HDU 3467 Song of the Siren(圆交)

Now iSea meet a group of very powerful opponent, he needs to use this skill to draw all of the enemy's five heroes into hypnosis, and only finishing this leaves the chance to win for him. If we have already got the coordinates of the opponents, in where can Slithice sing the song to hypnotize all the opponents?
Each test case begin with an integer R (1 ≤ R ≤ 1000), indicating the range of the song, all heroes are hypnotized if the distance between Slithice is no larger than R.
The following line contains ten integers, indicating the coordinates of the five opponents, and -10000 ≤ x, y ≤ 10000.
The input terminates by end of file marker.
If no such point, output "Poor iSea, maybe 2012 is coming!"
If only one such point, output "Only the point (x, y) is for victory." (x, y) that the only point Slithice can sing.
If there are plenty of such points, output "The total possible area is X." X indicating the total area Slithice can sing.
All the floating numbers should be rounded to two fractional digits.
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std; const double PI = acos(-1.0);
const double EPS = 1e-; double Deg2Rad(double deg){return (deg * PI / 180.0);}
double Rad2Deg(double rad){return (rad * 180.0 / PI);}
double Sin(double deg){return sin(Deg2Rad(deg));}
double Cos(double deg){return cos(Deg2Rad(deg));}
double ArcSin(double val){return Rad2Deg(asin(val));}
double ArcCos(double val){return Rad2Deg(acos(val));}
double Sqrt(double val){return sqrt(val);} inline int sgn(double x) {
return (x > EPS) - (x < -EPS);
} inline double sqr(double x) {
return x * x;
} struct Point {
double x, y;
Point() {}
Point(double x, double y): x(x), y(y) {}
void read() {
scanf("%lf%lf", &x, &y);
}
double length() const {
return sqrt(x * x + y * y);
}
Point operator + (const Point &rhs) const {
return Point(x + rhs.x, y + rhs.y);
}
Point operator - (const Point &rhs) const {
return Point(x - rhs.x, y - rhs.y);
}
Point operator * (double t) const {
return Point(x * t, y * t);
}
Point operator / (double t) const {
return Point(x / t, y / t);
}
Point unit() const {
double l = length();
return *this / l;
}
double angle() const {
return atan2(y, x);
}
}; double dist(const Point &a, const Point &b) {
return (a - b).length();
} Point rotate(const Point &p, double angle, const Point &o = Point(, )) {
Point t = p - o;
double x = t.x * cos(angle) - t.y * sin(angle);
double y = t.y * cos(angle) + t.x * sin(angle);
return Point(x, y) + o;
} double cross(const Point &a, const Point &b) {
return a.x * b.y - a.y * b.x;
} double cross(const Point &sp, const Point &ep, const Point &op) {
return cross(sp - op, ep - op);
} struct Region {
double st, ed;
Region() {}
Region(double st, double ed): st(st), ed(ed) {}
}; struct Circle {
Point c;
double r;
Circle() {}
Circle(Point c, double r): c(c), r(r) {}
void read() {
c.read();
scanf("%lf", &r);
}
double area() const {
return PI * r * r;
}
bool contain(const Circle &rhs) const {
return sgn(dist(c, rhs.c) + rhs.r - r) <= ;
}
bool contain(const Point &p) const {
return sgn(dist(c, p) - r) <= ;
}
bool intersect(const Circle &rhs) const {
return sgn(dist(c, rhs.c) - r - rhs.r) < ;
}
bool tangency(const Circle &rhs) const {
return sgn(dist(c, rhs.c) - r - rhs.r) == ;
}
Point pos(double angle) const {
Point p = Point(c.x + r, c.y);
return rotate(p, angle, c);
}
}; void intersection(const Circle &cir1, const Circle &cir2, Point &p1, Point &p2) {
double l = dist(cir1.c, cir2.c);
double d = (sqr(l) - sqr(cir2.r) + sqr(cir1.r)) / ( * l);
double d2 = sqrt(sqr(cir1.r) - sqr(d));
Point mid = cir1.c + (cir2.c - cir1.c).unit() * d;
Point v = rotate(cir2.c - cir1.c, PI / ).unit() * d2;
p1 = mid + v, p2 = mid - v;
} const int MAXN = ; struct Region_vector {
int n;
Region v[];
void clear() {
n = ;
}
void add(const Region &r) {
v[n++] = r;
}
} *last, *cur; Circle cir[MAXN];
bool del[MAXN];
double r;
int n = ; double CommonArea(const Circle &A, const Circle &B) {
double area = 0.0;
const Circle & M = (A.r > B.r) ? A : B;
const Circle & N = (A.r > B.r) ? B : A;
double D = dist(M.c, N.c);
if((D < M.r + N.r) && (D > M.r - N.r)) {
double cosM = (M.r * M.r + D * D - N.r * N.r) / (2.0 * M.r * D);
double cosN = (N.r * N.r + D * D - M.r * M.r) / (2.0 * N.r * D);
double alpha = 2.0 * ArcCos(cosM);
double beta = 2.0 * ArcCos(cosN);
double TM = 0.5 * M.r * M.r * Sin(alpha);
double TN = 0.5 * N.r * N.r * Sin(beta);
double FM = (alpha / 360.0) * M.area();
double FN = (beta / 360.0) * N.area();
area = FM + FN - TM - TN;
}
else if(D <= M.r - N.r) {
area = N.area();
}
return area;
} bool isOnlyOnePoint() {
bool flag = false;
Point t;
for(int i = ; i < n; ++i)
for(int j = i + ; j < n; ++j) {
if(cir[i].tangency(cir[j])) {
flag = true;
t = (cir[i].c + cir[j].c) / ;
break;
}
}
if(!flag) return false;
for(int i = ; i < n; ++i)
if(!cir[i].contain(t)) return false;
printf("Only the point (%.2f, %.2f) is for victory.\n", t.x + EPS, t.y + EPS);
return true;
} bool solve() {
if(isOnlyOnePoint()) return true;
memset(del, , sizeof(del));
for(int i = ; i < n; ++i)
for(int j = ; j < n; ++j) {
if(del[j] || i == j) continue;
if(cir[i].contain(cir[j])) {
del[i] = true;
break;
}
}
double ans = ;
for(int i = ; i < n; ++i) {
if(del[i]) continue;
last->clear();
Point p1, p2;
for(int j = ; j < n; ++j) {
if(del[j] || i == j) continue;
if(!cir[i].intersect(cir[j])) return false;
cur->clear();
intersection(cir[i], cir[j], p1, p2);
double rs = (p2 - cir[i].c).angle(), rt = (p1 - cir[i].c).angle();
if(sgn(rs) < ) rs += * PI;
if(sgn(rt) < ) rt += * PI;
if(last->n == ) {
if(sgn(rt - rs) < ) cur->add(Region(rs, * PI)), cur->add(Region(, rt));
else cur->add(Region(rs, rt));
} else {
for(int k = ; k < last->n; ++k) {
if(sgn(rt - rs) < ) {
if(sgn(last->v[k].st - rt) >= && sgn(rs - last->v[k].ed) >= ) continue;
if(sgn(last->v[k].st - rt) < ) cur->add(Region(last->v[k].st, min(last->v[k].ed, rt)));
if(sgn(rs - last->v[k].ed) < ) cur->add(Region(max(last->v[k].st, rs), last->v[k].ed));
} else {
if(sgn(rt - last->v[k].st) <= || sgn(last->v[k].ed - rs) <= ) continue;
cur->add(Region(max(rs, last->v[k].st), min(rt, last->v[k].ed)));
}
}
}
swap(last, cur);
if(last->n == ) break;
}
for(int j = ; j < last->n; ++j) {
p1 = cir[i].pos(last->v[j].st);
p2 = cir[i].pos(last->v[j].ed);
ans += cross(p1, p2) / ;
double angle = last->v[j].ed - last->v[j].st;
ans += 0.5 * sqr(cir[i].r) * (angle - sin(angle));
}
}
if(sgn(ans) == ) return false;
printf("The total possible area is %.2f.\n", ans + EPS);
//printf("%.2f\n", CommonArea(cir[0], cir[4]));
return true;
} int main() {
last = new Region_vector, cur = new Region_vector;
while(scanf("%lf", &r) != EOF) {
Point t;
for(int i = ; i < n; ++i) {
t.read();
cir[i] = Circle(t, r);
}
if(!solve()) puts("Poor iSea, maybe 2012 is coming!");
}
}
以下转自:http://hi.baidu.com/aekdycoin/item/7618bee9f473ed3e86d9ded6
给定N 个圆形,求出其交集.
【算法分析】
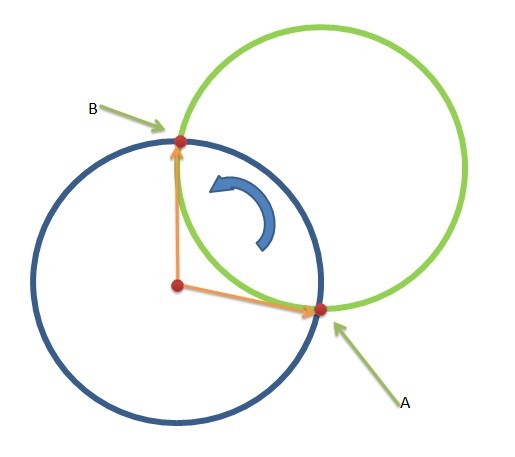
考虑上图中的蓝色圆,绿色的圆和蓝色的圆交于 A,B 2个交点 ,我们在逆时针系下考虑,那么 可以知道 对于蓝色的圆,它对应的某个 角度区间被覆盖了
假设 区间为 [A, B], 并且角度是按照 圆心到交点的 向量的 极角来定义 (为了方便,我一般都把角度转化到 [0,2pi]区间内) 那么可以知道在这种 标识情况下,可能存在以下情况
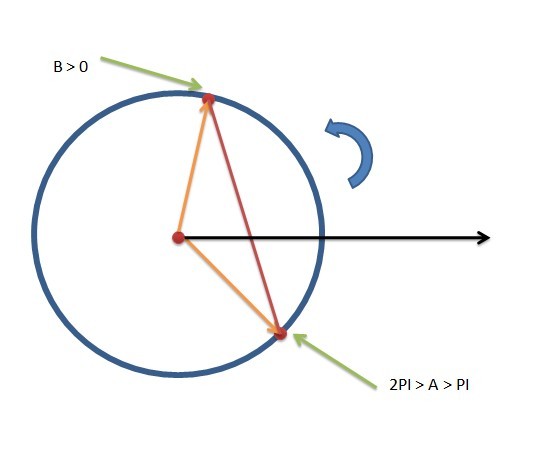
这种区间的跨度如何解决呢?实际上十分简单,只需要把[A,B] 拆成 [A, 2PI], [0,B]即可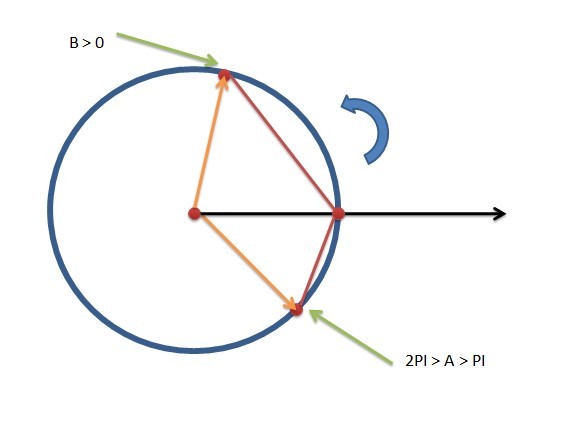
下面介绍一下 对于我们当前所求任务的实际运用( 利用上述做法)
首先 对于所给的N个圆,我们可以进行去冗杂,表现为:
(1) 去掉包含(内含 or 内切)了某些圆的大圆
(2) 去掉相同的圆
(3) 如果存在2个圆不交,则直接返回 0 (交集必然为空)
经过以上几步,可以发现得到的圆都是两两相交的。于是枚举一个圆,并对于剩下的圆和它求交点,对于所求的的交点,可以得到一个角度区间 [A,B], 当然区间如果跨越了(例如 [1.5PI, 0.5PI],注意这里是有方向的) 2PI那么需要拆 区间
可以知道,最后区间的交集必然是最后 所有圆交集的一个边界!
于是我们在得到区间的情况下累积弓形的面积
提示: 在获得区间的过程中可能存在下面的情况,请注意!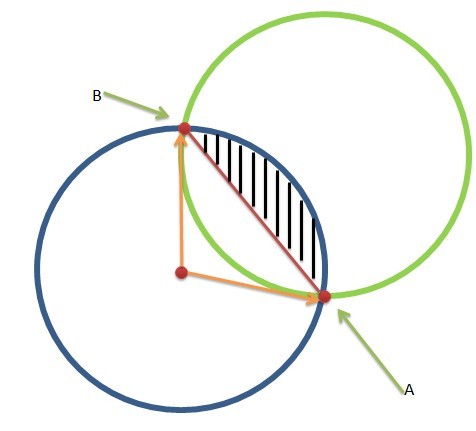
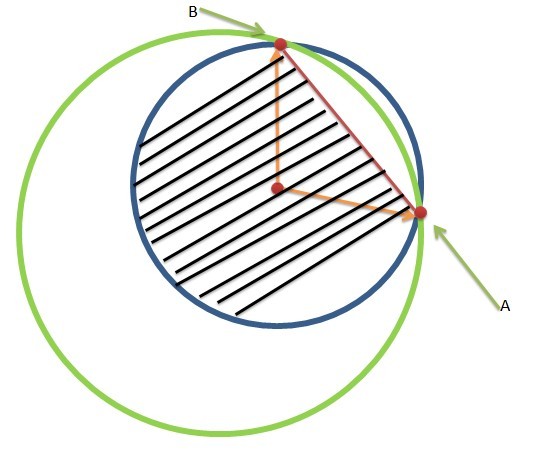
显然包括上面的2个情况,注意使用“归一化”的判断思想来获得区间! (左图是 [A,B],右图是 [B,A],注意顺序!)
之后把当前的"点" 假如S集合中
最后的答案累加上S的凸包的面积即可(XXXXX)
完全不需要再求一次凸包,获得区间以后就获得了唯一的S凸包中的一条边,那么我们只需要累加他们叉乘的和! (可以理解为一边保存边一边算面积!,代码长度缩短 10%以上)
枚举圆 O(n)
每一次求交O(n)
获得的交点区间排序,离散化,求交 O(nlogn) (至多 O(2* n)个区间)
最后的求凸包 O(nlogn) (交点不会太多,至多2*n)
所以总的复杂度为 O(n^2 log n)
【题目推荐】
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=3467
赤裸裸的圆交题目, 显然标程 被CHA ,此题数据比较水 (我至少用4个版本的错误代码AC)
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=3239
虽然没有上面那题那么赤裸裸,可是推出模型以后直接用容斥 + 求圆交……
PS.这种做法如果实现的好,那么精度是比较高的!
HDU 3467 Song of the Siren(圆交)的更多相关文章
- 计算几何(容斥原理,圆交):HDU 5120 Intersection
Matt is a big fan of logo design. Recently he falls in love with logo made up by rings. The followin ...
- HDU 3264 Open-air shopping malls ——(二分+圆交)
纯粹是为了改进牛吃草里的两圆交模板= =. 代码如下: #include <stdio.h> #include <algorithm> #include <string. ...
- hdu 1077 (圆交)
Problem - 1077 我们可以知道,当这个单位圆可以覆盖到最多的点的时候,必定最少有两个点位于这个圆的圆周上,于是就有网上众多的O(N^3)的枚举两个在圆上的点的暴搜做法. 然而这题是可以用圆 ...
- Intersection(HDU5120 + 圆交面积)
题目链接: http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5120 题目: 题意: 求两个圆环相交的面积. 思路: 两个大圆面积交-2×大圆与小圆面积交+两小圆面 ...
- CF 337D 求圆交
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/337/D 题意:就是一棵树上,有一些点被来自东方的神秘力量影响的,力量影响范围是d,为可能的力量源有几个. ...
- HDU 3467 (求五个圆相交面积) Song of the Siren
还没开始写题解我就已经内牛满面了,从晚饭搞到现在,WA得我都快哭了呢 题意: 在DotA中,你现在1V5,但是你的英雄有一个半径为r的眩晕技能,已知敌方五个英雄的坐标,问能否将该技能投放到一个合适的位 ...
- hdu 4404 Worms(多边形与圆的交)
求出爆炸点的坐标,就成了多边形与圆相交面积的模板题了... #include<algorithm> #include<iostream> #include<cstring ...
- Everything Has Changed(HDU6354+圆交+求周长)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=6354 题目: 题意:用一堆圆来切割一个圆心为原点,半径为R的圆A,问切割完毕后圆A外围剩余部分的周长( ...
- hdu4063(圆与圆交+线段与圆交+最短路)
写几何题总是提心吊胆.精度问题真心吓人. 其实思路挺简单的一道题,真是什么算法和几何double搞到一块,心里就虚虚的. 思路:求出所有圆之间的交点,然后用这些交点跑一遍最短路就可以了. Aircra ...
随机推荐
- iPhone 横竖屏切换,全屏播放的三种方式
1. 调用系统自带的强制屏幕旋转不过还得在AppDelegate中重写下面方法 - (UIInterfaceOrientationMask)application:(UIApplication *)a ...
- dataTable学习心得
1.引用文件 <link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdn.datatables.net/1.10.16/css/jquery. ...
- RPM包、YUM、system初始化进程基本知识
- ATM购物作业
一. 基本需求 模拟实现一个ATM + 购物商城程序 额度 15000或自定义 实现购物商城,买东西加入 购物车,调用信用卡接口结账 可以提现,手续费5% 支持多账户登录 支持账户间转账 记录日常消费 ...
- JSON字符串与JS对象格式转换
JSON通常用于服务器向客户端传送数据,传回来的JSON数据是字符串的形式,所以要转变为JS对象形式才方便我们使用. JSON字符串转变为JS对象:JSON.parse( ); JS对象转变为JSON ...
- ACM 2000~2002
ACM 2000 输入三个字符后,按各个字符的ASCⅡ码从小打到的顺序输出这三个字符. import java.util.Scanner; public class Lengxc {public ...
- mysql 多主多从配置,自增id解决方案
MySQL两主(多主)多从架构配置 一.角色划分 1.MySQL数据库规划 我现在的环境是:zhdy04和zhdy05已经做好了主主架构配置,现在需要的是把两台或者多台从服务器与主一一同步. 主机名 ...
- day 19 反射
1.isinstance, type, issubclass 的含义 isinstance: 判断你给对象时候是xxx类型的.(向上判断) type: 返回xxx对象的数据类型 issubclass ...
- 月薪30-50K的大数据工程师们,他们背后是如何学习的
这两天小编去了解了下大数据开发相关职位的薪资,主要有hadoop工程师,数据挖掘工程师.大数据算法工程师等,从平均薪资来看,目前大数据相关岗位的月薪均在2万以上,随着项目经验的增长工资会越来越高. ...
- 用 wait-notify 解决生产者-消费者问题
//生产者 package com.mzj.test; import java.util.Vector; import java.util.logging.Level; import java.uti ...
