uboot启动过程 2
512M内存, 地址范围 [0x80000000, 0xA0000000)
UBOOT原先位置 0x87800000, 移动后的位置0x9FF47000, 也就是最后 700多k, 前面的位置留给内核
https://www.cnblogs.com/kehuadong/p/14054220.html 中说到main调用了board_init_f, 参数0
void board_init_f(ulong boot_flags)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_SYS_GENERIC_GLOBAL_DATA
/*
* For some archtectures, global data is initialized and used before
* calling this function. The data should be preserved. For others,
* CONFIG_SYS_GENERIC_GLOBAL_DATA should be defined and use the stack
* here to host global data until relocation.
*/
gd_t data;
gd = &data;
/*
* Clear global data before it is accessed at debug print
* in initcall_run_list. Otherwise the debug print probably
* get the wrong vaule of gd->have_console.
*/
zero_global_data();
#endif
gd->flags = boot_flags;
gd->have_console = 0;
if (initcall_run_list(init_sequence_f))
hang();
#if !defined(CONFIG_ARM) && !defined(CONFIG_SANDBOX) && \
!defined(CONFIG_EFI_APP)
/* NOTREACHED - jump_to_copy() does not return */
hang();
#endif
/* Light up LED1 */
imx6_light_up_led1();
}
static init_fnc_t init_sequence_f[] = {
#ifdef CONFIG_SANDBOX
setup_ram_buf,
#endif
setup_mon_len,
#ifdef CONFIG_OF_CONTROL
fdtdec_setup,
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_TRACE
trace_early_init,
#endif
initf_malloc,
initf_console_record,
#if defined(CONFIG_MPC85xx) || defined(CONFIG_MPC86xx)
/* TODO: can this go into arch_cpu_init()? */
probecpu,
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_X86) && defined(CONFIG_HAVE_FSP)
x86_fsp_init,
#endif
arch_cpu_init, /* basic arch cpu dependent setup */
initf_dm,
arch_cpu_init_dm,
mark_bootstage, /* need timer, go after init dm */
#if defined(CONFIG_BOARD_EARLY_INIT_F)
board_early_init_f,
#endif
/* TODO: can any of this go into arch_cpu_init()? */
#if defined(CONFIG_PPC) && !defined(CONFIG_8xx_CPUCLK_DEFAULT)
get_clocks, /* get CPU and bus clocks (etc.) */
#if defined(CONFIG_TQM8xxL) && !defined(CONFIG_TQM866M) \
&& !defined(CONFIG_TQM885D)
adjust_sdram_tbs_8xx,
#endif
/* TODO: can we rename this to timer_init()? */
init_timebase,
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_ARM) || defined(CONFIG_MIPS) || \
defined(CONFIG_BLACKFIN) || defined(CONFIG_NDS32) || \
defined(CONFIG_SPARC)
timer_init, /* initialize timer */
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_SYS_ALLOC_DPRAM
#if !defined(CONFIG_CPM2)
dpram_init,
#endif
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_BOARD_POSTCLK_INIT)
board_postclk_init,
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_SYS_FSL_CLK) || defined(CONFIG_M68K)
get_clocks,
#endif
env_init, /* initialize environment */
#if defined(CONFIG_8xx_CPUCLK_DEFAULT)
/* get CPU and bus clocks according to the environment variable */
get_clocks_866,
/* adjust sdram refresh rate according to the new clock */
sdram_adjust_866,
init_timebase,
#endif
init_baud_rate, /* initialze baudrate settings */
serial_init, /* serial communications setup */
console_init_f, /* stage 1 init of console */
#ifdef CONFIG_SANDBOX
sandbox_early_getopt_check,
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_OF_CONTROL
fdtdec_prepare_fdt,
#endif
display_options, /* say that we are here */
display_text_info, /* show debugging info if required */
#if defined(CONFIG_MPC8260)
prt_8260_rsr,
prt_8260_clks,
#endif /* CONFIG_MPC8260 */
#if defined(CONFIG_MPC83xx)
prt_83xx_rsr,
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_PPC) || defined(CONFIG_M68K)
checkcpu,
#endif
print_cpuinfo, /* display cpu info (and speed) */
#if defined(CONFIG_MPC5xxx)
prt_mpc5xxx_clks,
#endif /* CONFIG_MPC5xxx */
#if defined(CONFIG_DISPLAY_BOARDINFO)
show_board_info,
#endif
INIT_FUNC_WATCHDOG_INIT
#if defined(CONFIG_MISC_INIT_F)
misc_init_f,
#endif
INIT_FUNC_WATCHDOG_RESET
#if defined(CONFIG_HARD_I2C) || defined(CONFIG_SYS_I2C)
init_func_i2c,
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_HARD_SPI)
init_func_spi,
#endif
announce_dram_init,
/* TODO: unify all these dram functions? */
#if defined(CONFIG_ARM) || defined(CONFIG_X86) || defined(CONFIG_NDS32) || \
defined(CONFIG_MICROBLAZE) || defined(CONFIG_AVR32)
dram_init, /* configure available RAM banks */
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_MIPS) || defined(CONFIG_PPC) || defined(CONFIG_M68K)
init_func_ram,
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_POST
post_init_f,
#endif
INIT_FUNC_WATCHDOG_RESET
#if defined(CONFIG_SYS_DRAM_TEST)
testdram,
#endif /* CONFIG_SYS_DRAM_TEST */
INIT_FUNC_WATCHDOG_RESET
#ifdef CONFIG_POST
init_post,
#endif
INIT_FUNC_WATCHDOG_RESET
/*
* Now that we have DRAM mapped and working, we can
* relocate the code and continue running from DRAM.
*
* Reserve memory at end of RAM for (top down in that order):
* - area that won't get touched by U-Boot and Linux (optional)
* - kernel log buffer
* - protected RAM
* - LCD framebuffer
* - monitor code
* - board info struct
*/
setup_dest_addr,
#if defined(CONFIG_BLACKFIN)
/* Blackfin u-boot monitor should be on top of the ram */
reserve_uboot,
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_SPARC)
reserve_prom,
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_LOGBUFFER) && !defined(CONFIG_ALT_LB_ADDR)
reserve_logbuffer,
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PRAM
reserve_pram,
#endif
reserve_round_4k,
#if !(defined(CONFIG_SYS_ICACHE_OFF) && defined(CONFIG_SYS_DCACHE_OFF)) && \
defined(CONFIG_ARM)
reserve_mmu,
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_DM_VIDEO
reserve_video,
#else
# ifdef CONFIG_LCD
reserve_lcd,
# endif
/* TODO: Why the dependency on CONFIG_8xx? */
# if defined(CONFIG_VIDEO) && (!defined(CONFIG_PPC) || defined(CONFIG_8xx)) && \
!defined(CONFIG_ARM) && !defined(CONFIG_X86) && \
!defined(CONFIG_BLACKFIN) && !defined(CONFIG_M68K)
reserve_legacy_video,
# endif
#endif /* CONFIG_DM_VIDEO */
reserve_trace,
#if !defined(CONFIG_BLACKFIN)
reserve_uboot,
#endif
#ifndef CONFIG_SPL_BUILD
reserve_malloc,
reserve_board,
#endif
setup_machine,
reserve_global_data,
reserve_fdt,
reserve_arch,
reserve_stacks,
setup_dram_config,
show_dram_config,
#if defined(CONFIG_PPC) || defined(CONFIG_M68K) || defined(CONFIG_MIPS)
setup_board_part1,
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_PPC) || defined(CONFIG_M68K)
INIT_FUNC_WATCHDOG_RESET
setup_board_part2,
#endif
display_new_sp,
#ifdef CONFIG_SYS_EXTBDINFO
setup_board_extra,
#endif
INIT_FUNC_WATCHDOG_RESET
reloc_fdt,
setup_reloc,
#if defined(CONFIG_X86) || defined(CONFIG_ARC)
copy_uboot_to_ram,
clear_bss,
do_elf_reloc_fixups,
#endif
#if !defined(CONFIG_ARM) && !defined(CONFIG_SANDBOX)
jump_to_copy,
#endif
NULL,
};
common/board_f.c
static int setup_mon_len(void)
{
#if defined(__ARM__) || defined(__MICROBLAZE__)
gd->mon_len = (ulong)&__bss_end - (ulong)_start;
#elif defined(CONFIG_SANDBOX) || defined(CONFIG_EFI_APP)
gd->mon_len = (ulong)&_end - (ulong)_init;
#elif defined(CONFIG_BLACKFIN) || defined(CONFIG_NIOS2)
gd->mon_len = CONFIG_SYS_MONITOR_LEN;
#elif defined(CONFIG_NDS32)
gd->mon_len = (ulong)(&__bss_end) - (ulong)(&_start);
#else
/* TODO: use (ulong)&__bss_end - (ulong)&__text_start; ? */
gd->mon_len = (ulong)&__bss_end - CONFIG_SYS_MONITOR_BASE;
#endif
return 0;
}
OUTPUT_FORMAT("elf32-littlearm", "elf32-littlearm", "elf32-littlearm")
OUTPUT_ARCH(arm)
ENTRY(_start)
SECTIONS
{
. = 0x00000000;
. = ALIGN(4);
.text :
{
*(.__image_copy_start)
*(.vectors) _start在这里
arch/arm/cpu/armv7/start.o (.text*)
*(.text*)
}
. = ALIGN(4);
.rodata : { *(SORT_BY_ALIGNMENT(SORT_BY_NAME(.rodata*))) }
. = ALIGN(4);
.data : {
*(.data*)
}
. = ALIGN(4);
. = .;
. = ALIGN(4);
.u_boot_list : {
KEEP(*(SORT(.u_boot_list*)));
}
. = ALIGN(4);
.image_copy_end :
{
*(.__image_copy_end)
}
.rel_dyn_start :
{
*(.__rel_dyn_start)
}
.rel.dyn : {
*(.rel*)
}
.rel_dyn_end :
{
*(.__rel_dyn_end)
}
.end :
{
*(.__end)
}
_image_binary_end = .;
. = ALIGN(4096);
.mmutable : {
*(.mmutable)
}
.bss_start __rel_dyn_start (OVERLAY) : {
KEEP(*(.__bss_start));
__bss_base = .;
}
.bss __bss_base (OVERLAY) : {
*(.bss*)
. = ALIGN(4);
__bss_limit = .;
}
.bss_end __bss_limit (OVERLAY) : {
KEEP(*(.__bss_end)); _bss_end在这里
}
common/dlmalloc.c
int initf_malloc(void)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_SYS_MALLOC_F_LEN
assert(gd->malloc_base); /* Set up by crt0.S */
gd->malloc_limit = CONFIG_SYS_MALLOC_F_LEN; // board_init_f_init_reserve中所预留的动态分配空间, 4*0x100=1k
gd->malloc_ptr = 0;
#endif
return 0;
}
common/board_f.c
static int initf_console_record(void)
{
#if defined(CONFIG_CONSOLE_RECORD) && defined(CONFIG_SYS_MALLOC_F_LEN)
return console_record_init(); // 不到这里,因为IMX6ULL没定义CONFIG_CONSOLE_RECORD
#else
return 0;
#endif
}
int arch_cpu_init(void)
{
if (!is_cpu_type(MXC_CPU_MX6SL) && !is_cpu_type(MXC_CPU_MX6SX)
&& !is_cpu_type(MXC_CPU_MX6UL) && !is_cpu_type(MXC_CPU_MX6ULL)
&& !is_cpu_type(MXC_CPU_MX6SLL)) {
/*
* imx6sl doesn't have pcie at all.
* this bit is not used by imx6sx anymore
*/
u32 val;
/*
* There are about 0.02% percentage, random pcie link down
* when warm-reset is used.
* clear the ref_ssp_en bit16 of gpr1 to workaround it.
* then warm-reset imx6q/dl/solo again.
*/
val = readl(IOMUXC_BASE_ADDR + 0x4);
if (val & (0x1 << 16)) {
val &= ~(0x1 << 16);
writel(val, IOMUXC_BASE_ADDR + 0x4);
reset_cpu(0);
}
}
init_aips();
/* Need to clear MMDC_CHx_MASK to make warm reset work. */
clear_mmdc_ch_mask();
/*
* Disable self-bias circuit in the analog bandap.
* The self-bias circuit is used by the bandgap during startup.
* This bit should be set after the bandgap has initialized.
*/
init_bandgap();
if (!is_cpu_type(MXC_CPU_MX6UL) && !is_cpu_type(MXC_CPU_MX6ULL)) {
/*
* When low freq boot is enabled, ROM will not set AHB
* freq, so we need to ensure AHB freq is 132MHz in such
* scenario.
*/
if (mxc_get_clock(MXC_ARM_CLK) == 396000000)
set_ahb_rate(132000000);
}
if (is_cpu_type(MXC_CPU_MX6UL)) {
if (is_soc_rev(CHIP_REV_1_0)) {
/*
* According to the design team's requirement on i.MX6UL,
* the PMIC_STBY_REQ PAD should be configured as open
* drain 100K (0x0000b8a0).
*/
writel(0x0000b8a0, IOMUXC_BASE_ADDR + 0x29c);
} else {
/*
* From TO1.1, SNVS adds internal pull up control for POR_B,
* the register filed is GPBIT[1:0], after system boot up,
* it can be set to 2b'01 to disable internal pull up.
* It can save about 30uA power in SNVS mode.
*/
writel((readl(MX6UL_SNVS_LP_BASE_ADDR + 0x10) & (~0x1400)) | 0x400,
MX6UL_SNVS_LP_BASE_ADDR + 0x10);
}
}
if (is_cpu_type(MXC_CPU_MX6ULL)) {
/*
* GPBIT[1:0] is suggested to set to 2'b11:
* 2'b00 : always PUP100K
* 2'b01 : PUP100K when PMIC_ON_REQ or SOC_NOT_FAIL
* 2'b10 : always disable PUP100K
* 2'b11 : PDN100K when SOC_FAIL, PUP100K when SOC_NOT_FAIL
* register offset is different from i.MX6UL, since
* i.MX6UL is fixed by ECO.
*/
writel(readl(MX6UL_SNVS_LP_BASE_ADDR) |0x3, MX6UL_SNVS_LP_BASE_ADDR);
}
/* Set perclk to source from OSC 24MHz */
#if defined(CONFIG_MX6SL)
set_preclk_from_osc();
#endif
if (is_cpu_type(MXC_CPU_MX6SX))
set_uart_from_osc();
imx_set_wdog_powerdown(false); /* Disable PDE bit of WMCR register */
if (!is_cpu_type(MXC_CPU_MX6SL) && !is_cpu_type(MXC_CPU_MX6UL) &&
!is_cpu_type(MXC_CPU_MX6ULL) && !is_cpu_type(MXC_CPU_MX6SLL))
imx_set_pcie_phy_power_down();
if (!is_mx6dqp() && !is_cpu_type(MXC_CPU_MX6UL) &&
!is_cpu_type(MXC_CPU_MX6ULL) && !is_cpu_type(MXC_CPU_MX6SLL))
imx_set_vddpu_power_down();
#ifdef CONFIG_APBH_DMA
/* Start APBH DMA */
mxs_dma_init();
#endif
init_src();
if (is_mx6dqp())
writel(0x80000201, 0xbb0608);
return 0;
}
common/board_f.c
static int initf_dm(void)
{
#if defined(CONFIG_DM) && defined(CONFIG_SYS_MALLOC_F_LEN)
int ret;
ret = dm_init_and_scan(true);
if (ret)
return ret;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_TIMER_EARLY
ret = dm_timer_init();
if (ret)
return ret;
#endif
return 0;
}
common/board_f.c
__weak int arch_cpu_init_dm(void)
{
return 0;
}
common/board_f.c
static int mark_bootstage(void)
{
bootstage_mark_name(BOOTSTAGE_ID_START_UBOOT_F, "board_init_f");
return 0;
}
int board_early_init_f(void)
{
setup_iomux_uart();
return 0;
}
arch/arm/imx-common/tiemr.c
int timer_init(void)
{
int i;
/* setup GP Timer 1 */
__raw_writel(GPTCR_SWR, &cur_gpt->control);
/* We have no udelay by now */
for (i = 0; i < 100; i++)
__raw_writel(0, &cur_gpt->control);
i = __raw_readl(&cur_gpt->control);
i &= ~GPTCR_CLKSOURCE_MASK;
#ifdef CONFIG_MXC_GPT_HCLK
if (gpt_has_clk_source_osc()) {
i |= GPTCR_CLKSOURCE_OSC | GPTCR_TEN;
/* For DL/S, SX, UL, ULL set 24Mhz OSC Enable bit and prescaler */
if (is_cpu_type(MXC_CPU_MX6DL) ||
is_cpu_type(MXC_CPU_MX6SOLO) ||
is_cpu_type(MXC_CPU_MX6SX) ||
is_cpu_type(MXC_CPU_MX7D) ||
is_cpu_type(MXC_CPU_MX6UL) ||
is_cpu_type(MXC_CPU_MX6ULL) ||
is_cpu_type(MXC_CPU_MX6SLL)) {
i |= GPTCR_24MEN;
/* Produce 3Mhz clock */
__raw_writel((7 << GPTPR_PRESCALER24M_SHIFT),
&cur_gpt->prescaler);
}
} else {
i |= GPTCR_CLKSOURCE_PRE | GPTCR_TEN;
}
#else
__raw_writel(0, &cur_gpt->prescaler); /* 32Khz */
i |= GPTCR_CLKSOURCE_32 | GPTCR_TEN;
#endif
__raw_writel(i, &cur_gpt->control);
gd->arch.tbl = __raw_readl(&cur_gpt->counter);
gd->arch.tbu = 0;
return 0;
}
{
/* NO LDO SOC on i.MX6SLL */
if (is_cpu_type(MXC_CPU_MX6SLL))
return 0;
set_ldo_voltage(LDO_SOC, 1175); /* Set VDDSOC to 1.175V */
return 0;
}
arch/arm/imx-common/speed.c
int get_clocks(void)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_FSL_ESDHC
#ifdef CONFIG_FSL_USDHC
#if CONFIG_SYS_FSL_ESDHC_ADDR == USDHC2_BASE_ADDR
gd->arch.sdhc_clk = mxc_get_clock(MXC_ESDHC2_CLK);
#elif CONFIG_SYS_FSL_ESDHC_ADDR == USDHC3_BASE_ADDR
gd->arch.sdhc_clk = mxc_get_clock(MXC_ESDHC3_CLK);
#elif CONFIG_SYS_FSL_ESDHC_ADDR == USDHC4_BASE_ADDR
gd->arch.sdhc_clk = mxc_get_clock(MXC_ESDHC4_CLK);
#else
gd->arch.sdhc_clk = mxc_get_clock(MXC_ESDHC_CLK);
#endif
#else
#if CONFIG_SYS_FSL_ESDHC_ADDR == MMC_SDHC2_BASE_ADDR
gd->arch.sdhc_clk = mxc_get_clock(MXC_ESDHC2_CLK);
#elif CONFIG_SYS_FSL_ESDHC_ADDR == MMC_SDHC3_BASE_ADDR
gd->arch.sdhc_clk = mxc_get_clock(MXC_ESDHC3_CLK);
#elif CONFIG_SYS_FSL_ESDHC_ADDR == MMC_SDHC4_BASE_ADDR
gd->arch.sdhc_clk = mxc_get_clock(MXC_ESDHC4_CLK);
#else
gd->arch.sdhc_clk = mxc_get_clock(MXC_ESDHC_CLK);
#endif
#endif
#endif
return 0;
}
common/env_mmc.c
int env_init(void)
{
/* use default */
gd->env_addr = (ulong)&default_environment[0];
gd->env_valid = 1;
return 0;
}
static int init_baud_rate(void)
{
gd->baudrate = getenv_ulong("baudrate", 10, CONFIG_BAUDRATE);
return 0;
}
int serial_init(void)
{
gd->flags |= GD_FLG_SERIAL_READY;
return get_current()->start();
}
int console_init_f(void)
{
gd->have_console = 1;
#ifdef CONFIG_SILENT_CONSOLE
if (getenv("silent") != NULL)
gd->flags |= GD_FLG_SILENT;
#endif
print_pre_console_buffer(PRE_CONSOLE_FLUSHPOINT1_SERIAL);
return 0;
}
common/board_f.c
int display_options (void)
{
#if defined(BUILD_TAG)
printf ("\n\n%s, Build: %s\n\n", version_string, BUILD_TAG);
#else
printf ("\n\n%s\n\n", version_string);
#endif
return 0;
}
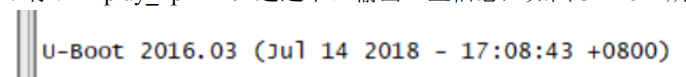
static int display_text_info(void)
{
#if !defined(CONFIG_SANDBOX) && !defined(CONFIG_EFI_APP)
ulong bss_start, bss_end, text_base;
bss_start = (ulong)&__bss_start;
bss_end = (ulong)&__bss_end;
#ifdef CONFIG_SYS_TEXT_BASE
text_base = CONFIG_SYS_TEXT_BASE;
#else
text_base = CONFIG_SYS_MONITOR_BASE;
#endif
debug("U-Boot code: %08lX -> %08lX BSS: -> %08lX\n",
text_base, bss_start, bss_end);
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_USE_IRQ
debug("IRQ Stack: %08lx\n", IRQ_STACK_START);
debug("FIQ Stack: %08lx\n", FIQ_STACK_START);
#endif
return 0;
}
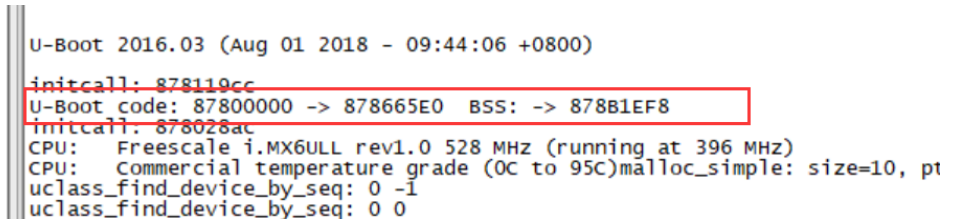
注意到setup_mon_len的_bss_end是878A8E74, 而这里的打印是878B1EF8, 因此需要实测去验证
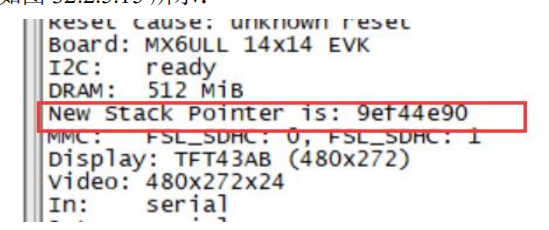
int print_cpuinfo(void)
{
u32 cpurev;
__maybe_unused u32 max_freq;
#if defined(CONFIG_DBG_MONITOR)
struct dbg_monitor_regs *dbg =
(struct dbg_monitor_regs *)DEBUG_MONITOR_BASE_ADDR;
#endif
cpurev = get_cpu_rev();
#if defined(CONFIG_IMX_THERMAL)
struct udevice *thermal_dev;
int cpu_tmp, minc, maxc, ret;
printf("CPU: Freescale i.MX%s rev%d.%d",
get_imx_type((cpurev & 0xFF000) >> 12),
(cpurev & 0x000F0) >> 4,
(cpurev & 0x0000F) >> 0);
max_freq = get_cpu_speed_grade_hz();
if (!max_freq || max_freq == mxc_get_clock(MXC_ARM_CLK)) {
printf(" at %dMHz\n", mxc_get_clock(MXC_ARM_CLK) / 1000000);
} else {
printf(" %d MHz (running at %d MHz)\n", max_freq / 1000000,
mxc_get_clock(MXC_ARM_CLK) / 1000000);
}
#else
printf("CPU: Freescale i.MX%s rev%d.%d at %d MHz\n",
get_imx_type((cpurev & 0xFF000) >> 12),
(cpurev & 0x000F0) >> 4,
(cpurev & 0x0000F) >> 0,
mxc_get_clock(MXC_ARM_CLK) / 1000000);
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_IMX_THERMAL)
puts("CPU: ");
switch (get_cpu_temp_grade(&minc, &maxc)) {
case TEMP_AUTOMOTIVE:
puts("Automotive temperature grade ");
break;
case TEMP_INDUSTRIAL:
puts("Industrial temperature grade ");
break;
case TEMP_EXTCOMMERCIAL:
puts("Extended Commercial temperature grade ");
break;
default:
puts("Commercial temperature grade ");
break;
}
printf("(%dC to %dC)", minc, maxc);
ret = uclass_get_device(UCLASS_THERMAL, 0, &thermal_dev);
if (!ret) {
ret = thermal_get_temp(thermal_dev, &cpu_tmp);
if (!ret)
printf(" at %dC\n", cpu_tmp);
else
debug(" - invalid sensor data\n");
} else {
debug(" - invalid sensor device\n");
}
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_DBG_MONITOR)
if (readl(&dbg->snvs_addr))
printf("DBG snvs regs addr 0x%x, data 0x%x, info 0x%x\n",
readl(&dbg->snvs_addr),
readl(&dbg->snvs_data),
readl(&dbg->snvs_info));
#endif
printf("Reset cause: %s\n", get_reset_cause());
return 0;
}

common/board_info.c
int show_board_info(void)
{
#if defined(CONFIG_OF_CONTROL) && !defined(CONFIG_CUSTOM_BOARDINFO)
DECLARE_GLOBAL_DATA_PTR;
const char *model;
model = fdt_getprop(gd->fdt_blob, 0, "model", NULL);
if (model)
printf("Model: %s\n", model);
#endif
return checkboard();
}
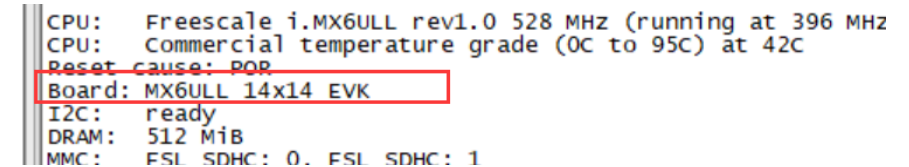
common/board_f.c
static int init_func_i2c(void)
{
puts("I2C: ");
#ifdef CONFIG_SYS_I2C
i2c_init_all();
#else
i2c_init(CONFIG_SYS_I2C_SPEED, CONFIG_SYS_I2C_SLAVE);
#endif
puts("ready\n");
return 0;
}
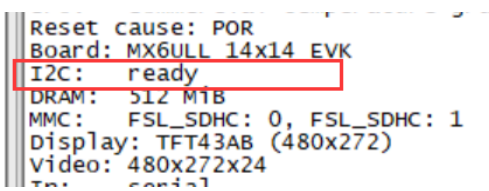
common/board_f.c
static int announce_dram_init(void)
{
puts("DRAM: ");
return 0;
}
int dram_init(void)
{
gd->ram_size = imx_ddr_size();
return 0;
}
arch/arm/imx-common/cpu.c
unsigned imx_ddr_size(void)
{
struct esd_mmdc_regs *mem = (struct esd_mmdc_regs *)MEMCTL_BASE;
unsigned ctl = readl(&mem->ctl);
unsigned misc = readl(&mem->misc);
int bits = 11 + 0 + 0 + 1; /* row + col + bank + width */
bits += ESD_MMDC_CTL_GET_ROW(ctl);
bits += col_lookup[ESD_MMDC_CTL_GET_COLUMN(ctl)];
bits += bank_lookup[ESD_MMDC_MISC_GET_BANK(misc)];
bits += ESD_MMDC_CTL_GET_WIDTH(ctl);
bits += ESD_MMDC_CTL_GET_CS1(ctl);
/* The MX6 can do only 3840 MiB of DRAM */
if (bits == 32)
return 0xf0000000;
return 1 << bits;
}
post/post.c
int post_init_f(void)
{
int res = 0;
unsigned int i;
for (i = 0; i < post_list_size; i++) {
struct post_test *test = post_list + i;
if (test->init_f && test->init_f())
res = -1;
}
gd->post_init_f_time = post_time_ms(0);
if (!gd->post_init_f_time)
printf("%s: post_time_ms not implemented\n", __FILE__);
return res;
}
static int setup_dest_addr(void)
{
debug("Monitor len: %08lX\n", gd->mon_len);
/*
* Ram is setup, size stored in gd !!
*/
debug("Ram size: %08lX\n", (ulong)gd->ram_size); // dram_init中初始化了ram_size
#ifdef CONFIG_SYS_MEM_RESERVE_SECURE
/* Reserve memory for secure MMU tables, and/or security monitor */
gd->ram_size -= CONFIG_SYS_MEM_RESERVE_SECURE;
/*
* Record secure memory location. Need recalcuate if memory splits
* into banks, or the ram base is not zero.
*/
gd->secure_ram = gd->ram_size;
#endif
/*
* Subtract specified amount of memory to hide so that it won't
* get "touched" at all by U-Boot. By fixing up gd->ram_size
* the Linux kernel should now get passed the now "corrected"
* memory size and won't touch it either. This has been used
* by arch/powerpc exclusively. Now ARMv8 takes advantage of
* thie mechanism. If memory is split into banks, addresses
* need to be calculated.
*/
gd->ram_size = board_reserve_ram_top(gd->ram_size);
#ifdef CONFIG_SYS_SDRAM_BASE
gd->ram_top = CONFIG_SYS_SDRAM_BASE;
#endif
gd->ram_top += get_effective_memsize();
gd->ram_top = board_get_usable_ram_top(gd->mon_len);
gd->relocaddr = gd->ram_top;
debug("Ram top: %08lX\n", (ulong)gd->ram_top);
#if defined(CONFIG_MP) && (defined(CONFIG_MPC86xx) || defined(CONFIG_E500))
/*
* We need to make sure the location we intend to put secondary core
* boot code is reserved and not used by any part of u-boot
*/
if (gd->relocaddr > determine_mp_bootpg(NULL)) {
gd->relocaddr = determine_mp_bootpg(NULL);
debug("Reserving MP boot page to %08lx\n", gd->relocaddr);
}
#endif
return 0;
}

common/board_f.c
static int reserve_round_4k(void)
{
gd->relocaddr &= ~(4096 - 1);
return 0;
}
common/board_f.c
static int reserve_mmu(void)
{
/* reserve TLB table */
gd->arch.tlb_size = PGTABLE_SIZE;
gd->relocaddr -= gd->arch.tlb_size;
/* round down to next 64 kB limit */
gd->relocaddr &= ~(0x10000 - 1);
gd->arch.tlb_addr = gd->relocaddr;
debug("TLB table from %08lx to %08lx\n", gd->arch.tlb_addr,
gd->arch.tlb_addr + gd->arch.tlb_size);
return 0;
}

common/board_f.c
static int reserve_trace(void)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_TRACE
gd->relocaddr -= CONFIG_TRACE_BUFFER_SIZE;
gd->trace_buff = map_sysmem(gd->relocaddr, CONFIG_TRACE_BUFFER_SIZE);
debug("Reserving %dk for trace data at: %08lx\n",
CONFIG_TRACE_BUFFER_SIZE >> 10, gd->relocaddr);
#endif
return 0;
}
static int reserve_uboot(void)
{
/*
* reserve memory for U-Boot code, data & bss
* round down to next 4 kB limit
*/
gd->relocaddr -= gd->mon_len;
gd->relocaddr &= ~(4096 - 1); // 4k对齐
#ifdef CONFIG_E500
/* round down to next 64 kB limit so that IVPR stays aligned */
gd->relocaddr &= ~(65536 - 1);
#endif
debug("Reserving %ldk for U-Boot at: %08lx\n", gd->mon_len >> 10,
gd->relocaddr);
gd->start_addr_sp = gd->relocaddr;
return 0;
}
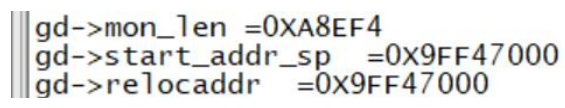
common/boad_f.c
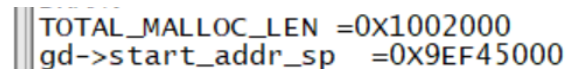
static int reserve_malloc(void)
{
gd->start_addr_sp = gd->start_addr_sp - TOTAL_MALLOC_LEN;
debug("Reserving %dk for malloc() at: %08lx\n",
TOTAL_MALLOC_LEN >> 10, gd->start_addr_sp);
return 0;
}
common/board_f.c
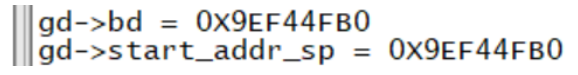
static int reserve_board(void)
{
if (!gd->bd) {
gd->start_addr_sp -= sizeof(bd_t);
gd->bd = (bd_t *)map_sysmem(gd->start_addr_sp, sizeof(bd_t));
memset(gd->bd, '\0', sizeof(bd_t));
debug("Reserving %zu Bytes for Board Info at: %08lx\n",
sizeof(bd_t), gd->start_addr_sp);
}
return 0;
}
common/board_f.c
static int setup_machine(void)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_MACH_TYPE
gd->bd->bi_arch_number = CONFIG_MACH_TYPE; /* board id for Linux */
#endif
return 0;
}
common/board_f.c
static int reserve_global_data(void)
{
gd->start_addr_sp -= sizeof(gd_t);
gd->new_gd = (gd_t *)map_sysmem(gd->start_addr_sp, sizeof(gd_t));
debug("Reserving %zu Bytes for Global Data at: %08lx\n",
sizeof(gd_t), gd->start_addr_sp);
return 0;
}
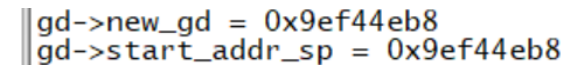
common/board_f.c
static int reserve_fdt(void)
{
#ifndef CONFIG_OF_EMBED
/*
* If the device tree is sitting immediately above our image then we
* must relocate it. If it is embedded in the data section, then it
* will be relocated with other data.
*/
if (gd->fdt_blob) {
gd->fdt_size = ALIGN(fdt_totalsize(gd->fdt_blob) + 0x1000, 32);
gd->start_addr_sp -= gd->fdt_size;
gd->new_fdt = map_sysmem(gd->start_addr_sp, gd->fdt_size);
debug("Reserving %lu Bytes for FDT at: %08lx\n",
gd->fdt_size, gd->start_addr_sp);
}
#endif
return 0;
}
common/board_f.c
static int reserve_stacks(void)
{
/* make stack pointer 16-byte aligned */
gd->start_addr_sp -= 16;
gd->start_addr_sp &= ~0xf;
/*
* let the architecture-specific code tailor gd->start_addr_sp and
* gd->irq_sp
*/
return arch_reserve_stacks();
}
int arch_reserve_stacks(void)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_SPL_BUILD
gd->start_addr_sp -= 128; /* leave 32 words for abort-stack */
gd->irq_sp = gd->start_addr_sp;
#else
/* setup stack pointer for exceptions */
gd->irq_sp = gd->start_addr_sp;
# if !defined(CONFIG_ARM64)
# ifdef CONFIG_USE_IRQ
gd->start_addr_sp -= (CONFIG_STACKSIZE_IRQ + CONFIG_STACKSIZE_FIQ);
debug("Reserving %zu Bytes for IRQ stack at: %08lx\n",
CONFIG_STACKSIZE_IRQ + CONFIG_STACKSIZE_FIQ, gd->start_addr_sp);
/* 8-byte alignment for ARM ABI compliance */
gd->start_addr_sp &= ~0x07;
# endif
/* leave 3 words for abort-stack, plus 1 for alignment */
gd->start_addr_sp -= 16;
# endif
#endif
return 0;
}
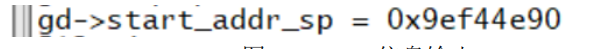
common/board_f.c
static int setup_dram_config(void)
{
/* Ram is board specific, so move it to board code ... */
dram_init_banksize();
return 0;
}
__weak void dram_init_banksize(void)
{
#if defined(CONFIG_NR_DRAM_BANKS) && defined(CONFIG_SYS_SDRAM_BASE)
gd->bd->bi_dram[0].start = CONFIG_SYS_SDRAM_BASE;
gd->bd->bi_dram[0].size = get_effective_memsize();
#endif
}

common/board_f.c
static int show_dram_config(void)
{
unsigned long long size;
#ifdef CONFIG_NR_DRAM_BANKS
int i;
debug("\nRAM Configuration:\n");
for (i = size = 0; i < CONFIG_NR_DRAM_BANKS; i++) {
size += gd->bd->bi_dram[i].size;
debug("Bank #%d: %llx ", i,
(unsigned long long)(gd->bd->bi_dram[i].start));
#ifdef DEBUG
print_size(gd->bd->bi_dram[i].size, "\n");
#endif
}
debug("\nDRAM: ");
#else
size = gd->ram_size;
#endif
print_size(size, "");
board_add_ram_info(0);
putc('\n');
return 0;
}
common/board_f.c
static int display_new_sp(void)
{
debug("New Stack Pointer is: %08lx\n", gd->start_addr_sp);
return 0;
}
common/board_f.c
static int reloc_fdt(void)
{
#ifndef CONFIG_OF_EMBED
if (gd->flags & GD_FLG_SKIP_RELOC)
return 0;
if (gd->new_fdt) {
memcpy(gd->new_fdt, gd->fdt_blob, gd->fdt_size);
gd->fdt_blob = gd->new_fdt;
}
#endif
return 0;
}
static int setup_reloc(void)
{
if (gd->flags & GD_FLG_SKIP_RELOC) {
debug("Skipping relocation due to flag\n");
return 0;
}
#ifdef CONFIG_SYS_TEXT_BASE
gd->reloc_off = gd->relocaddr - CONFIG_SYS_TEXT_BASE;
#ifdef CONFIG_M68K
/*
* On all ColdFire arch cpu, monitor code starts always
* just after the default vector table location, so at 0x400
*/
gd->reloc_off = gd->relocaddr - (CONFIG_SYS_TEXT_BASE + 0x400);
#endif
#endif
memcpy(gd->new_gd, (char *)gd, sizeof(gd_t));
debug("Relocation Offset is: %08lx\n", gd->reloc_off);
debug("Relocating to %08lx, new gd at %08lx, sp at %08lx\n",
gd->relocaddr, (ulong)map_to_sysmem(gd->new_gd),
gd->start_addr_sp);
return 0;
}

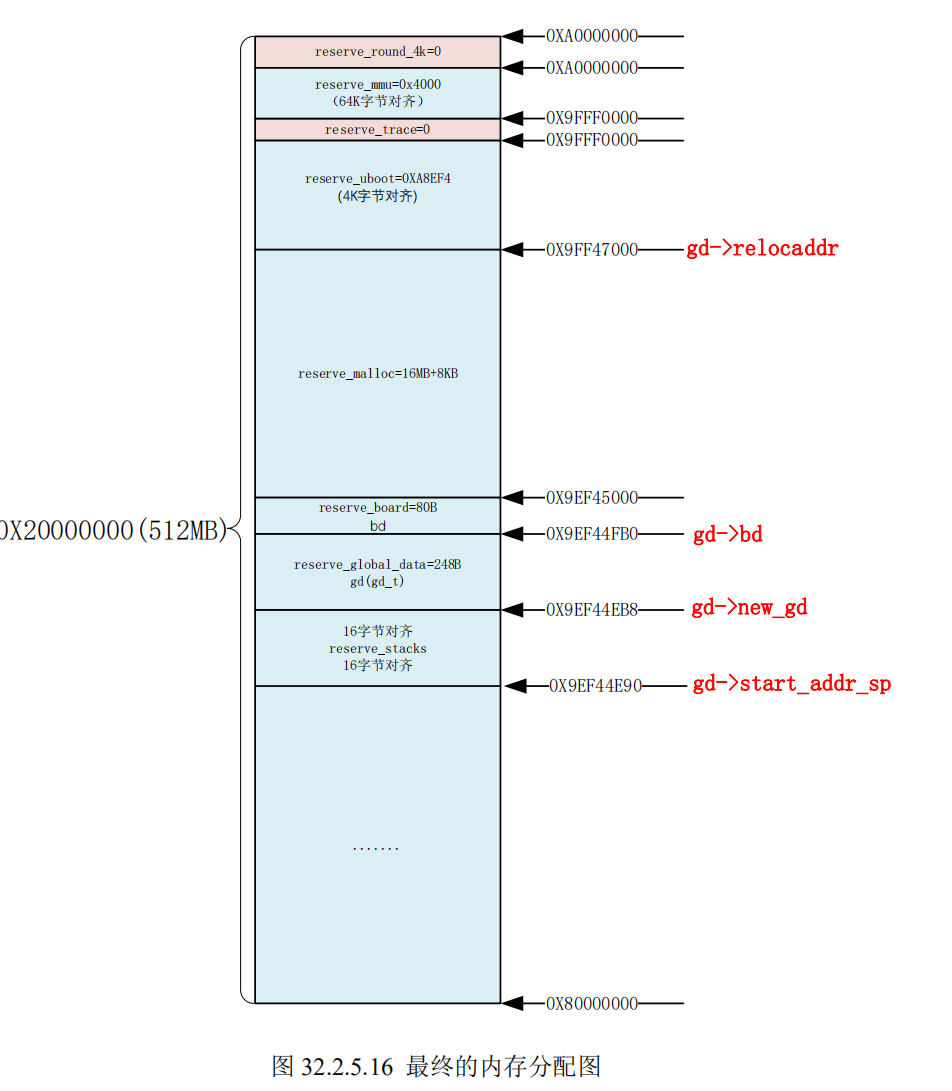
可以看到最后几个函数所进行的动作都是为各个区块预留内存空间
他们分别是mmu, uboot, 动态内存区,board, gd, 最后减了2次16字节,再16字节对齐, 得到start_addr_sp
uboot启动过程 2的更多相关文章
- U-Boot启动过程完全分析
U-Boot启动过程完全分析 1.1 U-Boot工作过程 U-Boot启动内核的过程可以分为两个阶段,两个阶段的功能如下: (1)第一阶段的功能 硬件设备初始化 加载U-Boot第二阶段 ...
- uboot启动过程理解
对于2440而言,启动的方式不多.一般就是外界一个NAND FLASH ,2440内部有个NAND FLASH Controller,会自动把NAND FLASH的前4K拷贝到2440的片内SRAM. ...
- U-Boot启动过程完全分析<转>
转载自:http://www.cnblogs.com/heaad/archive/2010/07/17/1779829.html 1.1 U-Boot工作过程 U-Boot启动内核的过程可 ...
- 【ARM-Linux开发】U-Boot启动过程--详细版的完全分析
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ...
- U-Boot启动过程
开发板上电后,执行U-Boot的第一条指令,然后顺序执行U-Boot启动函数.看一下board/smdk2410/u-boot.lds这个链接脚本,可以知道目标程序的各部分链接顺序.第一个要链接的是c ...
- tiny4412学习之u-boot启动过程
这个文档简要分析了tiny4412自带的u-boot的启动过程,这个u-boot启用了mmu,并且命令的接收和执行方式跟以前的不同. 文档下载地址: http://pan.baidu.com/s/1s ...
- U-Boot 启动过程和源码分析(第二阶段)-main_loop分析
1> main_loop common/main.c /******************************************************************** ...
- Am335x u-boot 启动过程中的系统频率配置
Am335x的时钟结构分为:ADPLLS和ADPLLLJ 1.ADPLLS用来配置Core_CLK,Dispaly_clk,ARM系统CLK(mpu_clk),DDR PLLs_clk 2.ADPLL ...
- (一)U-Boot启动过程--详细版的完全分析
博客地址:http://blog.csdn.net/hare_lee/article/details/6916325
- (转载)U-boot启动完全分析
1.1 U-Boot工作过程 U-Boot启动内核的过程可以分为两个阶段,两个阶段的功能如下: (1)第一阶段的功能 Ø 硬件设备初始化 Ø 加载U-Boot第二阶段代码到RAM空间 Ø 设置好栈 Ø ...
随机推荐
- i春秋Login
打开是个很普通的登录网页 查看源码看看有没有东西 找到绿色的提示,可能是账号密码,试试 成功进来了,再右键源码,没东西...抓包试试,传repeater里go一下 发现一个奇怪的变量,在request ...
- SSH SCP 使用秘钥验证 登录
从Win10连接到Ubuntu 22.04. 1. Win10 上生成秘钥公钥 ssh-keygen -t rsa -C "xxx@yyy.com" 2. Ubuntu 22.04 ...
- 斐波那契散列算法和hashMap实践
斐波那契散列和hashMap实践 适合的场景:抽奖(游戏.轮盘.活动促销等等) 如果有不对的地方,欢迎指正! HashMap实现数据散列: 配置项目,引入pom.xml: <dependency ...
- day27-过滤器Filter02
Filter过滤器02 5.Filter过滤器生命周期 Filter生命周期图解 验证-Tomcat来创建Filter实例,只会创建一个实例 package com.filter; import ja ...
- requests模块和openpyxl模块
第三方模块的下载和使用 1,第三方模块就是别人大神们已经写好的模块,功能特别强大.我们如果像使用第三方模块就先要进行下载.下载完成后 才可以在python中直接调用 2.下载方式一:pip工具 pip ...
- 玩转 Go 生态|Hertz WebSocket 扩展简析
WebSocket 是一种可以在单个 TCP 连接上进行全双工通信,位于 OSI 模型的应用层.WebSocket 使得客户端和服务器之间的数据交换变得更加简单,允许服务端主动向客户端推送数据.在 W ...
- go-micro v3 rpc服务一次改造经历
地址:https://github.com/go-micro/go-micro grpc-test-demo:https://gitee.com/jn-shao/go-gmicro-rpc-test. ...
- 第二篇:前端基础之CSS
CSS介绍 CSS(Cascading Style Sheet,层叠样式表)定义如何显示HTML元素. 当浏览器读到一个样式表,它就会按照这个样式表来对文档进行格式化(渲染). CSS语法 CSS实例 ...
- 洛谷P1434例题分析
[SHOI2002] 滑雪 题目描述 Michael 喜欢滑雪.这并不奇怪,因为滑雪的确很刺激.可是为了获得速度,滑的区域必须向下倾斜,而且当你滑到坡底,你不得不再次走上坡或者等待升降机来载你.Mic ...
- 快速排序算法实现 (y总课后)
主要思路: 1.确定 边界 l----------r (left right) 2.确定中间值 l--------x----------r 3.优雅快排: 设置两个指针i,j. i从左边开始运行 ...
