OO课程第二阶段(实验和期中试题)总结Blog2
OO课程第二阶段(实验和期中试题)总结Blog2
前言:学习OOP课程的第二阶段已经结束了,在此进行对于知识点,题量,难度的个人看法。
学习OOP课程的第二阶段已经结束了,较第一次阶段学习难度加大,学习的内容更多,但收获也更多。第二阶段通过三次题目集落下帷幕,第一次阶段总结的最高潮是类设计,而本次的几次题目集基本所有的题目都以类设计为基础,完成题目的构建。在类设计的基础上,通过对继承,多态,接口等多方面学习,认识到类设计不是单一的去设计一个方法完成功能。面向对象编程的思想,也在本次学习真正拉开了序幕。面向对象编程不同于面向过程编程,在创立一个对象后便有明确的功能性,通过继承,多态,接口可以实现不同对象实现不同的功能。其中在类设计上,通过学习类属性的访问权限,初步了解了四种访问权限:public,private,protected,default;以及不同类的类型:实体类,业务类,接口类;对于类设计上,学习的多,代表思路与编程思想变得更为开阔且严谨,开始真正考虑到如何将一个题目设计到恰如其分,不同的设计思路带来的不同效果。
各题目:设计与分析、采坑心得、改进建议 。
期中试题(1)
设计与分析
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
double x1 = input.nextDouble();
double y1 = input.nextDouble();
double x2 = input.nextDouble();
double y2 = input.nextDouble();
Point point1 = new Point(x1,y1);
Point point2 = new Point(x2,y2);
Line line = new Line();
line.setColor(input.nextLine());
line.display();
}
}
class Point{
private double x = 0;
private double y = 0;
Point(){} //无参构造
Point(double a,double b){
this.x = a;
this.y = b;
}
public double getX() {
return x;
}
public void setX(double x) {
this.x = x;
}
public double getY() {
return y;
}
public void setY(double y) {
this.y = y;
}
}
class Line{
private Point point1;
private Point point2;
private String color ;
Line(){}
Line(Point p1,Point p2,String color){
this.point1 = p1;
this.point2 = p2;
this.color = color;
}
public Point getPoint1() {
return point1;
}
public void setPoint1(Point point1) {
this.point1 = point1;
}
public Point getPoint2() {
return point2;
}
public void setPoint2(Point point2) {
this.point2 = point2;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public void display(){
double result = Math.sqrt(this.point2.getX()*this.point2.getX()-this.point1.getX()*this.point1.getX())+Math.sqrt(this.point2.getY()*this.point2.getY()-this.point1.getY()*this.point1.getY());
if(this.getColor() != null ){
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}else {
System.out.println("("+this.getPoint1()+")");
System.out.println("("+this.getPoint2()+")");
System.out.println("The line's color is:"+this.getColor());
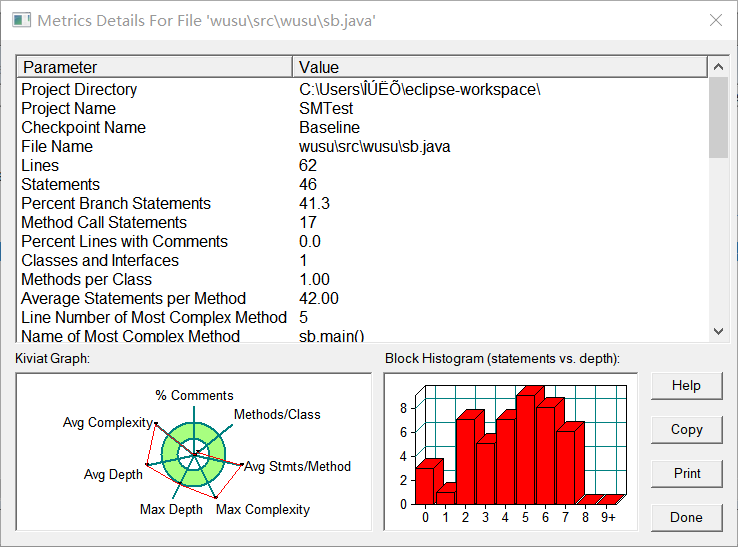
该题较简单,不需要构建多个类去完成,仅仅是通过简单的主函数便可以完成全部的功能,虽然形式简单,但是还是出现了对bug的不断调试。以下阐述我的采坑心得:
1)定义两个Point对象p1,p2;
2)写出有参构造方法,传递两个对象值给p1,p2
3)为p1,p2写出setters,和getters方法
4)为Line写出一个getLength方法求直线中两点的长度
5) 为LIne写一个ToString方法,方法如下所示:
public String toString() { return "Line [p1=" + p1 + ", p2=" + p2 + "]"; }
在Main类的main方法中,定义一个Line数组,数组长度通过键盘给出,然后通过键盘为每线段的两个Point对象的坐标赋值,并生成相应Line对象放入数组中,循环数组,输出每条直线的信息,以及两个点之间的距离。
期中考试(2)
设计与分析
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
double x1 = input.nextDouble();
double y1 = input.nextDouble();
double x2 = input.nextDouble();
double y2 = input.nextDouble();
Point point1 = new Point(x1,y1);
Point point2 = new Point(x2,y2);
Line line = new Line();
line.setColor(input.nextLine());
line.display();
}
}
class Point{
private double x = 0;
private double y = 0;
Point(){} //无参构造
Point(double a,double b){
this.x = a;
this.y = b;
}
public double getX() {
return x;
}
public void setX(double x) {
this.x = x;
}
public double getY() {
return y;
}
public void setY(double y) {
this.y = y;
}
}
class Line{
private Point point1;
private Point point2;
private String color ;
Line(){}
Line(Point p1,Point p2,String color){
this.point1 = p1;
this.point2 = p2;
this.color = color;
}
public Point getPoint1() {
return point1;
}
public void setPoint1(Point point1) {
this.point1 = point1;
}
public Point getPoint2() {
return point2;
}
public void setPoint2(Point point2) {
this.point2 = point2;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public void display(){
double result = Math.sqrt(this.point2.getX()*this.point2.getX()-this.point1.getX()*this.point1.getX())+Math.sqrt(this.point2.getY()*this.point2.getY()-this.point1.getY()*this.point1.getY());
if(this.getColor() != null ){
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}else {
System.out.println("("+this.getPoint1()+")");
System.out.println("("+this.getPoint2()+")");
System.out.println("The line's color is:"+this.getColor());
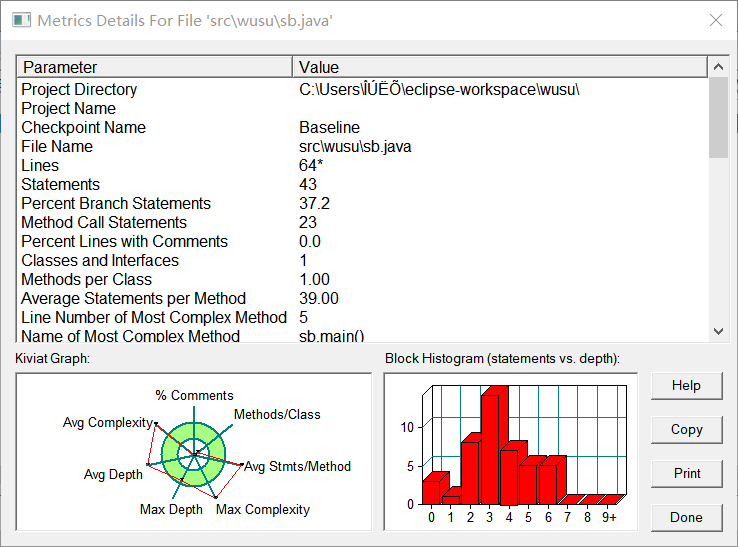
以下是我的踩坑心得:
继承的作用:
(1)使用继承可以有效实现代码复用,避免重复代码的出现。
(2)继承通过增强一致性来减少模块间的接口和界面,大大增加了程序的易维护性。
(3)继承可以更方便程序的维护和更新,像老师所说的那样,我们分成多个模块要是需要更新只需要更新对应模块的内容。
(4)继承是在一些比较一般的类的基础上构造、建立和扩充新类的最有效的手段。
多态的作用:
(1)可以增强程序的可扩展性及可维护性,使代码更加简洁。
(2)不但能减少编码的工作量,也能大大提高程序的可维护性及可扩展性。
(3)应用程序不必为每一个派生类编写功能调用,只需要对抽象基类进行处理即可。大大提高程序的可复用性。
期中考试(3)
分析和设计
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
double x1 = input.nextDouble();
double y1 = input.nextDouble();
double x2 = input.nextDouble();
double y2 = input.nextDouble();
Point point1 = new Point(x1,y1);
Point point2 = new Point(x2,y2);
Line line = new Line();
line.setColor(input.nextLine());
line.display();
}
}
class Point{
private double x = 0;
private double y = 0;
Point(){} //无参构造
Point(double a,double b){
this.x = a;
this.y = b;
}
public double getX() {
return x;
}
public void setX(double x) {
this.x = x;
}
public double getY() {
return y;
}
public void setY(double y) {
this.y = y;
}
}
class Line{
private Point point1;
private Point point2;
private String color ;
Line(){}
Line(Point p1,Point p2,String color){
this.point1 = p1;
this.point2 = p2;
this.color = color;
}
public Point getPoint1() {
return point1;
}
public void setPoint1(Point point1) {
this.point1 = point1;
}
public Point getPoint2() {
return point2;
}
public void setPoint2(Point point2) {
this.point2 = point2;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public void display(){
double result = Math.sqrt(this.point2.getX()*this.point2.getX()-this.point1.getX()*this.point1.getX())+Math.sqrt(this.point2.getY()*this.point2.getY()-this.point1.getY()*this.point1.getY());
if(this.getColor() != null ){
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}else {
System.out.println("("+this.getPoint1()+")");
System.out.println("("+this.getPoint2()+")");
System.out.println("The line's color is:"+this.getColor());

以下是我的踩坑心得:
ArrayList是采用数组实现的列表,因此它支持随机访问,不适合频繁删除和插入操作。对于需要经常进行查询的数据建议采用此结构。但是我对容器的使用不够熟练,经常使用越界,在下一阶段的学习中会更加注意这方面的学习。
实验
设计与分析
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List; public class CrossRiver {
List<String> listThis = new ArrayList<String>();
List<String> listThat = new ArrayList<String>();
public CrossRiver() {
listThis.add("狼");
listThis.add("草");
listThis.add("羊");
}
public boolean isSafe(List< String > list){
if(list.contains("狼")&&list.contains("羊")||list.contains("羊")&&list.contains("草")){
return false;
}else{
return true;
}
}
public void thisTothat(){
String str = listThis.get(0);
listThis.remove(str);
if(this.isSafe(listThis)){
System.out.println("农夫带着 " + str + " 从此岸到彼岸");
System.out.println("此岸" + listThis + "," + "彼岸" + listThat);
System.out.println();
listThat.add(str);
thatToThis();
}else{
listThis.add(str);
thisTothat();
}
}
public void thatToThis(){
if(listThis.isEmpty()){
System.out.println("此岸" + listThis + "," + "彼岸" + listThat);
return;
}
if(isSafe(listThat)){
System.out.println("农夫从彼岸到此岸");
System.out.println("此岸" + listThis + "," + "彼岸" + listThat);
System.out.println();
thisTothat();
}else{
String str = listThat.get(0);
listThat.remove(0);
if(isSafe(listThat)){
System.out.println("农夫带着 " + str + " 从彼岸到此岸");
System.out.println("此岸" + listThis + "," + "彼岸" + listThat);
System.out.println();
listThis.add(str);
thisTothat();
}else{
listThat.add(str);
thatToThis();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println("测试结果为:");
System.out.println();
new CrossRiver().thisTothat();
}
}
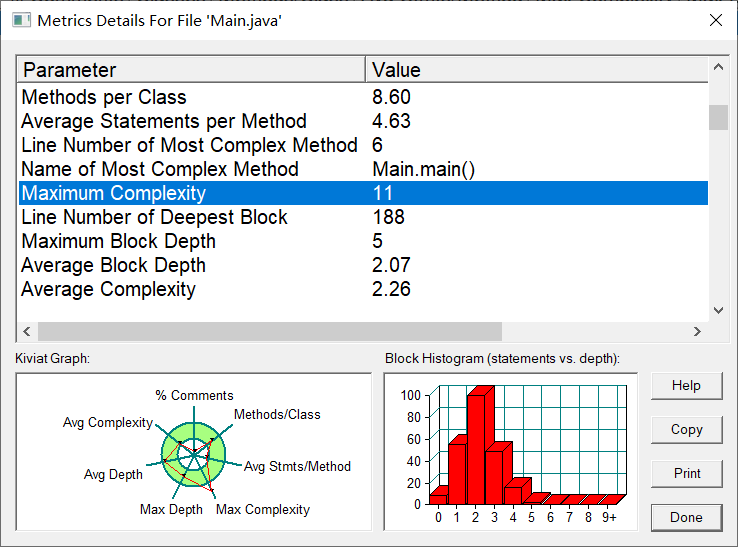
我的踩坑心得如下:
1、针对实现整个过程需要多步,不同步骤中各个事物所处位置不同的情况,可定义一个结构体来实现对四个对象狼、羊、白菜和农夫的表示。对于起始岸和目的岸,可以用0或者1来表示,以实现在程序设计中的简便性。
2、题目要求给出四种事物的过河步骤,没有对先后顺序进行约束,这就需要给各个事物依次进行编号,然后依次试探,若试探成功,进行下一步试探。这就需要使用循环或者递归算法,避免随机盲目运算且保证每种情况均试探到。
3、题目要求求出农夫带一只羊,一条狼和一颗白菜过河的办法,所以依次成功返回运算结果后,需要继续运算,直至求出结果,即给出农夫的过河方案。
4、输出界面要求具有每一步中农夫所带对象及每步之后各岸的物体,需要定义不同的数组来分别存储上述内容,并使界面所示方案清晰简洁。
mport java.unil.Scanner;
public class Crossriver{
public static void main(String[] args){
Game game = new Game();
game.play();
}
}
class GameGui{
public static void menu(){
System.out.println("please choose operation");
System.out.println("1.cross the river alone");
System.out.println("2.cross the river with wolf");
System.out.println("3.cross the river with sheep");
System.out.println("4.cross the river with cabbage");
System.out.println("0.quit");
}
public static void showStatus(Farmer farmer,Wolf wolf,Sheep sheep,Cabbage cabbage){
farmer.showStatus();
wolf.showStatus();
sheep.showStatus();
cabbage.showStatus();
}
}
class Game{
Wolf wolf;
Sheep sheep;
Cabbage cabbage;
Farmer farmer;
Boat boat;
Game(){
Scanner put = new Sanner(System.in);
System.out.println("输入羊的名字");
String sheepname = put.nextLine();
System.out.println("输入狼的名字");
String wolfname = put.nextLine();
wolf = new Wolf(wolfname);
sheep = new Sheep(sheepname);
cabbage = new Cabbage();
farmer = new Farmer();
boat = new Boat();
}
protected void play(){
Scanner input = new Sanner(System.in);
int choice = 0;
boolean gameOver = flase;
win = false;
while(!gameOver){
GameGui.menu();
choice = input.nextlnt();
switch(choice){
case 0:gameOver = true;
break;
case 1:if(boat.getcrossriver()==false){
farmer.setcrossriver(true);
boat.setcrossriver(true);
}
else{
farmer.setcrossriver(true);
boat.setcrossriver(false);
}
break;
case 2:if(boat.getcrossriver()==flase){
farmer.setcrossriver(true);
wolf.setcrossriver(true);
boat.setcrossriver(true);
}
else{
farmer.setcrossriver(true);
wolf.setcrossriver(false);
boat.setcrossriver(false);
}
break;
case 3:if(boat.crossriver()==false){
famer.setcrossriver(true);
sheep.setcrossriver(true);
boat.setcrossriver(true);
}
else{
farmer.setcrossriver(true);
sheep.setcrossriver(false);
boat.setcrossriver(false);
}
break;
case 4:if(boat.getcrossriver==false){
farmer.setcrossriver(true);
cabbage.setcrossriver(true);
boat.setcrossriver(true);
}
else{
famer.setcrossriver(true);
cabbage.setcrossriver(false);
boat.setcrossriver(false);
}
break;
default:fameOver = true;
break; }
wolf.eatSheep(sheep,boat);
sheep.eatCabbage(cabbage,boat);
GameGui.showStatus(farmer,wolf,sheep,cabbage);
gameOver = isGameOver(wolf,sheep,cabbage);
}
win = this.hasWin(wolf,sheep,cabbage);
if(win){
System.out.println("game over:you win !");
}
else{
System.out.println("game over:you lose !");
}
input.close();
}
public boolean isGameOver(Wolf wolf,Sheep sheep,Cabbage cabbage){
if(sheep.getIsAlive==false||cabbage.getlsAlive()==false){
return true;
}
if(wolf.getcrossriver()==true&&sheep.getcrosseriver()==true&&cabbage.getcrossriver()==true){
return true;
}
else{
return false;
}
}
}
class Total{
protected boolean iscrossriver = false;
protected boolean isAlive = true;
protected void setcrossrive(boolean iscrossriver){
this.iscrossriver = iscrossriver;
}
protected boolean getcrossriver(){
return iscrossriver;
}
protected void setlsAlive(boolean isAlive){
this.isAlive=isAlive;
}
protected boolearn getIsAlive(){
return isAlive;
}
}
class Sheep extends Total{
String name;
Sheep(String name){
this.name = name;
System.out.println("咩咩,我是可爱的小羊"+name);
}
public void eatCabbage(Cabbage cabbage,Boat boat){
if(isAlive==true&&iscrossriver==cabbage.getcrossriver()&&iscrossriver!=boat.getcrossriver()){
cabbage.seltsAlive(false);
}
}
public void showStatus(){
System.out.println("Sheep"+" "+"name"+"is alive "+"isAlive"+" "+"Wolf"+" "+"name"+" "+"has Cross");
}
}
class Cabbage extends Total{
public void showStatus(){
System.out.println("Cabbage is alive"+isAlive+" "+"Cabbage has Cross"+iscrossriver);
}
}
class Farmer extends Total{
public void showStatus(){
System.out.println("Farmer has Cross"+iscrossriver);
}
}
class Wolf extends Total{
String name;
Wolf(String name){
this.name = name;
System.out.println("我"+name+"狼回来了");
}
public void eatSheep(Sheep sheep,Boat boat){
if(iscrossriver==sheep.getcrossriver()&&iscrossriver!=boat.getcrossriver()){
sheep.setlsAlilve(false);
}
}
public void showStatus(){
System.out.println("Wolf"+" "+name+"is alive"+isAlive+" "+"Wolf"+name+"has cross");
}
}
class Boat{
protected bolean iscrossriver = false;
protected void setcrossriver(boolean iscrossriver){
this.iscrossriver = iscrossriver;
}
protected bloolean getcrossriver(){
return iscrossriver;
}
}
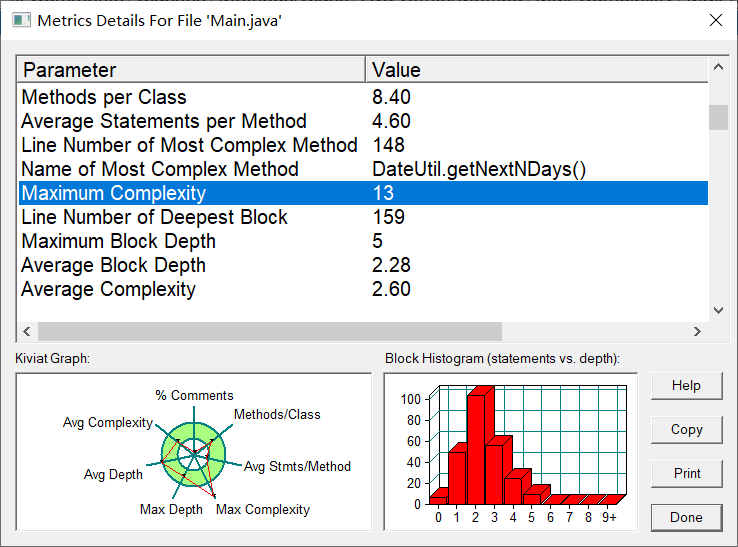
以下是我的踩坑心得:
创建一个Farmer类,其中包括cross_cabbage ()方法,cross_sheep()方法,cross_wolf()方法,这3个方法分别用来表示农夫和白菜,羊,狼过河的情况,而且农夫必须和物体在一边,否则会输出提示表示物体与农夫的位置不一样无法进行过河。
改进建议 :
对于技能上的学习,在对字符串的校验处理上,通过对正则表达式的深入学习,掌握对复杂数据的校验,截取,替换等,作为一项工具使用,在程序复杂度上大大降低。以及对于list的学习,可以对多对象处理上更为便捷可观,多对象处理上更为有效。还有对于hashmap的学习,对于其中遍历的运用进行了学习,对于多字符校验上有了更广阔的思路。不仅于此,题目集中许多边边角角运用的技能,也是会通过学习得以利用。
总结:
对于课程的学习建议,个人认为目前的pta便是不错的,有难有易,好上手,若想拿满分则必须要去自我学习。自我学习上,课程自带的SPOC课程则是选择之一,我们仍可自己去选择去论坛学习或者其他网课上学习。在实验上,目前进行的农夫过河的迭代性编程,面对同一个问题随着技术加深,我们需要运用更为上层的知识解决同一个问题,这是有趣也充满挑战的。线下课程中,希望老师不仅可以有对知识的讲解,与编程思想的演练,更可以对pta或者实验的难题加以点评与讲解,让作业不会得过且过,而是让我们更为深刻的了解一道题目应该如何去设计。作为学生自身,已经了解到这是一门需要自我探究,自我学习的课程。时间,精力,投入,缺一不可,不去假大空,而是去真正的做。
第二阶段于此就告一段落了,首先感谢OOP课程的老师与助教的付出,再而感谢还在学习的自己。希望有更好的心态迎接第三阶段!
OO课程第二阶段(实验和期中试题)总结Blog2的更多相关文章
- 面向对象设计与构造:oo课程总结
面向对象设计与构造:OO课程总结 第一部分:UML单元架构设计 第一次作业 UML图 MyUmlInteraction类实现接口方法,ClassUnit和InterfaceUnit管理UML图中的类和 ...
- OO第四单元——基于UML的UML解析器总结&OO课程总结
OO第四单元--基于UML的UML解析器总结&OO课程总结 前言:一学期愉快(痛苦)的OO课程学习结束了,OO几个单元作业都各有特色,实验也各有特色,仔细回味起来,不再是单纯的敲代码(但自己还 ...
- OO第四单元总结暨OO课程总结
一.第四单元作业总结 本单元的主要任务是对 Uml 图元素进行管理和查询,测试一开始会输入一个静态图,之后会对图中相关内容进行查询. 第13,14次作业 第14次作业新增内容很少,故与第13次作业放在 ...
- 2019OO第四单元作业总结&OO课程整体总结
第四单元作业总结 第四单元的作业主题是UML图的解析,通过对UML图代码的解析,我对UML图的结构以及各种元素之间的关系的理解更加深入了. ------------------------------ ...
- 第四单元博客总结——暨OO课程总结
第四单元博客总结--暨OO课程总结 第四单元架构设计 第一次UML作业 简单陈述 第一次作业较为简单,只需要实现查询功能,并在查询的同时考虑到性能问题,即我简单的将每一次查询的结果以及递归的上层结果都 ...
- OO课程第三次总结QWQ
调研,然后总结介绍规格化设计的大致发展历史和为什么得到了人们的重视 emmm为这个问题翻遍百度谷歌知乎也没有得到答案,那我就把自己认为最重要的两点简要说明一下吧,欢迎大家补充~ 1.便于完成代码的重用 ...
- OO课程中IDEA相关插件的使用
写在前面 由于OO课程博客作业的需要分析代码的复杂度并绘制UML图,但是课件上推荐的分析工具(http://metrics.sourceforge.net )经过自己几个小时的折腾还是没有安装成功 ...
- OO课程学期末总结
OO课程学期末总结 测试VS正确性论证 OCL vs JSF 对象约束语言(Object Constraint Language), 简称OCL, 是一种指示用户建模系统中的限制方式. 他是UML可选 ...
- OO课程总结
OO课程总结 OO终于划上了句号,这学期熬夜熬得最多的一门课,掉了最多头发的一门课. 一.测试与正确性 测试是最最最常见的用来找到程序错误以及验证程序正确的手段,在之前的作业中,写完代码还是会存在很多 ...
- OO第四单元总结——查询UML类图 暨 OO课程总结
一.本单元两次作业的架构设计总结 作业一.UML类图查询 1. 统计信息图 2. 复杂度分析 基本复杂度(Essential Complexity (ev(G)).模块设计复杂度(Module Des ...
随机推荐
- Visusl Studio使用技巧
一.快捷键的使用 1.使用Ctrl+K,Ctrl+E,可以清理代码,包括清理无用的using和对齐代码: 也可以使用快捷按钮实现该功能,如下图: 2.使用Ctrl+K,Ctrl+D,可以对齐代码 建议 ...
- python日志篇-基础版
对常用python日志语法做记录,方便以后重复使用 print内容记录到文件: #!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- ##____________ ...
- Linux上面配置Apache2支持Https(ssl)具体方案实现
虽然Nginx比较流行,但是由于一些老项目用到了Apache2来支持Web服务,最近想给服务上一个Https支持,虽然看似教程简单,但是也遇到一些特殊情况,经历了一番折腾也算是解决了所有问题,将过程记 ...
- SQL中各种join的区别
INNER JOIN 在表中存在至少一个匹配时,INNER JOIN 关键字返回行 返回的是一个交集 内连接就是等值连接 自然连接(outer join. left join, right join) ...
- ubuntu - 程序运行的一些基础知识
1.指定编码格式 -finput-charset=GB2312 指定 C 程序的编码方式为 GB2312,不指定时默认编码方式为 UTF-8 -fexec-charset=GB2312 指定 可执行程 ...
- Impala 学习笔记
VALUES Statement | 6.3.x | Cloudera Documentation SELECT now() as date_DES UNION ALL SELECT trunc(no ...
- h5py学习(一)核心概念
因pandas的to_hdf5函数有bug TypeError: object of type 'int' has no len(),写dataframe数据出现了报错,遂决定直接使用h5py来写数据 ...
- gl-ar750 配置
镜像下载https://docs.gl-inet.com/en/3/release_notes/gl-ar750/设置sd卡安装软件https://openwrt.org/docs/guide-use ...
- python批量更改文件名并移动到新的文件夹
python批量更改文件名并移动到新的文件夹 前言: 1. 这里的代码以批量命名如: 路径"E:\下载\1\xxxx.mp4"."E:\下载\2\xxxx.mp4&quo ...
- Adversarial seeded sequence growing for weakly-supervised temporal action localization概述
0.前言 相关资料: 论文 github 论文解读 论文基本信息: 领域:弱监督时序动作定位综述 更新时间:ACM MM2019(2019.8.7) 1.针对的问题 大多数现有的框架依赖于类激活序列( ...
