TF_RNNCell
参考:链接。
RNNCell
- BasicRNNCell
- GRUCell
- BasicLSTMCell
- LSTMCell
- MultiRNNCell
抽象类RNNCell
所有的rnncell均继承于RNNCell, RNNCell主要定义了几个抽象方法:
def __call__(self, inputs, state, scope=None):
raise NotImplementedError("Abstract method") @property
def state_size(self):
raise NotImplementedError("Abstract method") @property
def output_size(self):
raise NotImplementedError("Abstract method")
上述方法,__call__在对象被使用时调用,其他可以看做属性方法,主要用作获取状态state的大小,cell的输出大小。既然对象使用时会调用__call__,那么各类RNN的操作都定义在这个方法中。接下来,我们就针对各个不同的cell来详细介绍各类RNN。
BasicRNNCell
这个cell是最基础的一个RNNCell,可以看做是对一般全连接层的拓展,除了在水平方向加入时序关系,可以用下图表示:
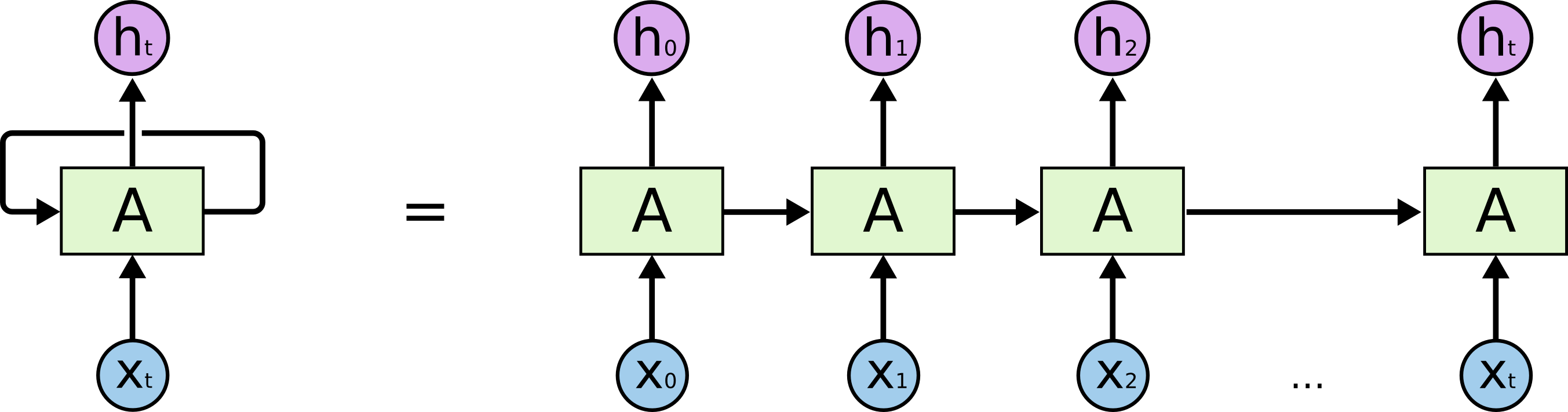
而BasicRNNCell的初始化方法可如代码所示:
def __init__(self, num_units, input_size=None, activation=tanh):
if input_size is not None:
logging.warn("%s: The input_size parameter is deprecated.", self)
self._num_units = num_units
self._activation = activation
初始化只需要给出num_units,用来指有多少个隐藏层单元;而activation指使用哪种激活函数用作激活输出。而对应的RNN操作定义在__call__方法中:
def __call__(self, inputs, state, scope=None):
"""Most basic RNN: output = new_state = activation(W * input + U * state + B)."""
with vs.variable_scope(scope or type(self).__name__): # "BasicRNNCell"
output = self._activation(_linear([inputs, state], self._num_units, True))
return output, output
很清晰,inputs表示隐藏层的输入,state表示上个时间的隐藏层状态,也可以说是上一次隐藏层向自身的输出,对于第一次输入,则需要初始化state,对应初始化方法有很多种,可以使用tensorflow提供的各种初始化函数。在__call__中,对输入inputs和state进行activation(wx+b),用作下次的输入。
GRUCell
GRU是对RNN的一种改进,相比LSTM来说,也可以看做是对LSTM的一种简化,是Bengio在14年提出来的,用作机器翻译。先看一下GRU的基本结构:
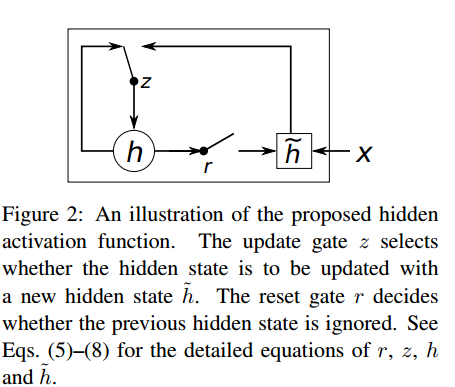
这里我们结合代码来看原理:
def __call__(self, inputs, state, scope=None):
"""Gated recurrent unit (GRU) with nunits cells."""
with vs.variable_scope(scope or type(self).__name__): # "GRUCell"
with vs.variable_scope("Gates"): # Reset gate and update gate.
# We start with bias of 1.0 to not reset and not update.
r, u = array_ops.split(1, 2, _linear([inputs, state],
2 * self._num_units, True, 1.0))
r, u = sigmoid(r), sigmoid(u)
with vs.variable_scope("Candidate"):
c = self._activation(_linear([inputs, r * state],
self._num_units, True))
new_h = u * state + (1 - u) * c
return new_h, new_h
GRUCell的初始化与RNN一样,给出输入和初始化的state,在使用对象时,利用输入和前一个时间的隐藏层状态,得到对应的Gates: r, u, 然后利用r更新cell状态,最后利用u得到新的隐藏层状态。对于RNN的改进,最厉害的莫过于下面的,而且有很多变种,这里tensorflow中只有几个简单常见的cell。接下来,我们开始看看LSTM。
BasicLSTMCell
这个cell可以看做是最简单的LSTM,在每个连接中没有额外的连接,即其他变种在连接中加入各种改进。对于BasicLSTMCell,可以如下图所示:
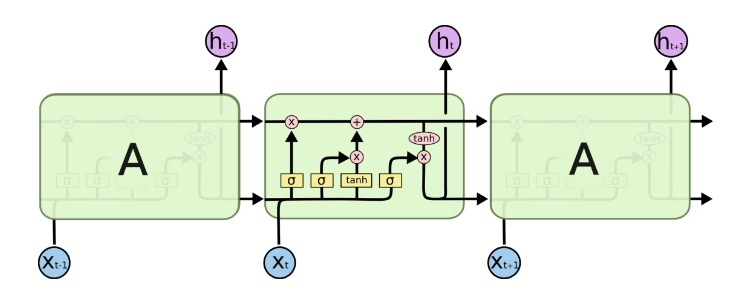
同样的,我们结合代码来看它的原理:
def __call__(self, inputs, state, scope=None):
"""Long short-term memory cell (LSTM)."""
with vs.variable_scope(scope or type(self).__name__): # "BasicLSTMCell"
# Parameters of gates are concatenated into one multiply for efficiency.
if self._state_is_tuple:
c, h = state
else:
c, h = array_ops.split(1, 2, state)
concat = _linear([inputs, h], 4 * self._num_units, True) # i = input_gate, j = new_input, f = forget_gate, o = output_gate
i, j, f, o = array_ops.split(1, 4, concat) new_c = (c * sigmoid(f + self._forget_bias) + sigmoid(i) *
self._activation(j))
new_h = self._activation(new_c) * sigmoid(o) if self._state_is_tuple:
new_state = LSTMStateTuple(new_c, new_h)
else:
new_state = array_ops.concat(1, [new_c, new_h])
return new_h, new_state
lstm有三个门,inputs, forget, output, 而中间cell用来管理结合他们生产需要的输出。在初始化结束之后,利用输入分别得到对应的门的输出,然后利用这三个门的信息分别更新cell和当前隐藏层状态。f 用来控制遗忘之前的信息和记忆当前信息的比例,进而更新cell,lstm可以看做是一种复杂的激活函数,它的存在依赖RNN的递归性。BasicLSTMCell只是个最基本的LSTM,而完整的LSTM可能比这个复杂,可以参看blog。
MultiRNNCell
对于MultiRNNCell,只能贴出完整代码来分析了:
class MultiRNNCell(RNNCell):
"""RNN cell composed sequentially of multiple simple cells.""" def __init__(self, cells, state_is_tuple=False):
"""Create a RNN cell composed sequentially of a number of RNNCells. Args:
cells: list of RNNCells that will be composed in this order.
state_is_tuple: If True, accepted and returned states are n-tuples, where
`n = len(cells)`. By default (False), the states are all
concatenated along the column axis. Raises:
ValueError: if cells is empty (not allowed), or at least one of the cells
returns a state tuple but the flag `state_is_tuple` is `False`.
"""
if not cells:
raise ValueError("Must specify at least one cell for MultiRNNCell.")
self._cells = cells
self._state_is_tuple = state_is_tuple
if not state_is_tuple:
if any(nest.is_sequence(c.state_size) for c in self._cells):
raise ValueError("Some cells return tuples of states, but the flag "
"state_is_tuple is not set. State sizes are: %s"
% str([c.state_size for c in self._cells])) @property
def state_size(self):
if self._state_is_tuple:
return tuple(cell.state_size for cell in self._cells)
else:
return sum([cell.state_size for cell in self._cells]) @property
def output_size(self):
return self._cells[-1].output_size def __call__(self, inputs, state, scope=None):
"""Run this multi-layer cell on inputs, starting from state."""
with vs.variable_scope(scope or type(self).__name__): # "MultiRNNCell"
cur_state_pos = 0
cur_inp = inputs
new_states = []
for i, cell in enumerate(self._cells):
with vs.variable_scope("Cell%d" % i):
if self._state_is_tuple:
if not nest.is_sequence(state):
raise ValueError(
"Expected state to be a tuple of length %d, but received: %s"
% (len(self.state_size), state))
cur_state = state[i]
else:
cur_state = array_ops.slice(
state, [0, cur_state_pos], [-1, cell.state_size])
cur_state_pos += cell.state_size
cur_inp, new_state = cell(cur_inp, cur_state)
new_states.append(new_state)
new_states = (tuple(new_states) if self._state_is_tuple
else array_ops.concat(1, new_states))
return cur_inp, new_states
创建对象时,可以看到初始化函数中不再是输入,而是变成了cells,,即一个cell是一层,多个cell便有多层RNNcell。而在使用对象时,单层可以看做多层的特例,对于输入inputs和state,同时得到多个cell的当前隐藏层状态,用作下个时间步。看似麻烦,其实很简洁,就是加入了对多个cell的计算,最后得到的新的隐藏层状态即每个cell的上个时间步的输出。
TF_RNNCell的更多相关文章
随机推荐
- IDEA 2019中一些有偏好设置
1.取消启动时自动进入上一次工程: 路径:Setting ——> Appearance & Behavior ——> System Setting 取消勾选Reopen last ...
- BiGAN的复现
数据集是10000个样本,前8000个训练集,后面的用来测试.每个样本是1*144(重构成12*12的矩阵),将原始BiGAN有编码器.判别器和生成器,将里面的全连接层全部替换成了卷积. from _ ...
- 【计算机视觉】Histogram of Oriented Gridients(HOG) 方向梯度直方图
Histogram of Oriented Gridients(HOG) 方向梯度直方图 Histogram of Oriented Gridients,缩写为HOG,是目前计算机视觉.模式识别领域很 ...
- JavaScript 控制台打印window对象
示例代码 <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF- ...
- JavaScript 3种内置对象
前面我们学了对象,如何创建对象及使用对象. 内置对象不需要实例化,就可以使用. 可以通俗地理解,在内存里的东东是对象,也就是实例化好的.在磁盘里的东东是类,需要实例化才能使用.实例化后的东东在内存里. ...
- 第八周课程总结&实验报告(六)
第八周课程总结 启动多线程售票(上课老师说要加入作业的部分) public class TestDemo { public static void main(StringD args) throws ...
- Windows 下部署 hadoop spark环境
一.先在本地安装jdk 我这里安装的jdk1.8,具体的安装过程这里不作赘述 二.部署安装maven 下载maven安装包,并解压 设置环境变量,MAVEN_HOME=D:\SoftWare\Mave ...
- [转帖]如何在Linux上使用命令行查看硬件信息
如何在Linux上使用命令行查看硬件信息 时间:2016-01-13 作者:admin 分类:新手入门 阅读:126次 http://embeddedlinux.org.cn/emb-linux/ ...
- 洛谷P2622 关灯问题II (二进制枚举+bfs
题目描述 现有n盏灯,以及m个按钮.每个按钮可以同时控制这n盏灯——按下了第i个按钮,对于所有的灯都有一个效果.按下i按钮对于第j盏灯,是下面3中效果之一:如果a[i][j]为1,那么当这盏灯开了的时 ...
- P1373 小a和uim之大逃离(DP)
(点击此处查看原题) 题意 中文题,题意看题面吧. 解题思路 注意到我们只能向右和下移动,由此想到开二维的dp数组dp[i][j],代表当前所在位置 我们需要让两人取数的差值为0,由于起点和走法的不同 ...
