iOS学习笔记36-Masonry自动布局
一、Masonry介绍
之前我们在屏幕适配的章节中学习过AutoLayout的使用,但那都是在可视化界面上进行添加约束完成的,我们很多时候都需要在代码中使用AutoLayout约束,苹果也为我们提供了实现,使用NSLayoutConstraint类表示约束,但使用起来比较复杂,代码量比较大,例如创建一个约束的方法:
+ (id)constraintWithItem:(id)view1 /* 一个UIView */
attribute:(NSLayoutAttribute)attribute1 /* 属性 */
relatedBy:(NSLayoutRelation)relation /* 关系 */
toItem:(id)view2 /* 另一个UIView */
attribute:(NSLayoutAttribute)attribute2 /* 属性 */
multiplier:(CGFloat)multiplier /* 倍数 */
constant:(CGFloat)constant; /* 偏移 */如果约束一多,这个方法调用次数就会越多,代码就会变得很长。
实际上我们可以使用第三方框架Masonry,该框架是一个轻量级的布局框架,封装了AutoLayout,拥有自己的描述语法,采用更优雅的链式语法,简洁明了,并具有高可读性。
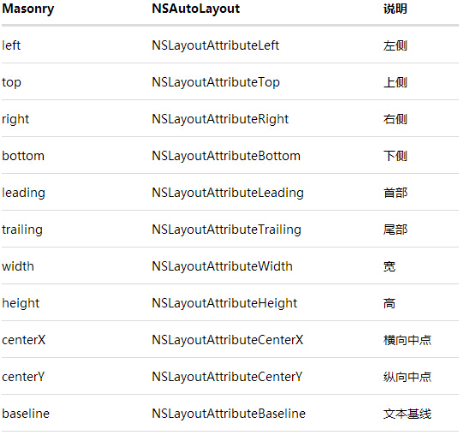
Masonry基本支持AutoLayout的所有属性:
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *left;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *top;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *right;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *bottom;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *leading;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *trailing;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *width;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *height;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *centerX;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *centerY;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *baseline;这些属性与NSLayoutAttrubute的对照表如下:
二、Masonry使用
Masonry的大部分方法都为UIView实现了分类,使我们可以十分简单的使用
下面是Masonry添加约束的方法:
/* 添加新约束,只负责新增约束,不能同时存在两条针对于同一对象的约束,否则会报错 */
- (NSArray *)mas_makeConstraints:(void(^)(MASConstraintMaker *make))block;
/* 更新原有的约束,针对上面的情况,会更新在block中出现的约束,不会导致出现两个相同约束的情况 */
- (NSArray *)mas_updateConstraints:(void(^)(MASConstraintMaker *make))block;
/* 删除之前约束,重新添加约束,会清除之前的所有约束,仅保留最新的约束 */
- (NSArray *)mas_remakeConstraints:(void(^)(MASConstraintMaker *make))block;
- 上面三个方法不仅只有
UIView可以调用,存有UIView的NSArray数组也可以调用,表示遍历数组中所有UIView进行调用
下面是Block中使用的常见约束语法,[attribute]表示属性,[value]表示值:
/*
属性attribute可以连用,比如top.right.bottom.left
加mas_前缀和没有mas_前缀效果差不多,只是加mas_前缀会对参数装箱,
参数有结构体的时候,需要使用mas_前缀,没有mas_前缀的参数必须为对象
*/
/* 数值约束,top对应NSInteger,center对应NSPoint,size对应NSSize */
make.[attribute].mas_equalTo([value]);
/* 等于约束,两个view之间比较,注意:没有other.edges的属性,edges对应otherView */
make.[attribute].equalTo(otherView.[attribute]);
/* 大于等于约束,两个view之间比较 */
make.[attribute].greaterThanOrEqualTo(otherView.[attribute]);
/* 小于等于约束,两个view之间比较 */
make.[attribute].lessThanOrEqualTo(otherView.[attribute]);
/* 偏移约束 */
make.[attribute].equalTo(otherView.[attribute]).offset([value]);
/* 边界约束,有上、下、左、右边界 */
make.edges.equalTo(otherView).insets(UIEdgeInsetsMake([topValue],[leftValue],[bottomValue],[rightValue]));
/* Margin约束 */
make.[attribute].equalTo(otherView.[attribute]Margin);注意:
添加约束前,必须先把
UIView添加到父视图中,否则会闪退
下面我们通过几个实例来理解:
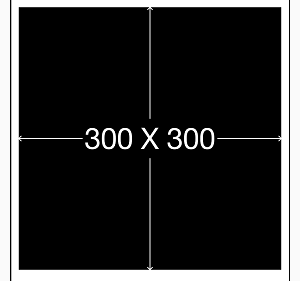
1. 实例一[基础]:居中显示一个view
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
UIView *sv = [[UIView alloc] init];
sv.backgroundColor = [UIColor blackColor];
//一定要先将view添加到superView上,否则会出错
[self.view addSubview:sv];
//Masonry的autolayout添加约束
__weak ViewController *weakSelf = self;
[sv mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.center.equalTo(weakSelf.view);//将sv居中
make.size.mas_equalTo(CGSizeMake(300, 300));//将sv的尺寸设置为(300,300)
}];
}
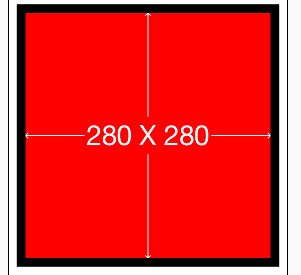
2. 实例二[初级]:让一个view略小于其superView(边距为10)
UIView *sv = [[UIView alloc] init];
sv.backgroundColor = [UIColor blackColor];
//一定要先将view添加到superView上,否则会出错
[self.view addSubview:sv];
//Masonry的autolayout添加约束
__weak ViewController *weakSelf = self;
[sv mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.center.equalTo(weakSelf.view);//将sv居中
make.size.mas_equalTo(CGSizeMake(300, 300));//将sv的尺寸设置为(300,300)
}];
UIView *sv1 = [[UIView alloc] init];
sv1.backgroundColor = [UIColor redColor];
//一定要先将view添加到superView上,否则会出错
[sv addSubview:sv1];
//Masonry的autolayout添加约束
[sv1 mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.edges.equalTo(sv).with.insets(UIEdgeInsetsMake(10, 10, 10, 10));
/* 等价于
make.top.equalTo(sv).with.offset(10);
make.left.equalTo(sv).with.offset(10);
make.bottom.equalTo(sv).with.offset(-10);
make.right.equalTo(sv).with.offset(-10);
*/
/* 也等价于
make.top.left.bottom.and.right.equalTo(sv).with.insets(UIEdgeInsetsMake(10, 10, 10, 10));
*/
}];
实际上and和with这两个方法什么事情都没做:
- (MASConstraint *)with {
return self;
}
- (MASConstraint *)and {
return self;
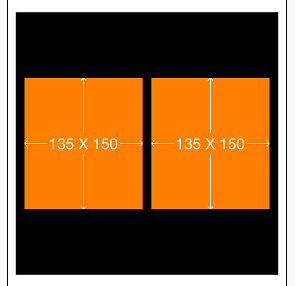
}3. 实例三[初级]:让两个高度为150的view垂直居中且等宽且等间隔排列,间隔为10(自动计算其宽度)
UIView *sv = [[UIView alloc] init];
sv.backgroundColor = [UIColor blackColor];
//一定要先将view添加到superView上,否则会出错
[self.view addSubview:sv];
//Masonry的autolayout添加约束
__weak ViewController *weakSelf = self;
[sv mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.center.equalTo(weakSelf.view);//将sv居中
make.size.mas_equalTo(CGSizeMake(300, 300));//将sv的尺寸设置为(300,300)
}];
int padding1 = 10;
UIView *leftView = [[UIView alloc] init];
leftView.backgroundColor = [UIColor orangeColor];
[sv addSubview:leftView];
UIView *rightView = [[UIView alloc] init];
rightView.backgroundColor = [UIColor orangeColor];
[sv addSubview:rightView];
//Masonry的autolayout添加约束
[leftView mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.centerY.mas_equalTo(sv.mas_centerY);//中心Y轴和sv中心Y轴相等
make.left.equalTo(sv.mas_left).with.offset(padding1);//左边距离sv的左边界10
make.right.equalTo(rightView.mas_left).with.offset(-padding1);//右边距离rightView的左边界-10
make.height.mas_equalTo(@150);//高度150
make.width.equalTo(rightView);//宽度等于rightView
}];
[rightView mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.centerY.mas_equalTo(sv.mas_centerY);//中心Y轴和sv中心Y轴相等
make.left.equalTo(leftView.mas_right).with.offset(padding1);//左边距离leftView的右边界10
make.right.equalTo(sv.mas_right).with.offset(-padding1);//右边距离sv的右边界-10
make.height.mas_equalTo(@150);//高度150
make.width.equalTo(leftView);//宽度等于leftView
}];
4. 实例四[中级]:在UIScrollView顺序排列一些view并自动计算contentSize
UIView *sv = [[UIView alloc] init];
sv.backgroundColor = [UIColor blackColor];
//一定要先将view添加到superView上,否则会出错
[self.view addSubview:sv];
//Masonry的autolayout添加约束
__weak ViewController *weakSelf = self;
[sv mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.center.equalTo(weakSelf.view);//将sv居中
make.size.mas_equalTo(CGSizeMake(300, 300));//将sv的尺寸设置为(300,300)
}];
/* 创建ScrollView */
UIScrollView *scrollView = [[UIScrollView alloc] init];
scrollView.backgroundColor = [UIColor whiteColor];
[sv addSubView:scrollView];
[scrollView mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
//设置边界约束
make.edges.equalTo(sv).with.insets(UIEdgeInsetsMake(5,5,5,5));
}];
//创建ScrollView子视图容器视图
UIView *container = [[UIView alloc] init];
[scrollView addSubView:container];
//添加container约束
[container mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.edges.equalTo(scrollView);//边界紧贴ScrollView边界
make.width.equalTo(scrollView);//宽度和ScrollView相等
}];
//向container添加多个View
int count = 10;
UIView *lastView = nil;
for(int i = 1;i <= count;++i ){
//创建一个View
UIView *subView = [[UIView alloc] init];
[container addSubView:subView];
//颜色随机
subView.backgroundColor = [UIColor colorWithRed:( arc4random() % 256 / 256.0 )
green:( arc4random() % 256 / 256.0 )
blue:( arc4random() % 256 / 256.0 )
alpha:1];
//向subView添加约束
[subView mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.left.and.right.equalTo(container);//左右边界和container紧贴
make.height.mas_equalTo(@(20*i));//高度随i递增
//判断是否有前一个子View
if ( lastView ) {
//如果有前一个View,上边界和前一个View的下边界紧贴
make.top.mas_equalTo(lastView.mas_bottom);
} else {
//如果没有前一个View,上边界和container的下边界紧贴
make.top.mas_equalTo(container.mas_top);
}
}];
//保存前一个View
lastView = subView;
}
//添加container的最后一个约束
[container mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
//container的下边界和最后一个View的下边界紧贴
make.bottom.equalTo(lastView.mas_bottom);
}];
三、Masonry进阶
Masonry为NSArray实现了2个特殊的分类方法:
/*
该方法只有存有UIView的NSArray数组可以调用,NSArray里面的UIView必须有共同的spuerView
该方法作用是UIView之间的水平等宽定距约束,或者垂直等高定距约束。
先确定间距,宽度或高度不确定,但相等
axisType只有MASAxisTypeHorizontal(水平间距类型)和MASAxisTypeVertical(垂直间距类型)
fixedSpacing是UIView两两之间的间距大小
leadSpacing是第一个UIView距离superView左(或上)边界的间距大小
tailSpacing是最后一个UIView距离superView右(或下)边界的间距大小
数组里的所有UIView水平宽度相等,或者垂直高度相等
*/
- (void)mas_distributeViewsAlongAxis:(MASAxisType)axisType
withFixedSpacing:(CGFloat)fixedSpacing
leadSpacing:(CGFloat)leadSpacing
tailSpacing:(CGFloat)tailSpacing;
/*
该方法只有存有UIView的NSArray数组可以调用,NSArray里面的UIView必须有共同的spuerView
该方法作用是UIView之间的水平定宽等距约束,或者垂直定高等距约束。
先确定宽度或高度,间距不确定,但相等
axisType只有MASAxisTypeHorizontal(水平间距类型)和MASAxisTypeVertical(垂直间距类型)
fixedSpacing是UIView两两之间的间距大小
leadSpacing是第一个UIView距离superView左(或上)边界的间距大小
tailSpacing是最后一个UIView距离superView右(或下)边界的间距大小
数组里的所有UIView间距相等
*/
- (void)mas_distributeViewsAlongAxis:(MASAxisType)axisType
withFixedItemLength:(CGFloat)fixedItemLength
leadSpacing:(CGFloat)leadSpacing
tailSpacing:(CGFloat)tailSpacing;下面是等间距方法的使用实例:
/*
设置水平等宽定距
UIView之间水平间距为20,第一个UIView距离superView左边6,
最后一个UIView距离superView右边7,UIView高度为60,距离顶部40
*/
[array mas_distributeViewsAlongAxis:MASAxisTypeHorizontal
withFixedSpacing:20
leadSpacing:6
tailSpacing:7];
[array mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.top.equalTo(@40);
make.height.equalTo(@60);
}];/*
设置水平定宽等距
所有UIView的宽度为20,第一个UIView距离superView左边6,
最后一个UIView距离superView右边7,UIView高度为60,距离顶部40
*/
[array mas_distributeViewsAlongAxis:MASAxisTypeHorizontal
withFixedItemLength:20
leadSpacing:6
tailSpacing:7];
[array mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.top.equalTo(@40);
make.height.equalTo(@60);
}];iOS学习笔记36-Masonry自动布局的更多相关文章
- IOS学习笔记48--一些常见的IOS知识点+面试题
IOS学习笔记48--一些常见的IOS知识点+面试题 1.堆和栈什么区别? 答:管理方式:对于栈来讲,是由编译器自动管理,无需我们手工控制:对于堆来说,释放工作由程序员控制,容易产生memor ...
- iOS学习笔记——AutoLayout的约束
iOS学习笔记——AutoLayout约束 之前在开发iOS app时一直以为苹果的布局是绝对布局,在IB中拖拉控件运行或者直接使用代码去调整控件都会发上一些不尽人意的结果,后来发现iOS在引入了Au ...
- IOS学习笔记25—HTTP操作之ASIHTTPRequest
IOS学习笔记25—HTTP操作之ASIHTTPRequest 分类: iOS2012-08-12 10:04 7734人阅读 评论(3) 收藏 举报 iosios5网络wrapper框架新浪微博 A ...
- IOS学习笔记之关键词@dynamic
IOS学习笔记之关键词@dynamic @dynamic这个关键词,通常是用不到的. 它与@synthesize的区别在于: 使用@synthesize编译器会确实的产生getter和setter方法 ...
- iOS学习笔记-精华整理
iOS学习笔记总结整理 一.内存管理情况 1- autorelease,当用户的代码在持续运行时,自动释放池是不会被销毁的,这段时间内用户可以安全地使用自动释放的对象.当用户的代码运行告一段 落,开始 ...
- iOS学习笔记10-UIView动画
上次学习了iOS学习笔记09-核心动画CoreAnimation,这次继续学习动画,上次使用的CoreAnimation很多人感觉使用起来很繁琐,有没有更加方便的动画效果实现呢?答案是有的,那就是UI ...
- iOS学习笔记总结整理
来源:http://mobile.51cto.com/iphone-386851_all.htm 学习IOS开发这对于一个初学者来说,是一件非常挠头的事情.其实学习IOS开发无外乎平时的积累与总结.下 ...
- iOS学习笔记之Category
iOS学习笔记之Category 写在前面 Category是类别(也称为类目或范畴),使用Category,程序员可以为任何已有的类添加方法.使用类别可以对框架提供的类(无法获取源码,不能直接修改) ...
- iOS学习笔记之ARC内存管理
iOS学习笔记之ARC内存管理 写在前面 ARC(Automatic Reference Counting),自动引用计数,是iOS中采用的一种内存管理方式. 指针变量与对象所有权 指针变量暗含了对其 ...
- IOS学习笔记(四)之UITextField和UITextView控件学习
IOS学习笔记(四)之UITextField和UITextView控件学习(博客地址:http://blog.csdn.net/developer_jiangqq) Author:hmjiangqq ...
随机推荐
- Codeforces Round #321 (Div. 2) D Kefa and Dishes(dp)
用spfa,和dp是一样的.转移只和最后一个吃的dish和吃了哪些有关. 把松弛改成变长.因为是DAG,所以一定没环.操作最多有84934656,514ms跑过,实际远远没这么多. 脑补过一下费用流, ...
- MyLinkedList
/** * 节点类 * @author JP * */ class Node { Object value;//节点元素值 Node pre;//上一个节点 Node next;//下一个节点 pub ...
- 2018.4.6 java交易记录系统
题目 ###1.交易明细文件内容如下例: 客户号 姓名 所述机构号 性别 帐号 发生时间 发生额 000001|刘德华|0000|1|4155990188888888|20060720200005|3 ...
- java abstraction and encapsulation
How is Abstraction different from Encapsulation? Abstraction happens at class level design. It resul ...
- Java的日期类和日期格式化类
日期类: Date date = new Date(); // 获取当前的系统时间 2 System.out.println("年份:"+ date.getYear()); Cal ...
- C语言单链表的实现
// // main.c // gfhjhgdf // // Created by chenhao on 13-12-23. // Copyright (c) 2013年 chenhao. A ...
- 从屏幕截取一块区域,将其赋给imageView
UIGraphicsBeginImageContext(self.bounds.size); [self.layerrenderInContext:UIGraphicsGetCurrentContex ...
- Pycharm安装类库
比如安装requests 打开settings,选择Project 下面的Project Interpreter,点击pip,在弹出窗口里输入requests然后点击install 即可!
- 批量ping IP并检测IP延迟率和丢包率脚本
脚本文件如下: #!/bin/bash #Author:Mr.Ding #Created Time:2018-08-26 07:23:44 #Name:ping.sh #Description: sh ...
- cols
题目描述 请设计一个函数,用来判断在一个矩阵中是否存在一条包含某字符串所有字符的路径.路径可以从矩阵中的任意一个格子开始,每一步可以在矩阵中向左,向右,向上,向下移动一个格子.如果一条路径经过了矩阵中 ...
