一文读懂,硬核 Apache DolphinScheduler3.0 源码解析
点亮 ️ Star · 照亮开源之路
https://github.com/apache/dolphinscheduler

本文目录
1 DolphinScheduler的设计与策略
1.1 分布式设计
1.1.1 中心化
1.1.2 去中心化
1.2 DophinScheduler架构设计
1.3 容错问题
1.3.1 宕机容错
1.3.2 失败重试
1.4 远程日志访问
2 DolphinScheduler源码分析
2.1 工程模块介绍与配置文件
2.1.1 工程模块介绍
2.1.2 配置文件
2.2 Api主要任务操作接口
2.3 Quaterz架构与运行流程
2.3.1 概念与架构
2.3.2 初始化与执行流程
2.3.3 集群运转
2.4 Master启动与执行流程
2.4.1 概念与执行逻辑
2.4.2 集群与槽(slot)
2.4.3 代码执行流程
2.5 Work启动与执行流程
2.5.1 概念与执行逻辑
2.5.2 代码执行流程
2.6 rpc交互
2.6.1 Master与Worker交互
2.6.2 其他服务与Master交互
2.7 负载均衡算法
2.7.1 加权随机
2.7.2 线性负载
2.7.3 平滑轮询
2.8 日志服务
2.9 报警
3 后记
3.1 Make friends
3.2 参考文献
前言
研究Apache Dolphinscheduler也是机缘巧合,平时负责基于xxl-job二次开发出来的调度平台,因为遇到了并发性能瓶颈,到了不得不优化重构的地步,所以搜索市面上应用较广的调度平台以借鉴优化思路。
在阅读完DolphinScheduler代码之后,便生出了将其设计与思考记录下来的念头,这便是此篇文章的来源。因为没有正式生产使用,业务理解不一定透彻,理解可能有偏差,欢迎大家交流讨论。
1 DolphinScheduler的设计与策略
大家能关注DolphinScheduler那么一定对调度系统有了一定的了解,对于调度所涉及的到一些专有名词在这里就不做过多的介绍,重点介绍一下流程定义,流程实例,任务定义,任务实例。(没有作业这个概念确实也很新奇,可能是不想和Quartz的JobDetail重叠)。
任务定义:各种类型的任务,是流程定义的关键组成,如sql,shell,spark,mr,python等;
任务实例:任务的实例化,标识着具体的任务执行状态;
流程定义:一组任务节点通过依赖关系建立的起来的有向无环图(DAG);
流程实例:通过手动或者定时调度生成的流程实例;
定时调度:系统采用Quartz 分布式调度器,并同时支持cron表达式可视化的生成;
1.1 分布式设计
分布式系统的架构设计基本分为中心化和去中心化两种,各有优劣,凭借各自的业务选择。
1.1.1 中心化
中心化设计比较简单,集群中的节点安装角色可以分为Master和Slave两种,如下图:
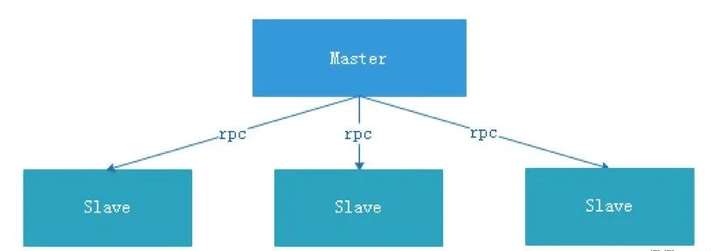
Master: Master的角色主要负责任务分发并监督Slave的健康状态,可以动态的将任务均衡到Slave上,以致Slave节点不至于“忙死”或”闲死”的状态。
中心化设计存在一些问题。
第一点,一旦Master出现了问题,则群龙无首,整个集群就会崩溃。
为了解决这个问题,大多数Master/Slave架构模式都采用了主备Master的设计方案,可以是热备或者冷备,也可以是自动切换或手动切换,而且越来越多的新系统都开始具备自动选举切换Master的能力,以提升系统的可用性。
第二点,如果Scheduler在Master上,虽然可以支持一个DAG中不同的任务运行在不同的机器上,但是会产生Master的过负载。如果Scheduler在Slave上,一个DAG中所有的任务都只能在某一台机器上进行作业提交,在并行任务比较多的时候,Slave的压力可能会比较大。
xxl-job就是采用这种设计方式,但是存在相应的问题。管理器(admin)宕机集群会崩溃,Scheduler在管理器上,管理器负责所有任务的校验和分发,管理器存在过载的风险,需要开发者想方案解决。
1.1.2 去中心化
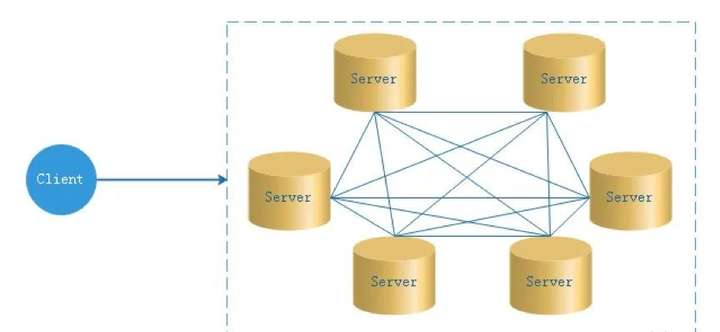
在去中心化设计里,通常没有Master/Slave的概念,所有的角色都是一样的,地位是平等的,去中心化设计的核心设计在于整个分布式系统中不存在一个区别于其他节点的“管理者”,因此不存在单点故障问题。
但由于不存在“管理者”节点所以每个节点都需要跟其他节点通信才得到必须要的机器信息,而分布式系统通信的不可靠性,则大大增加了上述功能的实现难度。实际上,真正去中心化的分布式系统并不多见。
反而动态中心化分布式系统正在不断涌出。在这种架构下,集群中的管理者是被动态选择出来的,而不是预置的,并且集群在发生故障的时候,集群的节点会自发的举行会议来选举新的管理者去主持工作。
一般都是基于Raft算法实现的选举策略。Raft算法,目前社区也有相应的PR,还没合并。
PR链接:https://github.com/apache/dolphinscheduler/issues/10874
动态展示见链接:http://thesecretlivesofdata.com/
DolphinScheduler的去中心化是Master/Worker注册到注册中心,实现Master集群和Worker集群无中心。
1.2 DophinScheduler架构设计
随手盗用一张官网的系统架构图,可以看到调度系统采用去中心化设计,由UI,API,MasterServer,Zookeeper,WorkServer,Alert等几部分组成。
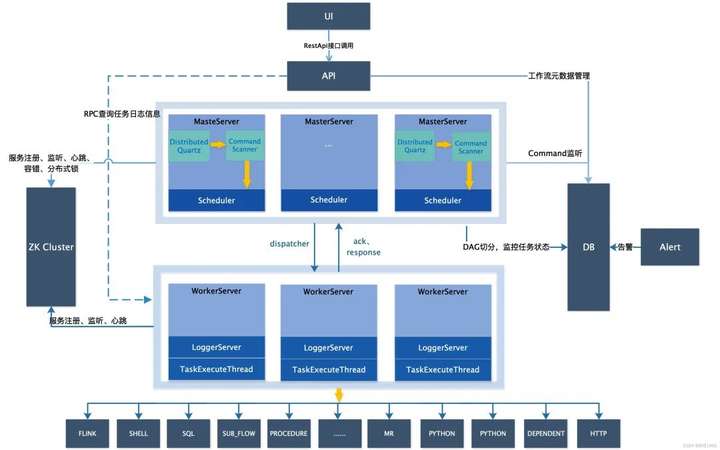
API: API接口层,主要负责处理前端UI层的请求。该服务统一提供RESTful api向外部提供请求服务。接口包括工作流的创建、定义、查询、修改、发布、下线、手工启动、停止、暂停、恢复、从该节点开始执行等等。
MasterServer: MasterServer采用分布式无中心设计理念,MasterServer集成了Quartz,主要负责 DAG 任务切分、任务提交监控,并同时监听其它MasterServer和WorkerServer的健康状态。MasterServer服务启动时向Zookeeper注册临时节点,通过监听Zookeeper临时节点变化来进行容错处理。WorkServer:WorkerServer也采用分布式无中心设计理念,WorkerServer主要负责任务的执行和提供日志服务。WorkerServer服务启动时向Zookeeper注册临时节点,并维持心跳。
ZooKeeper: ZooKeeper服务,系统中的MasterServer和WorkerServer节点都通过ZooKeeper来进行集群管理和容错。另外系统还基于ZooKeeper进行事件监听和分布式锁。
**Alert:**提供告警相关接口,接口主要包括两种类型的告警数据的存储、查询和通知功能,支持丰富的告警插件自由拓展配置。
1.3 容错问题
容错分为服务宕机容错和任务重试,服务宕机容错又分为Master容错和Worker容错两种情况;
1.3.1 宕机容错
服务容错设计依赖于ZooKeeper的Watcher机制,实现原理如图:
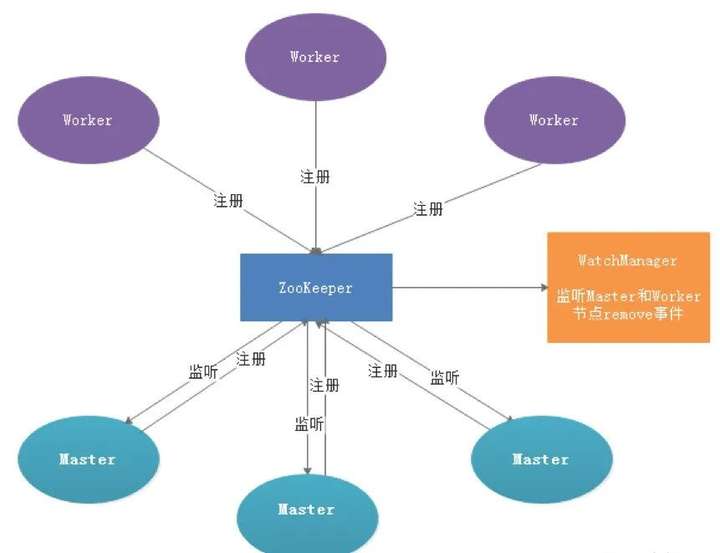
其中Master监控其他Master和Worker的目录,如果监听到remove事件,则会根据具体的业务逻辑进行流程实例容错或者任务实例容错,容错流程图相对官方文档里面的流程图,人性化了些,大家可以参考一下,具体如下所示。
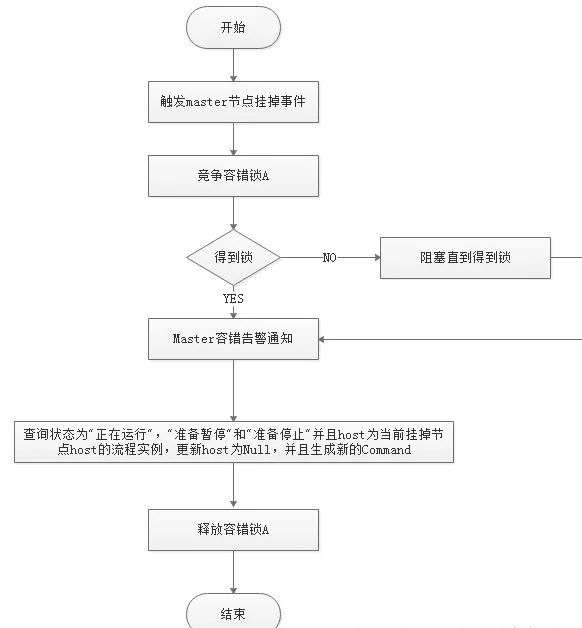
ZooKeeper Master容错完成之后则重新由DolphinScheduler中Scheduler线程调度,遍历 DAG 找到“正在运行”和“提交成功”的任务,对“正在运行”的任务监控其任务实例的状态,对“提交成功”的任务需要判断Task Queue中是否已经存在,如果存在则同样监控任务实例的状态,如果不存在则重新提交任务实例。
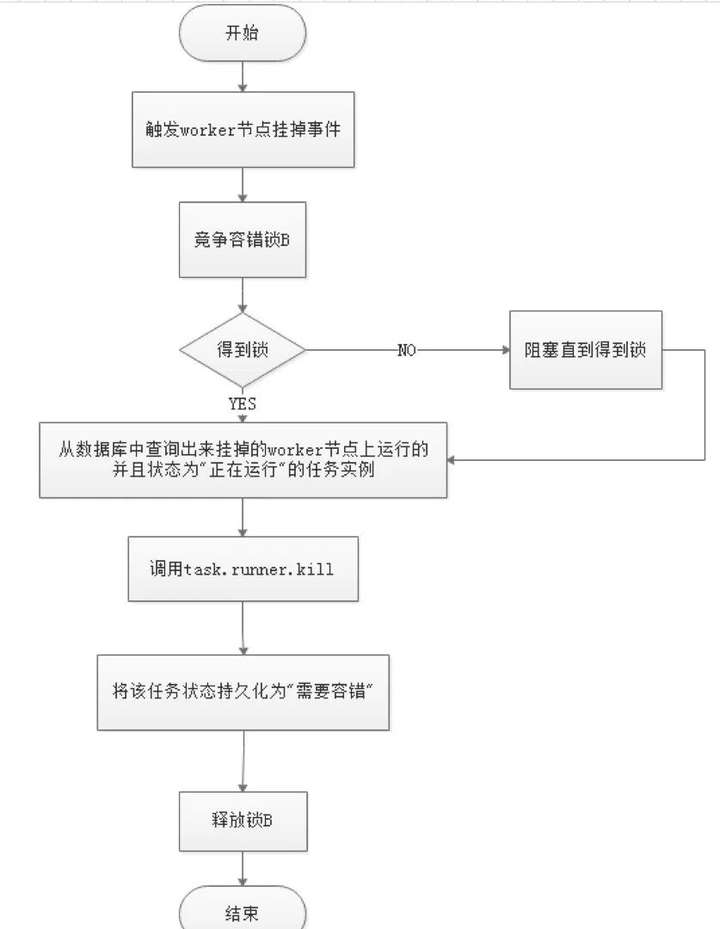
Master Scheduler线程一旦发现任务实例为” 需要容错”状态,则接管任务并进行重新提交。注意由于” 网络抖动”可能会使得节点短时间内失去和ZooKeeper的心跳,从而发生节点的remove事件。
对于这种情况,我们使用最简单的方式,那就是节点一旦和ZooKeeper发生超时连接,则直接将Master或Worker服务停掉。
1.3.2 失败重试
这里首先要区分任务失败重试、流程失败恢复、流程失败重跑的概念:
任务失败重试是任务级别的,是调度系统自动进行的,比如一个Shell任务设置重试次数为3次,那么在Shell任务运行失败后会自己再最多尝试运行3次。
流程失败恢复是流程级别的,是手动进行的,恢复是从只能从失败的节点开始执行或从当前节点开始执行。流程失败重跑也是流程级别的,是手动进行的,重跑是从开始节点进行。
接下来说正题,我们将工作流中的任务节点分了两种类型。
一种是业务节点,这种节点都对应一个实际的脚本或者处理语句,比如Shell节点、MR节点、Spark节点、依赖节点等。
还有一种是逻辑节点,这种节点不做实际的脚本或语句处理,只是整个流程流转的逻辑处理,比如子流程节等。
每一个业务节点都可以配置失败重试的次数,当该任务节点失败,会自动重试,直到成功或者超过配置的重试次数。逻辑节点不支持失败重试。但是逻辑节点里的任务支持重试。
如果工作流中有任务失败达到最大重试次数,工作流就会失败停止,失败的工作流可以手动进行重跑操作或者流程恢复操作。
1.4 远程日志访问
由于Web(UI)和Worker不一定在同一台机器上,所以查看日志不能像查询本地文件那样。
有两种方案:
将日志放到ES搜索引擎上;
通过netty通信获取远程日志信息;
介于考虑到尽可能的DolphinScheduler的轻量级性,所以选择了RPC实现远程访问日志信息,具体代码的实践见2.8章节。
2 DolphinScheduler源码分析
上一章的讲解可能初步看起来还不是很清晰,本章的主要目的是从代码层面一一介绍第一张讲解的功能。关于系统的安装在这里并不会涉及,安装运行请大家自行探索。
2.1 工程模块介绍与配置文件
2.1.1 工程模块介绍
dolphinscheduler-alert 告警模块,提供告警服务;
dolphinscheduler-api web应用模块,提供 Rest Api 服务,供 UI 进行调用;
dolphinscheduler-common 通用的常量枚举、工具类、数据结构或者基类 dolphinscheduler-dao 提供数据库访问等操作;
dolphinscheduler-remote 基于netty的客户端、服务端 ;
dolphinscheduler-server 日志与心跳服务 ;
dolphinscheduler-log-server LoggerServer 用于Rest Api通过RPC查看日志;
dolphinscheduler-master MasterServer服务,主要负责 DAG 的切分和任务状态的监控 ;
dolphinscheduler-worker WorkerServer服务,主要负责任务的提交、执行和任务状态的更新;
dolphinscheduler-service service模块,包含Quartz、Zookeeper、日志客户端访问服务,便于server模块和api模块调用 ;
dolphinscheduler-ui 前端模块;
2.1.2 配置文件
dolphinscheduler-common common.properties
#本地工作目录,用于存放临时文件
data.basedir.path=/tmp/dolphinscheduler
#资源文件存储类型: HDFS,S3,NONE
resource.storage.type=NONE
#资源文件存储路径
resource.upload.path=/dolphinscheduler
#hadoop是否开启kerberos权限
hadoop.security.authentication.startup.state=false
#kerberos配置目录
java.security.krb5.conf.path=/opt/krb5.conf
#kerberos登录用户
login.user.keytab.username=hdfs-mycluster@ESZ.COM
#kerberos登录用户keytab
login.user.keytab.path=/opt/hdfs.headless.keytab
#kerberos过期时间,整数,单位为小时
kerberos.expire.time=2
# 如果存储类型为HDFS,需要配置拥有对应操作权限的用户
hdfs.root.user=hdfs
#请求地址如果resource.storage.type=S3,该值类似为: s3a://dolphinscheduler. 如果resource.storage.type=HDFS, 如果 hadoop 配置了 HA,需要复制core-site.xml 和 hdfs-site.xml 文件到conf目录
fs.defaultFS=hdfs://mycluster:8020
aws.access.key.id=minioadmin
aws.secret.access.key=minioadmin
aws.region=us-east-1
aws.endpoint=http://localhost:9000
# resourcemanager port, the default value is 8088 if not specified
resource.manager.httpaddress.port=8088
#yarn resourcemanager 地址, 如果resourcemanager开启了HA, 输入HA的IP地址(以逗号分隔),如果resourcemanager为单节点, 该值为空即可
yarn.resourcemanager.ha.rm.ids=192.168.xx.xx,192.168.xx.xx
#如果resourcemanager开启了HA或者没有使用resourcemanager,保持默认值即可. 如果resourcemanager为单节点,你需要将ds1 配置为resourcemanager对应的hostname
yarn.application.status.address=http://ds1:%s/ws/v1/cluster/apps/%s
# job history status url when application number threshold is reached(default 10000, maybe it was set to 1000)
yarn.job.history.status.address=http://ds1:19888/ws/v1/history/mapreduce/jobs/%s
# datasource encryption enable
datasource.encryption.enable=false
# datasource encryption salt
datasource.encryption.salt=!@#$%^&*
# data quality option
data-quality.jar.name=dolphinscheduler-data-quality-dev-SNAPSHOT.jar
#data-quality.error.output.path=/tmp/data-quality-error-data
# Network IP gets priority, default inner outer
# Whether hive SQL is executed in the same session
support.hive.oneSession=false
# use sudo or not, if set true, executing user is tenant user and deploy user needs sudo permissions; if set false, executing user is the deploy user and doesn't need sudo permissions
sudo.enable=true
# network interface preferred like eth0, default: empty
#dolphin.scheduler.network.interface.preferred=
# network IP gets priority, default: inner outer
#dolphin.scheduler.network.priority.strategy=default
# system env path
#dolphinscheduler.env.path=dolphinscheduler_env.sh
#是否处于开发模式
development.state=false
# rpc port
alert.rpc.port=50052
# Url endpoint for zeppelin RESTful API
zeppelin.rest.url=http://localhost:8080


dolphinscheduler-api application.yaml
server:
port: 12345
servlet:
session:
timeout: 120m
context-path: /dolphinscheduler/
compression:
enabled: true
mime-types: text/html,text/xml,text/plain,text/css,text/javascript,application/javascript,application/json,application/xml
jetty:
max-http-form-post-size: 5000000
spring:
application:
name: api-server
banner:
charset: UTF-8
jackson:
time-zone: UTC
date-format: "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"
servlet:
multipart:
max-file-size: 1024MB
max-request-size: 1024MB
messages:
basename: i18n/messages
datasource:
# driver-class-name: org.postgresql.Driver
# url: jdbc:postgresql://127.0.0.1:5432/dolphinscheduler
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/dolphinscheduler?useUnicode=true&serverTimezone=UTC&characterEncoding=UTF-8&autoReconnect=true&useSSL=false&zeroDateTimeBehavior=convertToNull
username: root
password: root
hikari:
connection-test-query: select 1
minimum-idle: 5
auto-commit: true
validation-timeout: 3000
pool-name: DolphinScheduler
maximum-pool-size: 50
connection-timeout: 30000
idle-timeout: 600000
leak-detection-threshold: 0
initialization-fail-timeout: 1
quartz:
auto-startup: false
job-store-type: jdbc
jdbc:
initialize-schema: never
properties:
org.quartz.threadPool:threadPriority: 5
org.quartz.jobStore.isClustered: true
org.quartz.jobStore.class: org.quartz.impl.jdbcjobstore.JobStoreTX
org.quartz.scheduler.instanceId: AUTO
org.quartz.jobStore.tablePrefix: QRTZ_
org.quartz.jobStore.acquireTriggersWithinLock: true
org.quartz.scheduler.instanceName: DolphinScheduler
org.quartz.threadPool.class: org.quartz.simpl.SimpleThreadPool
org.quartz.jobStore.useProperties: false
org.quartz.threadPool.makeThreadsDaemons: true
org.quartz.threadPool.threadCount: 25
org.quartz.jobStore.misfireThreshold: 60000
org.quartz.scheduler.makeSchedulerThreadDaemon: true
# org.quartz.jobStore.driverDelegateClass: org.quartz.impl.jdbcjobstore.PostgreSQLDelegate
org.quartz.jobStore.driverDelegateClass: org.quartz.impl.jdbcjobstore.StdJDBCDelegate
org.quartz.jobStore.clusterCheckinInterval: 5000
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: '*'
metrics:
tags:
application: ${spring.application.name}
registry:
type: zookeeper
zookeeper:
namespace: dolphinscheduler
# connect-string: localhost:2181
connect-string: 10.255.158.70:2181
retry-policy:
base-sleep-time: 60ms
max-sleep: 300ms
max-retries: 5
session-timeout: 30s
connection-timeout: 9s
block-until-connected: 600ms
digest: ~
audit:
enabled: false
metrics:
enabled: true
python-gateway:
# Weather enable python gateway server or not. The default value is true.
enabled: true
# The address of Python gateway server start. Set its value to `0.0.0.0` if your Python API run in different
# between Python gateway server. It could be be specific to other address like `127.0.0.1` or `localhost`
gateway-server-address: 0.0.0.0
# The port of Python gateway server start. Define which port you could connect to Python gateway server from
# Python API side.
gateway-server-port: 25333
# The address of Python callback client.
python-address: 127.0.0.1
# The port of Python callback client.
python-port: 25334
# Close connection of socket server if no other request accept after x milliseconds. Define value is (0 = infinite),
# and socket server would never close even though no requests accept
connect-timeout: 0
# Close each active connection of socket server if python program not active after x milliseconds. Define value is
# (0 = infinite), and socket server would never close even though no requests accept
read-timeout: 0
# Override by profile
---
spring:
config:
activate:
on-profile: mysql
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/dolphinscheduler?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8
quartz:
properties:
org.quartz.jobStore.driverDelegateClass: org.quartz.impl.jdbcjobstore.StdJDBCDelegate


dolphinscheduler-master application.yaml
spring:
banner:
charset: UTF-8
application:
name: master-server
jackson:
time-zone: UTC
date-format: "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"
cache:
# default enable cache, you can disable by `type: none`
type: none
cache-names:
- tenant
- user
- processDefinition
- processTaskRelation
- taskDefinition
caffeine:
spec: maximumSize=100,expireAfterWrite=300s,recordStats
datasource:
#driver-class-name: org.postgresql.Driver
#url: jdbc:postgresql://127.0.0.1:5432/dolphinscheduler
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/dolphinscheduler?useUnicode=true&serverTimezone=UTC&characterEncoding=UTF-8&autoReconnect=true&useSSL=false&zeroDateTimeBehavior=convertToNull
username: root
password:
hikari:
connection-test-query: select 1
minimum-idle: 5
auto-commit: true
validation-timeout: 3000
pool-name: DolphinScheduler
maximum-pool-size: 50
connection-timeout: 30000
idle-timeout: 600000
leak-detection-threshold: 0
initialization-fail-timeout: 1
quartz:
job-store-type: jdbc
jdbc:
initialize-schema: never
properties:
org.quartz.threadPool:threadPriority: 5
org.quartz.jobStore.isClustered: true
org.quartz.jobStore.class: org.quartz.impl.jdbcjobstore.JobStoreTX
org.quartz.scheduler.instanceId: AUTO
org.quartz.jobStore.tablePrefix: QRTZ_
org.quartz.jobStore.acquireTriggersWithinLock: true
org.quartz.scheduler.instanceName: DolphinScheduler
org.quartz.threadPool.class: org.quartz.simpl.SimpleThreadPool
org.quartz.jobStore.useProperties: false
org.quartz.threadPool.makeThreadsDaemons: true
org.quartz.threadPool.threadCount: 25
org.quartz.jobStore.misfireThreshold: 60000
org.quartz.scheduler.makeSchedulerThreadDaemon: true
# org.quartz.jobStore.driverDelegateClass: org.quartz.impl.jdbcjobstore.PostgreSQLDelegate
org.quartz.jobStore.driverDelegateClass: org.quartz.impl.jdbcjobstore.StdJDBCDelegate
org.quartz.jobStore.clusterCheckinInterval: 5000
registry:
type: zookeeper
zookeeper:
namespace: dolphinscheduler
# connect-string: localhost:2181
connect-string: 10.255.158.70:2181
retry-policy:
base-sleep-time: 60ms
max-sleep: 300ms
max-retries: 5
session-timeout: 30s
connection-timeout: 9s
block-until-connected: 600ms
digest: ~
master:
listen-port: 5678
# master fetch command num
fetch-command-num: 10
# master prepare execute thread number to limit handle commands in parallel
pre-exec-threads: 10
# master execute thread number to limit process instances in parallel
exec-threads: 100
# master dispatch task number per batch
dispatch-task-number: 3
# master host selector to select a suitable worker, default value: LowerWeight. Optional values include random, round_robin, lower_weight
host-selector: lower_weight
# master heartbeat interval, the unit is second
heartbeat-interval: 10
# master commit task retry times
task-commit-retry-times: 5
# master commit task interval, the unit is millisecond
task-commit-interval: 1000
state-wheel-interval: 5
# master max cpuload avg, only higher than the system cpu load average, master server can schedule. default value -1: the number of cpu cores * 2
max-cpu-load-avg: -1
# master reserved memory, only lower than system available memory, master server can schedule. default value 0.3, the unit is G
reserved-memory: 0.3
# failover interval, the unit is minute
failover-interval: 10
# kill yarn jon when failover taskInstance, default true
kill-yarn-job-when-task-failover: true
server:
port: 5679
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: '*'
metrics:
tags:
application: ${spring.application.name}
metrics:
enabled: true
# Override by profile
---
spring:
config:
activate:
on-profile: mysql
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/dolphinscheduler?useUnicode=true&serverTimezone=UTC&characterEncoding=UTF-8&autoReconnect=true&useSSL=false&zeroDateTimeBehavior=convertToNull
quartz:
properties:
org.quartz.jobStore.driverDelegateClass: org.quartz.impl.jdbcjobstore.StdJDBCDelegate


dolphinscheduler-worker application.yaml
spring:
banner:
charset: UTF-8
application:
name: worker-server
jackson:
time-zone: UTC
date-format: "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"
datasource:
#driver-class-name: org.postgresql.Driver
#url: jdbc:postgresql://127.0.0.1:5432/dolphinscheduler
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/dolphinscheduler?useUnicode=true&serverTimezone=UTC&characterEncoding=UTF-8&autoReconnect=true&useSSL=false&zeroDateTimeBehavior=convertToNull
username: root
#password: root
password:
hikari:
connection-test-query: select 1
minimum-idle: 5
auto-commit: true
validation-timeout: 3000
pool-name: DolphinScheduler
maximum-pool-size: 50
connection-timeout: 30000
idle-timeout: 600000
leak-detection-threshold: 0
initialization-fail-timeout: 1
registry:
type: zookeeper
zookeeper:
namespace: dolphinscheduler
# connect-string: localhost:2181
connect-string: 10.255.158.70:2181
retry-policy:
base-sleep-time: 60ms
max-sleep: 300ms
max-retries: 5
session-timeout: 30s
connection-timeout: 9s
block-until-connected: 600ms
digest: ~
worker:
# worker listener port
listen-port: 1234
# worker execute thread number to limit task instances in parallel
exec-threads: 100
# worker heartbeat interval, the unit is second
heartbeat-interval: 10
# worker host weight to dispatch tasks, default value 100
host-weight: 100
# worker tenant auto create
tenant-auto-create: true
# worker max cpuload avg, only higher than the system cpu load average, worker server can be dispatched tasks. default value -1: the number of cpu cores * 2
max-cpu-load-avg: -1
# worker reserved memory, only lower than system available memory, worker server can be dispatched tasks. default value 0.3, the unit is G
reserved-memory: 0.3
# default worker groups separated by comma, like 'worker.groups=default,test'
groups:
- default
# alert server listen host
alert-listen-host: localhost
alert-listen-port: 50052
server:
port: 1235
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: '*'
metrics:
tags:
application: ${spring.application.name}
metrics:
enabled: true


主要关注数据库,quartz, zookeeper, masker, worker配置。
2.2 API主要任务操作接口
其他业务接口可以不用关注,只需要关注最最主要的流程上线功能接口,此接口可以发散出所有的任务调度相关的代码。
接口:/dolphinscheduler/projects/{projectCode}/schedules/{id}/online;此接口会将定义的流程提交到Quartz调度框架;代码如下:
public Map<String, Object> setScheduleState(User loginUser, long projectCode, Integer id, ReleaseState scheduleStatus) { Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<>();
Project project = projectMapper.queryByCode(projectCode); // check project auth boolean hasProjectAndPerm = projectService.hasProjectAndPerm(loginUser, project, result); if (!hasProjectAndPerm) { return result; }
// check schedule exists Schedule scheduleObj = scheduleMapper.selectById(id);
if (scheduleObj == null) { putMsg(result, Status.SCHEDULE_CRON_NOT_EXISTS, id); return result; } // check schedule release state if (scheduleObj.getReleaseState() == scheduleStatus) { logger.info("schedule release is already {},needn't to change schedule id: {} from {} to {}", scheduleObj.getReleaseState(), scheduleObj.getId(), scheduleObj.getReleaseState(), scheduleStatus); putMsg(result, Status.SCHEDULE_CRON_REALEASE_NEED_NOT_CHANGE, scheduleStatus); return result; } ProcessDefinition processDefinition = processDefinitionMapper.queryByCode(scheduleObj.getProcessDefinitionCode()); if (processDefinition == null || projectCode != processDefinition.getProjectCode()) { putMsg(result, Status.PROCESS_DEFINE_NOT_EXIST, String.valueOf(scheduleObj.getProcessDefinitionCode())); return result; } List<ProcessTaskRelation> processTaskRelations = processTaskRelationMapper.queryByProcessCode(projectCode, scheduleObj.getProcessDefinitionCode()); if (processTaskRelations.isEmpty()) { putMsg(result, Status.PROCESS_DAG_IS_EMPTY); return result; } if (scheduleStatus == ReleaseState.ONLINE) { // check process definition release state if (processDefinition.getReleaseState() != ReleaseState.ONLINE) { logger.info("not release process definition id: {} , name : {}", processDefinition.getId(), processDefinition.getName()); putMsg(result, Status.PROCESS_DEFINE_NOT_RELEASE, processDefinition.getName()); return result; } // check sub process definition release state List<Long> subProcessDefineCodes = new ArrayList<>(); processService.recurseFindSubProcess(processDefinition.getCode(), subProcessDefineCodes); if (!subProcessDefineCodes.isEmpty()) { List<ProcessDefinition> subProcessDefinitionList = processDefinitionMapper.queryByCodes(subProcessDefineCodes); if (subProcessDefinitionList != null && !subProcessDefinitionList.isEmpty()) { for (ProcessDefinition subProcessDefinition : subProcessDefinitionList) { /** * if there is no online process, exit directly */ if (subProcessDefinition.getReleaseState() != ReleaseState.ONLINE) { logger.info("not release process definition id: {} , name : {}", subProcessDefinition.getId(), subProcessDefinition.getName()); putMsg(result, Status.PROCESS_DEFINE_NOT_RELEASE, String.valueOf(subProcessDefinition.getId())); return result; } } } } }
// check master server exists List<Server> masterServers = monitorService.getServerListFromRegistry(true);
if (masterServers.isEmpty()) { putMsg(result, Status.MASTER_NOT_EXISTS); return result; }
// set status scheduleObj.setReleaseState(scheduleStatus);
scheduleMapper.updateById(scheduleObj);
try { switch (scheduleStatus) { case ONLINE: logger.info("Call master client set schedule online, project id: {}, flow id: {},host: {}", project.getId(), processDefinition.getId(), masterServers); setSchedule(project.getId(), scheduleObj); break; case OFFLINE: logger.info("Call master client set schedule offline, project id: {}, flow id: {},host: {}", project.getId(), processDefinition.getId(), masterServers); deleteSchedule(project.getId(), id); break; default: putMsg(result, Status.SCHEDULE_STATUS_UNKNOWN, scheduleStatus.toString()); return result; } } catch (Exception e) { result.put(Constants.MSG, scheduleStatus == ReleaseState.ONLINE ? "set online failure" : "set offline failure"); throw new ServiceException(result.get(Constants.MSG).toString(), e); }
putMsg(result, Status.SUCCESS); return result; }
public void setSchedule(int projectId, Schedule schedule) {
logger.info("set schedule, project id: {}, scheduleId: {}", projectId, schedule.getId());
quartzExecutor.addJob(ProcessScheduleJob.class, projectId, schedule);
}


public void addJob(Class<? extends Job> clazz, int projectId, final Schedule schedule) {
String jobName = this.buildJobName(schedule.getId());
String jobGroupName = this.buildJobGroupName(projectId);
Map<String, Object> jobDataMap = this.buildDataMap(projectId, schedule);
String cronExpression = schedule.getCrontab();
String timezoneId = schedule.getTimezoneId();
/**
* transform from server default timezone to schedule timezone
* e.g. server default timezone is `UTC`
* user set a schedule with startTime `2022-04-28 10:00:00`, timezone is `Asia/Shanghai`,
* api skip to transform it and save into databases directly, startTime `2022-04-28 10:00:00`, timezone is `UTC`, which actually added 8 hours,
* so when add job to quartz, it should recover by transform timezone
*/
Date startDate = DateUtils.transformTimezoneDate(schedule.getStartTime(), timezoneId);
Date endDate = DateUtils.transformTimezoneDate(schedule.getEndTime(), timezoneId);
lock.writeLock().lock();
try {
JobKey jobKey = new JobKey(jobName, jobGroupName);
JobDetail jobDetail;
//add a task (if this task already exists, return this task directly)
if (scheduler.checkExists(jobKey)) {
jobDetail = scheduler.getJobDetail(jobKey);
jobDetail.getJobDataMap().putAll(jobDataMap);
} else {
jobDetail = newJob(clazz).withIdentity(jobKey).build();
jobDetail.getJobDataMap().putAll(jobDataMap);
scheduler.addJob(jobDetail, false, true);
logger.info("Add job, job name: {}, group name: {}",
jobName, jobGroupName);
}
TriggerKey triggerKey = new TriggerKey(jobName, jobGroupName);
/*
* Instructs the Scheduler that upon a mis-fire
* situation, the CronTrigger wants to have it's
* next-fire-time updated to the next time in the schedule after the
* current time (taking into account any associated Calendar),
* but it does not want to be fired now.
*/
CronTrigger cronTrigger = newTrigger()
.withIdentity(triggerKey)
.startAt(startDate)
.endAt(endDate)
.withSchedule(
cronSchedule(cronExpression)
.withMisfireHandlingInstructionDoNothing()
.inTimeZone(DateUtils.getTimezone(timezoneId))
)
.forJob(jobDetail).build();
if (scheduler.checkExists(triggerKey)) {
// updateProcessInstance scheduler trigger when scheduler cycle changes
CronTrigger oldCronTrigger = (CronTrigger) scheduler.getTrigger(triggerKey);
String oldCronExpression = oldCronTrigger.getCronExpression();
if (!StringUtils.equalsIgnoreCase(cronExpression, oldCronExpression)) {
// reschedule job trigger
scheduler.rescheduleJob(triggerKey, cronTrigger);
logger.info("reschedule job trigger, triggerName: {}, triggerGroupName: {}, cronExpression: {}, startDate: {}, endDate: {}",
jobName, jobGroupName, cronExpression, startDate, endDate);
}
} else {
scheduler.scheduleJob(cronTrigger);
logger.info("schedule job trigger, triggerName: {}, triggerGroupName: {}, cronExpression: {}, startDate: {}, endDate: {}",
jobName, jobGroupName, cronExpression, startDate, endDate);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new ServiceException("add job failed", e);
} finally {
lock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}


2.3 Quaterz架构与运行流程
2.3.1 概念与架构
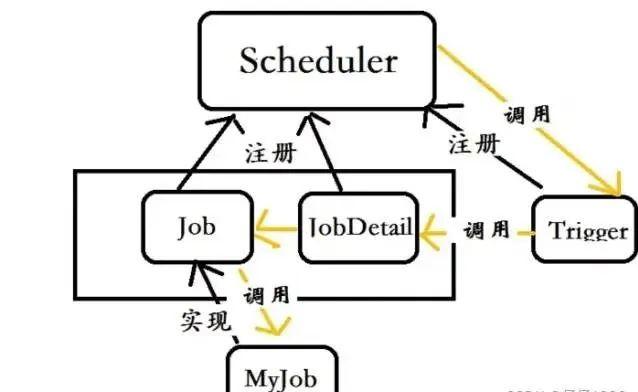
Quartz 框架主要包括如下几个部分:
SchedulerFactory:任务调度工厂,主要负责管理任务调度器;
Scheduler :任务调度器,主要负责任务调度,以及操作任务的相关接口;
Job :任务接口,实现类包含具体任务业务代码;
JobDetail:用于定义作业的实例;
Trigger:任务触发器,主要存放 Job 执行的时间策略。例如多久执行一次,什么时候执行,以什么频率执行等等;
JobBuilder :用于定义/构建 JobDetail 实例,用于定义作业的实例。
TriggerBuilder :用于定义/构建触发器实例;
Calendar:Trigger 扩展对象,可以排除或者包含某个指定的时间点(如排除法定节假日);
JobStore:存储作业和任务调度期间的状态Scheduler的生命期,从 SchedulerFactory 创建它时开始,到 Scheduler 调用Shutdown() 方法时结束;
Scheduler 被创建后,可以增加、删除和列举 Job 和 Trigger,以及执行其它与调度相关的操作(如暂停 Trigger)。但Scheduler 只有在调用 start() 方法后,才会真正地触发 trigger(即执行 job)
2.3.2 初始化与执行流程
Quartz的基本原理就是通过Scheduler来调度被JobDetail和Trigger定义的安装Job接口规范实现的自定义任务业务对象,来完成任务的调度。基本逻辑如下图:
代码时序图如下:
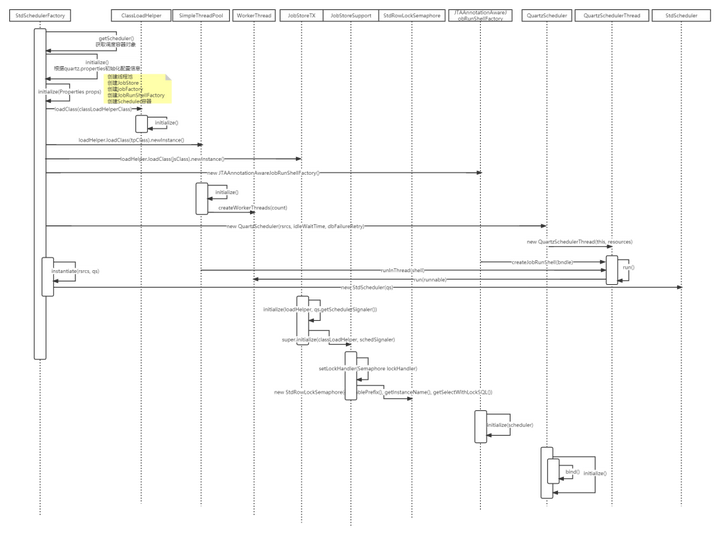
基本内容就是初始化任务调度容器Scheduler,以及容器所需的线程池,数据交互对象JobStore,任务处理线程QuartzSchedulerThread用来处理Job接口的具体业务实现类。
DolphinScheduler的业务类是ProcessScheduleJob,主要功能就是根据调度信息往commond表中写数据。
2.3.3 集群运转
需要注意的事:
当Quartz采用集群形式部署的时候,存储介质不能使用内存的形式,也就是不能使用JobStoreRAM。
Quartz集群对于对于需要被调度的Triggers实例的扫描是使用数据库锁TRIGGER_ACCESS来完成的,保障此扫描过程只能被一个Quartz实例获取到。代码如下:
public List<OperableTrigger> acquireNextTriggers(final long noLaterThan, final int maxCount, final long timeWindow) throws JobPersistenceException { String lockName; if(isAcquireTriggersWithinLock() || maxCount > 1) { lockName = LOCK_TRIGGER_ACCESS; } else { lockName = null; } return executeInNonManagedTXLock(lockName, new TransactionCallback<List<OperableTrigger>>() { public List<OperableTrigger> execute(Connection conn) throws JobPersistenceException { return acquireNextTrigger(conn, noLaterThan, maxCount, timeWindow); } }, new TransactionValidator<List<OperableTrigger>>() { public Boolean validate(Connection conn, List<OperableTrigger> result) throws JobPersistenceException { try { List<FiredTriggerRecord> acquired = getDelegate().selectInstancesFiredTriggerRecords(conn, getInstanceId()); Set<String> fireInstanceIds = new HashSet<String>(); for (FiredTriggerRecord ft : acquired) { fireInstanceIds.add(ft.getFireInstanceId()); } for (OperableTrigger tr : result) { if (fireInstanceIds.contains(tr.getFireInstanceId())) { return true; } } return false; } catch (SQLException e) { throw new JobPersistenceException("error validating trigger acquisition", e); } } }); }
3.集群失败实例恢复需要注意的是各个实例恢复各自实例对应的异常实例,因为数据库有调度容器的instanceId信息。代码如下:
protected void clusterRecover(Connection conn, List<SchedulerStateRecord> failedInstances)
throws JobPersistenceException {
if (failedInstances.size() > 0) {
long recoverIds = System.currentTimeMillis();
logWarnIfNonZero(failedInstances.size(),
"ClusterManager: detected " + failedInstances.size()
+ " failed or restarted instances.");
try {
for (SchedulerStateRecord rec : failedInstances) {
getLog().info(
"ClusterManager: Scanning for instance \""
+ rec.getSchedulerInstanceId()
+ "\"'s failed in-progress jobs.");
List<FiredTriggerRecord> firedTriggerRecs = getDelegate()
.selectInstancesFiredTriggerRecords(conn,
rec.getSchedulerInstanceId());
int acquiredCount = 0;
int recoveredCount = 0;
int otherCount = 0;
Set<TriggerKey> triggerKeys = new HashSet<TriggerKey>();
for (FiredTriggerRecord ftRec : firedTriggerRecs) {
TriggerKey tKey = ftRec.getTriggerKey();
JobKey jKey = ftRec.getJobKey();
triggerKeys.add(tKey);
// release blocked triggers..
if (ftRec.getFireInstanceState().equals(STATE_BLOCKED)) {
getDelegate()
.updateTriggerStatesForJobFromOtherState(
conn, jKey,
STATE_WAITING, STATE_BLOCKED);
} else if (ftRec.getFireInstanceState().equals(STATE_PAUSED_BLOCKED)) {
getDelegate()
.updateTriggerStatesForJobFromOtherState(
conn, jKey,
STATE_PAUSED, STATE_PAUSED_BLOCKED);
}
// release acquired triggers..
if (ftRec.getFireInstanceState().equals(STATE_ACQUIRED)) {
getDelegate().updateTriggerStateFromOtherState(
conn, tKey, STATE_WAITING,
STATE_ACQUIRED);
acquiredCount++;
} else if (ftRec.isJobRequestsRecovery()) {
// handle jobs marked for recovery that were not fully
// executed..
if (jobExists(conn, jKey)) {
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
SimpleTriggerImpl rcvryTrig = new SimpleTriggerImpl(
"recover_"
+ rec.getSchedulerInstanceId()
+ "_"
+ String.valueOf(recoverIds++),
Scheduler.DEFAULT_RECOVERY_GROUP,
new Date(ftRec.getScheduleTimestamp()));
rcvryTrig.setJobName(jKey.getName());
rcvryTrig.setJobGroup(jKey.getGroup());
rcvryTrig.setMisfireInstruction(SimpleTrigger.MISFIRE_INSTRUCTION_IGNORE_MISFIRE_POLICY);
rcvryTrig.setPriority(ftRec.getPriority());
JobDataMap jd = getDelegate().selectTriggerJobDataMap(conn, tKey.getName(), tKey.getGroup());
jd.put(Scheduler.FAILED_JOB_ORIGINAL_TRIGGER_NAME, tKey.getName());
jd.put(Scheduler.FAILED_JOB_ORIGINAL_TRIGGER_GROUP, tKey.getGroup());
jd.put(Scheduler.FAILED_JOB_ORIGINAL_TRIGGER_FIRETIME_IN_MILLISECONDS, String.valueOf(ftRec.getFireTimestamp()));
jd.put(Scheduler.FAILED_JOB_ORIGINAL_TRIGGER_SCHEDULED_FIRETIME_IN_MILLISECONDS, String.valueOf(ftRec.getScheduleTimestamp()));
rcvryTrig.setJobDataMap(jd);
rcvryTrig.computeFirstFireTime(null);
storeTrigger(conn, rcvryTrig, null, false,
STATE_WAITING, false, true);
recoveredCount++;
} else {
getLog()
.warn(
"ClusterManager: failed job '"
+ jKey
+ "' no longer exists, cannot schedule recovery.");
otherCount++;
}
} else {
otherCount++;
}
// free up stateful job's triggers
if (ftRec.isJobDisallowsConcurrentExecution()) {
getDelegate()
.updateTriggerStatesForJobFromOtherState(
conn, jKey,
STATE_WAITING, STATE_BLOCKED);
getDelegate()
.updateTriggerStatesForJobFromOtherState(
conn, jKey,
STATE_PAUSED, STATE_PAUSED_BLOCKED);
}
}
getDelegate().deleteFiredTriggers(conn,
rec.getSchedulerInstanceId());
// Check if any of the fired triggers we just deleted were the last fired trigger
// records of a COMPLETE trigger.
int completeCount = 0;
for (TriggerKey triggerKey : triggerKeys) {
if (getDelegate().selectTriggerState(conn, triggerKey).
equals(STATE_COMPLETE)) {
List<FiredTriggerRecord> firedTriggers =
getDelegate().selectFiredTriggerRecords(conn, triggerKey.getName(), triggerKey.getGroup());
if (firedTriggers.isEmpty()) {
if (removeTrigger(conn, triggerKey)) {
completeCount++;
}
}
}
}
logWarnIfNonZero(acquiredCount,
"ClusterManager: ......Freed " + acquiredCount
+ " acquired trigger(s).");
logWarnIfNonZero(completeCount,
"ClusterManager: ......Deleted " + completeCount
+ " complete triggers(s).");
logWarnIfNonZero(recoveredCount,
"ClusterManager: ......Scheduled " + recoveredCount
+ " recoverable job(s) for recovery.");
logWarnIfNonZero(otherCount,
"ClusterManager: ......Cleaned-up " + otherCount
+ " other failed job(s).");
if (!rec.getSchedulerInstanceId().equals(getInstanceId())) {
getDelegate().deleteSchedulerState(conn,
rec.getSchedulerInstanceId());
}
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new JobPersistenceException("Failure recovering jobs: "
+ e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
}


2.4 Master启动与执行流程
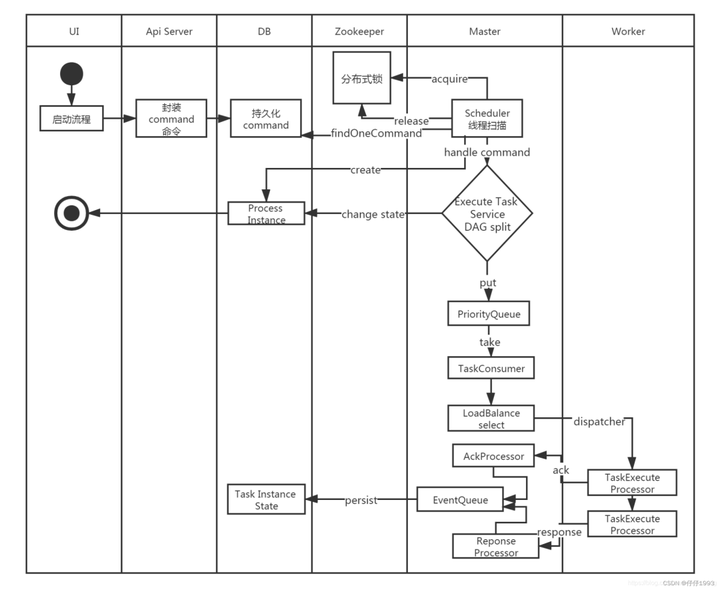
2.4.1 概念与执行逻辑
关键概念:
Quartz相关:
Scheduler(任务调度容器,一般都是StdScheduler实例)。
ProcessScheduleJob:(实现Quarts调度框架的Job接口的业务类,专门生成DolphinScheduler数据库业务表t_ds_commond数据);
DolphinScheduler相关:
NettyRemotingServer(netty服务端,包含netty服务端serverBootstrap对象与netty服务端业务处理对象serverHandler), NettyServerHandler:(netty服务端业务处理类:包含各类处理器以及处理器对应的执行线程池);
TaskPluginManager(任务插件管理器,不同类型的任务以插件的形式管理,在应用服务启动的时候,通过@AutoService加载实现了TaskChannelFactory接口的工厂信息到数据库,通过工厂对象来加载各类TaskChannel实现类到缓存);
MasterRegistryClient(master操作zk的客户端,封装了master对于zk的所有操作,注册,查询,删除等);
MasterSchedulerService(扫描服务,包含业务执行线程和work包含的nettyhe护短,负责任务调度业务,slot来控制集群模式下任务不被重复调度,底层实现是zookeeper分布式锁);
WorkflowExecuteThread(真正的业务处理线程,通过插槽获取命令commond,执行之前会校验slot的变化,如果变化不执行,关键功能就是构建任务相关的参数,定义,优先级等,然后发送到队列,供队列处理线程消费);
CommonTaskProcessor(普通任务处理器,实现ITaskProcessor接口,根据业务分为普通,依赖,子任务,阻塞,条件任务类型,包含了任务的提交,运行,分发,杀死等业务,通过@AutoService加载的类,根本就是封装了对);
TaskPriorityQueueImpl(任务队列,负责任务队列的存储控制);
TaskPriorityQueueConsumer(任务队列消费线程,负责任务的根据负载均衡策略在worker之间分发与执行);
ServerNodeManager (节点信息控制器,负责节点注册信息更新与槽位(slot)变更,底层实现是zookeeper分布式锁的应用);
EventExecuteService(事件处理线程,通过缓存起来的任务处理线程,处理每个任务在处理过程中注册在线程事件队列中的事件);
FailoverExecuteThread(故障转移线程,包含Master和worker的);
MasterRegistryDataListener(托管在zk管理框架cautor的故障监听器,负责对worker和master注册在zk上的节点的新增和删除)。
主节点容错代码如下,业务解释见1.5.1Master容错解释:
private void failoverMasterWithLock(String masterHost) {
String failoverPath = getFailoverLockPath(NodeType.MASTER, masterHost);
try {
registryClient.getLock(failoverPath);
this.failoverMaster(masterHost);
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error("{} server failover failed, host:{}", NodeType.MASTER, masterHost, e);
} finally {
registryClient.releaseLock(failoverPath);
}
}
/**
* failover master
* <p>
* failover process instance and associated task instance
*故障转移流程实例和关联的任务实例
* @param masterHost master host
*/
private void failoverMaster(String masterHost) {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(masterHost)) {
return;
}
Date serverStartupTime = getServerStartupTime(NodeType.MASTER, masterHost);
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
List<ProcessInstance> needFailoverProcessInstanceList = processService.queryNeedFailoverProcessInstances(masterHost);
LOGGER.info("start master[{}] failover, process list size:{}", masterHost, needFailoverProcessInstanceList.size());
List<Server> workerServers = registryClient.getServerList(NodeType.WORKER);
for (ProcessInstance processInstance : needFailoverProcessInstanceList) {
if (Constants.NULL.equals(processInstance.getHost())) {
continue;
}
List<TaskInstance> validTaskInstanceList = processService.findValidTaskListByProcessId(processInstance.getId());
for (TaskInstance taskInstance : validTaskInstanceList) {
LOGGER.info("failover task instance id: {}, process instance id: {}", taskInstance.getId(), taskInstance.getProcessInstanceId());
failoverTaskInstance(processInstance, taskInstance, workerServers);
}
if (serverStartupTime != null && processInstance.getRestartTime() != null
&& processInstance.getRestartTime().after(serverStartupTime)) {
continue;
}
LOGGER.info("failover process instance id: {}", processInstance.getId());
//updateProcessInstance host is null and insert into command
processInstance.setHost(Constants.NULL);
processService.processNeedFailoverProcessInstances(processInstance);
}
LOGGER.info("master[{}] failover end, useTime:{}ms", masterHost, System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime);
}


2.4.2 集群与槽(slot)
其实这里的采用Zookeer分布式锁准确也不准确,为什么这么说,因为Slot是CommondId对Master列表长度取模来计算的,而Master列表长度的刷新是Zookeeper分布式锁来控制,Master节点的调度数据扫描是通过Slot来控制的。
具体代码如下:
Slot刷新
private void updateMasterNodes() {
MASTER_SLOT = 0;
MASTER_SIZE = 0;
this.masterNodes.clear();
String nodeLock = Constants.REGISTRY_DOLPHINSCHEDULER_LOCK_MASTERS;
try {
registryClient.getLock(nodeLock);
Collection<String> currentNodes = registryClient.getMasterNodesDirectly();
List<Server> masterNodes = registryClient.getServerList(NodeType.MASTER);
syncMasterNodes(currentNodes, masterNodes);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("update master nodes error", e);
} finally {
registryClient.releaseLock(nodeLock);
}
}
/**
* sync master nodes
*
* @param nodes master nodes
*/
private void syncMasterNodes(Collection<String> nodes, List<Server> masterNodes) {
masterLock.lock();
try {
String addr = NetUtils.getAddr(NetUtils.getHost(), masterConfig.getListenPort());
this.masterNodes.addAll(nodes);
this.masterPriorityQueue.clear();
this.masterPriorityQueue.putList(masterNodes);
int index = masterPriorityQueue.getIndex(addr);
if (index >= 0) {
MASTER_SIZE = nodes.size();
MASTER_SLOT = index;
} else {
logger.warn("current addr:{} is not in active master list", addr);
}
logger.info("update master nodes, master size: {}, slot: {}, addr: {}", MASTER_SIZE, MASTER_SLOT, addr);
} finally {
masterLock.unlock();
}
}


Slot应用
/**
* 1. get command by slot
* 2. donot handle command if slot is empty
*/
/** * 1. 通过插槽获取命令 * 2. 如果插槽为空,则不处理命令 */
private void scheduleProcess() throws Exception {
List<Command> commands = findCommands();
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(commands)) {
//indicate that no command ,sleep for 1s
Thread.sleep(Constants.SLEEP_TIME_MILLIS);
return;
}
List<ProcessInstance> processInstances = command2ProcessInstance(commands);
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(processInstances)) {
return;
}
for (ProcessInstance processInstance : processInstances) {
if (processInstance == null) {
continue;
}
WorkflowExecuteThread workflowExecuteThread = new WorkflowExecuteThread(
processInstance
, processService
, nettyExecutorManager
, processAlertManager
, masterConfig
, stateWheelExecuteThread);
this.processInstanceExecCacheManager.cache(processInstance.getId(), workflowExecuteThread);
if (processInstance.getTimeout() > 0) {
stateWheelExecuteThread.addProcess4TimeoutCheck(processInstance);
}
workflowExecuteThreadPool.startWorkflow(workflowExecuteThread);
}
}
private List<Command> findCommands() {
int pageNumber = 0;
int pageSize = masterConfig.getFetchCommandNum();
List<Command> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (Stopper.isRunning()) {
int thisMasterSlot = ServerNodeManager.getSlot();
int masterCount = ServerNodeManager.getMasterSize();
if (masterCount > 0) {
result = processService.findCommandPageBySlot(pageSize, pageNumber, masterCount, thisMasterSlot);
}
}
return result;
}
@Override
public List<Command> findCommandPageBySlot(int pageSize, int pageNumber, int masterCount, int thisMasterSlot) {
if (masterCount <= 0) {
return Lists.newArrayList();
}
return commandMapper.queryCommandPageBySlot(pageSize, pageNumber * pageSize, masterCount, thisMasterSlot);
}
<select id="queryCommandPageBySlot" resultType="org.apache.dolphinscheduler.dao.entity.Command">
select *
from t_ds_command
where id % #{masterCount} = #{thisMasterSlot}
order by process_instance_priority, id asc
limit #{limit} offset #{offset}
</select>
##槽位检查
private List<ProcessInstance> command2ProcessInstance(List<Command> commands) {
List<ProcessInstance> processInstances = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>(commands.size()));
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(commands.size());
for (final Command command : commands) {
masterPrepareExecService.execute(() -> {
try {
// slot check again
SlotCheckState slotCheckState = slotCheck(command);
if (slotCheckState.equals(SlotCheckState.CHANGE) || slotCheckState.equals(SlotCheckState.INJECT)) {
logger.info("handle command {} skip, slot check state: {}", command.getId(), slotCheckState);
return;
}
ProcessInstance processInstance = processService.handleCommand(logger,
getLocalAddress(),
command);
if (processInstance != null) {
processInstances.add(processInstance);
logger.info("handle command {} end, create process instance {}", command.getId(), processInstance.getId());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("handle command error ", e);
processService.moveToErrorCommand(command, e.toString());
} finally {
latch.countDown();
}
});
}
try {
// make sure to finish handling command each time before next scan
latch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
logger.error("countDownLatch await error ", e);
}
return processInstances;
}
private SlotCheckState slotCheck(Command command) {
int slot = ServerNodeManager.getSlot();
int masterSize = ServerNodeManager.getMasterSize();
SlotCheckState state;
if (masterSize <= 0) {
state = SlotCheckState.CHANGE;
} else if (command.getId() % masterSize == slot) {
state = SlotCheckState.PASS;
} else {
state = SlotCheckState.INJECT;
}
return state;
}


2.4.3 代码执行流程

代码过于繁琐,此处不再一一粘贴代码解释各个类的功能,自行看代码更加清晰。
2.5Worker启动与执行流程
2.5.1 概念与执行逻辑
NettyRemotingServer(worker包含的netty服务端) WorkerRegistryClient(zk客户端,封装了worker与zk相关的操作,注册,查询,删除等) ;
TaskPluginManager(任务插件管理器,封装了插件加载逻辑和任务实际执行业务的抽象) ;
WorkerManagerThread(任务工作线程生成器,消费netty处理器推进队列的任务信息,并生成任务执行线程提交线程池管理) ;
TaskExecuteProcessor(Netty任务执行处理器,生成master分发到work的任务信息,并推送到队列) ;
TaskExecuteThread(任务执行线程) ;
TaskCallbackService(任务回调线程,与master包含的netty client通信);
AbstractTask(任务实际业务的抽象类,子类包含实际的任务执行业务,SqlTask,DataXTask等) ;
RetryReportTaskStatusThread(不关注)
2.5.2 代码执行流程
Worker节点代码时序图如下:
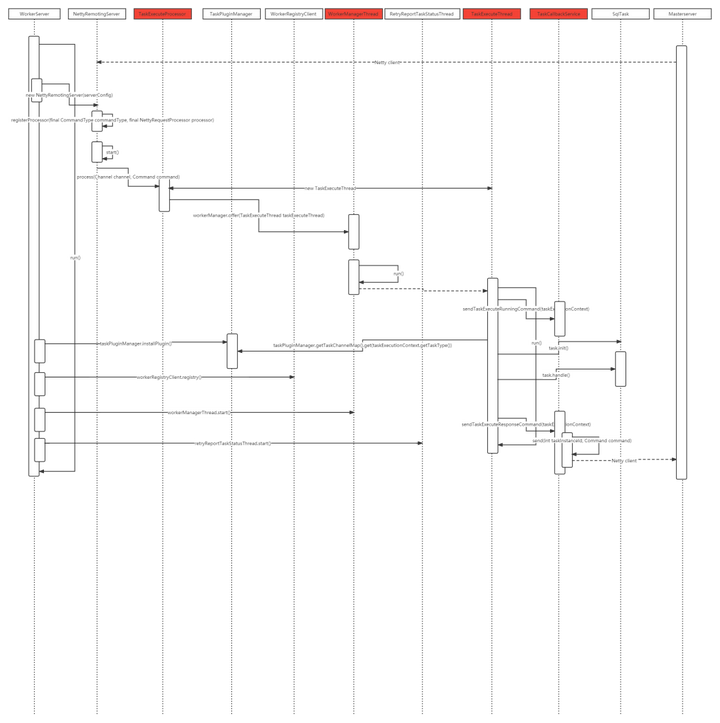
代码过于繁琐,此处不再一一粘贴代码解释各个类的功能,自行看代码更加清晰。
2.6 RPC交互
因为节点和应用服务之间的RPC通信都是基于Netty实现的,Netty相关知识不在这里过多的讲解,当前章节只涉及Master与Worker之间的交互模式的设计与实现。
整体设计如下
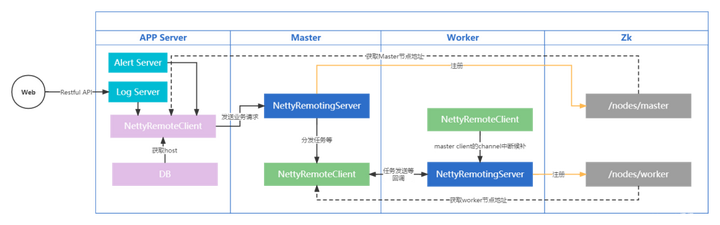
2.6.1 Master与Worker交互
Master与worker之间的业务逻辑的交互是基于Netty服务端与客户端来实现Rpc通信的,Master和Worker启动的时候会将自己的Netty服务端信息注册到ZK相应的节点上,Master的任务分发线程和任务杀死等业务运行时,拉取ZK上的Worker节点信息,根据负载均衡策略选择一个节点(下章介绍负载均衡),构建Netty客户端与Worker的Netty服务端通信,Worker收到Master的RPC请求之后会缓存Channel信息并处理对应业务,同时Callback回调线程会获取缓存的通道来执行回调操作,这样就形成的闭环。
任务的执行杀死,以及回调状态处理等操作都是通过Netty客户端与服务端绑定的Processer处理器来进行的。
Master部分具体代码如下:
Master启动的时候会初始化Nettyserver,注册对应的请求处理器到NettyHandler并启动:
@PostConstruct
public void run() throws SchedulerException {
// init remoting server
NettyServerConfig serverConfig = new NettyServerConfig();
serverConfig.setListenPort(masterConfig.getListenPort());
this.nettyRemotingServer = new NettyRemotingServer(serverConfig);
this.nettyRemotingServer.registerProcessor(CommandType.TASK_EXECUTE_RESPONSE, taskExecuteResponseProcessor);
this.nettyRemotingServer.registerProcessor(CommandType.TASK_EXECUTE_RUNNING, taskExecuteRunningProcessor);
this.nettyRemotingServer.registerProcessor(CommandType.TASK_KILL_RESPONSE, taskKillResponseProcessor);
this.nettyRemotingServer.registerProcessor(CommandType.STATE_EVENT_REQUEST, stateEventProcessor);
this.nettyRemotingServer.registerProcessor(CommandType.TASK_FORCE_STATE_EVENT_REQUEST, taskEventProcessor);
this.nettyRemotingServer.registerProcessor(CommandType.TASK_WAKEUP_EVENT_REQUEST, taskEventProcessor);
this.nettyRemotingServer.registerProcessor(CommandType.CACHE_EXPIRE, cacheProcessor);
// logger server
this.nettyRemotingServer.registerProcessor(CommandType.GET_LOG_BYTES_REQUEST, loggerRequestProcessor);
this.nettyRemotingServer.registerProcessor(CommandType.ROLL_VIEW_LOG_REQUEST, loggerRequestProcessor);
this.nettyRemotingServer.registerProcessor(CommandType.VIEW_WHOLE_LOG_REQUEST, loggerRequestProcessor);
this.nettyRemotingServer.registerProcessor(CommandType.REMOVE_TAK_LOG_REQUEST, loggerRequestProcessor);
this.nettyRemotingServer.start();
// install task plugin
this.taskPluginManager.installPlugin();
// self tolerant
this.masterRegistryClient.init();
this.masterRegistryClient.start();
this.masterRegistryClient.setRegistryStoppable(this);
this.masterSchedulerService.init();
this.masterSchedulerService.start();
this.eventExecuteService.start();
this.failoverExecuteThread.start();
this.scheduler.start();
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(() -> {
if (Stopper.isRunning()) {
close("shutdownHook");
}
}));
}
/**
* server start
*/
public void start() {
if (isStarted.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
this.serverBootstrap
.group(this.bossGroup, this.workGroup)
.channel(NettyUtils.getServerSocketChannelClass())
.option(ChannelOption.SO_REUSEADDR, true)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, serverConfig.getSoBacklog())
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, serverConfig.isSoKeepalive())
.childOption(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, serverConfig.isTcpNoDelay())
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_SNDBUF, serverConfig.getSendBufferSize())
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_RCVBUF, serverConfig.getReceiveBufferSize())
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
initNettyChannel(ch);
}
});
ChannelFuture future;
try {
future = serverBootstrap.bind(serverConfig.getListenPort()).sync();
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("NettyRemotingServer bind fail {}, exit", e.getMessage(), e);
throw new RemoteException(String.format(NETTY_BIND_FAILURE_MSG, serverConfig.getListenPort()));
}
if (future.isSuccess()) {
logger.info("NettyRemotingServer bind success at port : {}", serverConfig.getListenPort());
} else if (future.cause() != null) {
throw new RemoteException(String.format(NETTY_BIND_FAILURE_MSG, serverConfig.getListenPort()), future.cause());
} else {
throw new RemoteException(String.format(NETTY_BIND_FAILURE_MSG, serverConfig.getListenPort()));
}
}
}


Master的NettyExecutorManager初始化的时候会将NettyRemotingClient也初始化,并且会注册处理Worker回调请求的处理器,真正的端口绑定是在获取到执行器端口之后:
/**
* constructor
*/
public NettyExecutorManager() {
final NettyClientConfig clientConfig = new NettyClientConfig();
this.nettyRemotingClient = new NettyRemotingClient(clientConfig);
}
##注册处理worker回调的处理器
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
this.nettyRemotingClient.registerProcessor(CommandType.TASK_EXECUTE_RESPONSE, taskExecuteResponseProcessor);
this.nettyRemotingClient.registerProcessor(CommandType.TASK_EXECUTE_RUNNING, taskExecuteRunningProcessor);
this.nettyRemotingClient.registerProcessor(CommandType.TASK_KILL_RESPONSE, taskKillResponseProcessor);
}
public NettyRemotingClient(final NettyClientConfig clientConfig) {
this.clientConfig = clientConfig;
if (NettyUtils.useEpoll()) {
this.workerGroup = new EpollEventLoopGroup(clientConfig.getWorkerThreads(), new ThreadFactory() {
private final AtomicInteger threadIndex = new AtomicInteger(0);
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
return new Thread(r, String.format("NettyClient_%d", this.threadIndex.incrementAndGet()));
}
});
} else {
this.workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(clientConfig.getWorkerThreads(), new ThreadFactory() {
private final AtomicInteger threadIndex = new AtomicInteger(0);
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
return new Thread(r, String.format("NettyClient_%d", this.threadIndex.incrementAndGet()));
}
});
}
this.callbackExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(5, 10, 1, TimeUnit.MINUTES,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(1000), new NamedThreadFactory("CallbackExecutor", 10),
new CallerThreadExecutePolicy());
this.clientHandler = new NettyClientHandler(this, callbackExecutor);
this.responseFutureExecutor = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor(new NamedThreadFactory("ResponseFutureExecutor"));
this.start();
}
/**
* start
*/
private void start() {
this.bootstrap
.group(this.workerGroup)
.channel(NettyUtils.getSocketChannelClass())
.option(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, clientConfig.isSoKeepalive())
.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, clientConfig.isTcpNoDelay())
.option(ChannelOption.SO_SNDBUF, clientConfig.getSendBufferSize())
.option(ChannelOption.SO_RCVBUF, clientConfig.getReceiveBufferSize())
.option(ChannelOption.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, clientConfig.getConnectTimeoutMillis())
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
ch.pipeline()
.addLast("client-idle-handler", new IdleStateHandler(Constants.NETTY_CLIENT_HEART_BEAT_TIME, 0, 0, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS))
.addLast(new NettyDecoder(), clientHandler, encoder);
}
});
this.responseFutureExecutor.scheduleAtFixedRate(ResponseFuture::scanFutureTable, 5000, 1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
isStarted.compareAndSet(false, true);
}


任务分发代码如下:
/**
* task dispatch
*
* @param context context
* @return result
* @throws ExecuteException if error throws ExecuteException
*/
public Boolean dispatch(final ExecutionContext context) throws ExecuteException {
/**
* get executor manager
*/
ExecutorManager<Boolean> executorManager = this.executorManagers.get(context.getExecutorType());
if (executorManager == null) {
throw new ExecuteException("no ExecutorManager for type : " + context.getExecutorType());
}
/**
* host select
*/
Host host = hostManager.select(context);
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(host.getAddress())) {
throw new ExecuteException(String.format("fail to execute : %s due to no suitable worker, "
+ "current task needs worker group %s to execute",
context.getCommand(),context.getWorkerGroup()));
}
context.setHost(host);
executorManager.beforeExecute(context);
try {
/**
* task execute
*/
return executorManager.execute(context);
} finally {
executorManager.afterExecute(context);
}
}
/**
* execute logic
*
* @param context context
* @return result
* @throws ExecuteException if error throws ExecuteException
*/
@Override
public Boolean execute(ExecutionContext context) throws ExecuteException {
/**
* all nodes
*/
Set<String> allNodes = getAllNodes(context);
/**
* fail nodes
*/
Set<String> failNodeSet = new HashSet<>();
/**
* build command accord executeContext
*/
Command command = context.getCommand();
/**
* execute task host
*/
Host host = context.getHost();
boolean success = false;
while (!success) {
try {
doExecute(host, command);
success = true;
context.setHost(host);
} catch (ExecuteException ex) {
logger.error(String.format("execute command : %s error", command), ex);
try {
failNodeSet.add(host.getAddress());
Set<String> tmpAllIps = new HashSet<>(allNodes);
Collection<String> remained = CollectionUtils.subtract(tmpAllIps, failNodeSet);
if (remained != null && remained.size() > 0) {
host = Host.of(remained.iterator().next());
logger.error("retry execute command : {} host : {}", command, host);
} else {
throw new ExecuteException("fail after try all nodes");
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new ExecuteException("fail after try all nodes");
}
}
}
return success;
}
/**
* execute logic
*
* @param host host
* @param command command
* @throws ExecuteException if error throws ExecuteException
*/
public void doExecute(final Host host, final Command command) throws ExecuteException {
/**
* retry count,default retry 3
*/
int retryCount = 3;
boolean success = false;
do {
try {
nettyRemotingClient.send(host, command);
success = true;
} catch (Exception ex) {
logger.error(String.format("send command : %s to %s error", command, host), ex);
retryCount--;
ThreadUtils.sleep(100);
}
} while (retryCount >= 0 && !success);
if (!success) {
throw new ExecuteException(String.format("send command : %s to %s error", command, host));
}
}
/**
* send task
*
* @param host host
* @param command command
*/
public void send(final Host host, final Command command) throws RemotingException {
Channel channel = getChannel(host);
if (channel == null) {
throw new RemotingException(String.format("connect to : %s fail", host));
}
try {
ChannelFuture future = channel.writeAndFlush(command).await();
if (future.isSuccess()) {
logger.debug("send command : {} , to : {} successfully.", command, host.getAddress());
} else {
String msg = String.format("send command : %s , to :%s failed", command, host.getAddress());
logger.error(msg, future.cause());
throw new RemotingException(msg);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("Send command {} to address {} encounter error.", command, host.getAddress());
throw new RemotingException(String.format("Send command : %s , to :%s encounter error", command, host.getAddress()), e);
}
}


Worker部分具体代码如下:
同理Woker在启动的时候会初始化NettyServer,注册对应处理器并启动:
/**
* worker server run
*/
@PostConstruct
public void run() {
// init remoting server
NettyServerConfig serverConfig = new NettyServerConfig();
serverConfig.setListenPort(workerConfig.getListenPort());
this.nettyRemotingServer = new NettyRemotingServer(serverConfig);
this.nettyRemotingServer.registerProcessor(CommandType.TASK_EXECUTE_REQUEST, taskExecuteProcessor);
this.nettyRemotingServer.registerProcessor(CommandType.TASK_KILL_REQUEST, taskKillProcessor);
this.nettyRemotingServer.registerProcessor(CommandType.TASK_EXECUTE_RUNNING_ACK, taskExecuteRunningAckProcessor);
this.nettyRemotingServer.registerProcessor(CommandType.TASK_EXECUTE_RESPONSE_ACK, taskExecuteResponseAckProcessor);
this.nettyRemotingServer.registerProcessor(CommandType.PROCESS_HOST_UPDATE_REQUEST, hostUpdateProcessor);
// logger server
this.nettyRemotingServer.registerProcessor(CommandType.GET_LOG_BYTES_REQUEST, loggerRequestProcessor);
this.nettyRemotingServer.registerProcessor(CommandType.ROLL_VIEW_LOG_REQUEST, loggerRequestProcessor);
this.nettyRemotingServer.registerProcessor(CommandType.VIEW_WHOLE_LOG_REQUEST, loggerRequestProcessor);
this.nettyRemotingServer.registerProcessor(CommandType.REMOVE_TAK_LOG_REQUEST, loggerRequestProcessor);
this.nettyRemotingServer.start();
// install task plugin
this.taskPluginManager.installPlugin();
// worker registry
try {
this.workerRegistryClient.registry();
this.workerRegistryClient.setRegistryStoppable(this);
Set<String> workerZkPaths = this.workerRegistryClient.getWorkerZkPaths();
this.workerRegistryClient.handleDeadServer(workerZkPaths, NodeType.WORKER, Constants.DELETE_OP);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
// task execute manager
this.workerManagerThread.start();
// retry report task status
this.retryReportTaskStatusThread.start();
/*
* registry hooks, which are called before the process exits
*/
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(() -> {
if (Stopper.isRunning()) {
close("shutdownHook");
}
}));
}


回调线程对象初始化的时候,会将包含的Nettyremotingclient一起初始化,并注册好对应的业务处理器:
public TaskCallbackService() {
final NettyClientConfig clientConfig = new NettyClientConfig();
this.nettyRemotingClient = new NettyRemotingClient(clientConfig);
this.nettyRemotingClient.registerProcessor(CommandType.TASK_EXECUTE_RUNNING_ACK, taskExecuteRunningProcessor);
this.nettyRemotingClient.registerProcessor(CommandType.TASK_EXECUTE_RESPONSE_ACK, taskExecuteResponseAckProcessor);
}


回调线程会通过其他执行器中缓存下来的Chanel与Master的客户端进行通信:
/**
* send result
*
* @param taskInstanceId taskInstanceId
* @param command command
*/
public void send(int taskInstanceId, Command command) {
NettyRemoteChannel nettyRemoteChannel = getRemoteChannel(taskInstanceId);
if (nettyRemoteChannel != null) {
nettyRemoteChannel.writeAndFlush(command).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
if (future.isSuccess()) {
// remove(taskInstanceId);
return;
}
}
});
}
}


2.6.2 其他服务与Master交互
以日志服务为例,前端触发请求日志的接口,通过参数与数据库交互获取到Master的NettyServer信息,然后构建Netty客户端与Master进行通信获取日志并返回。具体代码如下
public Result<String> queryLog(@ApiIgnore @RequestAttribute(value = Constants.SESSION_USER) User loginUser,
@RequestParam(value = "taskInstanceId") int taskInstanceId,
@RequestParam(value = "skipLineNum") int skipNum,
@RequestParam(value = "limit") int limit) {
return loggerService.queryLog(taskInstanceId, skipNum, limit);
}


/**
* view log
*
* @param taskInstId task instance id
* @param skipLineNum skip line number
* @param limit limit
* @return log string data
*/
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Result<String> queryLog(int taskInstId, int skipLineNum, int limit) {
TaskInstance taskInstance = processService.findTaskInstanceById(taskInstId);
if (taskInstance == null) {
return Result.error(Status.TASK_INSTANCE_NOT_FOUND);
}
if (StringUtils.isBlank(taskInstance.getHost())) {
return Result.error(Status.TASK_INSTANCE_HOST_IS_NULL);
}
Result<String> result = new Result<>(Status.SUCCESS.getCode(), Status.SUCCESS.getMsg());
String log = queryLog(taskInstance,skipLineNum,limit);
result.setData(log);
return result;
}


/**
* query log
*
* @param taskInstance task instance
* @param skipLineNum skip line number
* @param limit limit
* @return log string data
*/
private String queryLog(TaskInstance taskInstance, int skipLineNum, int limit) {
Host host = Host.of(taskInstance.getHost());
logger.info("log host : {} , logPath : {} , port : {}", host.getIp(), taskInstance.getLogPath(),
host.getPort());
StringBuilder log = new StringBuilder();
if (skipLineNum == 0) {
String head = String.format(LOG_HEAD_FORMAT,
taskInstance.getLogPath(),
host,
Constants.SYSTEM_LINE_SEPARATOR);
log.append(head);
}
log.append(logClient
.rollViewLog(host.getIp(), host.getPort(), taskInstance.getLogPath(), skipLineNum, limit));
return log.toString();
}


/**
* roll view log
*
* @param host host
* @param port port
* @param path path
* @param skipLineNum skip line number
* @param limit limit
* @return log content
*/
public String rollViewLog(String host, int port, String path, int skipLineNum, int limit) {
logger.info("roll view log, host : {}, port : {}, path {}, skipLineNum {} ,limit {}", host, port, path, skipLineNum, limit);
RollViewLogRequestCommand request = new RollViewLogRequestCommand(path, skipLineNum, limit);
String result = "";
final Host address = new Host(host, port);
try {
Command command = request.convert2Command();
Command response = this.client.sendSync(address, command, LOG_REQUEST_TIMEOUT);
if (response != null) {
RollViewLogResponseCommand rollReviewLog = JSONUtils.parseObject(
response.getBody(), RollViewLogResponseCommand.class);
return rollReviewLog.getMsg();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("roll view log error", e);
} finally {
this.client.closeChannel(address);
}
return result;
}


/**
* sync send
*
* @param host host
* @param command command
* @param timeoutMillis timeoutMillis
* @return command
*/
public Command sendSync(final Host host, final Command command, final long timeoutMillis) throws InterruptedException, RemotingException {
final Channel channel = getChannel(host);
if (channel == null) {
throw new RemotingException(String.format("connect to : %s fail", host));
}
final long opaque = command.getOpaque();
final ResponseFuture responseFuture = new ResponseFuture(opaque, timeoutMillis, null, null);
channel.writeAndFlush(command).addListener(future -> {
if (future.isSuccess()) {
responseFuture.setSendOk(true);
return;
} else {
responseFuture.setSendOk(false);
}
responseFuture.setCause(future.cause());
responseFuture.putResponse(null);
logger.error("send command {} to host {} failed", command, host);
});
/*
* sync wait for result
*/
Command result = responseFuture.waitResponse();
if (result == null) {
if (responseFuture.isSendOK()) {
throw new RemotingTimeoutException(host.toString(), timeoutMillis, responseFuture.getCause());
} else {
throw new RemotingException(host.toString(), responseFuture.getCause());
}
}
return result;
}


Nettyclient随着日志业务对象初始化而初始化:
/**
* construct client
*/
public LogClientService() {
this.clientConfig = new NettyClientConfig();
this.clientConfig.setWorkerThreads(4);
this.client = new NettyRemotingClient(clientConfig);
this.isRunning = true;
}


2.7 负载均衡算法
Master在选择执行器的时候DolphinScheduler提供了三种负载均衡算法,且所有的算法都用到了节点权重:加权随机(random),平滑轮询(roundrobin),线性负载(lowerweight)。通过配置文件来控制到底使用哪一个负载均衡策略,默认配置是权重策略:host-selector: lower_weight。
@Bean
public HostManager hostManager() {
HostSelector selector = masterConfig.getHostSelector();
HostManager hostManager;
switch (selector) {
case RANDOM:
hostManager = new RandomHostManager();
break;
case ROUND_ROBIN:
hostManager = new RoundRobinHostManager();
break;
case LOWER_WEIGHT:
hostManager = new LowerWeightHostManager();
break;
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("unSupport selector " + selector);
}
beanFactory.autowireBean(hostManager);
return hostManager;
}


2.7.1 加权随机
看代码更好理解:按照全部权重值求和,然后取汇总结果的随机整数,随机整数对原先所有host的权重累差,返回小于零的时候的host,没有就随机返回一个。
@Override
public HostWorker doSelect(final Collection<HostWorker> source) {
List<HostWorker> hosts = new ArrayList<>(source);
int size = hosts.size();
int[] weights = new int[size];
int totalWeight = 0;
int index = 0;
for (HostWorker host : hosts) {
totalWeight += host.getHostWeight();
weights[index] = host.getHostWeight();
index++;
}
if (totalWeight > 0) {
int offset = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(totalWeight);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
offset -= weights[i];
if (offset < 0) {
return hosts.get(i);
}
}
}
return hosts.get(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(size));
}


2.7.2 线性负载
权重计算逻辑:利用注册的Cpu占用、内存占用以及加载因子还有启动时间消耗做计算。
private double calculateWeight(double cpu, double memory, double loadAverage, long startTime) {
double calculatedWeight = cpu * CPU_FACTOR + memory * MEMORY_FACTOR + loadAverage * LOAD_AVERAGE_FACTOR;
long uptime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
if (uptime > 0 && uptime < Constants.WARM_UP_TIME) {
// If the warm-up is not over, add the weight
return calculatedWeight * Constants.WARM_UP_TIME / uptime;
}
return calculatedWeight;
}


获取权重最小的节点,并把节点权重置为最大。
/**
* select
*
* @param sources sources
* @return HostWeight
*/
@Override
public HostWeight doSelect(Collection<HostWeight> sources) {
double totalWeight = 0;
double lowWeight = 0;
HostWeight lowerNode = null;
for (HostWeight hostWeight : sources) {
totalWeight += hostWeight.getWeight();
hostWeight.setCurrentWeight(hostWeight.getCurrentWeight() + hostWeight.getWeight());
if (lowerNode == null || lowWeight > hostWeight.getCurrentWeight()) {
lowerNode = hostWeight;
lowWeight = hostWeight.getCurrentWeight();
}
}
lowerNode.setCurrentWeight(lowerNode.getCurrentWeight() + totalWeight);
return lowerNode;
}


2.7.3 平滑轮询
这个算法不是很好的能够理解,所以我不知道我的理解是否正确,它有一个预热的过程,之前都是取第一个,等到累计的权重超过最大就整数就开始按权重轮询。
@Override
public HostWorker doSelect(Collection<HostWorker> source) {
List<HostWorker> hosts = new ArrayList<>(source);
String key = hosts.get(0).getWorkerGroup();
ConcurrentMap<String, WeightedRoundRobin> map = workGroupWeightMap.get(key);
if (map == null) {
workGroupWeightMap.putIfAbsent(key, new ConcurrentHashMap<>());
map = workGroupWeightMap.get(key);
}
int totalWeight = 0;
long maxCurrent = Long.MIN_VALUE;
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
HostWorker selectedHost = null;
WeightedRoundRobin selectWeightRoundRobin = null;
for (HostWorker host : hosts) {
String workGroupHost = host.getWorkerGroup() + host.getAddress();
WeightedRoundRobin weightedRoundRobin = map.get(workGroupHost);
int weight = host.getHostWeight();
if (weight < 0) {
weight = 0;
}
if (weightedRoundRobin == null) {
weightedRoundRobin = new WeightedRoundRobin();
// set weight
weightedRoundRobin.setWeight(weight);
map.putIfAbsent(workGroupHost, weightedRoundRobin);
weightedRoundRobin = map.get(workGroupHost);
}
if (weight != weightedRoundRobin.getWeight()) {
weightedRoundRobin.setWeight(weight);
}
long cur = weightedRoundRobin.increaseCurrent();
weightedRoundRobin.setLastUpdate(now);
if (cur > maxCurrent) {
maxCurrent = cur;
selectedHost = host;
selectWeightRoundRobin = weightedRoundRobin;
}
totalWeight += weight;
}
if (!updateLock.get() && hosts.size() != map.size() && updateLock.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
try {
ConcurrentMap<String, WeightedRoundRobin> newMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(map);
newMap.entrySet().removeIf(item -> now - item.getValue().getLastUpdate() > RECYCLE_PERIOD);
workGroupWeightMap.put(key, newMap);
} finally {
updateLock.set(false);
}
}
if (selectedHost != null) {
selectWeightRoundRobin.sel(totalWeight);
return selectedHost;
}
return hosts.get(0);
}


2.8 日志服务
2.6.2已经介绍不在做过多的说明。
2.9 报警
暂未研究,目测基本就是根据规则筛选数据,然后调用指定类型的报警服务接口做报警操作,比如邮件,微信,短信通知等。
3 后记
3.1 Make friends
因为没有正式生产使用,业务理解不一定透彻,理解可能有偏差,欢迎大家一起进入社区交流讨论。
Apache DolphinScheduler Slack群链接:https://join.slack.com/t/asf-dolphinscheduler/shared_invite/zt-1e36toy4n-5n9U2R__FDM05R~MJFFVBg
3.2 参考文献
https://dolphinscheduler.apache.org/zh-cn/development/architecture-design.html;
https://www.w3cschool.cn/quartz_doc/quartz_doc-1xbu2clr.html.
最后,感谢社区蔡顺峰、钟嘉杰和阮文俊对本文整理和修改提出建设性意见,以及对本文发布提供的帮助。

非常欢迎大家加入 DolphinScheduler 大家庭,融入开源世界!
我们鼓励任何形式的参与社区,最终成为 Committer 或 PPMC,如:
将遇到的问题通过 GitHub 上 issue 的形式反馈出来。
回答别人遇到的 issue 问题。
帮助完善文档。
帮助项目增加测试用例。
为代码添加注释。
提交修复 Bug 或者 Feature 的 PR。
发表应用案例实践、调度流程分析或者与调度相关的技术文章。
帮助推广 DolphinScheduler,参与技术大会或者 meetup 的分享等。
欢迎加入贡献的队伍,加入开源从提交第一个 PR 开始。
- 比如添加代码注释或找到带有 ”easy to fix” 标记或一些非常简单的 issue(拼写错误等) 等等,先通过第一个简单的 PR 熟悉提交流程。
注:贡献不仅仅限于 PR 哈,对促进项目发展的都是贡献。
相信参与 DolphinScheduler,一定会让您从开源中受益!
参与贡献
随着国内开源的迅猛崛起,Apache DolphinScheduler 社区迎来蓬勃发展,为了做更好用、易用的调度,真诚欢迎热爱开源的伙伴加入到开源社区中来,为中国开源崛起献上一份自己的力量,让本土开源走向全球。
参与 DolphinScheduler 社区有非常多的参与贡献的方式,包括:
贡献第一个PR(文档、代码) 我们也希望是简单的,第一个PR用于熟悉提交的流程和社区协作以及感受社区的友好度。
社区汇总了以下适合新手的问题列表:https://github.com/apache/dolphinscheduler/issues/5689
非新手问题列表:https://github.com/apache/dolphinscheduler/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A"volunteer+wanted"
如何参与贡献链接:https://dolphinscheduler.apache.org/zh-cn/community/development/contribute.html
来吧,DolphinScheduler开源社区需要您的参与,为中国开源崛起添砖加瓦吧,哪怕只是小小的一块瓦,汇聚起来的力量也是巨大的。
参与开源可以近距离与各路高手切磋,迅速提升自己的技能,如果您想参与贡献,我们有个贡献者种子孵化群,可以添加社区小助手,手把手教会您( 贡献者不分水平高低,有问必答,关键是有一颗愿意贡献的心 )。
添加小助手微信时请说明想参与贡献。来吧,开源社区非常期待您的参与。
一文读懂,硬核 Apache DolphinScheduler3.0 源码解析的更多相关文章
- apache mina2.0源码解析(一)
apache mina是一个基于java nio的网络通信框架,为TCP UDP ARP等协议提供了一致的编程模型:其源码结构展示了优秀的设计案例,可以为我们的编程事业提供参考. 依照惯例,首先搭建a ...
- 一文读懂Spring动态配置多数据源---源码详细分析
Spring动态多数据源源码分析及解读 一.为什么要研究Spring动态多数据源 期初,最开始的原因是:想将答题服务中发送主观题答题数据给批改中间件这块抽象出来, 但这块主要使用的是mq消息的方式 ...
- 即时通讯新手入门:一文读懂什么是Nginx?它能否实现IM的负载均衡?
本文引用了“蔷薇Nina”的“Nginx 相关介绍(Nginx是什么?能干嘛?)”一文部分内容,感谢作者的无私分享. 1.引言 Nginx(及其衍生产品)是目前被大量使用的服务端反向代理和负载均衡 ...
- 一文读懂高性能网络编程中的I/O模型
1.前言 随着互联网的发展,面对海量用户高并发业务,传统的阻塞式的服务端架构模式已经无能为力.本文(和下篇<高性能网络编程(六):一文读懂高性能网络编程中的线程模型>)旨在为大家提供有用的 ...
- 从HTTP/0.9到HTTP/2:一文读懂HTTP协议的历史演变和设计思路
本文原作者阮一峰,作者博客:ruanyifeng.com. 1.引言 HTTP 协议是最重要的互联网基础协议之一,它从最初的仅为浏览网页的目的进化到现在,已经是短连接通信的事实工业标准,最新版本 HT ...
- [转帖]从HTTP/0.9到HTTP/2:一文读懂HTTP协议的历史演变和设计思路
从HTTP/0.9到HTTP/2:一文读懂HTTP协议的历史演变和设计思路 http://www.52im.net/thread-1709-1-2.html 本文原作者阮一峰,作者博客:r ...
- 一文读懂HTTP/2及HTTP/3特性
摘要: 学习 HTTP/2 与 HTTP/3. 前言 HTTP/2 相比于 HTTP/1,可以说是大幅度提高了网页的性能,只需要升级到该协议就可以减少很多之前需要做的性能优化工作,当然兼容问题以及如何 ...
- 一文读懂AI简史:当年各国烧钱许下的愿,有些至今仍未实现
一文读懂AI简史:当年各国烧钱许下的愿,有些至今仍未实现 导读:近日,马云.马化腾.李彦宏等互联网大佬纷纷亮相2018世界人工智能大会,并登台演讲.关于人工智能的现状与未来,他们提出了各自的观点,也引 ...
- 一文读懂 深度强化学习算法 A3C (Actor-Critic Algorithm)
一文读懂 深度强化学习算法 A3C (Actor-Critic Algorithm) 2017-12-25 16:29:19 对于 A3C 算法感觉自己总是一知半解,现将其梳理一下,记录在此,也 ...
随机推荐
- Python实现中文字幕雨+源代码
写在前面的一些P话: 最近浏览了很多关于用Python和Pygame实现代码雨的案例,发现很多都是没有深入讲解代码的整个实现过程,从0到1教会你制作中文文字雨. 然后在介绍的过程中,我也将深入介绍Py ...
- 一文读懂数仓中的pg_stat
摘要:GaussDB(DWS)在SQL执行过程中,会记录表增删改查相关的运行时统计信息,并在事务提交或回滚后记录到共享的内存中.这些信息可以通过 "pg_stat_all_tables视图& ...
- 选择结构-单if语句和标准if else语句
判断语句1--if if语句第一种格式: if if(关系表达式){ 语句体; } 执行流程 首先判断关系表达式看其结果是true还是false 如果是true就执行语句体 如果是false就不执行语 ...
- 攻防世界MISC—进阶区32—37
32.normal_png 得到一张png,扔进kali中binwalk 和 pngcheck一下,发现CRC报错 尝试修改图片高度,我是把height的2改为4,得到flag 33.很普通的数独 得 ...
- Assembly.GetManifestResourceStream为null
想把某个项目的某个文件夹里面的ini文件生成的时候顺便生成为网站和服务文件夹项目 string _path = Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDir ...
- docker容器管理操作
Docker容器的四种状态: 运行 已暂停 重新启动 已退出 1.容器的创建 容器创建:就是将镜像加载到容器的过程. 创建容器时如果没有指定容器名称,系统会自动创建一个名称. 新创建的容器默认处于停止 ...
- ZJOI2016 小星星 题解
我一生之敌是状压 本文发表于 洛谷博客:https://www.luogu.com.cn/blog/LoveMC/solution-p3349 Cnblogs:https://www.cnblogs. ...
- Yii项目知识搜集
[['rId','advertiser_id','image_file'], 'unique','targetAttribute'=>['rId','advertiser_id','image_ ...
- php九个很有用的功能
1.任意数目的参数 // 两个默认参数的函数 function foo($arg1 = '', $arg2 = '') { echo "arg1: $arg1\n"; echo & ...
- 第三讲 Linux测试
3.1 Linux操作系统定义 Ø我们为什么要学习这个linux系统呢? 那是因为我们很多的服务都放在这个linux系统,那为什么很多服务都要放到这个linux系统?这是因为linux系统好,它系统稳 ...
