EntityFramework Code-First—领域类配置之DataAnnotations
本文出自:https://www.cnblogs.com/tang-tang/p/5510574.html
一、摘要
EF Code-First提供了一个可以用在领域类或其属性上的DataAnnotation特性集合,DataAnnotation特性会覆盖默认的EF约定。
DataAnnotation存在于两个命名空间里:
System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations
System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema
注意: DataAnnotations只提供了一部分的配置选项,全部的配置选项在Fluent API中。
二、System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations 包含的特性:
| Attribute | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Key | 标记一个属性,其将会在关系表中被映射成主键 |
| Timestamp | 标记一个属性,其将会在数据库中被映射成一个不为null的tiamestamp(时间戳)列 |
| ConcurrencyCheck | 这个属性允许你标记一个或多个属性,被标记的属性将会在用户编辑或删除entity的时候进行并发检查 |
| Required | 强制约束,该属性必须有数据,不能为null(同样适用MVC) |
| MinLength | 确保数组或字符串长度达到最小长度 |
| MaxLength | 数据库中列的长度的最大值 |
| StringLength | 在数据字段中指定字符允许的最大长度和最小长度 |
三、System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema 包含的特性:
| Attribute | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Table | 指定被映射的类在数据库生成的表名 |
| Column | 指定被映射的属性在表中的列名和数据类型 |
| Index | 在指定列上创建索引(仅EF6.1以上版本支持) |
| ForeignKey | 给导航属性指定外键属性 |
| NotMapped | 标记的属性不会被映射到数据库 |
| DatabaseGenerated | 指定的属性将会映射成数据库表中的计算列,所以这个属性应是只读的。也可以用在把属性映射成标识列(自增长列) |
| InverseProperty | 当两个类之间包含多重关系的时候,默认约定会排列组合他们的导航属性组合并一一创建外键,InverseProperty可以标记实际的主外键关系,从而过滤掉因排列组合出来的无用外键 |
| ComplexType | 标记一个类为复杂类型 |
四、特性详细介绍
1、Key
Key特性应用在类的属性上。Code-First默认约定将名称是"Id"或者{类名}+"Id"的属性创建为一个主键列,Key特性覆写了默认约定,我们可以把任何想要成为的主键的属性标记为Key而不管它是什么名称。
代码如下:
- using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
- public class Student
- {
- public Student()
- { }
- [Key]
- public int StudentKey { get; set; }
- public string StudentName { get; set; }
- }
结果如下:
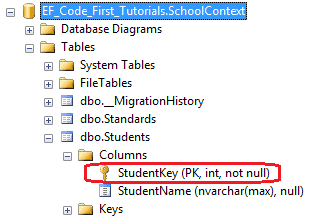
我们也可以用用Key特性和Column特性创建混合主键,如下代码所示:
- using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
- public class Student
- {
- public Student()
- { }
- [Key]
- [Column(Order=)]
- public int StudentKey1 { get; set; }
- [Key]
- [Column(Order=)]
- public int StudentKey2 { get; set; }
- public string StudentName { get; set; }
- }
结果如下:
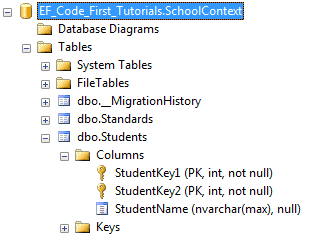
注:当Key特性应用在单整型类型的属性上时,会将其创建为一个标识列,而混合键无论它是不是整型类型,都不会创建标识列。Key特性除了无符号整型(unsinged integers),可以应用在如string、datatime、decimal等任何数据类型上。
2、TimeStamp
TimeStamp特性只能用在数据类型为byte array的属性上,TimeStamp特性会在数据库表中创建一个timestamp属性的列,Code-First自动使用TimeStamp列进行并发检查。
(关于并发检查,可以参考Gyoung的笔记:Entity Framework 并发处理)
代码如下:
- using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
- public class Student
- {
- public Student()
- { }
- public int StudentKey { get; set; }
- public string StudentName { get; set; }
- [TimeStamp]
- public byte[] RowVersion { get; set; }
- }
结果如下::
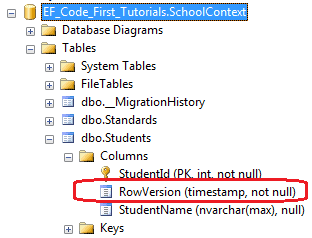
3、ConcurrencyCheck
当EF对表执行update命令时,Code-First会把标记了ConcurrencyCheck特性的列中的值插入到SQL语句的“where”子句中来进行并发检查。
如下代码:
- using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
- public class Student
- {
- public Student()
- {}
- public int StudentId { get; set; }
- [ConcurrencyCheck]
- public string StudentName { get; set; }
- }
如上所示,StudentName属性上标记了ConcurrencyCheck特性,所以Code-First会在update命令中把StudentName列包含进去以进行乐观并发检查(有关乐观并发和悲观并发,上面Gyoung的笔记有介绍,这里就不多讨论)。如下代码所示:
- exec sp_executesql N'UPDATE [dbo].[Students]
- SET [StudentName] = @0
- WHERE (([StudentId] = @1) AND ([StudentName] = @2))
- ',N'@0 nvarchar(max) ,@1 int,@2 nvarchar(max) ',@0=N'Steve',@1=1,@2=N'Bill'
- go
注意:TimeStamp特性只能用在single byte数组属性上,然而ConcurrencyCheck特性可以用在任何数量和任何数据类型的属性上。
4、Required
应用了Required特性的属性,将会在数据库表中创建一个不为null的列,需要留意的是,Required也是MVC的验证特性。
代码如下:
- using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
- public class Student
- {
- public Student()
- { }
- public int StudentID { get; set; }
- [Required]
- public string StudentName { get; set; }
- }
在数据库中,StudentName列已经被创建成不为空。
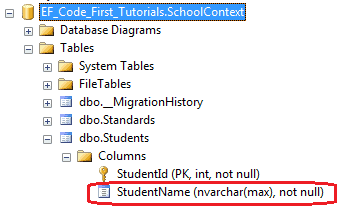
5、MaxLength
Maxlength特性用在String或array类型的属性上,EF Code-First将会把列的大小设置成指定值。值得注意的是,Maxlength也是MVC的验证特性。
代码如下:
- using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
- public class Student
- {
- public Student()
- { }
- public int StudentID { get; set; }
- [MaxLength()]
- public string StudentName { get; set; }
- }
因为StudentName属性被指定了[Maxlength(50)]特性,所以在数据库中StudentName列被创建成nvarchar(50)。
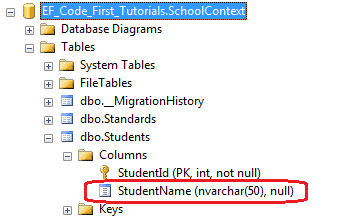
Entity Framework也会验证被标记了MaxLength特性的属性的值,如果该值大于被标记的最大值,EF将会抛出EntityValidationError。
6、MinLength
MinLength特性是EF的一个验证特性,其在数据库模式中不起作用。如果我们对标记了MinLength特性的属性赋值(string或者array),其长度小于指定的最小值,那么EF仍然会抛出EntityValidationError。
MinLength特性可以和MaxLength特性一起使用,如下代码所示:
- using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
- public class Student
- {
- public Student()
- { }
- public int StudentID { get; set; }
- [MaxLength(),MinLength()]
- public string StudentName { get; set; }
- }
如上代码所示,StudentName属性取值指定了只能是2-50个字符长度之间。
7、StringLength
StringLength应用在string类型的属性上,EF Code-First将会用StringLength指定的长度设置列的大小。和Required以及Maxlength一样,StringLength也是MVC的验证特性。
看下面的代码:
- using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
- public class Student
- {
- public Student()
- {}
- public int StudentID { get; set; }
- [StringLength()]
- public string StudentName { get; set; }
- }
根据代码中StudentName属性的[StringLength(50)]特性,在数据库中,将会创建一个nvarchar(50)的列,如下所示:

同理,EF也将会验证StringLength特性中的值,如果用户输入的值大于指定的长度,将会抛出EntityValidationError。
8、Table
Table特性应用在类上,默认的Code-First约定将会创建一个和类名同名的表名,Table特性覆写默认的约定,EF Code-First将会创建一个以Table特性里指定的字符串为名称的表。
代码如下:
- using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema;
- [Table("StudentMaster")]
- public class Student
- {
- public Student()
- { }
- public int StudentID { get; set; }
- public string StudentName { get; set; }
- }
如上所示,Student类上应用了Table["StudentMaster"]特性,所以Code-First会覆写默认的约定,创建一个名称为StudentMaster的表名
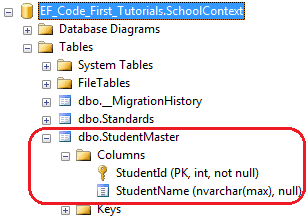
我们也可以用Table特性为表指定一个架构名,代码如下所示:
- using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema;
- [Table("StudentMaster", Schema="Admin")]
- public class Student
- {
- public Student()
- { }
- public int StudentID { get; set; }
- public string StudentName { get; set; }
- }
数据库如下,Code-First将会在Admin架构下创建一个StudentMaster表
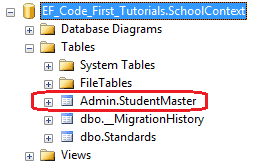
9、Column
Column特性应用在类的属性上,和Table特性一样,如果不指定Column特性的值,将会默认创建和属性同名的列,否则就会创建指定的值。
看如下代码:
- using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema;
- public class Student
- {
- public Student()
- { }
- public int StudentID { get; set; }
- [Column("Name")]
- public string StudentName { get; set; }
- }
如上所示,Column["Name"]特性应用在StudentName属性上,所以Code-First将会创建一个以"Name"为名的列来代替默认的"StudentName"列名。数据库如下:
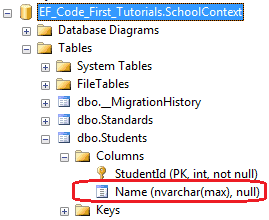
我们也可以使用Column特性为列指定排序(order)和类型(type),代码如下:
- using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema;
- public class Student
- {
- public Student()
- { }
- public int StudentID { get; set; }
- [Column("Name", Order=, TypeName="varchar")]
- public string StudentName { get; set; }
- }
上面的代码在数据库Students表中创建了一个属性为varchar,排序第一的列Name
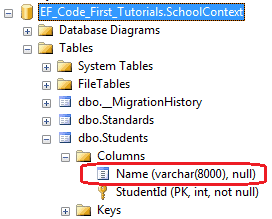
10、ForeignKey
ForeignKey特性应用在类的属性上。默认的Code-First约定预料外键属性名与主键属性名匹配,如下代码:
- public class Student
- {
- public Student()
- { }
- public int StudentID { get; set; }
- public string StudentName { get; set; }
- //Foreign key for Standard
- public int StandardId { get; set; }
- public Standard Standard { get; set; }
- }
- public class Standard
- {
- public Standard()
- { }
- public int StandardId { get; set; }
- public string StandardName { get; set; }
- public ICollection<Student> Students { get; set; }
- }
- }
如上代码所示,Student类包含了外键属性StandardId,其又是Standard类的主键属性,这样,Code-First将会在Students表中创建一个StandardId外键列。
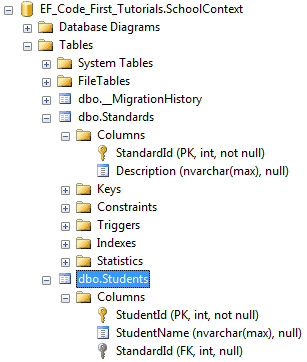
ForeignKey特性覆写了默认约定,我们可以把外键属性列设置成不同名称,代码如下:
- public class Student
- {
- public Student()
- { }
- public int StudentID { get; set; }
- public string StudentName { get; set; }
- //Foreign key for Standard
- public int StandardRefId { get; set; }
- [ForeignKey("StandardRefId")]
- public Standard Standard { get; set; }
- }
- public class Standard
- {
- public Standard()
- { }
- public int StandardId { get; set; }
- public string StandardName { get; set; }
- public ICollection<Student> Students { get; set; }
- }
如上代码所示,Student类包含了StandardRefId外键属性,我们使用ForeignKey["StandardRefId"]特性指定在Standard导航属性上,所以Code-First将会把StandardRefId作为外键,生成数据库如下所示:
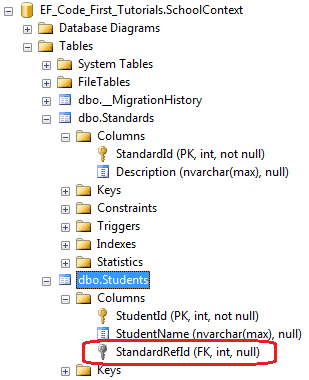
ForeignKey特性也可以用在外键属性上,只要指定好它的导航属性,即Standard属性,如下所示:
- public class Student
- {
- public Student()
- { }
- public int StudentID { get; set; }
- public string StudentName { get; set; }
- //Foreign key for Standard
- [ForeignKey("Standard")]
- public int StandardRefId { get; set; }
- public Standard Standard { get; set; }
- }
- public class Standard
- {
- public Standard()
- { }
- public int StandardId { get; set; }
- public string StandardName { get; set; }
- public ICollection<Student> Students { get; set; }
- }
这段代码和上面把ForeignKey特性定义在Standard属性上的效果是一样的,在数据库生成的Students表都创建了StandardRefId外键列。
11、NotMapped
NotMapped特性用在类的属性上,默认Code-First约定会为那些所有包含了getter和setter的属性创建列,
NotMapped可以覆写默认的约定,让那些标记了NotMapped特性的属性不会在数据库里创建列。代码如下:
- using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
- public class Student
- {
- public Student()
- { }
- public int StudentId { get; set; }
- public string StudentName { get; set; }
- [NotMapped]
- public int Age { get; set; }
- }
如上代码所示,NotMapped特性应用在Age属性上,所以Code-First不会在Students表中创建Age列。
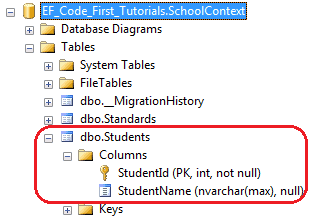
Code-First也不会为那些没有getter和setter的属性创建列,在下面代码例子中,Code-First不会为FirstName和Age创建列。
- using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
- public class Student
- {
- public Student()
- { }
- private int _age = ;
- public int StudentId { get; set; }
- public string StudentName { get; set; }
- public string FirstName { get{ return StudentName;} }
- public string Age { set{ _age = value;} }
- }
12、InverseProperty
我们已经知道,如果类中没有包含外键属性,Code-First默认约定会创建一个{类名}_{主键}的外键列。当我们类与类之间有多个关系的时候,就可以使用InverseProperty特性。
代码如下:
- public class Student
- {
- public Student()
- { }
- public int StudentID { get; set; }
- public string StudentName { get; set; }
- public Standard CurrentStandard { get; set; }
- public Standard PreviousStandard { get; set; }
- }
- public class Standard
- {
- public Standard()
- { }
- public int StandardId { get; set; }
- public string StandardName { get; set; }
- public ICollection<Student> CurrentStudents { get; set; }
- public ICollection<Student> PreviousStudents { get; set; }
- }
- }
如上代码所示,Student类包含了两个Standard类的导航属性,同样的,Standard类包含了两个Student类的集合导航属性,Code-First将会为这种关系创建4个列。如下所示:
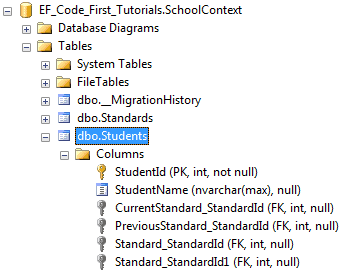
InverseProperty覆写了这种默认约定并且指定对齐属性,下面的代码在Standard类中使用InverseProperty特性修复这个问题。
- public class Student
- {
- public Student()
- { }
- public int StudentID { get; set; }
- public string StudentName { get; set; }
- public Standard CurrentStandard { get; set; }
- public Standard PreviousStandard { get; set; }
- }
- public class Standard
- {
- public Standard()
- { }
- public int StandardId { get; set; }
- public string StandardName { get; set; }
- [InverseProperty("CurrentStandard")]
- public ICollection<Student> CurrentStudents { get; set; }
- [InverseProperty("PreviousStandard")]
- public ICollection<Student> PreviousStudents { get; set; }
- }
- }
如上代码所示,我们在CurrentStudents和PreviousStudents属性上应用了InverseProperty特性,并且指定哪个Student类的引用属性属于它,所以现在,Code-First在Student表中仅仅会创建两个外键了。如下图所示:
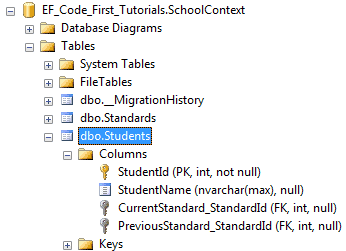
当然,如果你想改外键名称,我们就给导航属性加上ForeignKey特性,如下代码所示:
- public class Student
- {
- public Student()
- { }
- public int StudentID { get; set; }
- public string StudentName { get; set; }
- public int CurrentStandardId { get; set; }
- public int PreviousStandardId { get; set; }
- [ForeignKey("CurrentStandardId")]
- public Standard CurrentStandard { get; set; }
- [ForeignKey("PreviousStandardId")]
- public Standard PreviousStandard { get; set; }
- }
- public class Standard
- {
- public Standard()
- {}
- public int StandardId { get; set; }
- public string StandardName { get; set; }
- [InverseProperty("CurrentStandard")]
- public ICollection<Student> CurrentStudents { get; set; }
- [InverseProperty("PreviousStandard")]
- public ICollection<Student> PreviousStudents { get; set; }
- }
上面的代码将会创建出下面的数据库表和列,我们可以看出,外键的名称已经改变了。
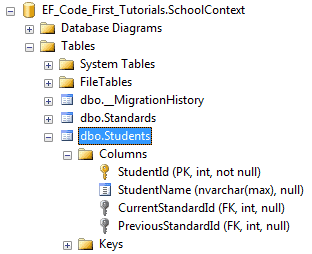
到此,DataAnnotation已经介绍完了,如果有什么不明白,或者我没讲清楚的地方,请大家留言~如有错误,也希望大神指出,不甚感激!
EntityFramework Code-First—领域类配置之DataAnnotations的更多相关文章
- EntityFramework Code-First 简易教程(六)-------领域类配置之DataAnnotations
EF Code-First提供了一个可以用在领域类或其属性上的DataAnnotation特性集合,DataAnnotation特性会覆盖默认的EF约定. DataAnnotation存在于两个命名空 ...
- EntityFramework Code-First 简易教程(七)-------领域类配置之Fluent API
Fluent API配置: 前面我们已经了解到使用DataAnotations特性来覆写Code-First默认约定,现在我们来学习Fluent API. Fluent API是另一种配置领域类的方法 ...
- EntityFramework Code-First 简易教程(五)-------领域类配置
前言:在前篇中,总是把领域类(Domain Class)翻译成模型类,因为我的理解它就是一个现实对象的抽象模型,不知道对不对.以防止将来可能的歧义,这篇开始还是直接对Domain Class直译. 前 ...
- EntityFramework Code-First-------领域类配置之DataAnnotations
EF Code-First提供了一个可以用在领域类或其属性上的DataAnnotation特性集合,DataAnnotation特性会覆盖默认的EF约定. DataAnnotation存在于两个命名空 ...
- EntityFramework 系列:实体类配置-根据依赖配置关系和关联
EF实体类的配置可以使用数据注释或Fluent API两种方式配置,Fluent API配置的关键在于搞清实体类的依赖关系,按此方法配置,快速高效合理.为了方便理解,我们使用简化的实体A和B以及A.B ...
- 6.Configure Domain Classes(配置领域类)【EF Code-First 系列】
在前面的部分中,我们学习了Code-First默认约定,Code-First使用默认的约定,根据你的领域类,然后生成概念模型. Code-First模式,发起了一种编程模式:约定大于配置.这也就是说, ...
- 8.翻译系列: EF 6中配置领域类(EF 6 Code-First 系列)
原文地址:http://www.entityframeworktutorial.net/code-first/configure-classes-in-code-first.aspx EF 6 Cod ...
- EF CodeFirst配置领域类
当我们不想使用EF的默认约定时,可以手动配置领域类,但还是推荐少配置,Simple is best! 两种配置方式: 1.Data Annotation Attributes[数据注解特性] 数据注 ...
- Entity Framework 6 Code First 实践系列(1):实体类配置-根据依赖配置关系和关联
EF实体类的配置可以使用数据注释或Fluent API两种方式配置,Fluent API配置的关键在于搞清实体类的依赖关系,按此方法配置,快速高效合理.为了方便理解,我们使用简化的实体A和B以及A.B ...
随机推荐
- CSS Grid布局,实现响应式设计
columns(列) 和 rows(行) 为了使其成为二维的网格容器,我们需要定义列和行.让我们创建3列和2行.我们将使用grid-template-row和grid-template-column属 ...
- js实现在当前页面搜索高亮显示字的方法
在html页面上,有时候会遇到一些检索高亮显示的问题,具体用js是实现的方式,代码展示. Jsp页面设置方式 <li class="pull-left" id="s ...
- 关于ORACLE的SQL语句拼接、替换、截取、排序,联表等...~持续汇总~
先看一下所有的数据.这里全部为VARCHAR2(255). 字段拼接 在所有的性别后面加% 字段替换,把性别TPF_SEX去除百分号% 字段截取 字段截取+拼接 字段替换,这里把百分号%替换为空,也 ...
- python线程(二)代码部分
使用threading创建线程: from threading import Thread def work(name): print(f"我是线程{name}") if __na ...
- 查找第三方银行官方app下载链接探索过程
需求:最近有个需求,点击按钮,弹出一个所需银行选项的非全屏弹出层,再点击某银行选项,随即跳转到该银行的app下载界面,如下图所示 注:这里只是引用相关银行的链接,不需要做什么逻辑处 ...
- WinServer配置MySQL主从同步
为什么要配置主从同步? 如果一台数据库服务器挂了,还有一个备用 为了方便配置,我采用两台WinServer2003虚拟机: 1.前期准备工作:安装好镜像文件,VMTOOLS,MySQL5.5 我这里以 ...
- 【Spark篇】---Spark中Shuffle文件的寻址
一.前述 Spark中Shuffle文件的寻址是一个文件底层的管理机制,所以还是有必要了解一下的. 二.架构图 三.基本概念: 1) MapOutputTracker MapOutputTracker ...
- 《深入理解Java虚拟机》-----第6章 类文件结构——Java高级开发必须懂的
代码编译的结果从本地机器码转变为字节码,是存储格式发展的一小步,却是编程语言发展的一大步. 6.1 概述 记得在第一节计算机程序课上我的老师就讲过:“计算机只认识0和1,所以我们写的程序需要经编译器翻 ...
- XPath和CssSelector定位总结
1. 介绍XPath和CssSelector 2. XPath有哪些方式 2.1 通过XPath语法 2.2 Contains关键字 2.3 Start-With 2.4 Or和And关键字 2.5 ...
- DS控件库 DS按钮多种样式
在DS控件库(DSControls)中,DS按钮的功能非常多,通过设置不同的属性值来使按钮呈现不同的效果.DS按钮的常用属性如下: 使用不同的属性调出不同的外观样式示例
