microkernel architecture - Proxy
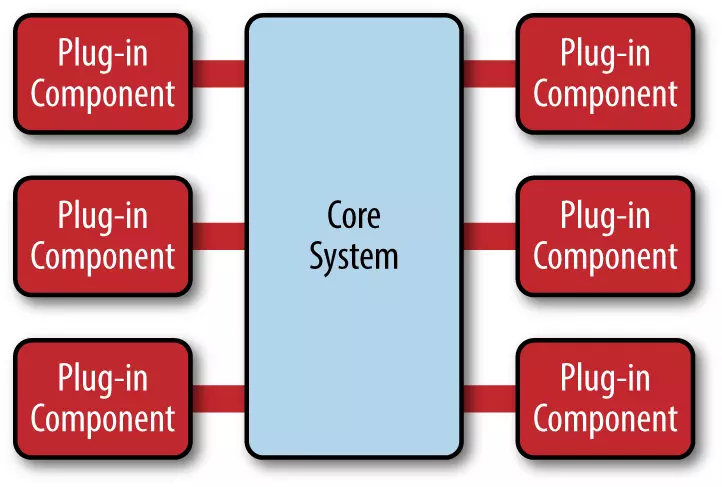
1: Oriented-Interface Plug-in development
2: Using Interceptor to develop Plug-in
3: Poxy or Reflection also can be used in Plug-in development (InvocationHandler)
https://blog.csdn.net/huxiaoyonglan1/article/details/72956184
https://blog.csdn.net/danchu/article/details/70238002
public class JavassistProxyFactory extends AbstractProxyFactory {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T getProxy(Invoker<T> invoker, Class<?>[] interfaces) {
return (T) Proxy.getProxy(interfaces).newInstance(
new InvokerInvocationHandler(invoker)
);
}
public <T> Invoker<T> getInvoker(T proxy, Class<T> type, URL url) {
final Wrapper wrapper = Wrapper.getWrapper(
proxy.getClass().getName().indexOf('$') < 0 ?
proxy.getClass() : type);
return new AbstractProxyInvoker<T>(proxy, type, url) {
@Override
protected Object doInvoke(T proxy, String methodName,
Class<?>[] parameterTypes,
Object[] arguments) throws Throwable {
return wrapper.invokeMethod(proxy, methodName, parameterTypes, arguments);
}
};
}
}
public static <T> T create(Class<T> interfaceClass) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(interfaceClass.getClassLoader(),new Class<?>[]{interfaceClass},new ObjectProxy<T>(interfaceClass)
);
}
public static <T> IAsyncObjectProxy createAsync(Class<T> interfaceClass) {
return new ObjectProxy<T>(interfaceClass);
}
public class ObjectProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, IAsyncObjectProxy {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ObjectProxy.class);
private Class<T> clazz;
public ObjectProxy(Class<T> clazz) {
this.clazz = clazz;
}
//for synchronized call, package the call with classname, method, arguments
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
if (Object.class == method.getDeclaringClass()) {
String name = method.getName();
if ("equals".equals(name)) {
return proxy == args[0];
} else if ("hashCode".equals(name)) {
return System.identityHashCode(proxy);
} else if ("toString".equals(name)) {
return proxy.getClass().getName() + "@" +
Integer.toHexString(System.identityHashCode(proxy)) +
", with InvocationHandler " + this;
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException(String.valueOf(method));
}
}
//package the classname, method, types of arguments and arguments,additional request id
RpcRequest request = new RpcRequest();
request.setRequestId(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
request.setClassName(method.getDeclaringClass().getName());
request.setMethodName(method.getName());
request.setParameterTypes(method.getParameterTypes());
request.setParameters(args);
// Debug
LOGGER.debug(method.getDeclaringClass().getName());
LOGGER.debug(method.getName());
for (int i = 0; i < method.getParameterTypes().length; ++i) {
LOGGER.debug(method.getParameterTypes()[i].getName());
}
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; ++i) {
LOGGER.debug(args[i].toString());
}
//get one client from list of client
RpcClientHandler handler = ConnectManage.getInstance().chooseHandler();
//send rpc message to rpc server and wait for results
RPCFuture rpcFuture = handler.sendRequest(request);
return rpcFuture.get();
}
@Override
public RPCFuture call(String funcName, Object... args) {
RpcClientHandler handler = ConnectManage.getInstance().chooseHandler();
RpcRequest request = createRequest(this.clazz.getName(), funcName, args);
RPCFuture rpcFuture = handler.sendRequest(request);
return rpcFuture;
}
}
public class RpcClient implements InvocationHandler {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T proxy(Class<T> interfaceClass) throws Throwable {
if (!interfaceClass.isInterface()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(interfaceClass.getName()
+ " is not an interface");
}
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(interfaceClass.getClassLoader(),new Class<?>[] { interfaceClass }, this);
}
@Override
public RpcClient interfaceClass(Class<?> interfaceClass) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
this.interfaceClass=interfaceClass;
return this;
}
@Override
public RpcClient version(String version) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
this.version=version;
return this;
}
@Override
public RpcClient clientTimeout(int clientTimeout) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
this.timeout=clientTimeout;
return this;
}
@Override
public RpcConsumer hook(ConsumerHook hook) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
this.hook=hook;
return this;
}
@Override
public Object instance() {
try {
return proxy(this.interfaceClass);
}
catch (Throwable e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
@Override
public void asynCall(String methodName) {
asynCall(methodName, null);
}
@Override
public <T extends ResponseCallbackListener> void asynCall(String methodName, T callbackListener) {
this.asyncMethods.put(methodName, callbackListener);
this.connection.setAsyncMethod(asyncMethods);
for (RpcConnection conn:connection_list)
{
conn.setAsyncMethod(asyncMethods);
}
}
@Override
public void cancelAsyn(String methodName) {
this.asyncMethods.remove(methodName);
this.connection.setAsyncMethod(asyncMethods);
for (RpcConnection conn:connection_list)
{
conn.setAsyncMethod(asyncMethods);
}
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
List<String> parameterTypes = new LinkedList<String>();
for (Class<?> parameterType : method.getParameterTypes()) {
parameterTypes.add(parameterType.getName());
}
RpcRequest request = new RpcRequest();
request.setRequestId(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
request.setClassName(method.getDeclaringClass().getName());
request.setMethodName(method.getName());
request.setParameterTypes(method.getParameterTypes());
request.setParameters(args);
if(hook!=null)
hook.before(request);
RpcResponse response = null;
try
{
request.setContext(RpcContext.props);
response = (RpcResponse) select().Send(request,asyncMethods.containsKey(request.getMethodName()));
if(hook!=null)
hook.after(request);
if(!asyncMethods.containsKey(request.getMethodName())&&response.getExption()!=null)
{
Throwable e=(Throwable) Tool.deserialize(response.getExption(),response.getClazz());
throw e.getCause();
}
}
catch (Throwable t)
{
//t.printStackTrace();
//throw new RuntimeException(t);
throw t;
}
finally
{
// if(asyncMethods.containsKey(request.getMethodName())&&asyncMethods.get(request.getMethodName())!=null)
// {
// cancelAsyn(request.getMethodName());
// }
}
if(response==null)
{
return null;
}
else if (response.getErrorMsg() != null)
{
throw response.getErrorMsg();
}
else
{
return response.getAppResponse();
}
}
}
public class ProxyFactory implements MethodInterceptor {
private Object obj;
public Object createProxy(Object target) {
this.obj = target;
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
enhancer.setSuperclass(this.obj.getClass());
enhancer.setCallback(this);
enhancer.setClassLoader(target.getClass().getClassLoader());
return enhancer.create();
}
@Override
public Object intercept(Object obj, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy proxy) throws Throwable {
Object result = null;
try {
before();
result = proxy.invokeSuper(obj, args);
after();
} catch (Exception e) {
exception();
}finally{
beforeReturning();
}
return result;
}
}
Hello hello = new Hello();
ProxyFactory cglibProxy = new ProxyFactory();
Hello proxy = (Hello) cglibProxy.createProxy(hello);
String result=proxy.sayHello(true);
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
enhancer.setSuperclass(SampleClass.class);
enhancer.setCallback(new FixedValue() {
@Override
public Object loadObject() throws Exception {
return "Hello cglib!";
}
});
SampleClass proxy = (SampleClass) enhancer.create();
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
enhancer.setSuperclass(SampleClass.class);
enhancer.setCallback(new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
throws Throwable {
if(method.getDeclaringClass() != Object.class && method.getReturnType() == String.class) {
return "Hello cglib!";
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Do not know what to do.");
}
}
});
SampleClass proxy = (SampleClass) enhancer.create();
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
enhancer.setSuperclass(SampleClass.class);
enhancer.setCallbackFilter(new filter());
enhancer.setCallback(new MethodInterceptor() {
@Override
public Object intercept(Object obj, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy proxy)
throws Throwable {
if(method.getDeclaringClass() != Object.class && method.getReturnType() == String.class) {
return "Hello cglib!";
} else {
return proxy.invokeSuper(obj, args);
}
}
});
SampleClass proxy = (SampleClass) enhancer.create();
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
https://www.jianshu.com/p/20203286ccd9
microkernel architecture - Proxy的更多相关文章
- 微内核架构(Microkernel Architecture)
微内核架构(Microkernel Architecture) 微内核架构有时也被成为插件架构模式(plug-in architecture pattern),通常用于实现基于产品的应用,如Eclip ...
- Software Architecture Pattern(Mark Richards)笔记
软件架构模式 缺少规范架构的程序通常会变得紧耦合.脆弱.难以更改,缺少清晰的发展方向和愿景.这本小书用50多页介绍了常用的5种常见架构模式,相信不管是大牛还是萌新都会有所收获,特别是对我这种偏爱系统设 ...
- 理解 Dubbo SPI 扩展机制
写在前面 最近接触了 gRPC 体会到虽然众多 RPC 框架各有各的特点但是他们提供的特性和功能有很多的相似之处 , 这就说明他们面对同样的分布式系统带来的问题.从 2016 年左右开始接触到 dub ...
- [转] 理解 Dubbo SPI 扩展机制
写在前面 最近接触了 gRPC 体会到虽然众多 RPC 框架各有各的特点但是他们提供的特性和功能有很多的相似之处 , 这就说明他们面对同样的分布式系统带来的问题.从 2016 年左右开始接触到 dub ...
- iOS动态部署方案
转载: iOS动态部署方案 前言 这里讨论的动态部署方案,就是指通过不发版的方式,将新的内容.新的业务流程部署进已发布的App.因为苹果的审核周期比较长,而且苹果的限制比较多,业界在这里也没有特别多的 ...
- Anatomy of the Linux kernel--转
ref:http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/linux/library/l-linux-kernel/?S_TACT=105AGX52&S_CMP=cn-a-l ...
- ssiOS应用架构谈 本地持久化方案及动态部署
本文转载至 http://casatwy.com/iosying-yong-jia-gou-tan-ben-di-chi-jiu-hua-fang-an-ji-dong-tai-bu-shu.html ...
- iOS应用架构谈part4-本地持久化方案及动态部署
前言 嗯,你们要的大招.跟着这篇文章一起也发布了CTPersistance和CTJSBridge这两个库,希望大家在实际使用的时候如果遇到问题,就给我提issue或者PR或者评论区.每一个issue和 ...
- 操作系统微内核和Dubbo微内核,有何不同?
你好,我是 yes. 在之前的文章已经提到了 RPC 的核心,想必一个 RPC 通信大致的流程和基本原理已经清晰了. 这篇文章借着 Dubbo 来说说微内核这种设计思想,不会扯到 Dubbo 某个具体 ...
随机推荐
- Could not get lock /var/lib/apt/lists/lock
执行: apt-get update 出现 Could not get lock /var/lib/apt/lists/lock 解决办法: 查询与apt相关的进程 ps -e | grep apt ...
- 图解SQL Server 2008入门必会
图解SQL Server 2008入门必会 https://jingyan.baidu.com/article/656db918eded1ee381249c0b.html 图解SQL Server ...
- 斐讯 N1 刷 Armbian 5.75
前言 不知不觉居然鸽了快半年的博客_(:3」∠)_ 好吧最近发现之前玩的 N1 Armbian 系统已经出到 5.75 了,之前刷 5.64 玩过,具体博文在此,说实话并不是很稳定,有线网络有时会卡死 ...
- Luogu P1801 黑匣子_NOI导刊2010提高(06)
P1801 黑匣子_NOI导刊2010提高(06) 题目描述 Black Box是一种原始的数据库.它可以储存一个整数数组,还有一个特别的变量i.最开始的时候Black Box是空的.而i等于0.这个 ...
- 动态规划 70.climbing Stairs
1. 记忆化搜索 - 自上向下的解决问题:使用vector来保存每次计算的结果,如果下次再碰到同样的需要计算的式子就不需要重复计算了. 2. 动态规划 - 自下向上的解决问题 解法一:自顶向下 解法二 ...
- QQ链接病毒分析
QQ链接病毒分析 特征 点击病毒链接后,自动会在每一时刻范围内通过所有途径群发新的病毒链接(途径包括Qzone,群聊等) 分析 首先看一下病毒链接的一个样例 http://news.soso.com/ ...
- CodeChef - NWAYS 组合数 朱世杰恒等式
这道题目数据有坑,白浪费一个小时! 题意:求\(\sum_{i=1}^n\sum_{j=1}^n{|i-j|+k \choose k}\) 知识点: 朱世杰恒等式,\(\sum_{i=r}^n{i \ ...
- PIE SDK打开Micaps数据
1. 功能简介 Micaps数据是气象信息处理和天气预报制作中的一种气象数据格式.其包含多种气象信息产品(地面常规气象观测数据产品.高空常规气象观测数据产品等),目前Micaps数据被Micaps软件 ...
- linux + eclipse C语言 开发环境搭建
经常与linux系统打交道,了解学习一下C语言,下载eclipse c/c++ linux版,直接在虚拟机linux系统上安装http://www.eclipse.org/downloads/pack ...
- kali 安装命令类
apt-get常用命令:update – 取回更新的软件包列表信息upgrade – 进行一次升级install – 安装新的软件包(注:软件包名称是 libc6 而非 libc6.deb)remov ...
