spring3: 延迟初始化Bean
3.3.1 延迟初始化Bean
延迟初始化也叫做惰性初始化,指不提前初始化Bean,而是只有在真正使用时才创建及初始化Bean。
配置方式很简单只需在<bean>标签上指定 “lazy-init” 属性值为“true”即可延迟初始化Bean。
Spring容器会在创建容器时提前初始化“singleton”作用域的Bean,“singleton”就是单例的意思即整个容器每个Bean只有一个实例,后边会详细介绍。Spring容器预先初始化Bean通常能帮助我们提前发现配置错误,所以如果没有什么情况建议开启,除非有某个Bean可能需要加载很大资源,而且很可能在整个应用程序生命周期中很可能使用不到,可以设置为延迟初始化。
延迟初始化的Bean通常会在第一次使用时被初始化;或者在被非延迟初始化Bean作为依赖对象注入时在会随着初始化该Bean时被初始化,因为在这时使用了延迟初始化Bean。
容器管理初始化Bean消除了编程实现延迟初始化,完全由容器控制,只需在需要延迟初始化的Bean定义上配置即可,比编程方式更简单,而且是无侵入代码的。
具体配置如下:
<bean id="helloApi" class="cn.javass.spring.chapter2.helloworld.HelloImpl" lazy-init="true"/>
3.3.2 使用depends-on
depends-on是指指定Bean初始化及销毁时的顺序,使用depends-on属性指定的Bean要先初始化完毕后才初始化当前Bean,由于只有“singleton”Bean能被Spring管理销毁,所以当指定的Bean都是“singleton”时,使用depends-on属性指定的Bean要在指定的Bean之后销毁。
配置方式如下:
<bean id="helloApi" class="cn.javass.spring.chapter2.helloworld.HelloImpl"/>
<bean id="decorator"
class="cn.javass.spring.chapter3.bean.HelloApiDecorator"
depends-on="helloApi">
<property name="helloApi"><ref bean="helloApi"/></property>
</bean>
“depends-on”属性可以指定多个Bean,若指定多个Bean可以用“;”、“,”、空格分割。
那“depends-on”有什么好处呢?主要是给出明确的初始化及销毁顺序,比如要初始化“decorator”时要确保“helloApi”Bean的资源准备好了,否则使用“decorator”时会看不到准备的资源;而在销毁时要先在“decorator”Bean的把对“helloApi”资源的引用释放掉才能销毁“helloApi”,否则可能销毁 “helloApi”时而“decorator”还保持着资源访问,造成资源不能释放或释放错误。
让我们看个例子吧,在平常开发中我们可能需要访问文件系统,而文件打开、关闭是必须配对的,不能打开后不关闭,从而造成其他程序不能访问该文件。让我们来看具体配置吧:
1)准备测试类:
ResourceBean从配置文件中配置文件位置,然后定义初始化方法init中打开指定的文件,然后获取文件流;最后定义销毁方法destroy用于在应用程序关闭时调用该方法关闭掉文件流。
DependentBean中会注入ResourceBean,并从ResourceBean中获取文件流写入内容;定义初始化方法init用来定义一些初始化操作并向文件中输出文件头信息;最后定义销毁方法用于在关闭应用程序时想文件中输出文件尾信息。
具体代码如下:
package cn.javass.spring.chapter3.bean;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ResourceBean {
private FileOutputStream fos;
private File file;
//初始化方法
public void init() {
System.out.println("ResourceBean:========初始化");
//加载资源,在此只是演示
System.out.println("ResourceBean:========加载资源,执行一些预操作");
try {
this.fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//销毁资源方法
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("ResourceBean:========销毁");
//释放资源
System.out.println("ResourceBean:========释放资源,执行一些清理操作");
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public FileOutputStream getFos() {
return fos;
}
public void setFile(File file) {
this.file = file;
}
}
package cn.javass.spring.chapter3.bean;
import java.io.IOException;
public class DependentBean {
ResourceBean resourceBean;
public void write(String ss) throws IOException {
System.out.println("DependentBean:=======写资源");
resourceBean.getFos().write(ss.getBytes());
}
//初始化方法
public void init() throws IOException {
System.out.println("DependentBean:=======初始化");
resourceBean.getFos().write("DependentBean:=======初始化=====".getBytes());
}
//销毁方法
public void destroy() throws IOException {
System.out.println("DependentBean:=======销毁");
//在销毁之前需要往文件中写销毁内容
resourceBean.getFos().write("DependentBean:=======销毁=====".getBytes());
} public void setResourceBean(ResourceBean resourceBean) {
this.resourceBean = resourceBean;
}
}
2)类定义好了,让我们来进行Bean定义吧,具体配置文件如下:
<bean id="resourceBean"
class="cn.javass.spring.chapter3.bean.ResourceBean"
init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy">
<property name="file" value="D:/test.txt"/>
</bean>
<bean id="dependentBean"
class="cn.javass.spring.chapter3.bean.DependentBean"
init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy" depends-on="resourceBean">
<property name="resourceBean" ref="resourceBean"/>
</bean>
<property name="file" value="D:/test.txt"/>配置:Spring容器能自动把字符串转换为java.io.File。
init-method="init" :指定初始化方法,在构造器注入和setter注入完毕后执行。
destroy-method="destroy":指定销毁方法,只有“singleton”作用域能销毁,“prototype”作用域的一定不能,其他作用域不一定能;后边再介绍。
在此配置中,resourceBean初始化在dependentBean之前被初始化,resourceBean销毁会在dependentBean销毁之后执行。
3)配置完毕,测试一下吧:
package cn.javass.spring.chapter3;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import cn.javass.spring.chapter3.bean.DependentBean;
public class MoreDependencyInjectTest {
@Test
public void testDependOn() throws IOException {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("chapter3/depends-on.xml");
//一点要注册销毁回调,否则我们定义的销毁方法不执行
context.registerShutdownHook();
DependentBean dependentBean =
context.getBean("dependentBean", DependentBean.class);
dependentBean.write("aaa");
}
}
测试跟其他测试完全一样,只是在此我们一定要注册销毁方法回调,否则销毁方法不会执行。
如果配置没问题会有如下输出:
ResourceBean:========初始化
ResourceBean:========加载资源,执行一些预操作
DependentBean:=========初始化
DependentBean:=========写资源
DependentBean:=========销毁
ResourceBean:========销毁
ResourceBean:========释放资源,执行一些清理操作
3.3.3 自动装配
自动装配就是指由Spring来自动地注入依赖对象,无需人工参与。
目前Spring3.0支持“no”、“byName ”、“byType”、“constructor”四种自动装配,默认是“no”指不支持自动装配的,其中Spring3.0已不推荐使用之前版本的“autodetect”自动装配,推荐使用Java 5+支持的(@Autowired)注解方式代替;如果想支持“autodetect”自动装配,请将schema改为“spring-beans-2.5.xsd”或去掉。
自动装配的好处是减少构造器注入和setter注入配置,减少配置文件的长度。自动装配通过配置<bean>标签的“autowire”属性来改变自动装配方式。接下来让我们挨着看下配置的含义。
一、default:表示使用默认的自动装配,默认的自动装配需要在<beans>标签中使用default-autowire属性指定,其支持“no”、“byName ”、“byType”、“constructor”四种自动装配,如果需要覆盖默认自动装配,请继续往下看;
二、no:意思是不支持自动装配,必须明确指定依赖。
三、byName:通过设置Bean定义属性autowire="byName",意思是根据名字进行自动装配,只能用于setter注入。比如我们有方法“setHelloApi”,则“byName”方式Spring容器将查找名字为helloApi的Bean并注入,如果找不到指定的Bean,将什么也不注入。
例如如下Bean定义配置:
<bean id="helloApi" class="cn.javass.spring.chapter2.helloworld.HelloImpl"/>
<bean id="bean" class="cn.javass.spring.chapter3.bean.HelloApiDecorator"
autowire="byName"/>
测试代码如下:
package cn.javass.spring.chapter3;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import cn.javass.spring.chapter2.helloworld.HelloApi;
public class AutowireBeanTest {
@Test
public void testAutowireByName() throws IOException {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("chapter3/autowire-byName.xml");
HelloApi helloApi = context.getBean("bean", HelloApi.class);
helloApi.sayHello();
}
}
是不是不要配置<property>了,如果一个bean有很多setter注入,通过“byName”方式是不是能减少很多<property>配置。此处注意了,在根据名字注入时,将把当前Bean自己排除在外:比如“hello”Bean类定义了“setHello”方法,则hello是不能注入到“setHello”的。
四、“byType”:通过设置Bean定义属性autowire="byType",意思是指根据类型注入,用于setter注入,比如如果指定自动装配方式为“byType”,而“setHelloApi”方法需要注入HelloApi类型数据,则Spring容器将查找HelloApi类型数据,如果找到一个则注入该Bean,如果找不到将什么也不注入,如果找到多个Bean将优先注入<bean>标签“primary”属性为true的Bean,否则抛出异常来表明有个多个Bean发现但不知道使用哪个。让我们用例子来讲解一下这几种情况吧。
1)根据类型只找到一个Bean,此处注意了,在根据类型注入时,将把当前Bean自己排除在外,即如下配置中helloApi和bean都是HelloApi接口的实现,而“bean”通过类型进行注入“HelloApi”类型数据时自己是排除在外的,配置如下(具体测试请参考AutowireBeanTest.testAutowireByType1方法):
<bean class="cn.javass.spring.chapter2.helloworld.HelloImpl"/>
<bean id="bean" class="cn.javass.spring.chapter3.bean.HelloApiDecorator" autowire="byType"/>
2)根据类型找到多个Bean时,对于集合类型(如List、Set)将注入所有匹配的候选者,而对于其他类型遇到这种情况可能需要使用“autowire-candidate”属性为false来让指定的Bean放弃作为自动装配的候选者,或使用“primary”属性为true来指定某个Bean为首选Bean:
2.1)通过设置Bean定义的“autowire-candidate”属性为false来把指定Bean后自动装配候选者中移除:
<bean class="cn.javass.spring.chapter2.helloworld.HelloImpl"/>
<!-- 从自动装配候选者中去除 -->
<bean class="cn.javass.spring.chapter2.helloworld.HelloImpl"
autowire-candidate="false"/>
<bean id="bean1" class="cn.javass.spring.chapter3.bean.HelloApiDecorator"
autowire="byType"/>
2.2)通过设置Bean定义的“primary”属性为true来把指定自动装配时候选者中首选Bean:
<bean class="cn.javass.spring.chapter2.helloworld.HelloImpl"/>
<!-- 自动装配候选者中的首选Bean-->
<bean class="cn.javass.spring.chapter2.helloworld.HelloImpl" primary="true"/>
<bean id="bean" class="cn.javass.spring.chapter3.bean.HelloApiDecorator"
autowire="byType"/>
具体测试请参考AutowireBeanTest类的testAutowireByType***方法。
五、“constructor”:通过设置Bean定义属性autowire="constructor",功能和“byType”功能一样,根据类型注入构造器参数,只是用于构造器注入方式,直接看例子吧:
<bean class="cn.javass.spring.chapter2.helloworld.HelloImpl"/>
<!-- 自动装配候选者中的首选Bean-->
<bean class="cn.javass.spring.chapter2.helloworld.HelloImpl" primary="true"/>
<bean id="bean"
class="cn.javass.spring.chapter3.bean.HelloApiDecorator"
autowire="constructor"/>
测试代码如下:
@Test
public void testAutowireByConstructor() throws IOException {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("chapter3/autowire-byConstructor.xml");
HelloApi helloApi = context.getBean("bean", HelloApi.class);
helloApi.sayHello();
}
3.3.5 方法注入
所谓方法注入其实就是通过配置方式覆盖或拦截指定的方法,通常通过代理模式实现。Spring提供两种方法注入:查找方法注入和方法替换注入。
因为Spring是通过CGLIB动态代理方式实现方法注入,也就是通过动态修改类的字节码来实现的,本质就是生成需方法注入的类的子类方式实现。
在进行测试之前,我们需要确保将“com.springsource.cn.sf.cglib-2.2.0.jar”放到lib里并添加到“Java Build Path”中的Libararies中。否则报错,异常中包含“nested exception is java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: cn/sf/cglib/proxy/CallbackFilter”。
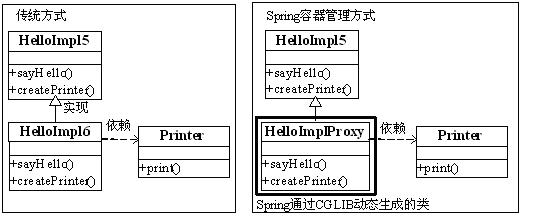
传统方式和Spring容器管理方式唯一不同的是不需要我们手动生成子类,而是通过配置方式来实现;其中如果要替换createPrinter()方法的返回值就使用查找方法注入;如果想完全替换sayHello()方法体就使用方法替换注入。 接下来让我们看看具体实现吧。
一、查找方法注入:又称为Lookup方法注入,用于注入方法返回结果,也就是说能通过配置方式替换方法返回结果。使用<lookup-method name="方法名" bean="bean名字"/>配置;其中name属性指定方法名,bean属性指定方法需返回的Bean。
方法定义格式:访问级别必须是public或protected,保证能被子类重载,可以是抽象方法,必须有返回值,必须是无参数方法,查找方法的类和被重载的方法必须为非final:
<public|protected> [abstract] <return-type> theMethodName(no-arguments);
因为“singleton”Bean在容器中只有一个实例,而“prototype”Bean是每次获取容器都返回一个全新的实例,所以如果“singleton”Bean在使用“prototype” Bean情况时,那么“prototype”Bean由于是“singleton”Bean的一个字段属性,所以获取的这个“prototype”Bean就和它所在的“singleton”Bean具有同样的生命周期,所以不是我们所期待的结果。因此查找方法注入就是用于解决这个问题。
1) 首先定义我们需要的类,Printer类是一个有状态的类,counter字段记录访问次数:
package cn.javass.spring.chapter3.bean;
public class Printer {
private int counter = 0;
public void print(String type) {
System.out.println(type + " printer: " + counter++);
}
}
HelloImpl5类用于打印欢迎信息,其中包括setter注入和方法注入,此处特别需要注意的是该类是抽象的,充分说明了需要容器对其进行子类化处理,还定义了一个抽象方法createPrototypePrinter用于创建“prototype”Bean,createSingletonPrinter方法用于创建“singleton”Bean,此处注意方法会被Spring拦截,不会执行方法体代码:
package cn.javass.spring.chapter3;
import cn.javass.spring.chapter2.helloworld.HelloApi;
import cn.javass.spring.chapter3.bean.Printer;
public abstract class HelloImpl5 implements HelloApi {
private Printer printer;
public void sayHello() {
printer.print("setter");
createPrototypePrinter().print("prototype");
createSingletonPrinter().print("singleton");
}
public abstract Printer createPrototypePrinter();
public Printer createSingletonPrinter() {
System.out.println("该方法不会被执行,如果输出就错了");
return new Printer();
}
public void setPrinter(Printer printer) {
this.printer = printer;
}
}
2) 开始配置了,配置文件在(resources/chapter3/lookupMethodInject.xml),其中“prototypePrinter”是“prototype”Printer,“singletonPrinter”是“singleton”Printer,“helloApi1”是“singleton”Bean,而“helloApi2”注入了“prototype”Bean:
<bean id="prototypePrinter"
class="cn.javass.spring.chapter3.bean.Printer" scope="prototype"/>
<bean id="singletonPrinter"
class="cn.javass.spring.chapter3.bean.Printer" scope="singleton"/>
<bean id="helloApi1" class="cn.javass.spring.chapter3.HelloImpl5" scope="singleton">
<property name="printer" ref="prototypePrinter"/>
<lookup-method name="createPrototypePrinter" bean="prototypePrinter"/>
<lookup-method name="createSingletonPrinter" bean="singletonPrinter"/>
</bean>
<bean id="helloApi2" class="cn.javass.spring.chapter3.HelloImpl5" scope="prototype">
<property name="printer" ref="prototypePrinter"/>
<lookup-method name="createPrototypePrinter" bean="prototypePrinter"/>
<lookup-method name="createSingletonPrinter" bean="singletonPrinter"/>
</bean>
3)测试代码如下:
package cn.javass.spring.chapter3;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import cn.javass.spring.chapter2.helloworld.HelloApi;
public class MethodInjectTest {
@Test
public void testLookup() {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("chapter3/lookupMethodInject.xml");
System.out.println("=======singleton sayHello======");
HelloApi helloApi1 = context.getBean("helloApi1", HelloApi.class);
helloApi1.sayHello();
helloApi1 = context.getBean("helloApi1", HelloApi.class);
helloApi1.sayHello();
System.out.println("=======prototype sayHello======");
HelloApi helloApi2 = context.getBean("helloApi2", HelloApi.class);
helloApi2.sayHello();
helloApi2 = context.getBean("helloApi2", HelloApi.class);
helloApi2.sayHello();
}}
其中“helloApi1”测试中,其输出结果如下:
=======singleton sayHello======
setter printer: 0
prototype printer: 0
singleton printer: 0
setter printer: 1
prototype printer: 0
singleton printer: 1
首先“helloApi1”是“singleton”,通过setter注入的“printer”是“prototypePrinter”,所以它应该输出“setter printer:0”和“setter printer:1”;而“createPrototypePrinter”方法注入了“prototypePrinter”,所以应该输出两次“prototype printer:0”;而“createSingletonPrinter”注入了“singletonPrinter”,所以应该输出“singleton printer:0”和“singleton printer:1”。
而“helloApi2”测试中,其输出结果如下:
=======prototype sayHello======
setter printer: 0
prototype printer: 0
singleton printer: 2
setter printer: 0
prototype printer: 0
singleton printer: 3
首先“helloApi2”是“prototype”,通过setter注入的“printer”是“prototypePrinter”,所以它应该输出两次“setter printer:0”;而“createPrototypePrinter”方法注入了“prototypePrinter”,所以应该输出两次“prototype printer:0”;而“createSingletonPrinter”注入了“singletonPrinter”,所以应该输出“singleton printer:2”和“singleton printer:3”。
大家是否注意到“createSingletonPrinter”方法应该输出“该方法不会被执行,如果输出就错了”,而实际是没输出的,这说明Spring拦截了该方法并使用注入的Bean替换了返回结果。
方法注入主要用于处理“singleton”作用域的Bean需要其他作用域的Bean时,采用Spring查找方法注入方式无需修改任何代码即能获取需要的其他作用域的Bean。
二、替换方法注入:也叫“MethodReplacer”注入,和查找注入方法不一样的是,他主要用来替换方法体。通过首先定义一个MethodReplacer接口实现,然后如下配置来实现:
<replaced-method name="方法名" replacer="MethodReplacer实现">
<arg-type>参数类型</arg-type>
</replaced-method>”
1)首先定义MethodReplacer实现,完全替换掉被替换方法的方法体及返回值,其中reimplement方法重定义方法 功能,参数obj为被替换方法的对象,method为被替换方法,args为方法参数;最需要注意的是不能再 通过“method.invoke(obj, new String[]{"hehe"});” 反射形式再去调用原来方法,这样会产生循环调用;如果返回值类型为Void,请在实现中返回null:
package cn.javass.spring.chapter3.bean;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.MethodReplacer;
public class PrinterReplacer implements MethodReplacer {
@Override
public Object reimplement(Object obj, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("Print Replacer");
//注意此处不能再通过反射调用了,否则会产生循环调用,知道内存溢出
//method.invoke(obj, new String[]{"hehe"});
return null;
}
}
2)配置如下,首先定义MethodReplacer实现,使用< replaced-method >标签来指定要进行替换方法,属性name指定替换的方法名字,replacer指定该方法的重新实现者,子标签< arg-type >用来指定原来方法参数的类型,必须指定否则找不到原方法:
<bean id="replacer" class="cn.javass.spring.chapter3.bean.PrinterReplacer"/>
<bean id="printer" class="cn.javass.spring.chapter3.bean.Printer">
<replaced-method name="print" replacer="replacer">
<arg-type>java.lang.String</arg-type>
</replaced-method>
</bean>
3)测试代码将输出“Print Replacer ”,说明方法体确实被替换了:
@Test
public void testMethodReplacer() {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("chapter3/methodReplacerInject.xml");
Printer printer = context.getBean("printer", Printer.class);
printer.print("我将被替换");
}
spring3: 延迟初始化Bean的更多相关文章
- Spring点滴九:Spring bean的延迟初始化
Spring bean延迟初始化: 官网API: By default, ApplicationContext implementations eagerly create and configure ...
- Spring:延迟初始化
ApplicationContext实现的默认行为就是在启动时将所有singleton bean提前进行实例化.提前实例化意味着作为初始化过程的一部分,ApplicationContext实例会创建并 ...
- ApplicationContext(九)初始化非延迟的 bean
ApplicationContext(九)初始化非延迟的 bean 此至,ApplicationContext 已经完成了全部的准备工作,开始初始化剩余的 bean 了(第 11 步). public ...
- (转)Android高性能编程(2)--延迟初始化
上一篇文章,讲到了很多Android应用开发中需要注意的性能和内存方面的技巧.这一篇文章就是从smali指令级来分析性能优化和内存优化的问题. 如何解决界面启动时间开销大的问题 我们在编写Androi ...
- Spring3.2 中 Bean 定义之基于 XML 配置方式的源码解析
Spring3.2 中 Bean 定义之基于 XML 配置方式的源码解析 本文简要介绍了基于 Spring 的 web project 的启动流程,详细分析了 Spring 框架将开发人员基于 XML ...
- C#性能优化之Lazy<T> 实现延迟初始化
在.NET4.0中,可以使用Lazy<T> 来实现对象的延迟初始化,从而优化系统的性能.延迟初始化就是将对象的初始化延迟到第一次使用该对象时.延迟初始化是我们在写程序时经常会遇到的情形,例 ...
- C#性能优化:延迟初始化Lazy<T>
1. 概述 我们创建某一个对象需要很大的消耗,而这个对象在运行过程中又不一定用到,为了避免每次运行都创建该对象,这时候延迟初始化(也叫延迟实例化)就出场了. 延迟初始化出现于.NET 4.0,主要用于 ...
- spring的初始化bean,销毁bean之前的操作详解
我所知道的在spring初始化bean,销毁bean之前的操作有三种方式: 第一种:通过@PostConstruct 和 @PreDestroy 方法 实现初始化和销毁bean之前进行的操作 第二种是 ...
- C# 延迟初始化
一个对象的延迟初始化意味着该对象的创建将会延迟至第一次使用该对象时.(在本主题中,术语“延迟初始化”和“延迟实例化”是同义词.)延迟初始化主要用于提高性能,避免浪费计算,并减少程序内存要求. 以下是最 ...
随机推荐
- netty + Protobuf (整合二)
[正文]Protobuf 消息设计 疯狂创客圈 死磕Netty 系列之12 [博客园 总入口 ] 本文说明 本篇是 netty+Protobuf 实战的第二篇,完成一个 基于Netty + Proto ...
- cocos2d 场景切换和弹出场景、收回场景
场景弹出收回很简单 用以下代码在任意一个地方显示“设置场景”: [[CCDirector sharedDirector] pushScene:[Settings scene]]; 如果你身处“设置场景 ...
- windows下安装Composer提示缺少openssl的解决方法
在Windows环境下安装Composer(注:Composer要求PHP版本在5.3.2+),你可能会遇到这种安装失败的情况:出错信息是 "The openssl extension is ...
- STL中使用reverse_iterator时,如何正确使用erase函数
假设有一个list容器,顺序存储了0-9一个10个整数.现在要使用reverse_iterator迭代器来查找值为8和5的元素,并且将这两个数删除.先来看以下的解决方法: #include <i ...
- (转)Android工程出现 java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError错误解决方法
在Eclipse中,导入Android工程,工程没有报错,运行时,出现 java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError类没有找到的错误.从问题上可以看出是导入包出错的原因.遂百度加谷歌. ...
- SSD(Single Shot MultiBox Detector)二读paper
SSD KeyWords:Real-time Object Detection; Convolutional Neural Network Introduction 目前最尖端(State-of-ar ...
- R-CNN for Small Object Detection
R-CNN for Small Object Detection 文章方法概括 这篇文章主要讨论针对小目标的目标检测 文章为了证明:对传统R-CNN style的方法进行改进,可以用于小目标检测,并且 ...
- Android Studio设置行宽、格式化断行
设置基于Android studio 1.2,其它版本可能位置不大一样,可以直接搜索 1.设置行宽 就是那条右标准线的位置:Setting-->Editor-->Code Style,右侧 ...
- 快速搭建vue脚手架
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000011275993
- 与进程相关的命令ps、kill
一.概述 Ubuntu中主要有如下操作进程的命令 二.进程查看命令 ps 2.1 ps –l PPID:父进程的 PID PID:进程的PID S:进程状态,S:是指sleep睡眠状态:T:是挂起状态 ...
