是内网拿机器得分的一环. 0x01影响版本Webmin<=1.920 0x02 环境搭建 建议大家以后用 ...
- 制作linux云主机镜像
目录 制作linux云主机镜像 1.物理机环境准备 2.安装kvm虚拟机 3.操作虚拟机 4.在物理机上处理镜像 5.拷贝制作好的raw格式的镜像 6.发布镜像到云平台 制作linux云主机镜像 1. ...
- Delphi MSComm控件事件的介绍
- XML基础介绍【一】
XML基础介绍[一] 1.XML简介(Extensible Markup Language)[可扩展标记语言] XML全称为Extensible Markup Language, 意思是可扩展的标记语 ...
- DA_06_iptables 与 firewalld 防火墙
8.1 防火墙管理工具 防火墙作为公网与内网之间的保护屏障,在保障数据的安全性方面起着至关重要的作用.主要功能都是依据策略对穿越防火墙自身的流量进行过滤.防火墙策略可以基于 流量的源目地址.端口号.协 ...
- Thymeleaf初探
Thymeleaf是一款用于渲染XML/XHTML/HTML5内容的模板引擎.类似JSP,Velocity,FreeMaker等,它也可以轻易的与Spring MVC等Web框架进行集成作为Web应用 ...
