java数据结构——单链表、双端链表、双向链表(Linked List)
1、继续学习单链表,终于摆脱数组的魔爪了,单链表分为数据域(前突)和引用域(指针域)(后继),还有一个头结点(就好比一辆火车,我们只关心火车头,不关心其它车厢,只需知晓车头顺藤摸瓜即可),头结点没有前突,尾结点没有后继,注意不是前仆后继。
public class Node {//包装车厢
/**
* 人无完人,如有bug,还请斧正
*/
public long data;// 数据域
public Node next;// 指针域,后指针
public Node previous;// 指针域,前指针
public Node(long value) {// 构造函数
this.data = value;
}
public void display() {
System.out.print(data + " ");
}
}
//单链表,头结点插入
public class LinkList {
private Node first;// 火车头,保存头结点的一个指向 public LinkList() {// 初始化
first = null;
} public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkList ll = new LinkList();
ll.insert(4);// 添加
ll.insert(57);
ll.insert(32);
ll.insert(68); ll.display();// 先进后出 ll.delete(32);// 删除32
System.out.println("");
System.out.println("--------");
ll.display(); System.out.println("");
System.out.println("--------"); ll.deleteFirst();// 删除头结点
ll.display(); System.out.println("");
System.out.println("--------");
Node node = ll.find(4);// 查找4
node.display();
} public Node deleteFirst() {// 删除头结点
first = first.next;// 头结点为头结点的下一个
return first;
} public Node find(long value) {// 按值查找,返回null或索引值
Node current = first;// 从头结点开始 while (current.data != value) { if (current.next == null) {// 尾结点后继为null
return null;
}
current = current.next;
}
return current;// 找到返回
} public Node delete(long value) {// 删除任意结点
Node current = first;
Node previous = first; while (current.data != value) {
if (current.next == null) {// 没有找到
return null;
}
previous = current;// 保存邻近的两个结点
current = current.next;
} if (current == first) {// 第一个结点
first = first.next;
} else {// 后面的结点
previous.next = current.next;// 上一个结点的下一个变为当前结点的下一个,当前结点删除
}
return current;// 结点类,返回结点类型
} public void insert(long value) {// 在头结点之后插入
Node node = new Node(value);// 创建新的结点
// 这里深深体会一下精妙之处,first保存着一个指向
node.next = first;// 图示第一步
first = node;// 图示第二步
} public void display() {// 显示
Node current = first;
while (current != null) {
current.display();
current = current.next;
}
}
}
单链表
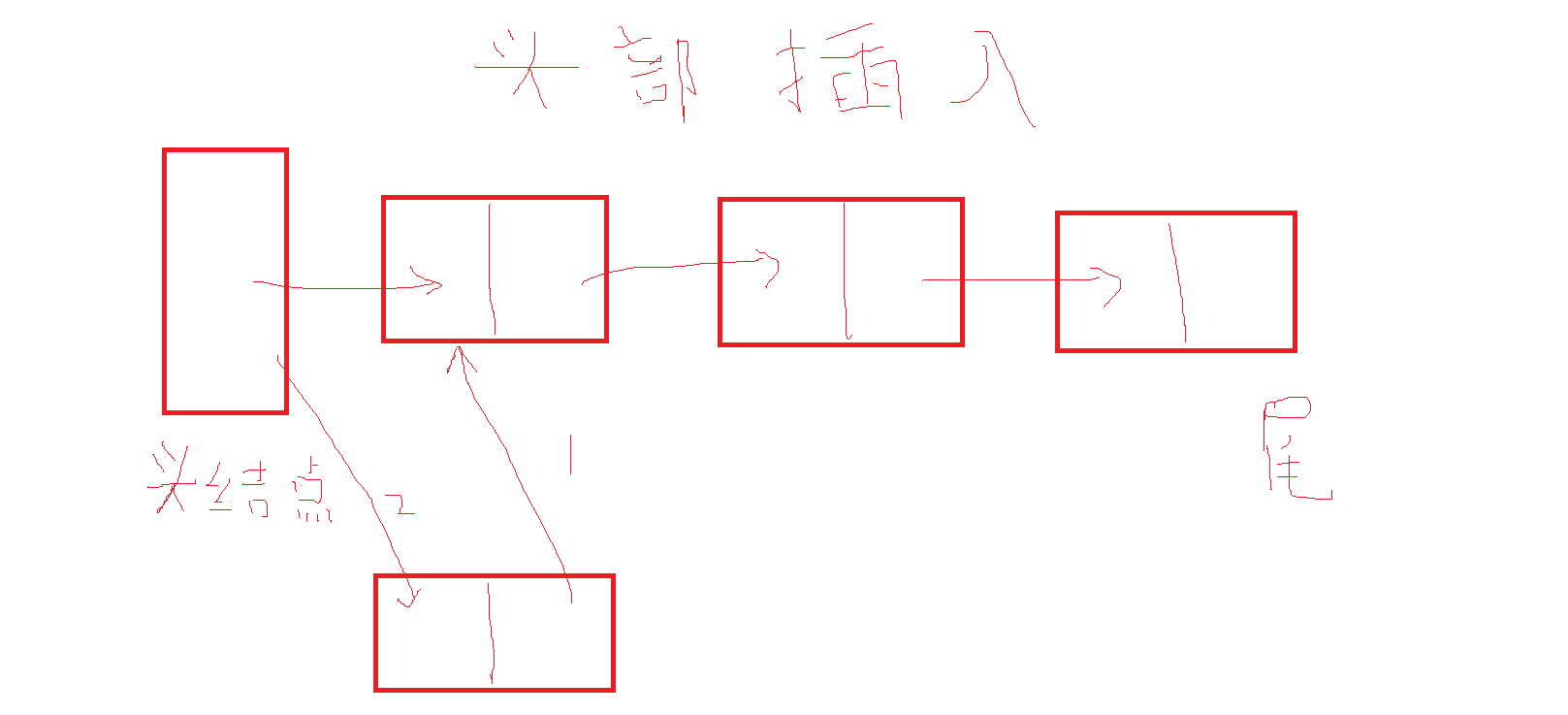
单链表时只能实现头部依次插入数据,为了弥补这个局限性,所以我们得学习双端链表,即链表中保存着对最后一个链结点引用的链表。
2、双端链表
//双端链表,头尾结点都可以插入
public class FirstLastLinkList {
private Node first;// 火车头,保存头结点的一个指向第一个node
private Node last;// 火车尾,保存头结点的一个指向最后一个node public FirstLastLinkList() {
first = null;
} public static void main(String[] args) {
FirstLastLinkList fll = new FirstLastLinkList(); fll.insertLast(26);
fll.insertLast(24);
fll.insertLast(65);
fll.insertLast(17);
fll.display();// 先进先出 System.out.println("");
System.out.println("--------"); fll.deleteFirst();
fll.display(); System.out.println("");
System.out.println("--------");
} public Node deleteFirst() {// 删除头结点
if (first.next == null) {
last = null;// 没有结点
}
first = first.next;
return first;
} public Node find(long value) {// 查找
Node current = first; while (current.data != value) { if (current.next == null) {
return null;
}
current = current.next;
}
return current;
} public Node delete(long value) {// 删除任意结点
Node current = first;
Node previous = first; while (current.data != value) {
if (current.next == null) {// 没有找到
return null;
}
previous = current;
current = current.next;
} if (current == first) {// 第一个结点
first = first.next;
} else {// 后面的结点
previous.next = current.next;
}
return current;
} public void insert(long value) {// 在头结点插入
Node node = new Node(value);// 创建新的结点
if (isEmpty()) {
last = node;
}
node.next = first;
first = node;
} public void insertLast(long value) {// 在尾结点插入
Node node = new Node(value);
if (isEmpty()) {// 为空
first = node;
} else {// 不为空
last.next = node;// 图示1
}
last = node;// 图示2
} public boolean isEmpty() {// 是否空
return first == null;
} public void display() {// 显示
Node current = first;
while (current != null) {
current.display();
current = current.next;
}
}
}
双端链表
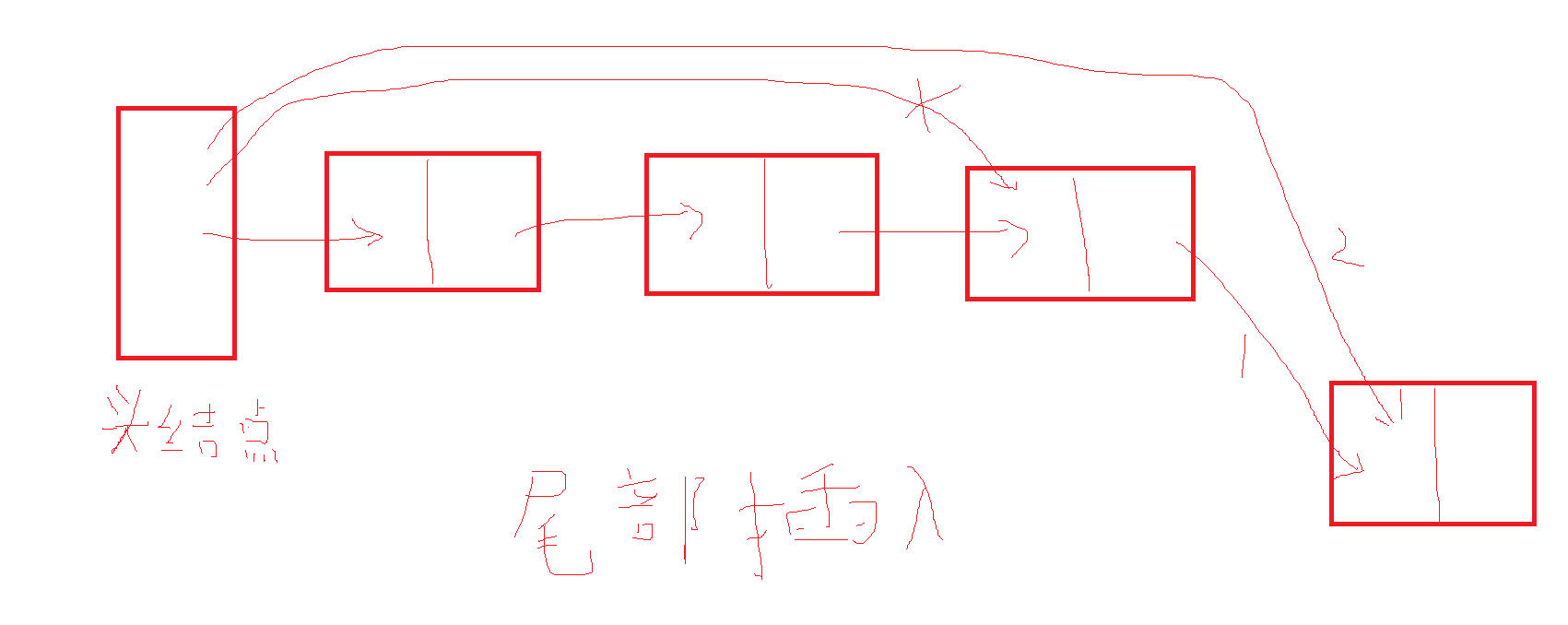
3、双向链表,Node就会多一个属性previous,每个结点除了保存对下一个结点的引用,同时还保存着对前一个结点的引用。
//双向链表,头尾结点都可以插入和删除
public class DoubleLinkList {
private Node first;// 火车头
private Node last;// 火车尾 public DoubleLinkList() {
first = null;
} public static void main(String[] args) {
DoubleLinkList dll = new DoubleLinkList();
dll.insertLast(342);
dll.insertLast(54);
dll.insertLast(24);
dll.display(); System.out.println("");
System.out.println("--------"); while (!dll.isEmpty()) {
dll.deleteFirst();
dll.display();
System.out.println("");
System.out.println("--------");
} System.out.println("");
System.out.println("--------"); System.out.println("");
System.out.println("--------");
} public Node deleteFirst() {// 从头结点开始删除
if (first.next == null) {// 判断头结点是否有下一个结点
last = null;// 没有结点
} else {
first.next.previous = null;// 设置头结点的下一个结点的previous为null
}
first = first.next;
return first;
} public Node deleteLast() {// 从尾结点开始删除
if (first.next == null) {// 头结点后面没有其它结点,当前为最后一个结点
first = null;
} else {
last.previous.next = null;// 设置尾结点的前一个结点的next为null
}
last = last.previous;
return last;
} public Node find(long value) {// 查找
Node current = first; while (current.data != value) { if (current.next == null) {
return null;
}
current = current.next;
}
return current;
} public Node delete(long value) {// 删除任意结点
Node current = first;
// 不需要临时的指针域
while (current.data != value) {
if (current.next == null) {// 没有找到
return null;
}
current = current.next;
}
if (current == first) {// 第一个结点
first = first.next;
} else {// 后面的结点
current.previous.next = current.next;
}
return current;
} public void insert(long value) {// 在头结点之后插入
Node node = new Node(value);// 创建新的结点
if (isEmpty()) {// 要对链表进行判断,为空则设置尾结点为新添加的结点
last = node;
} else {
first.previous = node;// 不为空,需要设置头结点前一个结点为新添加的结点
}
node.next = first;
first = node;
} public void insertLast(long value) {// 在尾结点之后插入
Node node = new Node(value);// 创建新的结点
if (isEmpty()) {// 为空,直接设置头结点为新添加的结点
first = node;
} else {
last.next = node;// 设置尾结点的后一个结点为新添加的结点,
}
node.previous = last;// 新添加的前一个结点为新添加的结点
last = node;
} public boolean isEmpty() {// 是否空
return first == null;
} public void display() {// 显示
Node current = first;
while (current != null) {
current.display();
current = current.next;
}
}
}
双向链表
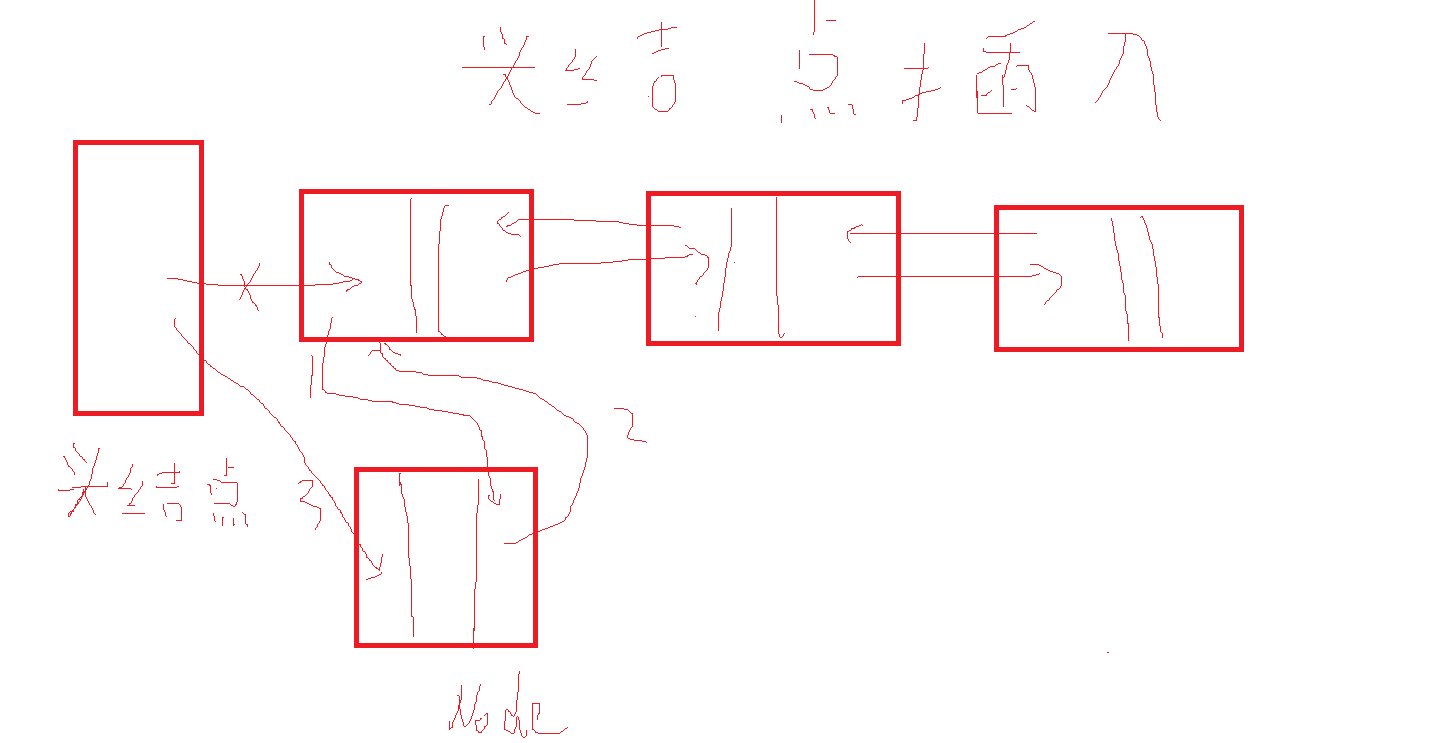
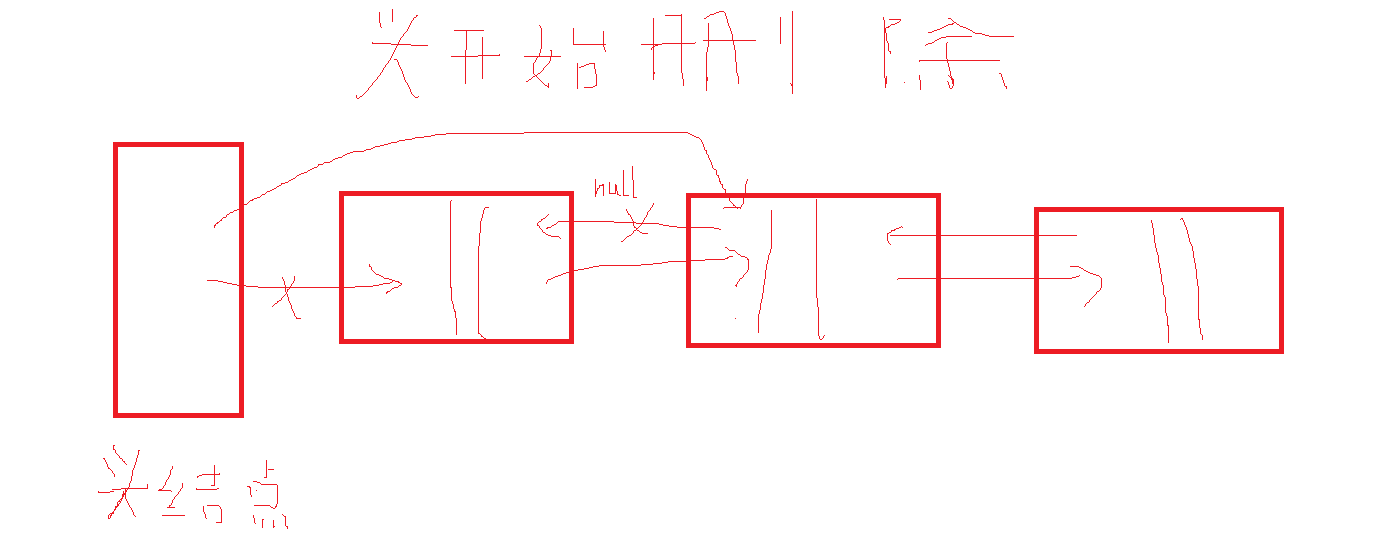
删除后JVM自动回收垃圾
java数据结构——单链表、双端链表、双向链表(Linked List)的更多相关文章
- java数据结构-11循环双端队列
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public class CircleDeque<E> { private int front; priv ...
- JAVA基础——链表结构之双端链表
双端链表:双端链表与传统链表非常相似.只是新增了一个属性-即对最后一个链结点的引用 如上图所示:由于有着对最后一个链结点的直接引用.所以双端链表比传统链表在某些方面要方便.比如在尾部插入一个链结点.双 ...
- Java单链表、双端链表、有序链表实现
单链表: insertFirst:在表头插入一个新的链接点,时间复杂度为O(1) deleteFirst:删除表头的链接点,时间复杂度为O(1) 有了这两个方法,就可以用单链表来实现一个栈了,见htt ...
- Java数据结构——用双端链表实现队列
//================================================= // File Name : LinkQueue_demo //---------------- ...
- 《Java数据结构与算法》笔记-CH5-链表-3双端链表
/** * 双端链表的实现 */ class LinkA { public long dData; public LinkA next; public LinkA(long d) { dData = ...
- java实现双端链表
PS:双端链表(持有对最后一个节点的引用,允许表尾操作与表头操作等效的功能) public class DoubleLinkedList { //节点类 static class Node { pub ...
- 队列(存储结构双端链表)--Java实现
/*用链表实现的队列--使用的是双端链表 *注意:空指针错误肯定是引用没有指向对象 * */ public class MyLinkedQueue { private MyFirstAndLastLi ...
- 双端链表--Java实现
/*双端链表--比普通链表多了一个指向最后一个节点的引用 * 特点: 链表可以进行尾巴插入--输出顺序和输入顺序一致 * 但是不可以进行尾巴删除因为没有倒数第二节点的引用 * */ public cl ...
- Java数据结构与算法(5) - ch05链表(LinkList)
双端链表与传统链表非常相似,但是它有一个新增的特性:即对最后一个链节点的引用,就像对第一个连接点的引用一样.注意与双向链表进行区别.
随机推荐
- 如何美观地打印 Python 对象?这个标准库可以简单实现
前不久,我写了一篇文章回顾 Python 中 print 的发展历史 ,提到了两条发展线索: 明线:早期的 print 语句带有 C 和 Shell 的影子,是个应用程序级的 statement,在最 ...
- Python|队列Queue
一 前言 本文算是一次队列的学习笔记,Queue 模块实现了三种类型的队列,它们的区别仅仅是队列中元素被取回的顺序.在 FIFO 队列中,先添加的任务先取回.在 LIFO 队列中,最近被添加的元素先取 ...
- Docker系列之镜像瘦身(五)
前言 本节我们来讲讲在我们在构建镜像过程中不出问题,同时使得最后所构建的镜像文件大小尽可能最小,温馨提示:文中大图均可点击放大查看详细信息. 缓存(cache) Docker的优势之一在于提供了缓存, ...
- go 学习笔记之万万没想到宠物店竟然催生出面向接口编程?
到底是要猫还是要狗 在上篇文章中,我们编撰了一则简短的小故事用于讲解了什么是面向对象的继承特性以及 Go 语言是如何实现这种继承语义的,这一节我们将继续探讨新的场景,希望能顺便讲解面向对象的接口概念. ...
- Delphi - Windows自动计划任务与ParamStr详解
Windows自动计划任务与ParamStr详解 ParamStr函数: ParamStr(1),..ParamStr(N) ParamStr(1)代表程序入口的第一个参数,同理,ParamStr(N ...
- Bootstrap如何禁止响应式布局
Bootstrap 会自动帮你针对不同的屏幕尺寸调整你的页面,使其在各个尺寸的屏幕上表现良好.下面我们列出了如何禁用这一特性,就像这个非响应式布局实例页面一样. 禁止响应式布局有如下几步: 移除 此 ...
- codeforces C. Sonya and Problem Wihtout a Legend(dp or 思维)
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/713/problem/C 题解:这题也算是挺经典的题目了,这里附上3种解法优化程度层层递进,还有这里a[i]-i<=a[i ...
- 携程PMO--小罗说敏捷之WIP限制在制品
转自本人运营的公众号“ 携程技术中心PMO”(ID:cso_pmo) WIP是什么? WIP(work in progress)指的就是工作中心在制品区.在经过部分制程之后,还没有 ...
- 常用logback.xml配置详解
选择logback的理由 ==logback==与==log4j==的简单对比一下: 1.首先,对于同样的代码路径,==logback==使用起来更快. 2.==logback==原生实现了log4j ...
- 【Redis】SpringBoot整合Redis
一.Maven依赖 <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId& ...
