18.Linux磁盘管理
1.磁盘分区工具fdisk
1. 添加一块小于2TB的磁盘进行使用,步骤如下:
- 给虚拟机添加一块新的硬盘
- 使用fdisk进行分区
- 使用mkfs进行格式化
- 使用mount进行挂载
PS: 生产分区建议,如无特殊需求直接使用整个磁盘即可,无需分区。
PS: 学习分区建议: 1P+1E(3L) 2P+1E(2L) 3P+1E(1L) (仅适用于练习)
[root@yinwucheng ~]# lsblkNAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINTsda 8:0 0 40G 0 disk├─sda1 8:1 0 1G 0 part /boot├─sda2 8:2 0 1G 0 part [SWAP]└─sda3 8:3 0 38G 0 part /sdb 8:16 0 300G 0 disksdc 8:32 0 300G 0 disksr0 11:0 1 4.3G 0 rom[root@yinwucheng ~]# fdisk /dev/sdbWelcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.23.2).Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.Be careful before using the write command.Device does not contain a recognized partition tableBuilding a new DOS disklabel with disk identifier 0x271d3013.Command (m for help): mCommand actiona toggle a bootable flag #切换分区启动标记b edit bsd disklabel #编辑sdb磁盘标签c toggle the dos compatibility flag #切换dos兼容模式d delete a partition #删除分区l list known partition types #显示分区类型m print this menu #显示帮助菜单n add a new partition #新建分区o create a new empty DOS partition table #创建新的空白分区表p print the partition table #显示分区表的信息q quit without saving changes #不保存退出s create a new empty Sun disklabel #创建新的Sun磁盘标签t change a partitions system id #修改分区ID,可以通过l查看idu change display/entry units #修改容量单位,磁柱或扇区v verify the partition table #检验分区表w write table to disk and exit #保存退出x extra functionality (experts only) #拓展功能
1.创建主分区
Command (m for help): nPartition type:p primary (0 primary, 0 extended, 4 free)e extended #扩展分区Select (default p): p #选择创建主分区Partition number (1-4, default 1): #默认创建第一个主分区First sector (2048-629145599, default 2048): #默认扇区-->回车即可Using default value 2048Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (2048-629145599, default 629145599): +150G #分配150GPartition 1 of type Linux and of size 150 GiB is set
2.fdisk创建扩展分区
Command (m for help): n #新建分区Partition type:p primary (1 primary, 0 extended, 3 free)e extendedSelect (default p): e #创建扩展分区Partition number (2-4, default 2):First sector (314574848-629145599, default 314574848):Using default value 314574848Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (314574848-629145599, default 629145599): #剩余容量都给到扩展分区Using default value 629145599Partition 2 of type Extended and of size 150 GiB is set
3.fdisk创建逻辑分区
Command (m for help): n #新建分区Partition type:p primary (1 primary, 1 extended, 2 free)l logical (numbered from 5)Select (default p): l #创建逻辑分区Adding logical partition 5First sector (314576896-629145599, default 314576896):Using default value 314576896Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (314576896-629145599, default 629145599): +50G #分配50G容量Partition 5 of type Linux and of size 50 GiB is set
4.fdisk查看分区情况,并保存
Command (m for help): p #查看创建的分区Disk /dev/sdb: 322.1 GB, 322122547200 bytes, 629145600 sectorsUnits = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytesSector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytesI/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytesDisk label type: dosDisk identifier: 0x271d3013Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System/dev/sdb1 2048 314574847 157286400 83 Linux/dev/sdb2 314574848 629145599 157285376 5 Extended/dev/sdb5 314576896 419434495 52428800 83 Linux#保存分区信息Command (m for help): wThe partition table has been altered!Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.Syncing disks.#检查磁盘是否是MBR格式[root@yinwucheng ~]# fdisk /dev/sdb -l |grep typeDisk label type: dos#安装parted, 刷新内核立即生效,无需重启[root@yinwucheng ~]# yum install parted -y[root@yinwucheng ~]# partprobe /dev/sdb
5.格式化磁盘
mkfs格式化磁盘,实质创建文件系统,文件系统类似于将房子装修成3室一厅,还是2室一厅。
#选项:-b 设定数据区块占用空间大小,目前支持1024、2048、4096 bytes每个块。-t 用来指定什么类型的文件系统,可以是ext4, xfs-i 设定inode的大小-N 设定inode数量,防止Inode数量不够导致磁盘不足#1.格式化整个磁盘[root@yinwucheng ~]# mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdbmke2fs 1.42.9 (28-Dec-2013)/dev/sdb is entire device, not just one partition!Proceed anyway? (y,n) yFilesystem label=OS type: LinuxBlock size=4096 (log=2)Fragment size=4096 (log=2)Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks19660800 inodes, 78643200 blocks3932160 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super userFirst data block=0Maximum filesystem blocks=22271754242400 block groups32768 blocks per group, 32768 fragments per group8192 inodes per groupSuperblock backups stored on blocks:32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736, 1605632, 2654208,4096000, 7962624, 11239424, 20480000, 23887872, 71663616Allocating group tables: doneWriting inode tables: doneCreating journal (32768 blocks): doneWriting superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done#2.格式化磁盘的某个分区[root@yinwucheng ~]# mkfs.xfs /dev/sdb1meta-data=/dev/sdb1 isize=512 agcount=4, agsize=9830400 blks= sectsz=512 attr=2, projid32bit=1= crc=1 finobt=0, sparse=0data = bsize=4096 blocks=39321600, imaxpct=25= sunit=0 swidth=0 blksnaming =version 2 bsize=4096 ascii-ci=0 ftype=1log =internal log bsize=4096 blocks=19200, version=2= sectsz=512 sunit=0 blks, lazy-count=1realtime =none extsz=4096 blocks=0, rtextents=0
6.使用mount挂载并使用
如果需要使用该磁盘的空间,需要准备一个空的目录作为挂载点,与该设备进行关联。

7.磁盘的基本分区Gdisk
前面我们已经了解到fdisk分区,但fdisk不支持给高于2TB的磁盘进行分区。如果有单块盘高于2TB,建议使用Gdisk进行分区。
1.使用gdisk进行磁盘分区
#1.安装gdisk分区工具[root@yinwucheng ~]# yum install gdisk -y#2.创建一个新分区,大小500MB[root@yinwucheng ~]# gdisk /dev/sdcGPT fdisk (gdisk) version 0.8.10Partition table scan:MBR: not presentBSD: not presentAPM: not presentGPT: not presentCreating new GPT entries.Command (? for help): nPartition number (1-128, default 1):First sector (34-629145566, default = 2048) or {+-}size{KMGTP}:Last sector (2048-629145566, default = 629145566) or {+-}size{KMGTP}: +500MCurrent type is 'Linux filesystem'Hex code or GUID (L to show codes, Enter = 8300):Changed type of partition to 'Linux filesystem'Command (? for help): pDisk /dev/sdc: 629145600 sectors, 300.0 GiBLogical sector size: 512 bytesDisk identifier (GUID): 0FE3F4A5-FBC9-4515-8C25-F24BB0553830Partition table holds up to 128 entriesFirst usable sector is 34, last usable sector is 629145566Partitions will be aligned on 2048-sector boundariesTotal free space is 628121533 sectors (299.5 GiB)Number Start (sector) End (sector) Size Code Name1 2048 1026047 500.0 MiB 8300 Linux filesystemCommand (? for help): w #保存分区Final checks complete. About to write GPT data. THIS WILL OVERWRITE EXISTINGPARTITIONS!!Do you want to proceed? (Y/N): YOK; writing new GUID partition table (GPT) to /dev/sdc.The operation has completed successfully.#3.创建完成后,可以尝试检查磁盘是否为gpt格式[root@yinwucheng ~]# fdisk /dev/sdc -l |grep typeWARNING: fdisk GPT support is currently new, and therefore in an experimental phase. Use at your own discretion.Disk label type: gpt#4.安装parted, 刷新内核立即生效,无需重启[root@yinwucheng ~]# yum install parted -y[root@yinwucheng ~]# partprobe /dev/sdc
2.使用mkfs进行格式化磁盘。前面已经介绍过,此处不反复介绍。
[root@yinwucheng ~]# mkfs.xfs /dev/sdc1
3.使用mount命令将某个目录挂载该分区,进行使用。
[root@yinwucheng ~]# mkdir /data2[root@yinwucheng ~]# mount /dev/sdc1 /data2
4.磁盘挂载方式Mount
前面我们已经提到过,如果需要使用磁盘的空间,需要准备一个空的目录作为挂载点,与该设备进行关联。mount主要是为文件系统指定一个访问入口。
PS: 类似我的商场没有门,那么就无法进入购买商品,此时通过mount命令可以创建一个入口。给超市安装一个门。如图:
1.通过mount进行挂载,但重启将会失效。我们称为临时生效。
选项:-t指定文件系统挂载分区-a 挂载/etc/fstab中的配置文件-o 指定挂载参数挂载/dev/sdb1至db1目录[root@yinwucheng ~]# mkdir /db1[root@yinwucheng ~]# mount -t xfs /dev/sdb1 /db1/
2.挂载的磁盘,如果不想使用可以使用umount进行卸载。
#选项: -l 强制卸载#1.卸载目录方式[root@yinwucheng ~]# umount /db1/#2.卸载设备方式[root@yinwucheng ~]# umount /dev/sdb1
3.umount不能卸载的情况
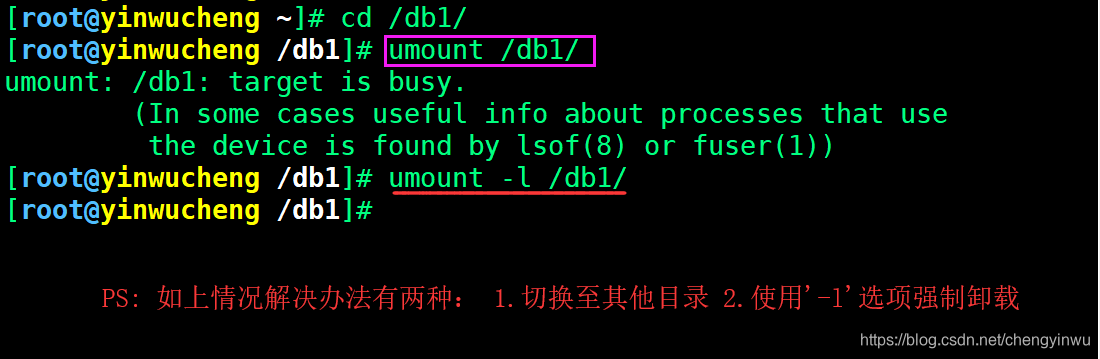
4.如果需要实现永久挂载则需要将挂载信息写入/etc/fstab配置文件中实现。
#1.使用blkid命令获取各设备的UUID[root@yinwucheng ~]# blkid |grep 'sdb1'/dev/sdb1: UUID="01353c25-0bde-49b6-a026-f805fc0de265" TYPE="xfs"#2.使用UUID挂载磁盘sdb1分区至于db1, 测试挂载[root@yinwucheng ~]# mount UUID="01353c25-0bde-49b6-a026-f805fc0de265" /db1#3.写入/etc/fstab中,实现开机自动挂载[root@yinwucheng ~]# vim /etc/fstabUUID=01353c25-0bde-49b6-a026-f805fc0de265 /db1 xfs defaults 0 0#4.加载fstab配置文件, 同时检测语法是否有错误[root@yinwucheng ~]# mount -a
5./etc/fstab配置文件编写格式
| 要挂载的设备 | 挂载点(入口) | 文件系统类型 | 挂载参数 | 是否备份 | 是否检查 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| /dev/sdb1 | /db1 | xfs | defaults | 0 | 0 |
第四列:挂载参数。挂载参数有很多,在这块我们了解即可,不必深究
| 参数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| async/sync | 是否为同步方式运行。默认async |
| user/nouser | 是否允许普通用户使用mount命令挂载。默认nouser |
| exec/noexe | 是否允许可执行文件执行。默认exec |
| suid/nosuid | 是否允许存在suid属性的文件。默认suid |
| auto/noauto | 执行mount -a 命令时,此文件系统是否被主动挂载。默认auto |
| rw/ro | 是否以只读或者读写模式进行挂载。默认rw |
| default | 具有rw,suid,dev,exec,auto,nouser,async等默认参数的设定 |
第五列:是否进行备份。通常这个参数的值为0或者1
| 选项 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| 0 | 代表不做备份 |
| 1 | 代表要每天进行备份操作 |
| 2 | 代表不定日期的进行备份操作 |
第六列:是否检验扇区:开机的过程中,系统默认会以fsck检验我们系统是否为完整
| 选项 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| 0 | 不要检验磁盘是否有坏道 |
| 1 | 检验 |
| 2 | 校验 (当1级别检验完成之后进行2级别检验) |
6.虚拟磁盘介绍SWAP
Swap分区在系统的物理内存不够时,将硬盘空间中的一部分空间释放出来,以供当前运行的程序使用。
PS: 当物理内存不够时会随机kill占用内存的进程,从而产生oom,临时使用swap可以解决。
1.创建分区,并格式化为swap分区。
[root@yinwucheng ~]# fdisk /dev/sdc ##大小分1G[root@yinwucheng ~]# mkswap /dev/sdc2 ##格式化为swapSetting up swapspace version 1, size = 1048572 KiBno label, UUID=f31cae8d-7bc8-4950-985f-94682b1a3718
2.查看当前swap分区大小,然后进行扩展和缩小
[root@yinwucheng ~]# free -mtotal used free shared buff/cache availableMem: 3931 109 3489 11 332 3574Swap: 1023 0 1023#1.扩展swap分区大小[root@yinwucheng ~]# swapon /dev/sdc2[root@yinwucheng ~]# free -mtotal used free shared buff/cache availableMem: 3931 110 3488 11 332 3574Swap: 2047 0 2047[root@yinwucheng ~]# swapon -a ##代表激活所有的swap#2.缩小swap分区大小[root@yinwucheng ~]# swapoff /dev/sdc2[root@yinwucheng ~]# free -mtotal used free shared buff/cache availableMem: 3931 110 3489 11 332 3574Swap: 1023 0 1023[root@yinwucheng ~]# swapoff -a ##代表关闭所有的swap
3.检查当前swap分区有哪些设备
[root@yinwucheng ~]# swapon -sFilename Type Size Used Priority/dev/sda2 partition 1048572 0 -2/dev/sdc2 partition 1048572 0 -3
4.如果磁盘没有过多的分区可用,也可以通过文件增加SWAP空间,本质上还是磁盘
[root@yinwucheng ~]# dd if=/dev/zero of=/opt/swap_file bs=1M count=500[root@yinwucheng ~]# chmod 0600 /opt/swap_file[root@yinwucheng ~]# mkswap -f /opt/swap_file[root@yinwucheng ~]# swapon /opt/swap_file[root@yinwucheng ~]# free -m
18.Linux磁盘管理的更多相关文章
- Linux 磁盘管理
Linux磁盘管理好坏管理直接关系到整个系统的性能问题. Linux磁盘管理常用三个命令为df.du和fdisk. df:列出文件系统的整体磁盘使用量 du:检查磁盘空间使用量 fdisk:用于磁盘分 ...
- df、du、fdisk:Linux磁盘管理三板斧的使用心得(转载)
From:http://os.51cto.com/art/201012/240726_all.htm 作者介绍:李洋(博客),博士毕业于中科院计算所.10多年来一直从事计算机网络信息安全研发工作,曾主 ...
- linux 磁盘管理学习笔记
磁盘管理命令:fdisk df du fdisk #查看硬盘分区表 df #查看分区使用情况 du #查看文件占用空间情况lvdisplay #逻辑分区 [1] 李洋.df.du.fdisk:Linu ...
- linux磁盘管理系列-软RAID的实现
1 什么是RAID RAID全称是独立磁盘冗余阵列(Redundant Array of Independent Disks),基本思想是把多个磁盘组合起来,组合一个磁盘阵列组,使得性能大幅提高. R ...
- linux磁盘管理系列-LVM的使用
LVM是什么 LVM是Linux操作系统的逻辑卷管理器. 现在有两个Linux版本的LVM,分别是 LVM1,LVM2.LVM1是一种已经被认为稳定了几年的成熟产品,LVM2 是最新最好的LVM版本. ...
- linux磁盘管理系列三:LVM的使用
磁盘管理系列 linux磁盘管理系列一:磁盘配额管理 http://www.cnblogs.com/zhaojiedi1992/p/zhaojiedi_linux_040_quota.html l ...
- linux磁盘管理系列二:软RAID的实现
磁盘管理系列 linux磁盘管理系列一:磁盘配额管理 http://www.cnblogs.com/zhaojiedi1992/p/zhaojiedi_linux_040_quota.html l ...
- linux磁盘管理系列一:磁盘配额管理
磁盘管理系列 linux磁盘管理系列一:磁盘配额管理 http://www.cnblogs.com/zhaojiedi1992/p/zhaojiedi_linux_040_quota.html l ...
- Linux磁盘管理,vi编辑器以及包管理器
一.Linux磁盘管理 Linux磁盘管理常用的三个命令为df,du,fdisk df:列出文件系统的整体磁盘使用量,利用这个命令来获取磁盘被占用了多少空间,,目前还剩下多少空间用法:df [-ahi ...
随机推荐
- 三、SpringBoot 整合mybatis 多数据源以及分库分表
前言 说实话,这章本来不打算讲的,因为配置多数据源的网上有很多类似的教程.但是最近因为项目要用到分库分表,所以让我研究一下看怎么实现.我想着上一篇博客讲了多环境的配置,不同的环境调用不同的数据库,那接 ...
- Spring Boot 多站点利用 Redis 实现 Session 共享
如何在不同站点(web服务进程)之间共享会话 Session 呢,原理很简单,就是把这个 Session 独立存储在一个地方,所有的站点都从这个地方读取 Session. 通常我们使用 Redis 来 ...
- Kylin配置Spark并构建Cube
HDP版本:2.6.4.0 Kylin版本:2.5.1 机器:三台 CentOS-7,8G 内存 Kylin 的计算引擎除了 MapReduce ,还有速度更快的 Spark ,本文就以 Kylin ...
- [Spark] 01 - What is Spark
大数据 云计算概念 课程:Spark编程基础(Python版) 大数据4V特性 Volumn, Variety, Velocity, Value. 思维方式 通过数据发现问题,再解决问题. 速度更重要 ...
- 推荐5款自学手机APP,请低调收藏,让你变得越来越优秀
现在的手机APP真的是太多了,但里面的功能同类性又非常大,很难找到实用并且符合要求的APP.接下来就为小伙伴们推荐5款非常实用的APP软件,保证你会爱不释手,轻松秒变手机达人. 1.清爽视频编辑器 一 ...
- 【Django】ajax(多对多表单)
1.前后端交互 <div class="shade hide"></div> <!--遮罩层,全屏--> <div class=" ...
- 还在用SVN的人,要不要学Git?
还在用SVN的人,要不要学Git? 提出这个问题,是因为很多小伙伴还不会使用Git. 在Git之前,是SVN的天下. SVN诞生于2001年,由于较为先进的管理方式而迅速取代了CVS. 很多80后小伙 ...
- Kurskal算法
Kruskal算法是以边为主要关注对象的最小生成树算法,是最小生成树最佳的算法实现. 其时间复杂度为O(ElogE)(E为边的数量),而Prime算法采用邻接矩阵的方法是O(V^2)(V为顶点数量). ...
- 阿里云服务器ecs配置之安装redis服务
一.介绍 Redis是当前比较热门的NOSQL系统之一,它是一个key-value存储系统.和Memcache类似,但很大程度补偿了Memcache的不足,它支持存储的value类型相对更多,包括st ...
- node学习笔记(二)流和缓冲区
内容 视频 第四章内容 菜鸟教程服务器 //复制文件 function de(x) { console.log(x); } var fs=require('fs'); fs.mkdir('stuff' ...
