[LeetCode] Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node II 每个节点的右向指针之二
Given a binary tree
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node *next;
}
Populate each next pointer to point to its next right node. If there is no next right node, the next pointer should be set to NULL.
Initially, all next pointers are set to NULL.
Example:
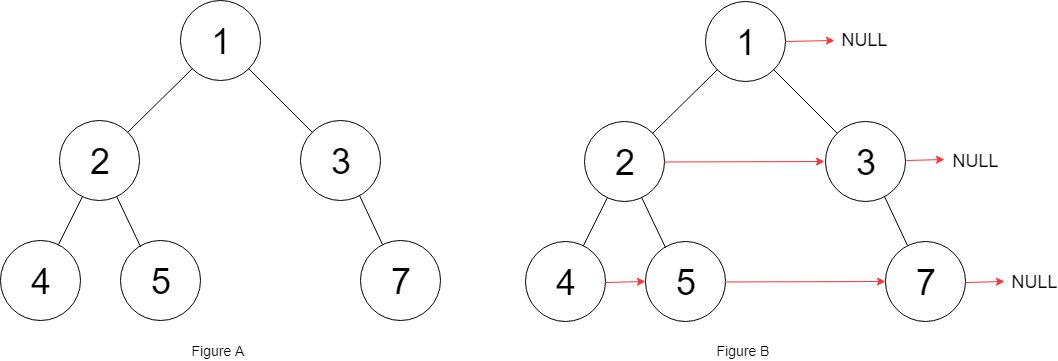
Input: {"$id":"1","left":{"$id":"2","left":{"$id":"3","left":null,"next":null,"right":null,"val":4},"next":null,"right":{"$id":"4","left":null,"next":null,"right":null,"val":5},"val":2},"next":null,"right":{"$id":"5","left":null,"next":null,"right":{"$id":"6","left":null,"next":null,"right":null,"val":7},"val":3},"val":1}
Output: {"$id":"1","left":{"$id":"2","left":{"$id":"3","left":null,"next":{"$id":"4","left":null,"next":{"$id":"5","left":null,"next":null,"right":null,"val":7},"right":null,"val":5},"right":null,"val":4},"next":{"$id":"6","left":null,"next":null,"right":{"$ref":"5"},"val":3},"right":{"$ref":"4"},"val":2},"next":null,"right":{"$ref":"6"},"val":1}
Explanation: Given the above binary tree (Figure A), your function should populate each next pointer to point to its next right node, just like in Figure B.
Note:
- You may only use constant extra space.
- Recursive approach is fine, implicit stack space does not count as extra space for this problem.
这道是之前那道 Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node 的延续,原本的完全二叉树的条件不再满足,但是整体的思路还是很相似,仍然有递归和非递归的解法。我们先来看递归的解法,这里由于子树有可能残缺,故需要平行扫描父节点同层的节点,找到他们的左右子节点。代码如下:
解法一:
class Solution {
public:
Node* connect(Node* root) {
if (!root) return NULL;
Node *p = root->next;
while (p) {
if (p->left) {
p = p->left;
break;
}
if (p->right) {
p = p->right;
break;
}
p = p->next;
}
if (root->right) root->right->next = p;
if (root->left) root->left->next = root->right ? root->right : p;
connect(root->right);
connect(root->left);
return root;
}
};
对于非递归的方法,我惊喜的发现之前的方法直接就能用,完全不需要做任何修改,算法思路可参见之前的博客 Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node,代码如下:
解法二:
// Non-recursion, more than constant space
class Solution {
public:
Node* connect(Node* root) {
if (!root) return NULL;
queue<Node*> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
int len = q.size();
for (int i = ; i < len; ++i) {
Node *t = q.front(); q.pop();
if (i < len - ) t->next = q.front();
if (t->left) q.push(t->left);
if (t->right) q.push(t->right);
}
}
return root;
}
};
虽然以上的两种方法都能通过OJ,但其实它们都不符合题目的要求,题目说只能使用constant space,可是OJ却没有写专门检测space使用情况的test,那么下面贴上constant space的解法,这个解法也是用的层序遍历,只不过没有使用queue了,我们建立一个dummy结点来指向每层的首结点的前一个结点,然后指针cur用来遍历这一层,我们实际上是遍历一层,然后连下一层的next,首先从根结点开始,如果左子结点存在,那么cur的next连上左子结点,然后cur指向其next指针;如果root的右子结点存在,那么cur的next连上右子结点,然后cur指向其next指针。此时root的左右子结点都连上了,此时root向右平移一位,指向其next指针,如果此时root不存在了,说明当前层已经遍历完了,我们重置cur为dummy结点,root此时为dummy->next,即下一层的首结点,然后dummy的next指针清空,或者也可以将cur的next指针清空,因为前面已经将cur赋值为dummy了。那么现在想一想,为什么要清空?因为我们用dummy的目的就是要指到下一行的首结点的位置即dummy->next,而一旦将root赋值为dummy->next了之后,这个dummy的使命就已经完成了,必须要断开,如果不断开的话,那么假设现在root是叶结点了,那么while循环还会执行,不会进入前两个if,然后root右移赋空之后,会进入最后一个if,之前没有断开dummy->next的话,那么root又指向之前的叶结点了,死循环诞生了,跪了。所以一定要记得清空哦,呵呵哒~
这里再来说下dummy结点是怎样指向每层的首结点的前一个结点的,过程是这样的,dummy是创建出来的一个新的结点,其目的是为了指向root结点的下一层的首结点的前一个,具体是这么做到的呢,主要是靠cur指针,首先cur指向dummy,然后cur再连上root下一层的首结点,这样dummy也就连上了。然后当root层遍历完了之后,root需要往下移动一层,这样dummy结点之后连接的位置就正好赋值给root,然后cur再指向dummy,dummy之后断开,这样又回到了初始状态,以此往复就可以都连上了,代码如下:
解法三:
// Non-recursion, constant space
class Solution {
public:
Node* connect(Node* root) {
Node *dummy = new Node(, NULL, NULL, NULL), *cur = dummy, *head = root;
while (root) {
if (root->left) {
cur->next = root->left;
cur = cur->next;
}
if (root->right) {
cur->next = root->right;
cur = cur->next;
}
root = root->next;
if (!root) {
cur = dummy;
root = dummy->next;
dummy->next = NULL;
}
}
return head;
}
};
类似题目:
Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node
参考资料:
https://leetcode.com/problems/populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node-ii/
LeetCode All in One 题目讲解汇总(持续更新中...)
[LeetCode] Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node II 每个节点的右向指针之二的更多相关文章
- [LeetCode] 117. Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node II 每个节点的右向指针 II
Follow up for problem "Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node". What if the given tre ...
- 117 Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node II 每个节点的右向指针 II
这是“每个节点的右向指针”问题的进阶.如果给定的树可以是任何二叉树,该怎么办?你以前的解决方案仍然有效吗?注意: 你只能使用恒定的空间.例如,给定以下二叉树, 1 / ...
- LeetCode: Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node II 解题报告
Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node IIFollow up for problem "Populating Next Right Poin ...
- LeetCode——Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node II
Follow up for problem "Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node". What if the given tre ...
- [leetcode]Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node II @ Python
原题地址:https://oj.leetcode.com/problems/populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node-ii/ 题意: Follow up ...
- LeetCode - Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node II
题目: Follow up for problem "Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node". What if the given ...
- [LeetCode] [LeetCode] Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node II
Follow up for problem "Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node". What if the given tre ...
- leetCode 116.Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node (为节点填充右指针) 解题思路和方法
Given a binary tree struct TreeLinkNode { TreeLinkNode *left; TreeLinkNode *right; TreeLinkNode *nex ...
- [Leetcode] Populating next right pointer in each node 填充每个节点的右指针
Given a binary tree struct TreeLinkNode { TreeLinkNode *left; TreeLinkNode *right; TreeLinkNode *nex ...
随机推荐
- 从N个元素的集合中随机取m个元素的算法实现
最近有一个需求,比较简单,就是如标题所说的,从N个元素中随机取m个元素,当然这m个元素是不能存在重复的.本以为这么简单的需求,应该有现成的工具类来实现,但是几次查找居然没找到(有知道的可以推荐下哈^_ ...
- Gatekeeper Pattern 把关(守门人)模式
Protect applications and services by using a dedicated host instance that acts as a broker between c ...
- 安装完成后在命令行运行bash时报错0x80070057
在命令运行bash 提示如下: 解决方法,不启用旧版本控制台: 右键命令提示栏 打开属性,把勾选去掉如下图红色边框标识: 然后重启,就可以使用,也包括可以打开Bash on Unbuntu on Wi ...
- 利用WCF双工模式实现即时通讯
概述 WCF陆陆续续也用过多次,但每次都是浅尝辄止,以将够解决问题为王道,这几天稍闲,特寻了些资料看,昨晚尝试使用WCF的双工模式实现了一个简单的即时通讯程序,通过服务端转发实现客户端之间的通讯.这只 ...
- 何时使用静态 API
看了<AutoMapper and the Static Class Debate>,记录一下自己的看法. 在进行API设计时,静态类的使用有时会为设计者带来一些烦恼.应该将某个函数暴露为 ...
- JavaScript jQuery 中定义数组与操作及jquery数组操作
首先给大家介绍javascript jquery中定义数组与操作的相关知识,具体内容如下所示: 1.认识数组 数组就是某类数据的集合,数据类型可以是整型.字符串.甚至是对象Javascript不支持多 ...
- [转载]IIS7报500.23错误的解决方法
原文出处: 原文作者:pizibaidu 原文链接:http://pizibaidu.blog.51cto.com/1361909/1794446 背景:今天公司终端上有一个功能打开异常,报500错误 ...
- Python开发【第二篇】:Python基础知识
Python基础知识 一.初识基本数据类型 类型: int(整型) 在32位机器上,整数的位数为32位,取值范围为-2**31-2**31-1,即-2147483648-2147483647 在64位 ...
- Vector Tile
Mapbox Vector Tile Specification A specification for encoding tiled vector data. <?XML:NAMESPACE ...
- SQL初级语句
一)SQL是什么? 结构化查询语言(Structured Query Language)简称SQL, 是一种特殊目的的编程语言,是一种数据库查询和程序设计语言,用于存取数据以及查询.更新和管理关系数据 ...
