Java Map hashCode深究
【Java心得总结七】Java容器下——Map 在自己总结的这篇文章中有提到hashCode,但是没有细究,今天细究整理一下hashCode相关问题
1.hashCode与equals
首先我们都知道hashCode()和equals()函数是java基类Object的一部分,我查阅了java7文档,其中对于两者的描述如下:

解读这里对hashCode的描述,不难发现:
- 首先hashCode必须是一个整数,即Integer类型的
- 其次满足一致性,即在程序的同一次执行无论调用该函数多少次都返回相同的整数。(这里注意是程序的一次执行,而程序不同的执行间是不保证返回相同结果,因为hashcode计算方式可能会涉及到物理地址,而程序的不同执行对象在内存的位置会不同)
- 另外与equas配合,如果两个对象调用equals相同那么一定拥有相同的hashcode,然而反之,如果两个对象调用equals不相等,hashcode不一定就不同(但是这里提到尽量产生不同的hashcode有利于提高哈希表的性能,减少了冲突嘛)

这里突然发现《java编程思想》中对于equals的描述原来出自这里:
- 自反性:对任意x,x.equals(x)一定返回true
- 对称性:对任意x,y如果x.equals(y)返回true,则y.equals(y)返回true
- 传递性:对任意x,y,z如果x.equals(y)和y.equals(z)都返回true,则x.equals(z)返回true
- 一致性:对任意x,y,equals函数返回的结果无论调用多少次都一致
- 另外还有就是任意x,x.equals(null)都会返回false
- 还需要注意的就是一旦equals函数被override,那么hashcode也一定要override以保持前面的原则
2.Map对hashCode的应用
Java中HashMap的实现,我截取了部分代码如下:
代码段-1
/* HashMap实现部分代码 */
public class HashMap<K,V>
extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable
{
/**
* The default initial capacity - MUST be a power of two.
*/
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16; /**
* The maximum capacity, used if a higher value is implicitly specified
* by either of the constructors with arguments.
* MUST be a power of two <= 1<<30.
*/
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30; /**
* The load factor used when none specified in constructor.
*/
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; /**
* The table, resized as necessary. Length MUST Always be a power of two.
*/
transient Entry<K,V>[] table; /**
* The number of key-value mappings contained in this map.
*/
transient int size; /**
* The next size value at which to resize (capacity * load factor).
* @serial
*/
int threshold; /**
* The load factor for the hash table.
*
* @serial
*/
final float loadFactor; /**
* Retrieve object hash code and applies a supplemental hash function to the
* result hash, which defends against poor quality hash functions. This is
* critical because HashMap uses power-of-two length hash tables, that
* otherwise encounter collisions for hashCodes that do not differ
* in lower bits. Note: Null keys always map to hash 0, thus index 0.
*/
final int hash(Object k) {
int h = 0;
if (useAltHashing) {
if (k instanceof String) {
return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k);
}
h = hashSeed;
} h ^= k.hashCode(); // This function ensures that hashCodes that differ only by
// constant multiples at each bit position have a bounded
// number of collisions (approximately 8 at default load factor).
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
} /**
* Returns index for hash code h.
*/
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
return h & (length-1);
} /**
* Adds a new entry with the specified key, value and hash code to
* the specified bucket. It is the responsibility of this
* method to resize the table if appropriate.
*
* Subclass overrides this to alter the behavior of put method.
*/
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {
resize(2 * table.length);
hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);
} createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
} /**
* Like addEntry except that this version is used when creating entries
* as part of Map construction or "pseudo-construction" (cloning,
* deserialization). This version needn't worry about resizing the table.
*
* Subclass overrides this to alter the behavior of HashMap(Map),
* clone, and readObject.
*/
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
size++;
} /**
* Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map.
* If the map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old
* value is replaced.
*
* @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated
* @param value value to be associated with the specified key
* @return the previous value associated with <tt>key</tt>, or
* <tt>null</tt> if there was no mapping for <tt>key</tt>.
* (A <tt>null</tt> return can also indicate that the map
* previously associated <tt>null</tt> with <tt>key</tt>.)
*/
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = hash(key);
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
} modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
} /**
* Returns the entry associated with the specified key in the
* HashMap. Returns null if the HashMap contains no mapping
* for the key.
*/
final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key);
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)];
e != null;
e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
}
return null;
} /**
* Removes and returns the entry associated with the specified key
* in the HashMap. Returns null if the HashMap contains no mapping
* for this key.
*/
final Entry<K,V> removeEntryForKey(Object key) {
int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key);
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
Entry<K,V> prev = table[i];
Entry<K,V> e = prev; while (e != null) {
Entry<K,V> next = e.next;
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
modCount++;
size--;
if (prev == e)
table[i] = next;
else
prev.next = next;
e.recordRemoval(this);
return e;
}
prev = e;
e = next;
} return e;
} /**
* Rehashes the contents of this map into a new array with a
* larger capacity. This method is called automatically when the
* number of keys in this map reaches its threshold.
*
* If current capacity is MAXIMUM_CAPACITY, this method does not
* resize the map, but sets threshold to Integer.MAX_VALUE.
* This has the effect of preventing future calls.
*
* @param newCapacity the new capacity, MUST be a power of two;
* must be greater than current capacity unless current
* capacity is MAXIMUM_CAPACITY (in which case value
* is irrelevant).
*/
void resize(int newCapacity) {
Entry[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
} Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
boolean oldAltHashing = useAltHashing;
useAltHashing |= sun.misc.VM.isBooted() &&
(newCapacity >= Holder.ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD);
boolean rehash = oldAltHashing ^ useAltHashing;
transfer(newTable, rehash);
table = newTable;
threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
} /**
* Transfers all entries from current table to newTable.
*/
void transfer(Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) {
int newCapacity = newTable.length;
for (Entry<K,V> e : table) {
while(null != e) {
Entry<K,V> next = e.next;
if (rehash) {
e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key);
}
int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity);
e.next = newTable[i];
newTable[i] = e;
e = next;
}
}
}
}
代码段-2
static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> next;
int hash;
/**
* Creates new entry.
*/
Entry(int h, K k, V v, Entry<K,V> n) {
value = v;
next = n;
key = k;
hash = h;
}
}
我将HahsMap中的增删改查以及相关用到的函数截取了出来以作分析:
- 存储方式:Java中的HashMap源码是通过Entry<K,V>[]即一个Entry数组实现的,在代码26行(前面加transient是多线程问题);
- 散列函数:53行的hash函数中我们可以看出Java源代码利用HashTable中的key的hashCode来计算哈希值,我们可以将这个函数看做散列函数;
- 扩展存储空间:在代码85行addEntry函数中我们看到当发生空间不足或者冲突的时候,java会利用代码205行的代码进行扩充,扩充方法就是new一个新的Entry数组,数组大小是原有数组大小的两倍,之后再将旧的表格中的数据全部拷贝到现有新的数组中。(注:Java在性能与空间之间做了权衡,即只有当size大于某一个阈值threshold且发生了冲突的时候才会进行存储数组的扩充)
- 存储位置:在代码89行addEntry函数中,当添加一个元素时,如何确定将该Entry添加到数组的什么位置:利用了代码74行的indexFor函数,通过利用hash函数计算的哈希值与数组长度进行与运算来获得(保证了返回的值不会超出数组界限);
- 冲突解决:哈希表结构不得不提的就是冲突问题,因为我们知道几乎不可能找到一个完美的散列函数把所有数据完全分散不冲突的散列在存储序列中(除非存储空间足够大),所以冲突时必不可少的,查看代码段-2,会发现每个Entry中会有一个指针指向下一个Entry,在代码段-1中的105行,会发现createEntry函数中会将最新插入的Entry放在table中,然后让它指向原有的链表。即Java HashMap中用了最传统的当发生冲突在后面挂链表的方式来解决。
- put函数:在代码121行我们看到我们最常用的HashMap插入元素方法put,当传入要添加的key和value时,它会遍历哈希表,来确定表中是否已经有key(确定两个key是否相等就要用到equals函数,所以如果我们在利用HashMap的时候key是自定义类,那么切记要override equals函数),如果没有则新添加,如果有则覆盖原有key的value值
- getEntry函数:在代码146行getEntry函数中会再次计算出传入key的hash值,然后还是通过代码74行的indexFor函数计算该元素在数组中的位置,我们发现函数中并不是O(1)的方式取到的,需要用到一个循环,因为我们上面提到了冲突,如果在某点发生了冲突,那么就要通过遍历冲突链表来进行查找
- removeEntry函数:同样涉及到一个查找的过程,而且还涉及到如果被删除元素在冲突链表中需要修改前后元素的指针
3.散列函数/哈希函数
通过上面的分析我们也会发现如何构造一个优良的散列函数是一件非常重要的事情,我们构造散列函数的基本原则就是:尽可能的减少冲突,尽可能的将元素“散列”在存储空间中
下面是我从维基上找到的一些方法,之后如果有好的想法再做补充:
- 直接定址法:取关键字或关键字的某个线性函数值为散列地址。即
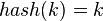 或
或 ,其中
,其中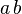 为常数(这种散列函数叫做自身函数)
为常数(这种散列函数叫做自身函数) - 数字分析法:假设关键字是以x为基的数,并且哈希表中可能出现的关键字都是事先知道的,则可取关键字的若干数位组成哈希地址。
- 平方取中法:取关键字平方后的中间几位为哈希地址。通常在选定哈希函数时不一定能知道关键字的全部情况,取其中的哪几位也不一定合适,而一个数平方后的中间几位数和数的每一位都相关,由此使随机分布的关键字得到的哈希地址也是随机的。取的位数由表长决定。
- 折叠法:将关键字分割成位数相同的几部分(最后一部分的位数可以不同),然后取这几部分的叠加和(舍去进位)作为哈希地址。
- 随机数法
- 除留余数法:取关键字被某个不大于散列表表长m的数p除后所得的余数为散列地址。即
 ,
,  。不仅可以对关键字直接取模,也可在折叠法、平方取中法等运算之后取模。对p的选择很重要,一般取素数或m,若p选择不好,容易产生碰撞。
。不仅可以对关键字直接取模,也可在折叠法、平方取中法等运算之后取模。对p的选择很重要,一般取素数或m,若p选择不好,容易产生碰撞。
而在反观Java中的散列函数:
代码段-3
/**
* A randomizing value associated with this instance that is applied to
* hash code of keys to make hash collisions harder to find.
*/
transient final int hashSeed = sun.misc.Hashing.randomHashSeed(this); /**
* Retrieve object hash code and applies a supplemental hash function to the
* result hash, which defends against poor quality hash functions. This is
* critical because HashMap uses power-of-two length hash tables, that
* otherwise encounter collisions for hashCodes that do not differ
* in lower bits. Note: Null keys always map to hash 0, thus index 0.
*/
final int hash(Object k) {
int h = 0;
if (useAltHashing) {
if (k instanceof String) {
return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k);
}
h = hashSeed;
} h ^= k.hashCode(); // This function ensures that hashCodes that differ only by
// constant multiples at each bit position have a bounded
// number of collisions (approximately 8 at default load factor).
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
}
- Java会利用随机数法产生一个hashSeed
- 利用这个随机数再与key的hashcode进行异或运算
- 然后通过各种移位异或来算出一个哈希值(这里搞不清楚什么意思,看下别的书,以后补充吧)
似乎Java是综合运用了上面几种方法来计算哈希值
上面有些地方是自己的一些理解,如果碰巧某位仁兄看到那里说的不对了还请指正~
Java Map hashCode深究的更多相关文章
- java 覆盖hashCode()深入探讨 代码演示样例
java 翻盖hashCode()深入探讨 代码演示样例 package org.rui.collection2.hashcode; /** * 覆盖hashcode * 设计HashCode时最重要 ...
- Java中 hashCode()方法详解
先来看下Object源码里hashcode方法: /** * Returns a hash code value for the object. This method is * s ...
- Java map 详解 - 用法、遍历、排序、常用API等
尊重原创: http://www.cnblogs.com/lzq198754/p/5780165.html 概要: java.util 中的集合类包含 Java 中某些最常用的类.最常用的集合类是 L ...
- Java Map 及相应的一些操作总结
Map是我们在开发的时候经常会用到的,大致有以下几个操作,其中putAll方法是针对集合而言的操作,故不再进行说明,下面请看一下常用的知识点吧,尤其是keySet和Values两个方法及相应值的获取方 ...
- Java中hashcode的理解
Java中hashcode的理解 原文链接http://blog.csdn.net/chinayuan/article/details/3345559 怎样理解hashCode的作用: 以 java. ...
- java:Map借口及其子类HashMap四
java:Map借口及其子类HashMap四 使用非系统对象作为key,使用匿名对象获取数据 在Map中可以使用匿名对象找到一个key对应的value. person: public class Ha ...
- BAT面试笔试33题:JavaList、Java Map等经典面试题!答案汇总!
JavaList面试题汇总 1.List集合:ArrayList.LinkedList.Vector等. 2.Vector是List接口下线程安全的集合. 3.List是有序的. 4.ArrayLis ...
- java集合-hashCode
hashCode 的作用 在 Java 集合中有两类,一类是 List,一类是 Set 他们之间的区别就在于 List 集合中的元素师有序的,且可以重复,而 Set 集合中元素是无序不可重复的.对于 ...
- Java中hashCode的作用
转 http://blog.csdn.net/fenglibing/article/details/8905007 Java中hashCode的作用 2013-05-09 13:54 64351人阅 ...
随机推荐
- 通过AngularJS实现前端与后台的数据对接(二)——服务(service,$http)篇
什么是服务? 服务提供了一种能在应用的整个生命周期内保持数据的方法,它能够在控制器之间进行通信,并且能保证数据的一致性. 服务是一个单例对象,在每个应用中只会被实例化一次(被$injector实例化) ...
- 轻量级“集合”迭代器-Generator
Generator是PHP 5.5加入的新语言特性.但是,它似乎并没有被很多PHP开发者广泛采用.因此,在我们了解PHP 7对Generator的改进之前,我们先通过一个简单却显而易见的例子来了解下G ...
- [Java 缓存] Java Cache之 DCache的简单应用.
前言 上次总结了下本地缓存Guava Cache的简单应用, 这次来继续说下项目中使用的DCache的简单使用. 这里分为几部分进行总结, 1)DCache介绍; 2)DCache配置及使用; 3)使 ...
- ASP.NET Core中如影随形的”依赖注入”[下]: 历数依赖注入的N种玩法
在对ASP.NET Core管道中关于依赖注入的两个核心对象(ServiceCollection和ServiceProvider)有了足够的认识之后,我们将关注的目光转移到编程层面.在ASP.NET ...
- iOS开发之Masonry框架源码深度解析
Masonry是iOS在控件布局中经常使用的一个轻量级框架,Masonry让NSLayoutConstraint使用起来更为简洁.Masonry简化了NSLayoutConstraint的使用方式,让 ...
- 【走过巨坑】android studio对于jni调用及运行闪退无法加载库的问题解决方案
相信很多小伙伴都在android开发中遇到调用jni的各种巨坑,因为我们不得不在很多地方用到第三方库so文件,然而第三方官方通常都只会给出ADT环境下的集成方式,而谷歌亲儿子android studi ...
- 深入Java虚拟机--判断对象存活状态
程序计数器,虚拟机栈和本地方法栈 首先我们先来看下垃圾回收中不会管理到的内存区域,在Java虚拟机的运行时数据区我们可以看到,程序计数器,虚拟机栈,本地方法栈这三个地方是比较特别的.这个三个部分的特点 ...
- [转载]SQL Server 2008 R2安装时选择的是windows身份验证,未选择混合身份验证的解决办法
安装过程中,SQL Server 数据库引擎设置为 Windows 身份验证模式或 SQL Server 和 Windows 身份验证模式.本文介绍如何在安装后更改安全模式. 如果在安装过程中选择&q ...
- 安卓客户端a标签长按弹框提示解决办法
昨天工作时候发现一个bug,是关于a标签的,在安卓客户端中,如果是a标签的话,长按会出现一个弹框,如图所示 是因为安卓客户端的长按触发机制,以后进行wap端开发的时候,如果用到跳转页面尽量不要用a标签 ...
- IT雇员及外包商选择:人品第一
最近,苹果iOS操作系统和智能手机爆出了一个奇葩故障,在播放特定一段五秒钟的视频时能导致手机死机.唯一的解决办法是按住电源键和Home按键进行手机的重启. 第十八届中国国际高新技术成果交易会在深圳举办 ...
