使用Python处理CSV文件的一些代码示例
笔记:使用Python处理CSV文件的一些代码示例,来自于《Python数据分析基础》一书,有删改
# 读写CSV文件,不使用CSV模块,仅使用基础Python
# 20181110 wangml #!/usr/bin/env python3 input_file = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python\supplier_data.csv'
output_file = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python\supplier_data_out.csv' # 分别以读、写方式打开input_file、output_file,当以 w 方式打开的文件不存在,则创建它
with open(input_file, 'r', newline='') as filereader:
with open(output_file, 'w', newline='') as filewriter:
# 读取一行文件内容
header = filereader.readline()
header = header.strip()
header_list = header.split(',')
print(header_list)
filewriter.write(','.join(map(str, header_list))+'\n')
for row in filereader:
row = row.strip()
row_list = row.split(',')
print(row_list)
filewriter.write(','.join(map(str, row_list))+'\n')
# 使用CSV模块读写CSV文件
# 20181112 wangml
# csv_pandas_1
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# 导入CSV库
import csv
input_file = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python\supplier_data.csv'
output_file = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python\supplier_data_out.csv'
with open(input_file, 'r', newline='') as csv_in_file:
with open(output_file, 'w', newline='') as csv_out_file:
# 使用CVS模块中csv.reader()、csv.writer()函数,创建一个读取对象、一个写入对象
# delimiter指定CSV文件的分隔符,默认为 , 逗号
filereader = csv.reader(csv_in_file, delimiter=',')
filewriter = csv.writer(csv_out_file, delimiter=',')
header = next(filereader)
filewriter.writerow(header)
# 循环,每次从CSV读取文件中读取一行数据,并将其打印出来,然后写入CSV写入对象
for row_list in filereader:
print(row_list)
filewriter.writerow(row_list)
# 筛选符合条件的行
for row_list in filereader:
#print(row_list[1])
name = str(row_list[0]).strip()
#print(row_list[3])
cost = str(row_list[3]).strip('$').replace(',', '')
#print(cost)
#print(type(cost))
# 选择name为z或者cost大于600的row,此处使用float()函数将cost由str类型转换为flost
if name == 'z' or float(cost) > 600.0:
filewriter.writerow(row_list)
# # csv_pandas_1
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import pandas as pd
input_file = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python\supplier_data.csv'
output_file = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python\supplier_data_out.csv'
# 使用pandas库函数pandas.read_csv()读取一个CSV文件,并由此创建一个数据框对象
data_frame = pd.read_csv(input_file)
# 通过列名作为index选取该数据框中的指定列
data_frame['Cost'] = data_frame['Cost'].str.strip('$').astype(float)
#print(type(data_frame['Cost']))
data_frame_value_meets_condition = data_frame.loc[(data_frame['Name'].str.contains('Z')) | (data_frame['Cost'] > 600.0), :]
# 此处导致CSV文件的Cost列的$消失了
# 下面的语句并没有将$加上去,暂时不知道怎么弄
data_frame['Cost'] = '$' + str(data_frame['Cost'])
# 将data_frame_value_meets_condition写入输出文件
data_frame_value_meets_condition.to_csv(output_file, index=False)
#
# csv_pandas_2
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# 导入CSV库
import csv
input_file = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python\supplier_data.csv'
output_file = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python\supplier_data_out.csv'
important_dates = ['1/1/2018', '2/1/2018']
with open(input_file, 'r', newline='') as csv_in_file:
with open(output_file, 'w', newline='') as csv_out_file:
filereader = csv.reader(csv_in_file)
filewriter = csv.writer(csv_out_file)
header = next(filereader)
filewriter.writerow(header)
for row_list in filereader:
a_date = row_list[4]
# 选取date值在important_dates中的行
if a_date in important_dates:
filewriter.writerow(row_list)
# # csv_pandas_2
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import pandas as pd
input_file = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python\supplier_data.csv'
output_file = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python\supplier_data_out.csv'
# 使用pandas库函数pandas.read_csv()读取一个CSV文件,并由此创建一个数据框对象
data_frame = pd.read_csv(input_file)
important_dates = ['1/1/2018', '2/1/2018']
# 选取date值在important_dates中的行
data_frame_value_set = data_frame.loc[data_frame['Date'].isin(important_dates), :]
data_frame_value_set.to_csv(output_file, index=False)
#
# csv_pandas_3
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# 导入CSV库、正则表达式库
import csv
import re
input_file = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python\supplier_data.csv'
output_file = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python\supplier_data_out.csv'
# 使用re.compile(正则表达式),创建一个正则表达式变量
# 元字符?P<my_pattern_group>捕获了名为<my_pattern_group>的组中匹配了的字符串
# pattern表示满足以:'001-'开头,后面可跟除任意字串的字符串
# re.I表示大小写敏感
pattern = re.compile(r'(?P<my_pattern_group>^001-.*)', re.I)
with open(input_file, 'r', newline='') as csv_in_file:
with open(output_file, 'w', newline='') as csv_out_file:
filereader = csv.reader(csv_in_file)
filewriter = csv.writer(csv_out_file)
header = next(filereader)
filewriter.writerow(header)
for row_list in filereader:
id_number = row_list[1]
if pattern.search(id_number):
filewriter.writerow(row_list)
#
# csv_pandas_3
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import pandas as pd
input_file = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python\supplier_data.csv'
output_file = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python\supplier_data_out.csv'
# 使用pandas库函数pandas.read_csv()读取一个CSV文件,并由此创建一个数据框对象
data_frame = pd.read_csv(input_file)
# 筛选出ID值以001-开头的行
data_frame_value_matches_pattern = data_frame.loc[data_frame['ID'].str.startswith("001-"), :]
data_frame_value_matches_pattern.to_csv(output_file, index=False)
# 选取CSV文件中符合条件的列 #
# csv_pandas_4
# 通过列索引值选取特定列
# 在只知道需要选取的列名称时,我们可以通过列名称取得相应的索引值,在进行选取
# 具体方法是判断相应标题行每个元素是否在已知列名称中,若是,记下该item的index
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import csv
input_file = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python\supplier_data.csv'
output_file = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python\supplier_data_out.csv'
my_columns = [0, 3]
with open(input_file, 'r', newline='') as csv_in_file:
with open(output_file, 'w', newline='') as csv_out_file:
filereader = csv.reader(csv_in_file)
filewriter = csv.writer(csv_out_file)
for row_list in filereader:
# 每次向输出文件中写入的一行值
row_list_output = []
for index_value in my_columns:
row_list_output.append(row_list[index_value])
filewriter.writerow(row_list_output)
# 选取CSV文件中符合条件的列 #
# csv_pandas_4
# 通过列索引值选取特定列
# 在只知道需要选取的列名称时,不需要像基本Python一样处理标题行,pandas可以将列名称当做index一样处理
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import pandas as pd
input_file = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python\supplier_data.csv'
output_file = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python\supplier_data_out.csv'
# 使用pandas库函数pandas.read_csv()读取一个CSV文件,并由此创建一个数据框对象
data_frame = pd.read_csv(input_file)
# 选取data_frame数据框对象中的所有行的列索引值为0,3的列
# iloc(行,列)函数可以选取数据框中选定的行、列
data_frame_value_column_by_value = data_frame.iloc[:, [0, 3]]
# data_frame_value_column_by_value = data_frame.iloc[:, [‘Name’, 'Cost']]
data_frame_value_column_by_value.to_csv(output_file, index=False) # 给一个CSV文件添加标题行,在基础Python中,可能是将标题行通过csv库的writerow()函数写入
# 而pandas库提供了更加简单的方法
# title = [‘One’, 'Two'...]
# data_frame = pd.read_csv(input_file, header=None, names=title)
# 读取多个CSV文件,输出读取了多少个CSV文件
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import csv
import glob
import os input_path = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python'
file_counter = 0
for input_file in glob.glob(os.path.join(input_path, '*.csv')):
file_counter = file_counter + 1
#row_counter = 1
#with open(input_file, 'r', newline='') as csv_input_file:
#filereader = csv.reader(csv_input_file)
#...
print(file_counter)
#
# 合并多个CSV文件
#!/usv/bin/env python3
import pandas as pd
import os
import glob
input_path = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python'
output_file = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python\supplier_data_out.csv'
#all_files = glob.glob(os.path.join(input_path, 'supplier_data_副本*'))
# OSError: Initializing from file failed上面这句出现错误,因为文件名含有中文,改成下面这句就行了
all_files = glob.glob(os.path.join(input_path, 'supplier_data_copy*'))
all_data_frame = []
for file in all_files:
data_frame = pd.read_csv(file, index_col=None)
all_data_frame.append(data_frame)
# pandas.concat()函数将数据框数据垂直堆叠(axis=0), 当水平连接数据时(asis=1)
data_frame_concat = pd.concat(all_data_frame, axis=0, ignore_index=True)
data_frame_concat.to_csv(output_file, index=False)
# 分别计算多个CSV文件中的某项数据的和、平均值等
# 在基本python中,可以读取多个CSV文件,然后要被计算的项的值一个一个取出来,然后计算
# 这里展示了使用pandas提供的方法
#!/usv/bin/env python3
import pandas as pd
import os
import glob
input_path = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python'
output_file = 'D:\wangm\Documents\learning\code\python\supplier_data_out.csv'
all_files = glob.glob(os.path.join(input_path, 'supplier_data_copy*'))
all_data_frame = []
for file in all_files:
data_frame = pd.read_csv(file, index_col=None)
# 和
total_cost = pd.DataFrame([float(str(value).strip('$').replace(',', '')) \
for value in data_frame.loc[:, 'Cost']]).sum()
# 平均值
average_cost = pd.DataFrame([float(str(value).strip('$').replace(',', '')) \
for value in data_frame.loc[:, 'Cost']]).mean()
data = {'file_name': os.path.basename(file),
'total_cost': total_cost,
'average_cost': average_cost}
all_data_frame.append(pd.DataFrame(data, columns=['file_name', 'total_cost', 'average_cost']))
data_frames_concat = pd.concat(all_data_frame, axis=0, ignore_index=True)
data_frames_concat.to_csv(output_file, index=False)
代码示例中使用的CSV文件:
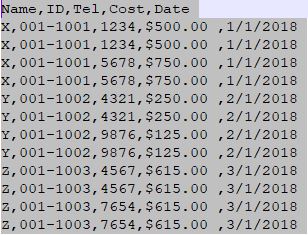
上述代码分别使用CSV库、pandas库来对CSV文件进行相同的操作
上述代码运行在Python 3.6版本下,在Win10、Spyder中
有关Python的csv库的详细介绍:https://docs.python.org/2/library/csv.html
使用Python处理CSV文件的一些代码示例的更多相关文章
- 使用Python处理Excel文件的一些代码示例
笔记:使用Python处理Excel文件的一些代码示例,以下代码来自于<Python数据分析基础>一书,有删改 #!/usr/bin/env python3 # 导入读取Excel文件的库 ...
- 使用Python读写csv文件的三种方法
Python读写csv文件 觉得有用的话,欢迎一起讨论相互学习~Follow Me 前言 逗号分隔值(Comma-Separated Values,CSV,有时也称为字符分隔值,因为分隔字符也可以不是 ...
- python读写csv文件
文章链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/cloud-ken/p/8432999.html Python读写csv文件 觉得有用的话,欢迎一起讨论相互学习~Follow Me 前言 逗 ...
- python导入csv文件时,出现SyntaxError
背景 np.loadtxt()用于从文本加载数据. 文本文件中的每一行必须含有相同的数据. *** loadtxt(fname, dtype=<class 'float'>, commen ...
- 数学建模之Python操作csv文件
1.用Python通过csv文件里面的某一列,形成键值,然后统计键在其他列出现的次数. import pandas as pd import numpy as np import csv import ...
- (Python基础教程之十二)Python读写CSV文件
Python基础教程 在SublimeEditor中配置Python环境 Python代码中添加注释 Python中的变量的使用 Python中的数据类型 Python中的关键字 Python字符串操 ...
- Python处理csv文件
Python处理csv文件 CSV(Comma-Separated Values)即逗号分隔值,可以用Excel打开查看.由于是纯文本,任何编辑器也都可打开.与Excel文件不同,CSV文件中: 值没 ...
- 使用python读写CSV文件
# -*- coding:UTF-8 -*- __autor__ = 'zhouli' __date__ = '2018/10/25 21:14' import csv with open('resu ...
- 解决python中csv文件中文写入问题
一.前言 一般来说,为了方便,使用python的时候都会使用csv模块去写数据到csv文件,但是写入中文的时候,经常会报错: UnicodeEncodeError: 'ascii' codec can ...
随机推荐
- 解决 Could not load hsdis-amd64.dll
win10下想查看JIT编译的汇编源码 结果提示: Could not load hsdis-amd64.dll; library not loadable; PrintAssembly is dis ...
- python object与dict互相转换
代码如下 # 将class转dict,以_开头的属性不要 def props(obj): pr = {} for name in dir(obj): value = getattr(obj, name ...
- xml文档绑定某个属性值到treeview算法
原文发布时间为:2008-08-10 -- 来源于本人的百度文章 [由搬家工具导入] using System.Xml; protected void Button2_Click(object sen ...
- 机器人操作系统ROS Indigo 入门学习(1)——安装ROS Indigo【转】
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/bobsweetie/article/details/43638761 Ubuntu14.04安装ROS Indigo 一.安装ROS 1.1配置Ubu ...
- C语言处理json字符串
JSON语法说明 先来看一个简单的JSON 1 { 2 "stars": [ 3 { 4 "name": "Faye", 5 "a ...
- php接口开发时,数据解析失败问题,字符转义,编码问题
php接口开发时,数据解析失败问题,字符转义,编码问题 情景: A平台--->向接口请求数据---->接口向B平台请求数据---->B平台返回数据给接口---->接口返回数据给 ...
- AC日记——背包问题 V2 51nod 1086
有N种物品,每种物品的数量为C1,C2......Cn.从中任选若干件放在容量为W的背包里,每种物品的体积为W1,W2......Wn(Wi为整数),与之相对应的价值为P1,P2......Pn(Pi ...
- AC日记——旅行 洛谷 P3313
题目描述 S国有N个城市,编号从1到N.城市间用N-1条双向道路连接,满足从一个城市出发可以到达其它所有城市.每个城市信仰不同的宗教,如飞天面条神教.隐形独角兽教.绝地教都是常见的信仰. 为了方便,我 ...
- linux source filename
简单来说:source filename即把filename文件里的命令(命令集脚本文件)执行一遍,相当于在shell里逐个执行单条命令
- ListView 在设备切换横竖屏时保存状态
比如listview在设备切换横竖屏时,仍然需要保证position, activity - > onSaveInstanceState - > restoreInstanceState ...
