Linux内核修炼之framebuffer分析
Linux源代码包中/document/fb/framebuffer.txt有例如以下介绍:
The frame buffer device provides an abstraction for the graphics hardware. It represents the frame buffer of some video hardware and allows application software to access the graphics hardware through a well-defined interface, so the software doesn't need to know anything about the low-level (hardware register) stuff.
Frame buffer机制为图形显示卡提供了一个抽象层。
能够使得应用程序不用考虑底层硬件的实现细节而通过一些API接口就可以訪问到显示设备。 但Framebuffer本身不具备不论什么运算数据的能力,就仅仅好比是一个临时存放水的水池。水池里的水就是显示的东西。CPU将运算后的结果放到这个水池,水池再将结果流到显示器(通常通过DMA传输). 所以应用程序通过读写这个水池。就可以相当于操作了显示卡。系统中能够在/dev/fb*看到framebuffer设备。
以下这幅图非常好的描写叙述了framebuffer执行机制:

framebuffer子系统的层次结构:
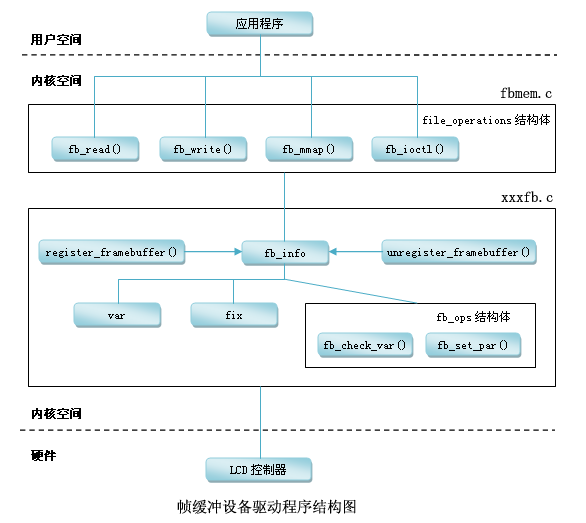
上图主要在以下文件里:
drivers/vedio/fbmem.c 该文件是framebuffer实现的核心。与硬件无关
drivers/vedio/xxxfb.c 该文件主要是framebuffer 设备驱动的实现,如s3c2410fb.c实现了framebuffer设备驱动
fbmem.c是实现framebuffer的核心。与硬件无关。
它使用了以下这些数据结构:
struct fb_info *fb_info 该数据结构描写叙述了一个framebuffer device相关一系列信息struct fb_ops *fb_ops 该数据结构描写叙述了一个framebuffer device的操作函数集合。相似file_operations,但仅仅供内核使用
static const struct file_operations fb_fops 该数据结构为文件操作函数集合。当应用程序打开设备时。用户能够read,write,ioctl等
struct fb_var_screeninfo var 该数据结构描写叙述了framebuffer device显示特性,是能够更改的
struct fb_fix_screeninfo fix 该数据结构用于保存framebuffer device显示特性,是固定不变的,不能够更改
详细数据结构:
- struct fb_var_screeninfo {
- __u32 xres; /* visible resolution */
- __u32 yres;
- __u32 xres_virtual; /* virtual resolution */
- __u32 yres_virtual;
- __u32 xoffset; /* offset from virtual to visible */
- __u32 yoffset; /* resolution */
- __u32 bits_per_pixel; /* guess what */
- __u32 grayscale; /* != 0 Graylevels instead of colors */
- struct fb_bitfield red; /* bitfield in fb mem if true color, */
- struct fb_bitfield green; /* else only length is significant */
- struct fb_bitfield blue;
- struct fb_bitfield transp; /* transparency */
- __u32 nonstd; /* != 0 Non standard pixel format */
- __u32 activate; /* see FB_ACTIVATE_* */
- __u32 height; /* height of picture in mm */
- __u32 width; /* width of picture in mm */
- __u32 accel_flags; /* (OBSOLETE) see fb_info.flags */
- /* Timing: All values in pixclocks, except pixclock (of course) */
- __u32 pixclock; /* pixel clock in ps (pico seconds) */
- __u32 left_margin; /* time from sync to picture */
- __u32 right_margin; /* time from picture to sync */
- __u32 upper_margin; /* time from sync to picture */
- __u32 lower_margin;
- __u32 hsync_len; /* length of horizontal sync */
- __u32 vsync_len; /* length of vertical sync */
- __u32 sync; /* see FB_SYNC_* */
- __u32 vmode; /* see FB_VMODE_* */
- __u32 rotate; /* angle we rotate counter clockwise */
- __u32 reserved[5]; /* Reserved for future compatibility */
- };
- struct fb_fix_screeninfo {
- char id[16]; /* identification string eg "TT Builtin" */
- unsigned long smem_start; /* Start of frame buffer mem */
- /* (physical address) */
- __u32 smem_len; /* Length of frame buffer mem */
- __u32 type; /* see FB_TYPE_* */
- __u32 type_aux; /* Interleave for interleaved Planes */
- __u32 visual; /* see FB_VISUAL_* */
- __u16 xpanstep; /* zero if no hardware panning */
- __u16 ypanstep; /* zero if no hardware panning */
- __u16 ywrapstep; /* zero if no hardware ywrap */
- __u32 line_length; /* length of a line in bytes */
- unsigned long mmio_start; /* Start of Memory Mapped I/O */
- /* (physical address) */
- __u32 mmio_len; /* Length of Memory Mapped I/O */
- __u32 accel; /* Indicate to driver which */
- /* specific chip/card we have */
- __u16 reserved[3]; /* Reserved for future compatibility */
- };
- struct fb_info {
- int node;
- int flags;
- struct mutex lock; /* Lock for open/release/ioctl funcs */
- struct fb_var_screeninfo var; /* Current var */
- struct fb_fix_screeninfo fix; /* Current fix */
- struct fb_monspecs monspecs; /* Current Monitor specs */
- struct work_struct queue; /* Framebuffer event queue */
- struct fb_pixmap pixmap; /* Image hardware mapper */
- struct fb_pixmap sprite; /* Cursor hardware mapper */
- struct fb_cmap cmap; /* Current cmap */
- struct list_head modelist; /* mode list */
- struct fb_videomode *mode; /* current mode */
- ...
- struct fb_ops *fbops;
- struct device *device; /* This is the parent */
- struct device *dev; /* This is this fb device */
- int class_flag; /* private sysfs flags */
- #ifdef CONFIG_FB_TILEBLITTING
- struct fb_tile_ops *tileops; /* Tile Blitting */
- #endif
- char __iomem *screen_base; /* Virtual address */
- unsigned long screen_size; /* Amount of ioremapped VRAM or 0 */
- void *pseudo_palette; /* Fake palette of 16 colors */
- ...
- };
- struct fb_ops {
- /* open/release and usage marking */
- struct module *owner;
- int (*fb_open)(struct fb_info *info, int user);
- int (*fb_release)(struct fb_info *info, int user);
- /* For framebuffers with strange non linear layouts or that do not
- * work with normal memory mapped access
- */
- ssize_t (*fb_read)(struct fb_info *info, char __user *buf,
- size_t count, loff_t *ppos);
- ssize_t (*fb_write)(struct fb_info *info, const char __user *buf,
- size_t count, loff_t *ppos);
- /* checks var and eventually tweaks it to something supported,
- * DO NOT MODIFY PAR */
- int (*fb_check_var)(struct fb_var_screeninfo *var, struct fb_info *info);
- /* set the video mode according to info->var */
- int (*fb_set_par)(struct fb_info *info);
- /* set color register */
- int (*fb_setcolreg)(unsigned regno, unsigned red, unsigned green,
- unsigned blue, unsigned transp, struct fb_info *info);
- /* set color registers in batch */
- int (*fb_setcmap)(struct fb_cmap *cmap, struct fb_info *info);
- /* blank display */
- int (*fb_blank)(int blank, struct fb_info *info);
- /* pan display */
- int (*fb_pan_display)(struct fb_var_screeninfo *var, struct fb_info *info);
- /* Draws a rectangle */
- void (*fb_fillrect) (struct fb_info *info, const struct fb_fillrect *rect);
- /* Copy data from area to another */
- void (*fb_copyarea) (struct fb_info *info, const struct fb_copyarea *region);
- /* Draws a image to the display */
- void (*fb_imageblit) (struct fb_info *info, const struct fb_image *image);
- /* Draws cursor */
- int (*fb_cursor) (struct fb_info *info, struct fb_cursor *cursor);
- /* Rotates the display */
- void (*fb_rotate)(struct fb_info *info, int angle);
- /* wait for blit idle, optional */
- int (*fb_sync)(struct fb_info *info);
- /* perform fb specific ioctl (optional) */
- int (*fb_ioctl)(struct fb_info *info, unsigned int cmd,
- unsigned long arg);
- /* Handle 32bit compat ioctl (optional) */
- int (*fb_compat_ioctl)(struct fb_info *info, unsigned cmd,
- unsigned long arg);
- /* perform fb specific mmap */
- int (*fb_mmap)(struct fb_info *info, struct vm_area_struct *vma);
- /* save current hardware state */
- void (*fb_save_state)(struct fb_info *info);
- /* restore saved state */
- void (*fb_restore_state)(struct fb_info *info);
- /* get capability given var */
- void (*fb_get_caps)(struct fb_info *info, struct fb_blit_caps *caps,
- struct fb_var_screeninfo *var);
- };
- static const struct file_operations fb_fops = {
- .owner = THIS_MODULE,
- .read = fb_read,
- .write = fb_write,
- .check_flags = my_check,
- .unlocked_ioctl = fb_ioctl,
- #ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
- .compat_ioctl = fb_compat_ioctl,
- #endif
- .mmap = fb_mmap,
- .open = fb_open,
- .release = fb_release,
- #ifdef HAVE_ARCH_FB_UNMAPPED_AREA
- .get_unmapped_area = get_fb_unmapped_area,
- #endif
- #ifdef CONFIG_FB_DEFERRED_IO
- .fsync = fb_deferred_io_fsync,
- #endif
- };
framebuffer设备的注冊与注销:
register_framebuffer(struct fb_info *fb_info);
unregister_framebuffer(struct fb_info *fb_info);
以下看看fb_ioctl 都做了什么?
static long do_fb_ioctl(struct fb_info *info, unsigned int cmd,
unsigned long arg)
{
struct fb_ops *fb;
struct fb_var_screeninfo var;
struct fb_fix_screeninfo fix;
struct fb_con2fbmap con2fb;
struct fb_cmap cmap_from;
struct fb_cmap_user cmap;
struct fb_event event;
void __user *argp = (void __user *)arg;
long ret = 0; switch (cmd) {
case FBIOGET_VSCREENINFO:
if (!lock_fb_info(info))
return -ENODEV;
var = info->var;
unlock_fb_info(info); ret = copy_to_user(argp, &var, sizeof(var)) ? -EFAULT : 0;
break;
case FBIOPUT_VSCREENINFO:
if (copy_from_user(&var, argp, sizeof(var)))
return -EFAULT;
if (!lock_fb_info(info))
return -ENODEV;
console_lock();
info->flags |= FBINFO_MISC_USEREVENT;
ret = fb_set_var(info, &var);
info->flags &= ~FBINFO_MISC_USEREVENT;
console_unlock();
unlock_fb_info(info);
if (!ret && copy_to_user(argp, &var, sizeof(var)))
ret = -EFAULT;
break;
case FBIOGET_FSCREENINFO:
if (!lock_fb_info(info))
return -ENODEV;
fix = info->fix;
unlock_fb_info(info); ret = copy_to_user(argp, &fix, sizeof(fix)) ? -EFAULT : 0;
break;
case FBIOPUTCMAP:
if (copy_from_user(&cmap, argp, sizeof(cmap)))
return -EFAULT;
ret = fb_set_user_cmap(&cmap, info);
break;
case FBIOGETCMAP:
if (copy_from_user(&cmap, argp, sizeof(cmap)))
return -EFAULT;
if (!lock_fb_info(info))
return -ENODEV;
cmap_from = info->cmap;
unlock_fb_info(info);
ret = fb_cmap_to_user(&cmap_from, &cmap);
break;
case FBIOPAN_DISPLAY:
if (copy_from_user(&var, argp, sizeof(var)))
return -EFAULT;
if (!lock_fb_info(info))
return -ENODEV;
console_lock();
ret = fb_pan_display(info, &var);
console_unlock();
unlock_fb_info(info);
if (ret == 0 && copy_to_user(argp, &var, sizeof(var)))
return -EFAULT;
break;
case FBIO_CURSOR:
ret = -EINVAL;
break;
case FBIOGET_CON2FBMAP:
if (copy_from_user(&con2fb, argp, sizeof(con2fb)))
return -EFAULT;
if (con2fb.console < 1 || con2fb.console > MAX_NR_CONSOLES)
return -EINVAL;
con2fb.framebuffer = -1;
event.data = &con2fb;
if (!lock_fb_info(info))
return -ENODEV;
event.info = info;
fb_notifier_call_chain(FB_EVENT_GET_CONSOLE_MAP, &event);
unlock_fb_info(info);
ret = copy_to_user(argp, &con2fb, sizeof(con2fb)) ? -EFAULT : 0;
break;
case FBIOPUT_CON2FBMAP:
if (copy_from_user(&con2fb, argp, sizeof(con2fb)))
return -EFAULT;
if (con2fb.console < 1 || con2fb.console > MAX_NR_CONSOLES)
return -EINVAL;
if (con2fb.framebuffer < 0 || con2fb.framebuffer >= FB_MAX)
return -EINVAL;
if (!registered_fb[con2fb.framebuffer])
request_module("fb%d", con2fb.framebuffer);
if (!registered_fb[con2fb.framebuffer]) {
ret = -EINVAL;
break;
}
event.data = &con2fb;
if (!lock_fb_info(info))
return -ENODEV;
event.info = info;
ret = fb_notifier_call_chain(FB_EVENT_SET_CONSOLE_MAP, &event);
unlock_fb_info(info);
break;
case FBIOBLANK:
if (!lock_fb_info(info))
return -ENODEV;
console_lock();
info->flags |= FBINFO_MISC_USEREVENT;
ret = fb_blank(info, arg);
info->flags &= ~FBINFO_MISC_USEREVENT;
console_unlock();
unlock_fb_info(info);
break;
default:
if (!lock_fb_info(info))
return -ENODEV;
fb = info->fbops;
if (fb->fb_ioctl)
ret = fb->fb_ioctl(info, cmd, arg);
else
ret = -ENOTTY;
unlock_fb_info(info);
}
return ret;
} static long fb_ioctl(struct file *file, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg)
{
struct fb_info *info = file_fb_info(file); printk(\nfb_ioctl mem\n);
if (!info)
return -ENODEV;
return do_fb_ioctl(info, cmd, arg);
}
依据文件操作的static const struct file_operations fb_fops,应用程序在打开一个framebuffer设备时。能够使用read,write,ioctl来直接操作设备。
应用例程:
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #include <unistd.h>
- #include <sys/ioctl.h>
- #include <fcntl.h>
- #include <linux/fb.h>
- #include <sys/mman.h>
- struct fb_var_screeninfo vinfo;
- struct fb_fix_screeninfo finfo;
- static void fb_var_printf(struct fb_var_screeninfo tmp)
- {
- printf("fb_var_screeninfo:\n");
- printf("xres =%d, yres =%d, bits_per_pixel = %d\n",tmp.xres,tmp.yres,tmp.bits_per_pixel);
- printf("height=%d,width = %d\n",tmp.height,tmp.width);
- printf("xres_virtual =%d, yres_virtual =%d, xoffset=%d,yoffset=%d\n",tmp.xres_virtual,tmp.yres_virtual,tmp.xoffset,tmp.yoffset);
- return ;
- }
- int main(void)
- {
- int fbfd;
- int fbsize;
- unsigned char *fbbuf;
- char buf[100];
- int i,res,adc_data;
- for (i=0; i<100; i++) buf[i] = 0xaa;
- if ((fbfd = open("/dev/fb0", O_RDWR)) < 0) {
- printf("open fb0 failed\n");
- return 1;
- }
- printf("fbfd = %d\n", fbfd);
- if ((res =ioctl(fbfd, FBIOGET_VSCREENINFO, &vinfo))) { //获取设备显示特性信息
- printf("bad vscreeninfo ioctl.error = %d\n",res);
- }
- fb_var_printf(vinfo);
- fbsize = vinfo.xres * vinfo.yres * (vinfo.bits_per_pixel/8); //计算显卡(LCD控制器)显存大小。也就是一整屏共占多少个字节
- printf("fbisze: %d\n",fbsize);
- if ((fbbuf = mmap(0, fbsize, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, fbfd, 0)) == (void*) -1) //映射显卡设备的内存到用户控件,使得用户直接訪问设备内存(显存)
- {
- printf("map video error.\n");
- }
- for (i = 0; i< fbsize; i++) { //填充farmebuffer缓冲区
- *(fbbuf+i) = 0xaa; //颜色信息
- }
- munmap(fbbuf, fbsize);
- close(fbfd);
- return 0;
- }

Linux内核修炼之framebuffer分析的更多相关文章
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(十一)--驱动程序层(下)
本文分析基于Linux Kernel 1.2.13 原创作品,转载请标明http://blog.csdn.net/yming0221/article/details/7555870 更多请查看专栏,地 ...
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(七)--数据包的传递过程(下)
本文分析基于Linux Kernel 1.2.13 原创作品,转载请标明http://blog.csdn.net/yming0221/article/details/7545855 更多请查看专栏,地 ...
- linux内核SPI总线驱动分析(一)(转)
linux内核SPI总线驱动分析(一)(转) 下面有两个大的模块: 一个是SPI总线驱动的分析 (研究了具体实现的过程) 另一个是SPI总线驱动的编写(不用研究具体的实现过程) ...
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(二)--数据包的传递过程--转
转载地址http://blog.csdn.net/yming0221/article/details/7492423 作者:闫明 本文分析基于Linux Kernel 1.2.13 注:标题中的”(上 ...
- Linux内核态抢占机制分析(转)
Linux内核态抢占机制分析 http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_502c8cc401012pxj.html 摘 要]本文首先介绍非抢占式内核(Non-Preemptive ...
- linux内核中链表代码分析---list.h头文件分析(一)【转】
转自:http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-30254565-id-5637596.html linux内核中链表代码分析---list.h头文件分析(一) 16年2月27日17 ...
- linux内核中链表代码分析---list.h头文件分析(二)【转】
转自:http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-30254565-id-5637598.html linux内核中链表代码分析---list.h头文件分析(二) 16年2月28日16 ...
- Linux内核哈希表分析与应用
目录(?)[+] Linux内核哈希表分析与应用 Author:tiger-johnTime:2012-12-20mail:jibo.tiger@gmail.comBlog:http:// ...
- Linux内核抢占实现机制分析【转】
Linux内核抢占实现机制分析 转自:http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-24227137-id-3050754.html [摘要]本文详解了Linux内核抢占实现机制.首先介 ...
随机推荐
- DP-hdu1176
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1176 这道题与动态规划中的数塔问题十分类似,因此如果对于数塔问题还不太明白的,可以先参考一下博客: 数 ...
- Mac配置Eclipse CDT的Debug出现的问题(转)
问题1:出现 Could not determine GDB version using command: gdb --version 原因: mac上没有安装gdb或者gdb位置配置有问题 解决 ...
- 001.Linux网路配置
一 Linux的IP别名功能 1.1 简介 一块网卡具有多个IP地址的功能称为IP别名,即一块网卡可以绑定多个IP地址. 1.2 实现 [root@master ~]# vi /etc/sysconf ...
- spring中整合ssm框架注解版
和xml版差不多,只不过创建对象的方式是由spring自动扫描包名,然后命名空间多一行context代码在application.xml中,然后将每个对象通过注解创建和注入: 直接上代码: 1.use ...
- POJ.3710.Christmas Game(博弈论 树上删边游戏 Multi-SG)
题目链接 \(Description\) 给定n棵"树",每棵"树"的节点可能"挂着"一个环,保证没有环相交,且与树只有一个公共点. 两人轮 ...
- ssm中从页面到controller和数据库出现乱码问题的解决
1.确保项目编码为utf8,点击项目右键,点击properties 2.确保数据库编码为utf8,以MySQL为例,可到mysql目录下,my.ini文件中修改后,重启mysql服务 重启mysql服 ...
- CocosCreator的Sprite的更换
先上图,左侧是运行的效果, cc.Class({ extends: cc.Component, /* * cocos creator动态更换纹理 *方法一,预先在编辑器里设置好所有的纹理,绑定到对应的 ...
- win2008R2管理员密码修改文档
场景:忘记了win2008R2服务器的管理员密码.解决办法:1. 制作一个U盘启动盘:2. 系统通过U盘启动进入WINpe系统3. 在知道Win2008安装位置的情况下:查找C:\windows\sy ...
- [转]delphi 有授权许可的字符串拷贝函数源码
一段看上去“貌不惊人”的Delphi插入汇编代码,却需要授权许可,但是与经典的同类型函数比较,确实“身手不凡”. 研究代码的目的在于借鉴,本文通过分析,并用C++重写代码进行比较,再次证明这段代码效率 ...
- Unity Shader-后处理:简单均值模糊
一.简介 今天来学习一下后处理中比较常用的一种效果,屏幕模糊效果.模糊效果,在图像处理中经常用到,Photoshop中也有类似的滤镜.我们在游戏中也会经常用到.因为屏幕模糊效果是一些高级后处理效果 ...
