常见设计模式 (python代码实现)
1.创建型模式
单例模式
单例模式(Singleton Pattern)是一种常用的软件设计模式,该模式的主要目的是确保某一个类只有一个实例存在。当你希望在整个系统中,某个类只能出现一个实例时,单例对象就能派上用场。
比如,某个服务器程序的配置信息存放在一个文件中,客户端通过一个 AppConfig 的类来读取配置文件的信息。如果在程序运行期间,有很多地方都需要使用配置文件的内容,也就是说,很多地方都需要创建 AppConfig 对象的实例,这就导致系统中存在多个 AppConfig 的实例对象,而这样会严重浪费内存资源,尤其是在配置文件内容很多的情况下。事实上,类似 AppConfig 这样的类,我们希望在程序运行期间只存在一个实例对象
class Singleton(object):
def __init__(self):
pass def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs):
if not hasattr(Singleton, "_instance"): # 反射
Singleton._instance = object.__new__(cls)
return Singleton._instance obj1 = Singleton()
obj2 = Singleton()
print(obj1, obj2) #<__main__.Singleton object at 0x004415F0> <__main__.Singleton object at 0x004415F0>
单例模式
工厂模式
工厂模式是一个在软件开发中用来创建对象的设计模式。
工厂模式包涵一个超类。这个超类提供一个抽象化的接口来创建一个特定类型的对象,而不是决定哪个对象可以被创建。
为了实现此方法,需要创建一个工厂类创建并返回。
当程序运行输入一个“类型”的时候,需要创建于此相应的对象。这就用到了工厂模式。在如此情形中,实现代码基于工厂模式,可以达到可扩展,可维护的代码。当增加一个新的类型,不在需要修改已存在的类,只增加能够产生新类型的子类。
简短的说,当以下情形可以使用工厂模式:
1.不知道用户想要创建什么样的对象
2.当你想要创建一个可扩展的关联在创建类与支持创建对象的类之间。
一个例子更能很好的理解以上的内容:
- 我们有一个基类Person ,包涵获取名字,性别的方法 。有两个子类male 和female,可以打招呼。还有一个工厂类。
- 工厂类有一个方法名getPerson有两个输入参数,名字和性别。
- 用户使用工厂类,通过调用getPerson方法。
在程序运行期间,用户传递性别给工厂,工厂创建一个与性别有关的对象。因此工厂类在运行期,决定了哪个对象应该被创建
class Person:
def __init__(self):
self.name = None
self.gender = None def getName(self):
return self.name def getGender(self):
return self.gender class Male(Person):
def __init__(self, name):
print "Hello Mr." + name class Female(Person):
def __init__(self, name):
print "Hello Miss." + name class Factory:
def getPerson(self, name, gender):
if gender == ‘M':
return Male(name)
if gender == 'F':
return Female(name) if __name__ == '__main__':
factory = Factory()
person = factory.getPerson("Chetan", "M")
工厂模式
建造者模式
将一个复杂对象的构建与它的表示分离,使得同样的构建过程可以创建不同的表示。
相关模式:思路和模板方法模式很像,模板方法是封装算法流程,对某些细节,提供接口由子类修改,建造者模式更为高层一点,将所有细节都交由子类实现
一个例子更能很好的理解以上的内容:
1. 有一个接口类,定义创建对象的方法。一个指挥员类,接受创造者对象为参数。两个创造者类,创建对象方法相同,内部创建可自定义
2.一个指挥员,两个创造者(瘦子 胖子),指挥员可以指定由哪个创造者来创造
from abc import ABCMeta, abstractmethod class Builder():
__metaclass__ = ABCMeta @abstractmethod
def draw_left_arm(self):
pass @abstractmethod
def draw_right_arm(self):
pass @abstractmethod
def draw_left_foot(self):
pass @abstractmethod
def draw_right_foot(self):
pass @abstractmethod
def draw_head(self):
pass @abstractmethod
def draw_body(self):
pass class Thin(Builder):
def draw_left_arm(self):
print '画左手' def draw_right_arm(self):
print '画右手' def draw_left_foot(self):
print '画左脚' def draw_right_foot(self):
print '画右脚' def draw_head(self):
print '画头' def draw_body(self):
print '画瘦身体' class Fat(Builder):
def draw_left_arm(self):
print '画左手' def draw_right_arm(self):
print '画右手' def draw_left_foot(self):
print '画左脚' def draw_right_foot(self):
print '画右脚' def draw_head(self):
print '画头' def draw_body(self):
print '画胖身体' class Director():
def __init__(self, person):
self.person=person def draw(self):
self.person.draw_left_arm()
self.person.draw_right_arm()
self.person.draw_left_foot()
self.person.draw_right_foot()
self.person.draw_head()
self.person.draw_body() if __name__=='__main__':
thin=Thin()
fat=Fat()
director_thin=Director(thin)
director_thin.draw()
director_fat=Director(fat)
director_fat.draw()
建造者模式
原型模式

用原型实例指定创建对象的种类,并且通过拷贝这些原型创建新的对象。
原型模式本质就是克隆对象,所以在对象初始化操作比较复杂的情况下,很实用,能大大降低耗时,提高性能,因为“不用重新初始化对象,而是动态地获得对象运行时的状态”。
浅拷贝(Shallow Copy):指对象的字段被拷贝,而字段引用的对象不会被拷贝,拷贝的对象和源对象只是名称相同,但是他们共用一个实体。
深拷贝(deep copy):对对象实例中字段引用的对象也进行拷贝。
import copy
from collections import OrderedDict class Book:
def __init__(self, name, authors, price, **rest):
'''rest的例子有:出版商、长度、标签、出版日期'''
self.name = name
self.authors = authors
self.price = price # 单位为美元
self.__dict__.update(rest) def __str__(self):
mylist = []
ordered = OrderedDict(sorted(self.__dict__.items()))
for i in ordered.keys():
mylist.append('{}: {}'.format(i, ordered[i]))
if i == 'price':
mylist.append('$')
mylist.append('\n')
return ''.join(mylist) class Prototype:
def __init__(self):
self.objects = dict() def register(self, identifier, obj):
self.objects[identifier] = obj def unregister(self, identifier):
del self.objects[identifier] def clone(self, identifier, **attr):
found = self.objects.get(identifier)
if not found:
raise ValueError('Incorrect object identifier: {}'.format(identifier))
obj = copy.deepcopy(found)
obj.__dict__.update(attr)
return obj def main():
b1 = Book('The C Programming Language', ('Brian W. Kernighan', 'Dennis M.Ritchie'),
price=118, publisher='Prentice Hall', length=228, publication_date='1978-02-22',
tags=('C', 'programming', 'algorithms', 'data structures'))
prototype = Prototype()
cid = 'k&r-first'
prototype.register(cid, b1)
b2 = prototype.clone(cid, name='The C Programming Language(ANSI)', price=48.99,
length=274, publication_date='1988-04-01', edition=2)
for i in (b1, b2):
print(i)
print("ID b1 : {} != ID b2 : {}".format(id(b1), id(b2))) if __name__ == '__main__':
main() """
>>> python3 prototype.py
authors: ('Brian W. Kernighan', 'Dennis M. Ritchie')
length: 228
name: The C Programming Language
price: 118$
publication_date: 1978-02-22
publisher: Prentice Hall
tags: ('C', 'programming', 'algorithms', 'data structures') authors: ('Brian W. Kernighan', 'Dennis M. Ritchie')
edition: 2
length: 274
name: The C Programming Language (ANSI)
price: 48.99$
publication_date: 1988-04-01
publisher: Prentice Hall
tags: ('C', 'programming', 'algorithms', 'data structures') ID b1 : 140004970829304 != ID b2 : 140004970829472
"""
原型模式
2.结构型模式
适配器模式
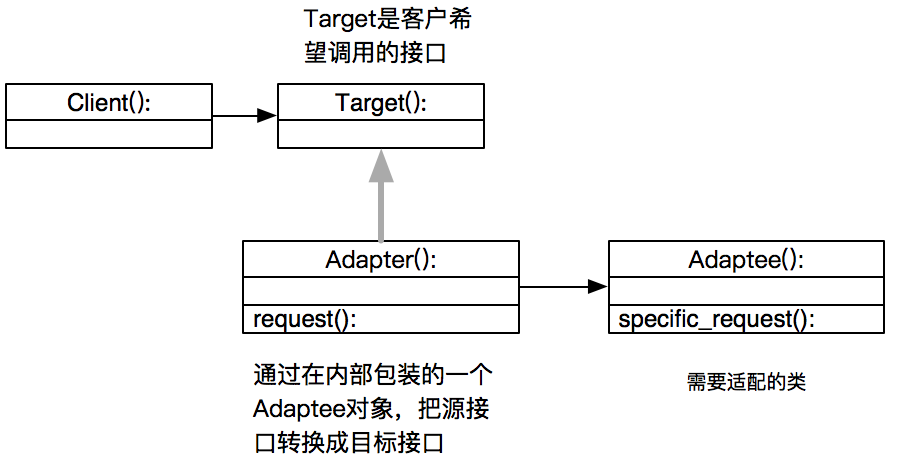
所谓适配器模式是指是一种接口适配技术,它可通过某个类来使用另一个接口与之不兼容的类,运用此模式,两个类的接口都无需改动。
适配器模式主要应用于希望复用一些现存的类,但是接口又与复用环境要求不一致的情况,比如在需要对早期代码复用一些功能等应用上很有实际价值。
解释二:
适配器模式(Adapter Pattern):将一个类的接口转换成为客户希望的另外一个接口.Adapter Pattern使得原本由于接口不兼容而不能一起工作的那些类可以一起工作.
应用场景:系统数据和行为都正确,但接口不符合时,目的是使控制范围之外的一个原有对象与某个接口匹配,适配器模式主要应用于希望复用一些现存的类,但接口又与复用环境不一致的情况
class Target(object):
def request(self):
print "普通请求" class Adaptee(object): def specific_request(self):
print "特殊请求" class Adapter(Target): def __init__(self):
self.adaptee = Adaptee() def request(self):
self.adaptee.specific_request() if __name__ == "__main__":
target = Adapter()
target.request()
适配器模式
修饰器模式
该模式虽名为修饰器,但这并不意味着它应该只用于让产品看起来更漂亮。修饰器模式通常用于扩展一个对象的功能。这类扩展的实际例子有,给枪加一个消音器、使用不同的照相机镜头
import functools
def memoize(fn):
known = dict()
@functools.wraps(fn)
def memoizer(*args):
if args not in known:
known[args] = fn(*args)
return known[args]
return memoizer
@memoize
def nsum(n):
'''返回前n个数字的和'''
assert(n >= 0), 'n must be >= 0'
return 0 if n == 0 else n + nsum(n-1)
@memoize
def fibonacci(n):
'''返回斐波那契数列的第n个数'''
assert(n >= 0), 'n must be >= 0'
return n if n in (0, 1) else fibonacci(n-1) + fibonacci(n-2)
if __name__ == '__main__':
from timeit import Timer
measure = [ {'exec':'fibonacci(100)', 'import':'fibonacci',
'func':fibonacci},{'exec':'nsum(200)', 'import':'nsum',
'func':nsum} ]
for m in measure:
t = Timer('{}'.format(m['exec']), 'from __main__ import{}'.format(m['import']))
print('name: {}, doc: {}, executing: {}, time:{}'.format(m['func'].__name__, m['func'].__doc__,m['exec'], t.timeit())) """
>>> python3 mymath.py
name: fibonacci, doc: Returns the nth number of the Fibonacci
sequence, executing: fibonacci(100), time: 0.4169441329995607
name: nsum, doc: Returns the sum of the first n numbers,
executing: nsum(200), time: 0.4160157349997462
"""
修饰器模式
外观模式
外观模式又叫做门面模式。在面向对象程序设计中,解耦是一种推崇的理念。但事实上由于某些系统中过于复杂,从而增加了客户端与子系统之间的耦合度。例如:在家观看多媒体影院时,更希望按下一个按钮就能实现影碟机,电视,音响的协同工作,而不是说每个机器都要操作一遍。这种情况下可以采用外观模式,即引入一个类对子系统进行包装,让客户端与其进行交互。
外观模式(Facade Pattern):外部与一个子系统的通信必须通过一个统一的外观对象进行,为子系统中的一组接口提供一个一致的界面,外观模式定义了一个高层接口,这个接口使得这一子系统更加容易使用。外观模式又称为门面模式,它是一种对象结构型模式。
from enum import Enum
from abc import ABCMeta, abstractmethod State = Enum('State', 'new running sleeping restart zombie') class User:
pass class Process:
pass class File:
pass class Server(metaclass=ABCMeta):
@abstractmethod
def __init__(self):
pass def __str__(self):
return self.name @abstractmethod
def boot(self):
pass @abstractmethod
def kill(self, restart=True):
pass class FileServer(Server):
def __init__(self):
'''初始化文件服务进程要求的操作'''
self.name = 'FileServer'
self.state = State.new def boot(self):
print('booting the {}'.format(self))
'''启动文件服务进程要求的操作'''
self.state = State.running def kill(self, restart=True):
print('Killing {}'.format(self))
'''终止文件服务进程要求的操作'''
self.state = State.restart if restart else State.zombie def create_file(self, user, name, permissions):
'''检查访问权限的有效性、用户权限等'''
print("trying to create the file '{}' for user '{}' with permissions{}".format(name, user, permissions)) class ProcessServer(Server):
def __init__(self):
'''初始化进程服务进程要求的操作'''
self.name = 'ProcessServer'
self.state = State.new def boot(self):
print('booting the {}'.format(self))
'''启动进程服务进程要求的操作'''
self.state = State.running def kill(self, restart=True):
print('Killing {}'.format(self))
'''终止进程服务进程要求的操作'''
self.state = State.restart if restart else State.zombie def create_process(self, user, name):
'''检查用户权限和生成PID等'''
print("trying to create the process '{}' for user '{}'".format(name, user)) class WindowServer:
pass class NetworkServer:
pass class OperatingSystem:
'''外观''' def __init__(self):
self.fs = FileServer()
self.ps = ProcessServer() def start(self):
[i.boot() for i in (self.fs, self.ps)] def create_file(self, user, name, permissions):
return self.fs.create_file(user, name, permissions) def create_process(self, user, name):
return self.ps.create_process(user, name) def main():
os = OperatingSystem()
os.start()
os.create_file('foo', 'hello', '-rw-r-r')
os.create_process('bar', 'ls /tmp') if __name__ == '__main__':
main() """
booting the FileServer
booting the ProcessServer
trying to create the file 'hello' for user 'foo' with permissions-rw-r-r
trying to create the process 'ls /tmp' for user 'bar'
"""
外观模式
享元模式
运用共享技术有效地支持大量细粒度的对象。
内部状态:享元对象中不会随环境改变而改变的共享部分。比如围棋棋子的颜色。
外部状态:随环境改变而改变、不可以共享的状态就是外部状态。比如围棋棋子的位置。
应用场景:程序中使用了大量的对象,如果删除对象的外部状态,可以用相对较少的共享对象取代很多组对象,就可以考虑使用享元模式。
import random
from enum import Enum
TreeType = Enum('TreeType', 'apple_tree cherry_tree peach_tree') class Tree:
pool = dict()
def __new__(cls, tree_type):
obj = cls.pool.get(tree_type, None)
if not obj:
obj = object.__new__(cls)
cls.pool[tree_type] = obj
obj.tree_type = tree_type
return obj def render(self, age, x, y):
print('render a tree of type {} and age {} at ({}, {})'.format(self.tree_type, age, x, y)) def main():
rnd = random.Random()
age_min, age_max = 1, 30 # 单位为年
min_point, max_point = 0, 100
tree_counter = 0
for _ in range(10):
t1 = Tree(TreeType.apple_tree)
t1.render(rnd.randint(age_min, age_max),
rnd.randint(min_point, max_point),
rnd.randint(min_point, max_point))
tree_counter += 1
for _ in range(3):
t2 = Tree(TreeType.cherry_tree)
t2.render(rnd.randint(age_min, age_max),
rnd.randint(min_point, max_point),
rnd.randint(min_point, max_point))
tree_counter += 1
for _ in range(5):
t3 = Tree(TreeType.peach_tree)
t3.render(rnd.randint(age_min, age_max),
rnd.randint(min_point, max_point),
rnd.randint(min_point, max_point))
tree_counter += 1 print('trees rendered: {}'.format(tree_counter))
print('trees actually created: {}'.format(len(Tree.pool)))
t4 = Tree(TreeType.cherry_tree)
t5 = Tree(TreeType.cherry_tree)
t6 = Tree(TreeType.apple_tree)
print('{} == {}? {}'.format(id(t4), id(t5), id(t4) == id(t5)))
print('{} == {}? {}'.format(id(t5), id(t6), id(t5) == id(t6))) main() """
render a tree of type TreeType.apple_tree and age 28 at (29, 80)
render a tree of type TreeType.apple_tree and age 28 at (38, 94)
render a tree of type TreeType.apple_tree and age 16 at (82, 84)
render a tree of type TreeType.apple_tree and age 18 at (43, 98)
render a tree of type TreeType.apple_tree and age 2 at (84, 72)
render a tree of type TreeType.apple_tree and age 16 at (89, 29)
render a tree of type TreeType.apple_tree and age 30 at (91, 53)
render a tree of type TreeType.apple_tree and age 12 at (92, 73)
render a tree of type TreeType.apple_tree and age 3 at (11, 54)
render a tree of type TreeType.apple_tree and age 1 at (34, 59)
render a tree of type TreeType.cherry_tree and age 11 at (67, 72)
render a tree of type TreeType.cherry_tree and age 27 at (65, 81)
render a tree of type TreeType.cherry_tree and age 27 at (10, 48)
render a tree of type TreeType.peach_tree and age 11 at (35, 38)
render a tree of type TreeType.peach_tree and age 3 at (58, 83)
render a tree of type TreeType.peach_tree and age 18 at (73, 50)
render a tree of type TreeType.peach_tree and age 24 at (94, 3)
render a tree of type TreeType.peach_tree and age 4 at (2, 9)
trees rendered: 18
trees actually created: 3
4866032 == 4866032? True
4866032 == 4742704? False """
享元模式
模型-视图-控制器模式
代理模式
3.行为型模式
责任链模式
命令模式
解释器模式
观察者模式
状态模式
策略模式
模板模式
常见设计模式 (python代码实现)的更多相关文章
- 研磨设计模式解析及python代码实现——(二)外观模式(Facade)
一.外观模式定义 为子系统中的一组接口提供一个一致的界面,使得此子系统更加容易使用. 二.书中python代码实现 class AModuleApi: def testA(self): pass cl ...
- Python代码样例列表
扫描左上角二维码,关注公众账号 数字货币量化投资,回复“1279”,获取以下600个Python经典例子源码 ├─algorithm│ Python用户推荐系统曼哈顿算法实现.py│ ...
- 学习 27 门编程语言的长处,提升你的 Python 代码水平
Python猫注:Python 语言诞生 30 年了,如今的发展势头可谓如火如荼,这很大程度上得益于其易学易用的优秀设计,而不可否认的是,Python 从其它语言中偷师了不少.本文作者是一名资深的核心 ...
- [转] Python 代码性能优化技巧
选择了脚本语言就要忍受其速度,这句话在某种程度上说明了 python 作为脚本的一个不足之处,那就是执行效率和性能不够理想,特别是在 performance 较差的机器上,因此有必要进行一定的代码优化 ...
- Python代码性能优化技巧
摘要:代码优化能够让程序运行更快,可以提高程序的执行效率等,对于一名软件开发人员来说,如何优化代码,从哪里入手进行优化?这些都是他们十分关心的问题.本文着重讲了如何优化Python代码,看完一定会让你 ...
- Python 代码性能优化技巧(转)
原文:Python 代码性能优化技巧 Python 代码优化常见技巧 代码优化能够让程序运行更快,它是在不改变程序运行结果的情况下使得程序的运行效率更高,根据 80/20 原则,实现程序的重构.优化. ...
- Python 代码性能优化技巧
选择了脚本语言就要忍受其速度,这句话在某种程度上说明了 python 作为脚本的一个不足之处,那就是执行效率和性能不够理想,特别是在 performance 较差的机器上,因此有必要进行一定的代码优化 ...
- 六行python代码的爱心曲线
前些日子在做绩效体系的时候,遇到了一件囧事,居然忘记怎样在Excel上拟合正态分布了,尽管在第二天重新拾起了Excel中那几个常见的函数和图像的做法,还是十分的惭愧.实际上,当时有效偏颇了,忽略了问题 ...
- 200行Python代码实现2048
200行Python代码实现2048 一.实验说明 1. 环境登录 无需密码自动登录,系统用户名shiyanlou 2. 环境介绍 本实验环境采用带桌面的Ubuntu Linux环境,实验中会用到桌面 ...
随机推荐
- redis 系列19 客户端
一. 概述 Redis服务器是可以与多个客户端建立网络连接,每个客户端可以向服务器发送命令请求,而服务器则接收并处理客户端发送的命令请求,并向客户端返回命令回复.通过使用I/O多路复用技术实现的文件事 ...
- 2016年,总结篇 续 如何从 JQ 转到 VueJS 开发(一)
接着 2016 年的总结,我们来看看 2016年 国内最火且没有之一的前端MVVM 框架 VueJs 虽然 到写文章的这个时间点,VueJs已经发布了 2.1.x 了, 但是对于很多 Vuejs 的初 ...
- SpringBoot入门教程(十九)@ControllerAdvice+@ExceptionHandler全局捕获Controller异常
在spring 3.2中,新增了@ControllerAdvice 注解,可以用于定义@ExceptionHandler.@InitBinder.@ModelAttribute,并应用到所有@Requ ...
- 前端笔记之JavaScript(四)关于函数、作用域、闭包那点事
一.自定义函数function 函数就是功能.方法的封装.函数能够帮我们封装一段程序代码,这一段代码会具备某一项功能,函数在执行时,封装的这一段代码都会执行一次,实现某种功能.而且,函数可以多次调用. ...
- tensorflow机器学习模型的跨平台上线
在用PMML实现机器学习模型的跨平台上线中,我们讨论了使用PMML文件来实现跨平台模型上线的方法,这个方法当然也适用于tensorflow生成的模型,但是由于tensorflow模型往往较大,使用无法 ...
- centos7安装xfce桌面
用了centos自带的gnome桌面 太重了 启动超慢 内存占用近2G 因此打算换一个轻量级的桌面xfce 先安装桌面协议yum groupinstall "X Window system& ...
- Python迭代和解析(2):迭代初探
解析.迭代和生成系列文章:https://www.cnblogs.com/f-ck-need-u/p/9832640.html 在Python中支持两种循环格式:while和for.这两种循环的类型不 ...
- 第5章 支持和咨询选项 - Identity Server 4 中文文档(v1.0.0)
我们为IdentityServer提供了多种免费和商业支持和咨询选项. 5.1 免费支持 免费支持是基于社区的,并使用公共论坛 5.1.1 StackOverflow StackOverflow 社区 ...
- bootstrap之弹出框
1.模态框的核心在于 首先声明一个 模态框,标记其位置 <div class="modal fade" id="myModal" tabindex=&qu ...
- 配置多个 git 账号的 ssh密钥
背景 在工作中,我们通常会以 ssh 的方式配置公司的 git 账号,但是平时也会使用 github 管理自己的项目.因此,我们需要为自己的 github 创建一个新的 git 账号,这就需要生成新的 ...
