前端框架之Vue(9)-组件基础&vue-cli
组件基础
基本示例
这里有一个 Vue 组件的示例:
- <!DOCTYPE html>
- <html lang="en">
- <head>
- <meta charset="UTF-8">
- <title></title>
- <script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
- </head>
- <body>
- <div id="components-demo">
- <button-counter></button-counter>
- </div>
- <script>
- // 定义一个名为 button-counter 的新组件
- Vue.component('button-counter', {
- data: function() {
- return {
- count: 0
- }
- },
- template: '<button v-on:click="count++">You clicked me {{ count }} times.</button>'
- })
- new Vue({ el: '#components-demo' })
- </script>
- </body>
- </html>
组件是可复用的 Vue 实例,且带有一个名字:在这个例子中是在一个通过 new Vue 创建的 Vue 根实例中,把这个组件作为自定义元素来使用。
因为组件是可复用的 Vue 实例,所以它们与 new Vue 接收相同的选项,例如 data 、 computed 、 watch 、 methods 以及生命周期钩子等。仅有的例外是像 el 这样根实例特有的选项。
data必须是一个函数
当我们定义这个 <button-counter> 组件时,你可能会发现它的 data 并不是像这样直接提供一个对象:
- data: {
- count: 0
- }
取而代之的是,一个组件的 data 选项必须是一个函数,因此每个实例可以维护一份被返回对象的独立的拷贝:
- data: function () {
- return {
- count: 0
- }
- }
组件的组织
通常一个应用会以一棵嵌套的组件树的形式来组织:
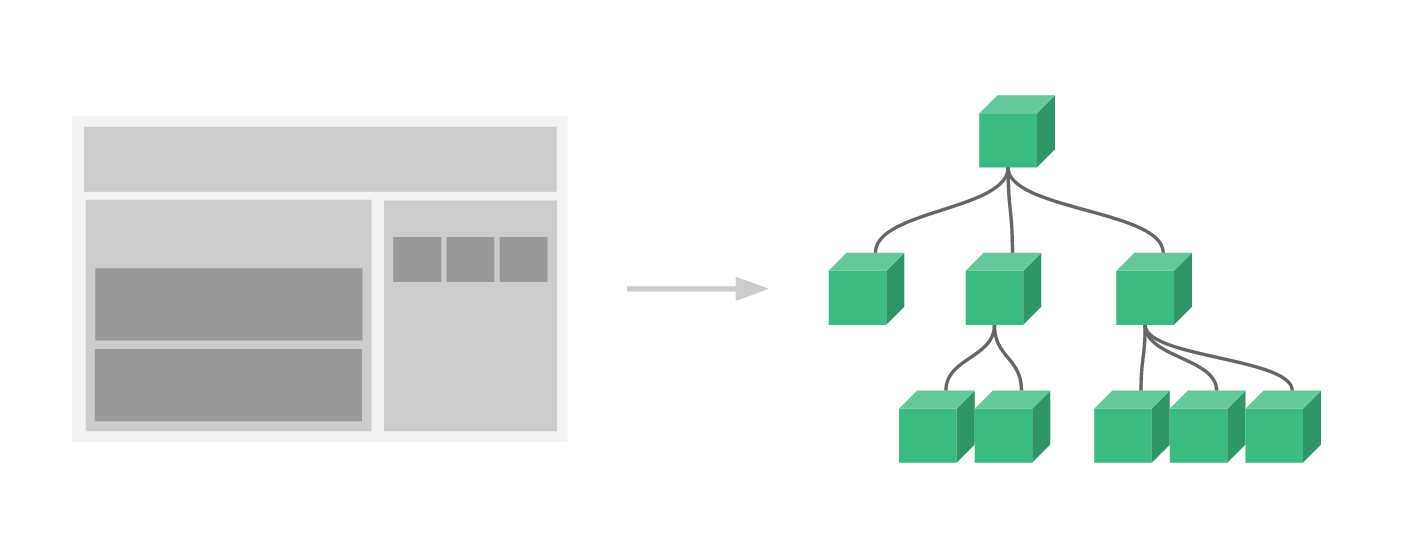
例如,你可能会有页头、侧边栏、内容区等组件,每个组件又包含了其它的像导航链接、博文之类的组件。
为了能在模板中使用,这些组件必须先注册以便 Vue 能够识别。这里有两种组件的注册类型:全局注册和局部注册。至此,我们的组件都只是通过 Vue.component 全局注册的。
- Vue.component('my-component-name', {
- // ... options ...
- })
全局注册的组件可以用在其被注册之后的任何 (通过 new Vue ) 新创建的 Vue 根实例,也包括其组件树中的所有子组件的模板中。
通过Prop向子组件传递数据
Prop 是你可以在组件上注册的一些自定义特性。当一个值传递给一个 prop 特性的时候,它就变成了那个组件实例的一个属性。为了给下面组件传递一个标题,我们可以用一个 props 选项将其包含在该组件可接受的 prop 列表中:
- Vue.component('blog-post', {
- props: ['title'],
- template: '<h3>{{ title }}</h3>'
- })
一个组件默认可以拥有任意数量的 prop ,任何值都可以传递给任何 prop 。在上述模板中,你会发现我们能够在组件实例中访问这个值,就像访问 data 中的值一样。
一个 prop 被注册之后,你就可以像这样把数据作为一个自定义特性传递进来:
- <blog-post title="My journey with Vue"></blog-post>
- <blog-post title="Blogging with Vue"></blog-post>
- <blog-post title="Why Vue is so fun"></blog-post>
效果:

然而在一个典型的应用中,你可能在 data 里有一个博文的数组:
- Vue.component('blog-post', {
- props: ['id','title'],
- template: '<h3>{{ id }}:{{ title }}</h3>'
- })
- new Vue({
- el: '#blog-post-demo',
- data: {
- posts: [
- { id: 1, title: 'My journey with Vue' },
- { id: 2, title: 'Blogging with Vue' },
- { id: 3, title: 'Why Vue is so fun' }
- ]
- }
- })
并想要为每篇博文渲染一个组件:
- <blog-post v-for="post in posts" v-bind:id="post.id" v-bind:title="post.title"></blog-post>
如上所示,你会发现我们可以使用 v-bind 来动态传递 prop 。这在你一开始不清楚要渲染的具体内容,比如从一个 API 获取博文列表的时候,是非常有用的。
单个根元素
当构建一个 <blog-post> 组件时,你的模板最终会包含的东西远不止一个标题,最最起码,会包含这篇博文的正文:
- <h3>{{ title }}</h3>
- <div v-html="content"></div>
然而如果你在模板中尝试这样写,Vue 会显示一个错误,并解释道 every component must have a single root element (每个组件必须只有一个根元素) 。你可以将模板的内容包裹在一个父元素内,来修复这个问题,例如:
- <div class="blog-post">
- <h3>{{ title }}</h3>
- <div v-html="content"></div>
- </div>
看起来当组件变得越来越复杂的时候,我们的博文不只需要标题和内容,还需要发布日期、评论等等。为每个相关的信息定义一个 prop 会变得很麻烦:
- <blog-post
- v-for="post in posts"
- v-bind:key="post.id"
- v-bind:title="post.title"
- v-bind:content="post.content"
- v-bind:publishedAt="post.publishedAt"
- v-bind:comments="post.comments"
- ></blog-post>
所以是时候重构一下这个组件了,让它变成接受一个单独的 post prop :
- <blog-post
- v-for="post in posts"
- v-bind:key="post.id"
- v-bind:post="post"
- ></blog-post>
- Vue.component('blog-post', {
- props: ['post'],
- template: `
- <div class="blog-post">
- <h3>{{ post.title }}</h3>
- <div v-html="post.content"></div>
- </div>
- `
- })
通过事件向父级组件发送消息
在我们开发 <blog-post> 组件时,它的一些功能可能要求我们和父级组件进行沟通。例如我们可能会引入一个可访问性的功能来放大博文的字号,同时让页面的其它部分保持默认的字号。
在其父组件中,我们可以通过添加一个 postFontSize 数据属性来支持这个功能,它可以在模板中用来控制所有博文的字号:
- <div id="blog-posts-events-demo">
- <div :style="{ fontSize: postFontSize + 'em' }">
- <blog-post
- v-for="post in posts"
- v-bind:key="post.id"
- v-bind:post="post"
- ></blog-post>
- </div>
- </div>
现在我们在每篇博文正文之前添加一个按钮来放大字号:
- Vue.component('blog-post', {
- props: ['post'],
- template: `
- <div class="blog-post">
- <h3>{{ post.title }}</h3>
- <button @click="$emit('enlarge-text')">
- Enlarge text
- </button>
- <div v-html="post.content"></div>
- </div>
- `
- });
- new Vue({
- el: '#blog-posts-events-demo',
- data: {
- posts: [
- { id: 1, title: 'My journey with Vue' },
- { id: 2, title: 'Blogging with Vue' },
- { id: 3, title: 'Why Vue is so fun' }
- ],
- postFontSize: 1
- }
- });
当点击这个按钮时,我们需要告诉父级组件放大所有博文的文本。幸好 Vue 实例提供了一个自定义事件的系统来解决这个问题。我们可以调用内建的 $emit 方法并传入事件的名字,来向父级组件触发一个事件:
- <button v-on:click="$emit('enlarge-text')">
- Enlarge text
- </button>
然后我们可以用 v-on 在博文组件上监听这个事件,就像监听一个原生 DOM 事件一样:
- <blog-post
- ...
- v-on:enlarge-text="postFontSize += 0.1"
- ></blog-post>
使用事件抛出一个值
有的时候用一个事件来抛出一个特定的值是非常有用的。例如我们可能想让 <blog-post> 组件决定它的文本要放大多少。这时可以使用 $emit 的第二个参数来提供这个值:
- <button v-on:click="$emit('enlarge-text', 0.1)">
- Enlarge text
- </button>
然后当在父级组件监听这个事件的时候,我们可以通过 $event 访问到被抛出的这个值:
- <blog-post
- ...
- v-on:enlarge-text="postFontSize += $event"
- ></blog-post>
或者,如果这个事件处理函数是一个方法:
- <blog-post
- ...
- v-on:enlarge-text="onEnlargeText"
- ></blog-post>
那么这个值将会作为第一个参数传入这个方法:
- methods: {
- onEnlargeText: function (enlargeAmount) {
- this.postFontSize += enlargeAmount
- }
- }
- <button v-on:click="$emit('enlarge-text', 0.1)">
在组件上使用v-model
自定义事件也可以用于创建支持 v-model 的自定义输入组件。记住:
- <input v-model="searchText">
等价于:
- <input
- v-bind:value="searchText"
- v-on:input="searchText = $event.target.value"
- >
当用在组件上时, v-model 则会这样:
- <custom-input
- v-bind:value="searchText"
- v-on:input="searchText = $event"
- ></custom-input>
- 为了让它正常工作,这个组件内的 <input> 必须:
- 将其 value 特性绑定到一个名叫 value 的 prop 上
- 在其 input 事件被触发时,将新的值通过自定义的 input 事件抛出
写成代码之后是这样的:
- Vue.component('custom-input', {
- props: ['value'],
- template: `
- <input
- v-bind:value="value"
- v-on:input="$emit('input', $event.target.value)"
- >
- `
- })
现在 v-model 就应该可以在这个组件上完美地工作起来了:
- <!DOCTYPE html>
- <html lang="en">
- <head>
- <meta charset="UTF-8">
- <title></title>
- <script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
- </head>
- <body>
- <div id='demo'>
- <custom-input v-bind:value="searchText" v-on:input="searchText = $event"></custom-input>
- <custom-input v-model='searchText'></custom-input>
- {{searchText}}
- </div>
- <script>
- Vue.component('custom-input', {
- props: ['value'],
- template: `
- <input
- v-bind:value="value"
- v-on:input="$emit('input', $event.target.value)"
- >
- `
- });
- var vm = new Vue({
- el: "#demo",
- data: {
- searchText: ''
- }
- })
- </script>
- </body>
- </html>
例:
通过插槽分发内容
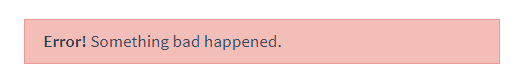
和 HTML 元素一样,我们经常需要向一个组件传递内容,像这样:
- <alert-box>
- Something bad happened.
- </alert-box>
可能会渲染出这样的东西:
幸好,Vue 自定义的 元素让这变得非常简单:
- Vue.component('alert-box', {
- template: `
- <div class="demo-alert-box">
- <strong>Error!</strong>
- <slot></slot>
- </div>
- `
- })
如你所见,我们只要在需要的地方加入插槽就行了——就这么简单!
- <!DOCTYPE html>
- <html lang="en">
- <head>
- <meta charset="UTF-8">
- <title></title>
- <script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
- </head>
- <body>
- <div id="components-demo">
- <alert-box>通过插件传入</alert-box>
- </div>
- <script>
- Vue.component('alert-box', {
- template: `
- <div class="demo-alert-box">
- <strong>组件自己内容</strong>
- <h3><slot></slot></h3>
- </div>
- `
- })
- new Vue({ el: '#components-demo' })
- </script>
- </body>
- </html>
例:
动态组件
有的时候,在不同组件之间进行动态切换是非常有用的,比如在一个多标签的界面里:

上述内容可以通过 Vue 的元素加一个特殊的 is 特性来实现:
- <!-- 组件会在 `currentTabComponent` 改变时改变 -->
- <component v-bind:is="currentTabComponent"></component>
在上述示例中, currentTabComponent 可以包括已注册组件的名字:
- <!DOCTYPE html>
- <html lang="en">
- <head>
- <meta charset="UTF-8">
- <title></title>
- <script src="https://unpkg.com/vue"></script>
- <style>
- .tab-button {
- padding: 6px 10px;
- border-top-left-radius: 3px;
- border-top-right-radius: 3px;
- border: 1px solid #ccc;
- cursor: pointer;
- background: #f0f0f0;
- margin-bottom: -1px;
- margin-right: -1px;
- }
- .tab-button:hover {
- background: #e0e0e0;
- }
- .tab-button.active {
- background: #e0e0e0;
- }
- .tab {
- border: 1px solid #ccc;
- padding: 10px;
- }
- </style>
- </head>
- <body>
- <div id="dynamic-component-demo" class="demo">
- <button v-for="tab in tabs" v-bind:key="tab" v-bind:class="['tab-button', { active: currentTab === tab }]" v-on:click="currentTab = tab">{{ tab }}</button>
- <component v-bind:is="currentTabComponent" class="tab"></component>
- </div>
- <script>
- Vue.component('tab-home', {
- template: '<div>Home component</div>'
- })
- Vue.component('tab-posts', {
- template: '<div>Posts component</div>'
- })
- Vue.component('tab-archive', {
- template: '<div>Archive component</div>'
- })
- new Vue({
- el: '#dynamic-component-demo',
- data: {
- currentTab: 'Home',
- tabs: ['Home', 'Posts', 'Archive']
- },
- computed: {
- currentTabComponent: function() {
- return 'tab-' + this.currentTab.toLowerCase()
- }
- }
- })
- </script>
- </body>
- </html>
例:
或一个组件的选项对象:
- <!DOCTYPE html>
- <html lang="en">
- <head>
- <meta charset="UTF-8">
- <title></title>
- <script src="https://unpkg.com/vue"></script>
- <style>
- .tab-button {
- padding: 6px 10px;
- border-top-left-radius: 3px;
- border-top-right-radius: 3px;
- border: 1px solid #ccc;
- cursor: pointer;
- background: #f0f0f0;
- margin-bottom: -1px;
- margin-right: -1px;
- }
- .tab-button:hover {
- background: #e0e0e0;
- }
- .tab-button.active {
- background: #e0e0e0;
- }
- .tab {
- border: 1px solid #ccc;
- padding: 10px;
- }
- </style>
- </head>
- <body>
- <script src="https://unpkg.com/vue"></script>
- <div id="dynamic-component-demo" class="demo">
- <button v-for="tab in tabs" v-bind:key="tab.name" v-bind:class="['tab-button', { active: currentTab.name === tab.name }]" v-on:click="currentTab = tab">{{ tab.name }}</button>
- <component v-bind:is="currentTab.component" class="tab"></component>
- </div>
- <script>
- var tabs = [{
- name: 'Home',
- component: {
- template: '<div>Home component</div>'
- }
- },
- {
- name: 'Posts',
- component: {
- template: '<div>Posts component</div>'
- }
- },
- {
- name: 'Archive',
- component: {
- template: '<div>Archive component</div>',
- }
- }
- ]
- new Vue({
- el: '#dynamic-component-demo',
- data: {
- tabs: tabs,
- currentTab: tabs[0]
- }
- })
- </script>
- </body>
- </html>
例:
通过vue-cli使用组件
准备
安装
- npm install vue-cli -g
初始化项目目录
- vue init webpack-simple [项目目录名]
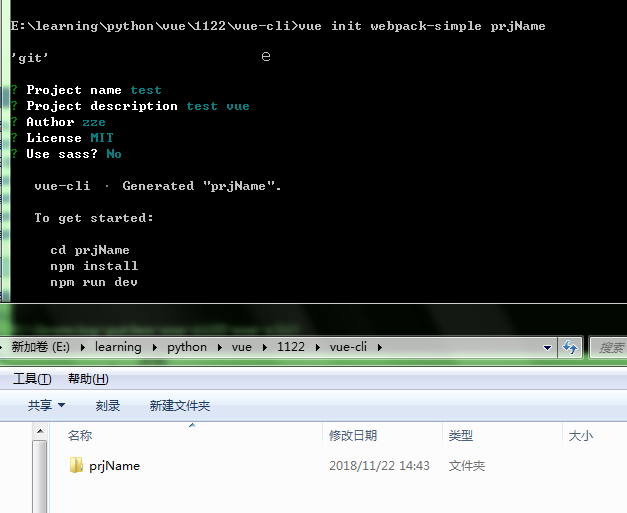
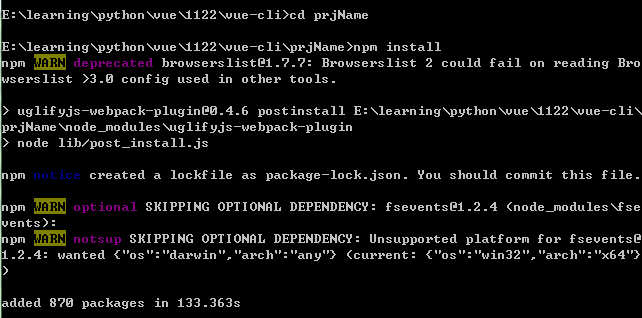
按提示依次执行
- cd prjName
- npm install
- cd prjName
运行
- npm run dev
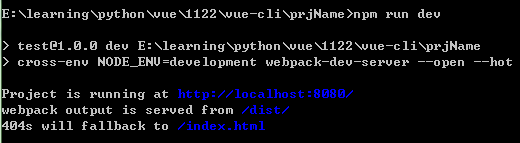
使用
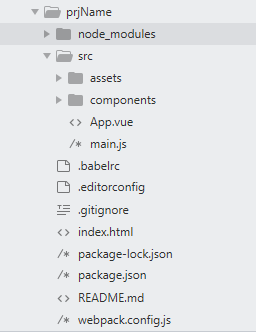
目录结构
完成上述准备后会生成如下目录结构:
新建组件
在 components 目录下新建如下组件:
- <template>
- <div>
- <h3>{{msg}}</h3>
- </div>
- </template>
- <script>
- export default{
- name:'header',
- data(){
- return {
- msg:'这是头部分'
- }
- }
- }
- </script>
- <style scoped>
- h3{
- background-color: blue;
- }
- </style>
/src/components/VHeader.vue
- <template>
- <div>
- <h3>{{msg}}</h3>
- </div>
- </template>
- <script>
- export default{
- name:'content',
- data(){
- return {
- msg:'这是内容部分'
- }
- }
- }
- </script>
- <!-- scoped可使当前样式块只对当前组件生效 -->
- <style scoped>
- h3{
- background-color: red;
- }
- </style>
/src/components/VContent.vue
- <template>
- <div>
- <h3>{{msg}}</h3>
- </div>
- </template>
- <script>
- export default{
- name:'header',
- data(){
- return {
- msg:'这是尾部分'
- }
- }
- }
- </script>
- <style scoped>
- h3{
- background-color: yellow;
- }
- </style>
/src/components/VFooter.vue
- <template>
- <div>
- <h2>{{msg}}</h2>
- <VHeader></VHeader>
- <VContent></VContent>
- <VFooter></VFooter>
- </div>
- </template>
- <script>
- // 引入子组件
- import VHeader from './VHeader.vue'
- import VContent from './VContent.vue'
- import VFooter from './VFooter.vue'
- export default{
- name:'page',
- data(){
- return {
- msg:'page组件'
- }
- },
- // 挂载子组件
- components:{
- VHeader,
- VContent,
- VFooter
- }
- }
- </script>
- <style></style>
/src/components/VPage.vue
在上述文件中的 style 块中有一个 scoped 属性(例如在 VContent.vue 的 17 行),这个属性的作用是让当前样式块只对当前组件生效。
- <template>
配置组件
- import Vue from 'vue'
- import VPage from './components/VPage.vue'
- var page_vm = new Vue({
- el: "#page", //对应 /index.html 中div元素的id
- render: h => h(VPage) // 将指定组件(这里是VPage)渲染到上面el属性对应位置
- })
- console.info(page_vm.$children[0]); //VueComponent {_uid: 1, _isVue: true, $options: {…}, _renderProxy: Proxy, _self: VueComponent, …}
/src/main.js
- <!DOCTYPE html>
- <html lang="en">
- <head>
- <meta charset="utf-8">
- <title>test</title>
- </head>
- <body>
- <div id="page"></div>
- <script src="/dist/build.js"></script>
- </body>
- </html>
/index.html
- import Vue from 'vue'
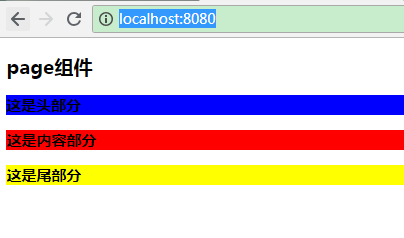
效果
访问运行时输出的地址,默认是 http://localhost:8080/ :
前端框架之Vue(9)-组件基础&vue-cli的更多相关文章
- vue的组件基础
组件分为全局组件和局部组件. 组件的核心是template:所有的数据都为template服务. 父组件子组件传值:因为子组件是父组件的个标签,完全等同于添加动态属性: 然后子组件能够通过props: ...
- vue入门——组件基础todolist
1. 以下是 todolist 的例子,没有用到组件:下面的3 会通过组件拆分todolist <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"&g ...
- vue 父子组件 基础应用scrollball v-model sync
# 组件之间通信 可以通过 v-model 子组件可以通过 改变数据来改变父组件的数组 * v-model 子组件需要接受value属性,需要出发this.$emit("input&qu ...
- 前端框架Vue------>第一天学习、Vue学习的路径、Vue官网(1)
文章目录 1.学习目标 2.前端知识体系 2.1 前端三要素 2.2.MVVM 3.第一个Vue程序 4.Vue实例的生命周期 vue的官方文档:https://cn.vuejs.org/ 1.学习目 ...
- vue自定义组件(vue.use(),install)+全局组件+局部组件
相信大家都用过element-ui.mintui.iview等诸如此类的组件库,具体用法请参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/wangtong111/p/11522520.html ...
- vue自定义组件(通过Vue.use()来使用)即install的使用
在vue项目中,我们可以自定义组件,像element-ui一样使用Vue.use()方法来使用,具体实现方法: 1.首先新建一个loading.vue文件 // Cmponent.vue <te ...
- 【面试问题】—— 2019.3月前端面试之JS原理&CSS基础&Vue框架
前言:三月中旬面试了两家公司,一家小型公司只有面试,另一家稍大型公司笔试之后一面定夺.笔试部分属于基础类型,网上的复习资料都有. 面试时两位面试官都有考到一些实际工作中会用到,但我还没接触过的知识点. ...
- 组件基础—Vue学习笔记
ammm学习Vue有好几天了,今天遇到难点所以打算写一点随笔加深印象. 一.首先最简单的创建组件 1全局组件 Vue.component() Vue.component('hello',{ tem ...
- [转] vue自定义组件(通过Vue.use()来使用)即install的使用
在vue项目中,我们可以自定义组件,像element-ui一样使用Vue.use()方法来使用,具体实现方法: 1.首先新建一个Cmponent.vue文件 // Cmponent.vue<te ...
随机推荐
- "佛祖保佑 永无bug" 注释模板设置详解(仅供娱乐)
1.注释模板效果图 今天在网上看到一段有趣的注释,佛祖保佑 永无bug, 效果如下图所示: 代码如下所示: /** * _ooOoo_ * o8888888o * 88" . " ...
- (转)使用 CJSON 在C语言中进行 JSON 的创建和解析的实例讲解
使用 CJSON 在C语言中进行 JSON 的创建和解析的实例讲解 本文用代码简单介绍cjson的使用方法,1)创建json,从json中获取数据.2)创建json数组和解析json数组 1. 创 ...
- MyEclipse启动Tomcat缓慢的原因及解决办法
不知道朋友们是否有一种烦恼:有时候使用MyEclipse启动Tomcat十分缓慢,可能在几分钟前20秒以内,但现在却需要200秒开外:其间内存和CPU都被占用地厉害,而控制台的输出似乎有重复的迹象:而 ...
- Java基础语法<八> 继承 多态 抽象 反射
1.超类和子类 超类和子类 父类与子类 多态: 一个对象变量可以指示多种实际类型的现象称为多态 一个变量可以引用父类对象,也可以引用其子类对象,这就是多态. 不能将一个超类的引用赋给子类变量,因为调用 ...
- 强大的Android基地 论坛
强大的Android基地 论坛 [非常值得推荐,需要的自己动手去看...] 地址:http://www.eoeandroid.com/forum-15-1.html 大家论坛:http://club. ...
- 常见的压缩文件格式案例tarZ
在AIX上最常见的压缩文件就是.tar压缩格式的文件了. 而除了tar文件以外,有时会遇到数据是用其它的压缩文件格式,所以偶顺手整理了一些常见的压缩文件格式,在AIX要怎么解压缩 : 一. .tar ...
- Luogu 1603 - 斯诺登的密码 - [简单字符串操作]
题目链接:https://www.luogu.org/problemnew/show/P1603 题目背景 根据斯诺登事件出的一道水题 题目描述 2013年X月X日,俄罗斯办理了斯诺登的护照,于是他混 ...
- [No000015B]三十分钟说清经济机器是怎样运行的
https://v.qq.com/x/page/z01685nf12f.html
- [No0000125]WCF安全体系
WCF的安全体系主要包括三个方面:传输安全(Transfer Security).授权或者访问控制(Authorization OR Access Control)以及审核(Auditing).而传输 ...
- spring @Order标记
@Order标记定义了组件的加载顺序. @Order标记从spring 2.0出现,但是在spring 4.0之前,@Order标记只支持AspectJ的切面排序.spring 4.0对@Order做 ...
