Word2Vec原理及代码
一、Word2Vec简介
Word2Vec 是 Google 于 2013 年开源推出的一款将词表征为实数值向量的高效工具,采用的模型有CBOW(Continuous Bag-Of-Words,连续的词袋模型)和Skip-gram两种。Word2Vec通过训练,可以把对文本内容的处理简化为K维向量空间中的向量运算,而向量空间上的相似度可以用来表示文本语义上的相似度。因此,Word2Vec输出的词向量可以被用来做很多NLP相关的工作,比如聚类、找同义词、词性分析等等。经过训练,部分单词向量的加法组合运算能达到类似于下面公式的效果:
vector('Paris') - vector('France') + vector('Italy') ≈ vector('Rome')
此外,下图也简洁明了的展示的Word2Vec的词向量特征。
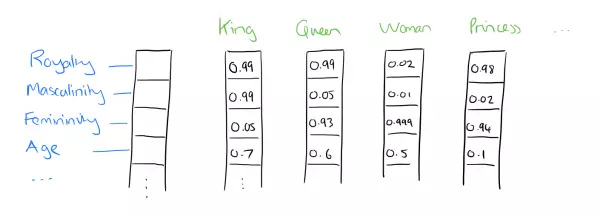
Word2Vec受欢迎的另一个原因是它的高效,具体思想可由Tomas Mikolov的两篇论文一探究竟。此文是我对Word2Vec学习的笔记。
二、分布式词表示(Distributed Representation)
自然语言处理的相关任务中,要想将自然语言处理交给机器学习中的算法处理,首先应该将语言数学化。在计算机运算中,向量可以说是人对机器输入的主要方式。而词向量,顾名思义,就是把一个词表示成一个向量,主要分为两种表示方法:One-Hot Representation 和 Distributed Representation。
我们知道,最简单的一种词表示方式是One-Hot表示,它的优点是很容易表示出不同的词,但是缺点也是巨大的:一、所有词向量正交,即无法刻画词与词之间的相似性。二、当有非常大的数据量时,向量的维度会因此扩大而造成维度灾难。如下所示,如果用One-Hot方式来表示自然界生物,自然界的动物种类数以百万记,因为数据量庞大,基本不可能用这种方式来表示动物类别,并且也无法表示诸如河虾、鲤鱼都生活在水里的这一相似性。
鲤鱼 [0,0,0,0,1,0,……,0,0,0,0,0,0,0]
河虾 [0,0,0,0,0,0,……,1,0,0,0,0,0,0]
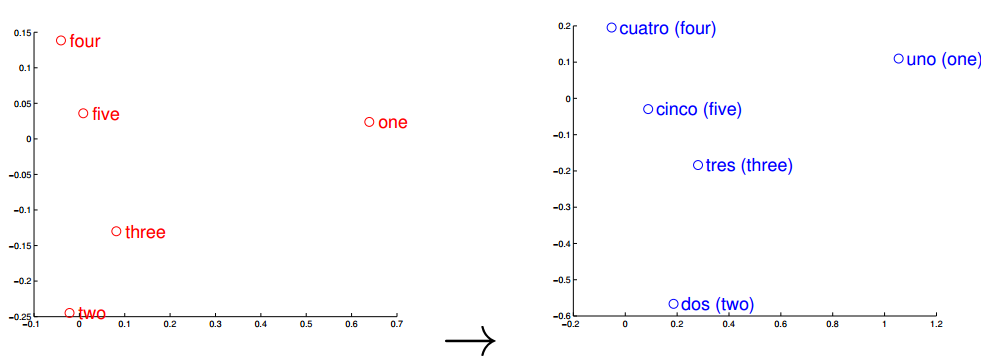
观察左右两图,可以发现:五个词在两个向量空间的相对位置差不多,说明了两种语言对应向量空间结构之间具有相似性,进一步说明词向量在刻画词与词相关性是合理的。
三、CBOW与skip-gram
语言模型形式化的描述就是给定一个T个词的字符串s,看他是自然语言的概率。举个例子:P(我,爱,学习,机器学习)= P(我)P(爱 | 我)P(学习 | 我,爱)P(机器学习 | 我,爱,学习)。这就是一种上下文相关的语言模型。但当碰到一个很长的语料,如果把一个词的出现要和前边所有出现过的单词联系起来,是非常复杂并且难以计算的。19世纪到20世纪初,俄罗斯数学家马尔科夫(Andrey Markov) 提出:假设任意一个词 wt 出现的概率只同他前面的词 wt-1 有关,问题就变得简单了。这种假设在数学上称为马尔科夫假设。
CBOW全称Continuous Bag-of-Words Model,Skip-Gram全称Continuous skip-gram Model。两者是Word2Vec里重要的两种模型,CBOW模型的训练输入是某一个特征词的上下文相关的词对应的词向量,而输出就是这特定的一个词的词向量。Skip-Gram模型和CBOW的思路是反着来的,即输入是特定的一个词的词向量,而输出是特定词对应的上下文词向量。这两种模型都包含三层,输入层、投影层、输出层:
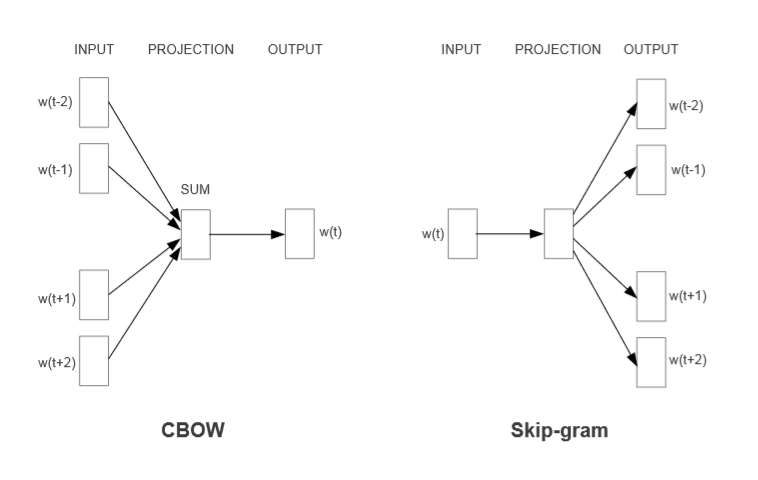
由上图可见,CBOW是在已知当前词 wt 的上下文 wt-2,wt-1,wt+1,wt+2 的前提下预测当前词wt;而Skip-gram则是已知当前词 wt 的前提下 ,去预测 wt-2,wt-1,wt+1,wt+2 。
四、Hierarchical Softmax框架与Negative Sampling框架
这两者并不是Word2Vec的精髓,只是Word2Vec的训练技巧。Hierarchical Softmax本质是把 N 分类问题变成 log(N) 次二分类; Negative Sampling 本质是预测总体类别的一个子集。
Hierarchical Softmax 和 Negative Sampling是Word2Vec设计的两种实现框架。Hierachical Softmax的基本思想是:它把训练语料中的词当成叶子节点,其在语料中出现的次数当做权值,通对于词典Dictionary中的任意词 w,Huffman 树中必存在一条从根节点到词 w 对应结点的路径,由此每个词对应一个Huffman编码。而 Negative Sampling 不再使用复杂的 Huffman树,而是采用随机负采样,可以减少训练时间和大幅度提高性能。
何为负采样算法呢?训练一个神经网络,样本只要有所改变(添加、修改、删除)就需要稍微调整所有的神经网络权重,这样才能确保训练结果的准确性。如果有一个巨大数据集,一个样本的改变都会改变神经网络的权重,代价是高昂的。而负采样的好处是,每一个训练样本仅仅改变一小部分的权重而不是所有的权重,解决了这个问题。比如,当我要进行对 ”ready“ 这个单词进行训练时,使用负采样,随机选择较少数目(小样本一般为5~20个,大样本为2~5个)的 ”负“ 样本进行权重更新,并且仍然为我们的 ”正“ 单词更新其对应的权重。词典 Dictionary 中的词在语料Corpus中出现的次数不同,那么对于高频词而言,被选为负样本的概率就应该比较大,而对于低频词,被选中的概率就应该小。
如果我们的输出层大约有 300 x 10,000 维度的权重矩阵,对 ”quick“ 一次进行权重更新,加上额外5个 负样本的权重更新,一共是6个输出神经元,和1800个权重值。这些值,仅仅只占输出层 3,000,000 神经元中的 0.06%。
五、代码实现
此代码已上传github,点击此处查看。网上有很多关于Word2Vec的实现,本文最初参考此代码以及一些现成代码,在后边的参考文章中列举。
import collections
import math
import os
import random
import zipfile
import numpy as np
import urllib
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.manifold import TSNE # Step 1 : 准备数据文档 url = 'http://mattmahoney.net/dc/' def download_check(filename, expected_bytes):
"""下载数据集,如果存在就确认跳过."""
if not os.path.exists(filename):
print('正在下载所需数据包 …')
filename, _ = urllib.request.urlretrieve(url + filename, filename)
statinfo = os.stat(filename)
if statinfo.st_size == expected_bytes:
print('确认为目标文件 ', filename)
else:
print(statinfo.st_size)
raise Exception(
'文件大小不对应 ' + filename + '请前往 http://mattmahoney.net/dc/text8.zip 获取数据集')
return filename filename = download_check('text8.zip', 31344016) # Step 2 : 解压文件 def read_data(filename):
"""读取zip的第一个文件并且分割单词为字符串数组"""
with zipfile.ZipFile(filename) as f:
data = tf.compat.as_str(f.read(f.namelist()[0])).split()
return data words = read_data(filename)
print('数据长度', len(words)) vocabulary_size = 50000 # Step 3 : 准备数据集 def build_dataset(words):
"""在字典第一个位置插入一项“UNK"代表不能识别的单词,也就是未出现在字典的单词统一用UNK表示"""
# [['UNK', -1], ['i', 500], ['the', 498], ['man', 312], ...]
count = [['UNK', -1]]
# dictionary {'UNK':0, 'i':1, 'the': 2, 'man':3, ...} 收集所有单词词频
count.extend(collections.Counter(words).most_common(vocabulary_size - 1))
# python中K/V的一种数据结构"字典
dictionary = dict()
for word, _ in count:
dictionary[word] = len(dictionary)
data = list()
unk_count = 0
for word in words:
if word in dictionary:
index = dictionary[word]
else:
index = 0 # dictionary['UNK']
unk_count += 1
data.append(index)
count[0][1] = unk_count
reverse_dictionary = dict(zip(dictionary.values(), dictionary.keys()))
return data, count, dictionary, reverse_dictionary data, count, dictionary, reverse_dictionary = build_dataset(words) del words
print('词频最高的词', count[:5])
print('数据样例', data[:10], [reverse_dictionary[i] for i in data[:10]]) data_index = 0 # Step 4 : skip-gram def generate_batch(batch_size, num_skips, skip_window):
global data_index #global关键字 使data_index 可在其他函数中修改其值
assert batch_size % num_skips == 0 #assert断言用于判断后者是否为true,如果返回值为假,处罚异常
assert num_skips <= 2 * skip_window
batch = np.ndarray(shape=(batch_size), dtype=np.int32) #ndarray对象用于存放多维数组
labels = np.ndarray(shape=(batch_size, 1), dtype=np.int32)
span = 2 * skip_window + 1 # [ skip_window target skip_window]
# 初始化最大长度为span的双端队列,超过最大长度后再添加数据,会从另一端删除容不下的数据
# buffer: 1, 21, 124, 438, 11
buffer = collections.deque(maxlen=span) #创建一个队列,模拟滑动窗口
for _ in range(span):
buffer.append(data[data_index])
data_index = (data_index + 1) % len(data)
for i in range(batch_size // num_skips): # // 是整数除
# target : 2
target = skip_window # target label at the center of the buffer
# target_to_avoid : [2]
targets_to_avoid = [ skip_window ] # 需要忽略的词在当前的span位置
# 更新源单词为当前5个单词的中间单词
source_word = buffer[skip_window]
# 随机选择的5个span单词中除了源单词之外的4个单词中的两个
for j in range(num_skips):
while target in targets_to_avoid:
target = random.randint(0, span - 1)
targets_to_avoid.append(target) # 已经经过的target放入targets_to_avoid
#batch中添加源单词
batch[i * num_skips + j] = source_word
#labels添加目标单词,单词来自随机选择的5个span单词中除了源单词之外的4个单词中的两个
labels[i * num_skips + j, 0] = buffer[target]
# 往双端队列中添加下一个单词,双端队列会自动将容不下的数据从另一端删除
buffer.append(data[data_index])
data_index = (data_index + 1) % len(data)
return batch, labels # Step 5 : 构建一个包含隐藏层的神经网络,隐藏层包含300节点,与我们要构造的WordEmbedding维度一致 batch, labels = generate_batch(batch_size=8, num_skips=2, skip_window=1)
# 打印数据样例中的skip-gram样本
for i in range(8):
print('(',batch[i], reverse_dictionary[batch[i]],
',', labels[i, 0], reverse_dictionary[labels[i, 0]],')')
"""
( 3081 originated , 12 as )
( 3081 originated , 5234 anarchism )
( 12 as , 6 a )
( 12 as , 3081 originated )
( 6 a , 12 as )
( 6 a , 195 term )
( 195 term , 6 a )
( 195 term , 2 of )
"""
batch_size = 128
embedding_size = 128 # Demension of the embedding vector
skip_window = 1 # How many words to consider left and right
num_skips = 2 # How many times to reuse an input to generate a label valid_size = 16 # Random set of words to evaluate similarity on
valid_window = 100 # Only pick dev samples in the head of the distribution
valid_examples = np.random.choice(valid_window, valid_size, replace=False)
num_sampled = 64 # Number of negative examples to sample graph = tf.Graph()
with graph.as_default():
# 定义输入输出
train_inputs = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=[batch_size])
train_labels = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=[batch_size, 1])
valid_dataset = tf.constant(valid_examples, dtype=tf.int32) # 当缺少GPU时,用CPU来进行训练和操作变量
with tf.device('/cpu:0'):
# 初始化embedding矩阵,后边经过多次训练后我们得到的结果就放在此embedding矩阵;
# tf.Variable是图变量,tf.radom_uniform产生一个在[-1,1]间均匀分布的size为[vocabulary_size, embedding_size]的矩阵
embeddings = tf.Variable(
tf.random_uniform([vocabulary_size, embedding_size], -1.0, 1.0))
# 将输入序列转换成embedding表示, [batch_size, embedding_size]
# tf.nn.embedding_lookup的作用就是找到要寻找的embedding data中的对应的行下的vector
emded = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(embeddings, train_inputs) # 初始化权重,此处使用负例采样NCE loss损失函数
# tf.truncated_normal(shape, mean, stddev) :shape表示生成张量的维度,mean是均值,stddev是标准差。这个函数产生正太分布,
# 均值和标准差自己设定。这是一个截断的产生正太分布的函数,就是说产生正太分布的值如果与均值的差值大于两倍的标准差,那就重新生成。
nce_weights = tf.Variable(
tf.truncated_normal([vocabulary_size, embedding_size],
stddev=1.0 / math.sqrt(embedding_size)))
nce_biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([vocabulary_size]))
# Compute the average NCE loss for the batch
# tf.nce_loss automatically draws a new sample of the negative labels each
# time we evalute the loss
loss = tf.reduce_mean(
tf.nn.nce_loss(weights = nce_weights,
biases = nce_biases,
labels = train_labels,
inputs = emded,
num_sampled = num_sampled,
num_classes = vocabulary_size ))
# 使用1.0的速率来构造SGD优化器
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(1.0).minimize(loss)
# 计算 minibatch 和 all embeddings的余弦相似度
# tf.reduce_sum() 按照行的维度求和
norm = tf.sqrt(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(embeddings), 1, keep_dims=True))
normalized_embeddings = embeddings / norm
valid_embeddings = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(normalized_embeddings, valid_dataset)
# tf.matmul 矩阵相乘
similarity = tf.matmul(valid_embeddings, normalized_embeddings, transpose_b=True)
# 添加变量初始化程序
init = tf.global_variables_initializer() # Step 6 : 开始训练
# 训练次数
num_steps = 100001
# tf.Session 用于运行TensorFlow操作的类
with tf.Session(graph=graph) as session:
# 我们必须在使用之前初始化所有变量
init.run()
print("Initialized")
average_loss = 0
for step in range(num_steps):
batch_inputs, batch_labels = generate_batch(
batch_size, num_skips, skip_window)
feed_dict = {train_inputs : batch_inputs, train_labels : batch_labels}
# We perform one update step by evaluating the optimizer op( including it
# in the list of returned values for session.run())
_, loss_val = session.run([optimizer, loss], feed_dict=feed_dict)
average_loss += loss_val
if step % 2000 == 0:
if step > 0:
average_loss /= 2000
#The average loss is an estimate of the loss over the last 2000 batches.
print("Average loss at step", step, ": ", average_loss)
average_loss = 0
# Note that this is expensive ( ~20% slowdown if computed every 500 steps)
if step % 10000 == 0:
sim = similarity.eval()
for i in range(valid_size):
valid_word = reverse_dictionary[valid_examples[i]]
top_k = 8 # number of nearest neighbors
nearest = (-sim[i, : ]).argsort()[1:top_k+1]
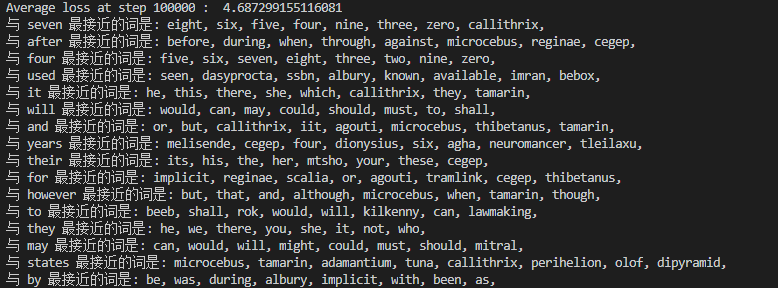
log_str = "与 %s 最接近的词是:" % valid_word
for k in range(top_k):
close_word = reverse_dictionary[nearest[k]]
log_str = "%s %s," % (log_str, close_word)
print(log_str)
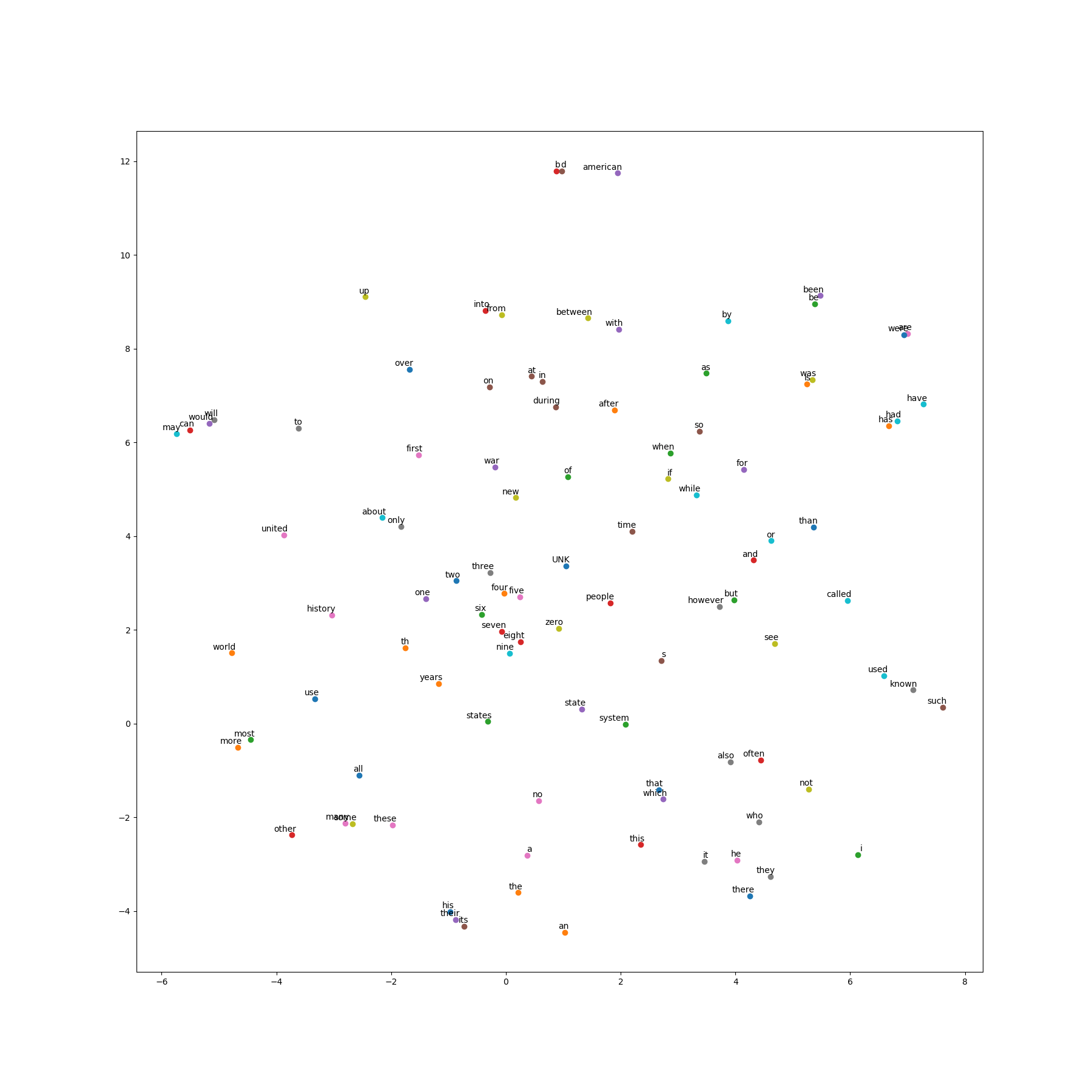
final_embeddings = normalized_embeddings.eval() # Step 7 : 绘制结果
def plot_with_labels(low_dim_embs, labels, filename='TSNE_result.png'):
assert low_dim_embs.shape[0] >= len(labels), "More labels than embeddings"
plt.figure(figsize=(18, 18)) # in inches
for i, label in enumerate(labels):
x, y = low_dim_embs[i,:]
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.annotate(label,
xy=(x, y),
xytext=(5, 2),
textcoords='offset points',
ha='right',
va='bottom')
plt.savefig(filename) # 使用T-SNE算法将128维降低到2维
tsne = TSNE(perplexity= 30, n_components = 2, init = 'pca', n_iter = 5000, random_state = 1)
# 绘制点的个数
plot_only = 100
low_dim_embs = tsne.fit_transform(final_embeddings[: plot_only, :])
labels = [reverse_dictionary[i] for i in range(plot_only)]
plot_with_labels(low_dim_embs, labels)
plt.show()
六、训练结果
参考资料:
1、https://www.jianshu.com/p/471d9bfbd72f
2、https://www.jianshu.com/p/0bb00eed9c63
3、https://blog.csdn.net/itplus/article/details/37998797
4、https://blog.csdn.net/qq_28444159/article/details/77514563
Word2Vec原理及代码的更多相关文章
- word2vec原理与代码
目录 前言 CBOW模型与Skip-gram模型 基于Hierarchical Softmax框架的CBOW模型 基于Negative Sampling框架的CBOW模型 负采样算法 结巴分词 wor ...
- word2vec原理(一) CBOW与Skip-Gram模型基础
word2vec原理(一) CBOW与Skip-Gram模型基础 word2vec原理(二) 基于Hierarchical Softmax的模型 word2vec原理(三) 基于Negative Sa ...
- word2vec原理(一) CBOW与Skip-Gram模型基础——转载自刘建平Pinard
转载来源:http://www.cnblogs.com/pinard/p/7160330.html word2vec是google在2013年推出的一个NLP工具,它的特点是将所有的词向量化,这样词与 ...
- word2vec原理(一) CBOW+Skip-Gram模型基础
word2vec是google在2013年推出的一个NLP工具,它的特点是将所有的词向量化,这样词与词之间就可以定量的去度量他们之间的关系,挖掘词之间的联系.本文的讲解word2vec原理以Githu ...
- word2vec原理CBOW与Skip-Gram模型基础
转自http://www.cnblogs.com/pinard/p/7160330.html刘建平Pinard word2vec是google在2013年推出的一个NLP工具,它的特点是将所有的词向量 ...
- 图机器学习(GML)&图神经网络(GNN)原理和代码实现(前置学习系列二)
项目链接:https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/4990947?contributionType=1 欢迎fork欢迎三连!文章篇幅有限, ...
- flume原理及代码实现
转载标明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/adealjason/p/6240122.html 最近想玩一下流计算,先看了flume的实现原理及源码 源码可以去apache 官网下载 ...
- Java Base64加密、解密原理Java代码
Java Base64加密.解密原理Java代码 转自:http://blog.csdn.net/songylwq/article/details/7578905 Base64是什么: Base64是 ...
- Base64加密解密原理以及代码实现(VC++)
Base64加密解密原理以及代码实现 转自:http://blog.csdn.net/jacky_dai/article/details/4698461 1. Base64使用A--Z,a--z,0- ...
随机推荐
- 从YouTube改版看“移动优先”——8个移动优先网站设计案例赏析
2011年,Luke Wroblewski大神提出了移动优先的设计理念.在当时看来这无疑是一个打破行业常规的新型设计原则.而在移动互联网大行其道的今天,谁遵守移动优先的设计理念,设计出最好的移动端网站 ...
- 本周MySQL官方verified/open的bug列表(11月15日至11月21日)
本周MySQL verified的bug列表(11月15日至11月21日) 1. Bug #70923 Replication failure on multi-statement INSERT ...
- live kalilinux能保存文件和设置
win32diskimager写入kalilinux镜像,建议用parrot sec os gparted /dev/sdb,新建分区sdb3,Lable输入persistence 挂载/dev/sd ...
- ETL的测试
二.ETL测试过程: 在独立验证与确认下,与任何其他测试一样,ETL也经历同样的阶段. 1)业务和需求分析并验证. 2)测试方案编写 3)从所有可用的输入条件来设计测试用例和测试场景进行测试 4)执行 ...
- 洛谷P4556 [Vani有约会]雨天的尾巴(线段树合并)
题目背景 深绘里一直很讨厌雨天. 灼热的天气穿透了前半个夏天,后来一场大雨和随之而来的洪水,浇灭了一切. 虽然深绘里家乡的小村落对洪水有着顽固的抵抗力,但也倒了几座老房子,几棵老树被连根拔起,以及田地 ...
- 18-10-30 Scrum Meeting 2
目录 站立式会议 工作记录 昨天完成的工作 1 主要完成了单词简单释义浏览和单词详细释义浏览的功能 并且已经测试和上传eolinker 2 3 主要搭建起爬虫的框架平台,并且测试了py连接服务器的功能 ...
- 自我简介与Github的注册和使用
我叫陈鑫,学号1413042059,来自网络工程142班.喜欢打乒乓球,玩策略类游戏,团队竞技. ...
- .net core 2.1-----Sql Server数据库初体验
刚开始接触asp.net core,在学习的过程中遇到了一些小问题,在这里记录一下! 在我们项目的开发过程中,肯定会和数据库打交道,所以我尝试了一下用asp.net core链接数据库,并读取表中的数 ...
- struts2 Convention插件好处及使用
现在JAVA开发都流行SSH.而很大部分公司也使用了struts2进行开发..因为struts2提供了很多插件和标签方便使用..在之前开发过程中总发现使用了struts2会出现很多相应的配合文件.如果 ...
- 销售系统项目业务分析和Java中使用邮箱
项目一般大致可分为三个模块, 我们以销售系统为例 分为 基础模块 进货模块 财务模块三个 基础模块分为:权限模块 产品模块和基础代码,基础模块的设计十分重要会影响到整个项目, 代码较为简单 核心模块 ...
