9. Lab: file system
1. Large files (moderate)
1.1 要求
Modify bmap() so that it implements a doubly-indirect block, in addition to direct blocks and a singly-indirect block. You'll have to have only 11 direct blocks, rather than 12, to make room for your new doubly-indirect block; you're not allowed to change the size of an on-disk inode. The first 11 elements of ip->addrs[] should be direct blocks; the 12th should be a singly-indirect block (just like the current one); the 13th should be your new doubly-indirect block. You are done with this exercise when bigfile writes 65803 blocks and usertests runs successfully:
要求扩大 xv6 中文件大小上限。目前 xv6 文件限制为 268 个块,或 268*BSIZE 字节(在 xv6 中 BSIZE 为 1024)。 因为一个 xv6 inode 包含 12 个“直接”块号和一个“单独间接”块号,这是指一个块最多可以容纳 256 个块号,总共 12+256=268 块。
因此需要更改 xv6 文件系统代码以支持每个 inode 中的“双重间接”块,其中包含 256 个单间接块地址,每个块最多可包含 256 个数据块地址。 结果将是一个文件将能够包含多达 65803 个块,或 256*256+256+11 个块(11 个而不是 12 个,因为我们将为双间接块牺牲一个直接块号)
原来的结构如图下:
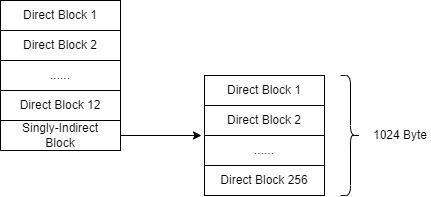
修改后的结构应当如下:
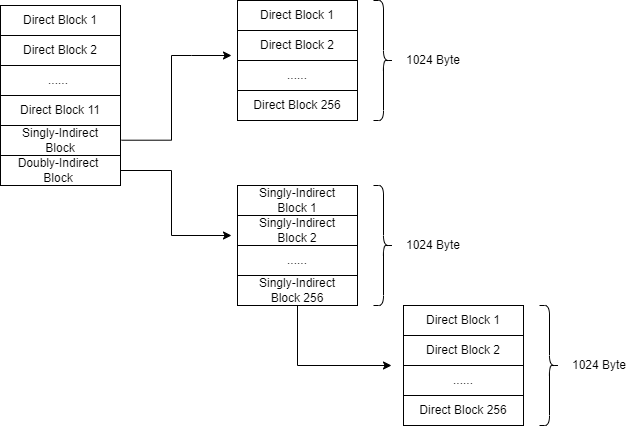
可以看到,有点类似多级页表的思路。
1.2 分析
要注意的点如下:
- 因为
inode.addrs固定为13 个,因此需要减少一个DirectBlock给Doubly-Indirect使用 bmap的函数签名如右:bmap(struct inode *ip, uint bn),bn为 block number。需要注意,当bn大于 256 + 11 的时候,需要开始在Doubly-Indirect中找到合适的Direct-Block,可以通过bn=bn-256-11去掉偏移,然后bn/256得到在第几块Singly-Indirect,bn%256得到目标块在Singly-Indirect中的偏移。- 通过
bread获取buf之后,修改buf后需要通过log_write操作写入更新。
1.3 实现
- 修改直接块数量,注意需要修改
dinode和inode的addrs大小
#define NDOUBLEINDIRECT (NINDIRECT * NINDIRECT)
#define NDIRECT 11
// On-disk inode structure
struct dinode {
short type; // File type
short major; // Major device number (T_DEVICE only)
short minor; // Minor device number (T_DEVICE only)
short nlink; // Number of links to inode in file system
uint size; // Size of file (bytes)
uint addrs[NDIRECT+2]; // Data block addresses
};
// in-memory copy of an inode
struct inode {
uint dev; // Device number
uint inum; // Inode number
int ref; // Reference count
struct sleeplock lock; // protects everything below here
int valid; // inode has been read from disk?
short type; // copy of disk inode
short major;
short minor;
short nlink;
uint size;
uint addrs[NDIRECT+2];
};
- 分配间接块,此处需要注意,只有当用到时才分配块,其次修改块时需要记得
log_write
static uint
bmap(struct inode *ip, uint bn)
{
uint addr, *a;
struct buf *bp, *inbp;
if(bn < (NDIRECT)){
if((addr = ip->addrs[bn]) == 0)
ip->addrs[bn] = addr = balloc(ip->dev);
return addr;
}
bn -= NDIRECT;
if(bn < NINDIRECT){
// Load indirect block, allocating if necessary.
if((addr = ip->addrs[NDIRECT]) == 0)
ip->addrs[NDIRECT] = addr = balloc(ip->dev);
bp = bread(ip->dev, addr);
a = (uint*)bp->data;
if((addr = a[bn]) == 0){
a[bn] = addr = balloc(ip->dev);
log_write(bp);
}
brelse(bp);
return addr;
}
bn -= NINDIRECT;
// load doublely-indirect block
if(bn < NDOUBLEINDIRECT){
if((addr = ip->addrs[NDIRECT + 1]) == 0)
ip->addrs[NDIRECT + 1] = addr = balloc(ip->dev); // alloc doublely-indirect block
// get indirect block index
inbp = bread(ip->dev, addr);
a = (uint*)(inbp->data);
uint in_index = bn / NINDIRECT;
uint bn_index = bn % NINDIRECT;
// Load indirect block, allocating if necessary.
if ((addr = a[in_index]) == 0){
a[in_index] = addr = balloc(ip->dev);
log_write(inbp);
}
brelse(inbp);
bp = bread(ip->dev, addr);
a = (uint*)bp->data;
if ((addr = a[bn_index]) == 0){
a[bn_index] = addr = balloc(ip->dev);
log_write(bp);
}
brelse(bp);
return addr;
}
panic("bmap: out of range");
}
- 释放块
// Truncate inode (discard contents).
// Caller must hold ip->lock.
void
itrunc(struct inode *ip)
{
int i, j, k;
struct buf *bp, *inbp;
uint *a;
uint *tmp;
for(i = 0; i < NDIRECT; i++){
if(ip->addrs[i]){
bfree(ip->dev, ip->addrs[i]);
ip->addrs[i] = 0;
}
}
if(ip->addrs[NDIRECT]){
bp = bread(ip->dev, ip->addrs[NDIRECT]);
a = (uint*)bp->data;
for(j = 0; j < NINDIRECT; j++){
if(a[j])
bfree(ip->dev, a[j]);
}
brelse(bp);
bfree(ip->dev, ip->addrs[NDIRECT]);
ip->addrs[NDIRECT] = 0;
}
if(ip->addrs[NDIRECT + 1]){
inbp = bread(ip->dev, ip->addrs[NDIRECT + 1]);
a = (uint*)(inbp->data);
for (j = 0; j < NINDIRECT; j++){
if (a[j]) {
bp = bread(ip->dev, a[j]);
tmp = (uint*)bp->data;
for(k = 0; k < NINDIRECT; k++){
if(tmp[k])
bfree(ip->dev, tmp[k]);
}
brelse(bp);
bfree(ip->dev, a[j]);
a[j] = 0;
}
}
brelse(inbp);
bfree(ip->dev, ip->addrs[NDIRECT + 1]);
ip->addrs[NDIRECT + 1] = 0;
}
ip->size = 0;
iupdate(ip);
}
2. Symbolic links(moderate)
2.1 要求
You will implement the symlink(char *target, char *path) system call, which creates a new symbolic link at path that refers to file named by target. For further information, see the man page symlink. To test, add symlinktest to the Makefile and run it. Your solution is complete when the tests produce the following output (including usertests succeeding).
实现 symlink 接口,比较简单,与 link 的区别在于,symlink 会创建文件,而 link 接口只是增加目标文件的引用计数,并写入目录。
2.2 分析
实现主要有 2 点:
- 创建链接文件,通过
sys_symlink接口创建 - 访问链接文件,通过
sys_open访问
2.3 实现
- 创建文件
在 inode 结构中增加 char symlinkpath[128];,用于存储目标文件的名字。
uint64 sys_symlink(void)
{
char path[MAXPATH], target[MAXPATH];
struct inode *ip;
if(argstr(0, target, MAXPATH) < 0 || argstr(1, path, MAXPATH) < 0)
return -1;
begin_op();
if ((ip = namei(path)) == 0){
ip = create(path, T_SYMLINK, 0, 0);
if (ip == 0){
end_op();
return -1;
}
}else if (ip->type != T_SYMLINK){
end_op();
return -1;
}else{
ilock(ip);
}
memset(ip->symlinkpath, 0, MAXPATH);
memmove(ip->symlinkpath, target, sizeof(target));
iunlockput(ip);
end_op();
return 0;
}
- 访问文件
需要注意如果有 O_NOFOLLOW 的 flag,则直接访问链接文件,而不是访问 inode.symlinkpath 的文件。
其次要注意存在链接文件 链接 链接文件的操作,有点套娃,比如 a->b,b->c,c->a,此时如果没有防范措施会无限套娃,因此根据 hints 加了个递归层次限制。
uint64 sys_open(void)
{
char path[MAXPATH];
int fd, omode;
struct file *f;
struct inode *ip, *symip;
int n;
if((n = argstr(0, path, MAXPATH)) < 0 || argint(1, &omode) < 0)
return -1;
begin_op();
if(omode & O_CREATE){
ip = create(path, T_FILE, 0, 0);
if(ip == 0){
end_op();
return -1;
}
}
else {
if((ip = namei(path)) == 0){
end_op();
return -1;
}
ilock(ip);
if(ip->type == T_DIR && omode != O_RDONLY){
iunlockput(ip);
end_op();
return -1;
}
}
int cnt = 0;
while(ip->type == T_SYMLINK && !(omode & O_NOFOLLOW)){
if (cnt >= 10) {
iunlockput(ip);
end_op();
return -1;
}
symip = namei(ip->symlinkpath);
if (symip) {
cnt++;
iunlockput(ip);
ip = symip;
ilock(ip);
}
else {
break;
}
}
if (cnt == 0 && ip->type == T_SYMLINK && !(omode & O_NOFOLLOW)){
iunlockput(ip);
end_op();
return -1;
}
if(ip->type == T_DEVICE && (ip->major < 0 || ip->major >= NDEV)){
iunlockput(ip);
end_op();
return -1;
}
if((f = filealloc()) == 0 || (fd = fdalloc(f)) < 0){
if(f)
fileclose(f);
iunlockput(ip);
end_op();
return -1;
}
if(ip->type == T_DEVICE){
f->type = FD_DEVICE;
f->major = ip->major;
} else {
f->type = FD_INODE;
f->off = 0;
}
f->ip = ip;
f->readable = !(omode & O_WRONLY);
f->writable = (omode & O_WRONLY) || (omode & O_RDWR);
if((omode & O_TRUNC) && ip->type == T_FILE){
itrunc(ip);
}
iunlock(ip);
end_op();
return fd;
}
9. Lab: file system的更多相关文章
- MIT 6.S081 Lab File System
前言 打开自己的blog一看,居然三个月没更新了...回想一下前几个月,开题 + 实验室杂活貌似也没占非常多的时间,还是自己太懈怠了吧,掉线城和文明6真的是时间刹手( 不过好消息是把15445的所有l ...
- RH133读书 笔记(4) - Lab 4 System Services
Lab 4 System Services Goal: Develop skills using system administration tools and setting up and admi ...
- RH253读书笔记(1)-Lab 1 System Monitoring
Lab 1 System Monitoring Goal: To build skills to better assess system resources, performance and sec ...
- RH133读书笔记(11)-Lab 11 System Rescue and Troubleshooting
Lab 11 System Rescue and Troubleshooting Goal: To build skills in system rescue procedures. Estimate ...
- MIT-6.828-JOS-lab5:File system, Spawn and Shell
Lab 5: File system, Spawn and Shell tags: mit-6.828 os 概述 本lab将实现JOS的文件系统,只要包括如下四部分: 引入一个文件系统进程(FS进程 ...
- Can Microsoft’s exFAT file system bridge the gap between OSes?
转自:http://arstechnica.com/information-technology/2013/06/review-is-microsofts-new-data-sharing-syste ...
- File System Design Case Studies
SRC=http://www.cs.rutgers.edu/~pxk/416/notes/13-fs-studies.html Paul Krzyzanowski April 24, 2014 Int ...
- MIT6.828 La5 File system, Spawn and Shell
Lab 5: File system, Spawn and Shell 1. File system preliminaries 在lab中我们要使用的文件系统比大多数"真实"文件 ...
- Design and Implementation of the Sun Network File System
Introduction The network file system(NFS) is a client/service application that provides shared file ...
随机推荐
- go1.18泛型的简单尝试
今天golang终于发布了1.18版本,这个版本最大的一个改变就是加入了泛型.虽然没有在beta版本的时候尝试泛型,但是由于在其他语言的泛型经验,入手泛型不是件难事~ 官方示例 Tutorial: G ...
- 深度学习(一)之MNIST数据集分类
任务目标 对MNIST手写数字数据集进行训练和评估,最终使得模型能够在测试集上达到\(98\%\)的正确率.(最终本文达到了\(99.36\%\)) 使用的库的版本: python:3.8.12 py ...
- 1357:车厢调度(train) ybt
1357:车厢调度(train) [题目描述] 有一个火车站,铁路如图所示,每辆火车从A驶入,再从B方向驶出,同时它的车厢可以重新组合.假设从A方向驶来的火车有nn节(n≤1000n≤1000),分别 ...
- oracle中regexp_like/instr/substr/replace介绍和例子
ORACLE中的支持正则表达式的函数主要有下面四个: 1,REGEXP_LIKE :与LIKE的功能相似 2,REGEXP_INSTR :与INSTR的功能相似 3,REGEXP_SUBSTR :与S ...
- Linux 查看文件大小并按照大小排序
使用df 命令查看当前系统磁盘的使用情况: [root@node ~]# df -Th Filesystem Type Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/map ...
- SQL注入常用命令
1. 数据库查询版本 Mssql select @@version Mysql select vresion()/select @@version oracle select banner from ...
- PCIe Tandem PROM 方法
PCIe Tandem PROM 方法 什么是Tandem PROM? 简单总结:市面多数的FPGA都是SRAM型,需要在上电时从外部存储器件完成代码的加载,对于具有PCIe功能的SRAM FPGA而 ...
- mysql主从异步复制过程
mysql是现在普遍使用的数据库,但是如果宕机了必然会造成数据丢失.为了保证mysql数据库的可靠性.就要会一些提高可靠性的技术. 主从复制原理如下. slave(从服务器) master(主服务器) ...
- cookie可设置哪些属性?httponly?
chrome控制台的application下可查看: cookie name 字段为一个cookie的名称. value 字段为一个cookie的值. domain 字段为可以访问此cookie的域名 ...
- 你是怎么看Spring框架的?
Spring是一个轻量级的容器,非侵入性的框架.最重要的核心概念是IOC,并提供AOP概念的实现方式,提供对持久层,事务的支持,对当前流行的一些框架(Struts,Hibernate,MVC),Spi ...
