<一>智能指针基础
代码1
int main(){
//裸指针,手动开辟,需要自己释放,如果忘记了或者因为
//程序逻辑导致p没有释放,那么就会导致内存泄漏
int *p=new int(10);
if(***){
retur -1;
}
delete p;
return 0;
}
有没有什么办法帮我们管理指针,确保资源释放?
智能指针
利用栈上的对象出作用域时自动析构的特征,来做到资源的自动释放
问题:是否可以在堆上创建裸指针?语法上没有问题,但是我们正式希望
栈上对象出作用域能自动析构的特征来达到自动管理指针的目的,如果
将智能指针创建在堆上,那又和原来的裸指针使用遇到的问题是一样的了
需要手动delete
代码2
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template<typename T>
class MySmartPtr1 {
public:
MySmartPtr1(T * ptr=nullptr) : _mptr(ptr) { }
~MySmartPtr1() {
delete _mptr;
_mptr = nullptr;
}
T & operator*() { return *_mptr; }//返回的 是 & , 需要修改值
T * operator->() { return _mptr; }
private:
T * _mptr;
};
int main() {
MySmartPtr1<int> ptr(new int(10));
*ptr= 200;
return 0;
}
代码2的问题
int main() {
MySmartPtr1<int> ptr(new int(10));
//使用ptr 拷贝构造ptr2,默认的拷贝构造方式是值拷贝,所以底层
//_mptr指针 指向的是同一块内存,那么ptr2 和ptr析构的时候就会有问题了,两次析构同一片内存
MySmartPtr1<int> ptr2(ptr);
*mptr = 200;
return 0;
}
如何解决呢?
1:不带引用计数的智能指针
auto_ptr C++库提供
C++11 新标准
scoped_ptr
unique_ptr
代码 关于 auto_ptr
int main() {
auto_ptr<int> ptr1(new int(100));
auto_ptr<int> ptr2(ptr1);
*ptr2 = 200;
cout<<*ptr1<<endl;//执行报错,原因见下图
return 0;
}
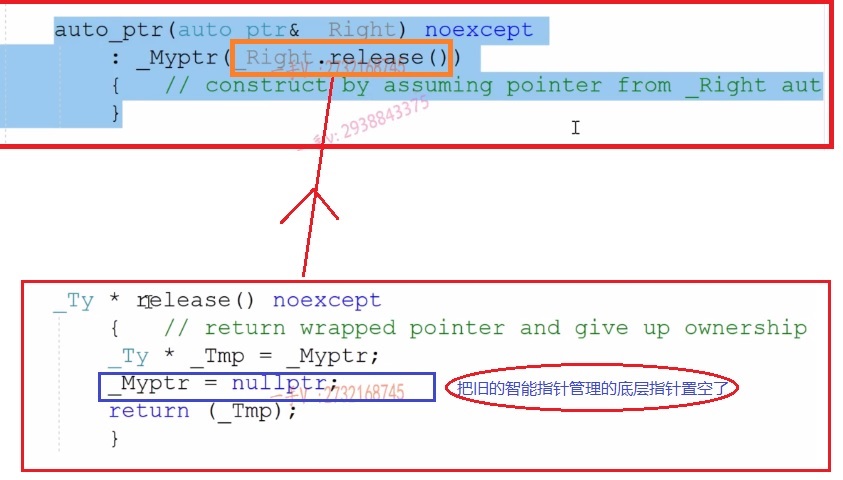
现在不推荐使用auto_ptr
容器中推荐用auto_ptr吗? vector<auto_ptr> v1; v2(v1); 容器的拷贝构造和容器的赋值容易引起容器元素的拷贝构造和赋值,而auto_ptr的拷贝构造会将原来管理的底层资源(指针)置空
代码关于 scoped_ptr
int main() {
scope_ptr的处理方式
scope_ptr<int>(const scope_ptr<int> & src)=delete;//通过直接和谐掉这两个方法
scope_ptr<int> & operator=(const scope_ptr<int> & src))=delete;//通过直接和谐掉这两个方法
return 0;
}
所以scoped_ptr使用的也很少
代码关于 unique_ptr
int main() {
unique_ptr的处理方式
unique_ptr<int>(const unique_ptr<int> & src)=delete;//通过直接和谐掉这两个方法
unique_ptr<int> & operator=(const unique_ptr<int> & src))=delete;//通过直接和谐掉这两个方法
unique_ptr<int> ptr1(new int(100));
unique_ptr<int> ptr2(ptr1);//编译报错,尝试使用已经删除的函数, 要改成如下!!!
unique_ptr<int> ptr1(new int(100));
unique_ptr<int> ptr2(std::move(ptr1));//编译OK,为什么可以呢?因为unique_ptr提供了右值引用的拷贝构造和右值引用的赋值函数,如下
unique_ptr<int>(const unique_ptr<int> && src){};
unique_ptr<int> & operator=(const unique_ptr<int> && src)){};
return 0;
}
//推荐使用
2:带引用计数的智能指针(share_ptr,weak_ptr)
带引用计数的好处:多个智能指针可以管理同一个资源
带引用计数:给每一个对象资源,匹配一个引用计数,
智能指针引用一个资源的时候,给这个资源引用计数加1
当这个智能指针出作用域不再使用资源的时候,给这个资源引用计数-1,当引用计数不为0的时候,还不能析构这个资源,
当引用计数为0的时候,说明已经没有外部资源使用这个资源了,那么就可以析构这个资源了
代码3 简单实现share_ptr
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template<typename T>
class RefCount {
public:
RefCount(T * pSrc = nullptr, int refCount = 0):_pSrc(pSrc),_refCount(refCount) {
}
void addCount() { this->_refCount++; }
void deleltCount() { --this->_refCount; }
int refCount() { return this->_refCount; }
private:
T * _pSrc;
int _refCount = 0;
};
template<typename T>
class MySmartPtr2 {
public:
//新创建的智能指针,默认计数器为1
MySmartPtr2<T> (T * mptr=nullptr): _mptr(mptr){
_pRef = new RefCount<T>(_mptr,1);
}
//拷贝构造
MySmartPtr2<T>(const MySmartPtr2<T> & _rval) {
//两个智能指针指向相同的资源
this->_mptr = _rval._mptr;
this->_pRef = _rval._pRef;
this->_pRef->addCount();
}
//赋值重载
MySmartPtr2<T> & operator=(const MySmartPtr2<T> & _rval) {
if (this == &_rval) { retur *this; }
else {
this->_pRef->deleltCount();
int currentCount = this->_pRef->refCount();
if (currentCount == 0) {
delete this->_mptr;//销毁指向的资源
this->_mptr = nullptr;
delete _pRef;
_rPef = nullptr;
}
this->_pRef = _rval._pRef;
this->_mptr = _rval._mptr;
this->_pRef->addCount();
return *this;
}
}
~MySmartPtr2<T>() {
this->_pRef->deleltCount();
int currentCount = this->_pRef->refCount();
if (currentCount == 0) {
delete this->_mptr;//销毁指向的资源
this->_mptr = nullptr;
delete _pRef;
_pRef = nullptr;
}
}
int getRefCount() { return this->_pRef->refCount(); }
private:
T * _mptr;
RefCount<T> * _pRef;
};
int main() {
MySmartPtr2<int> ms1(new int(100)) ;
{
MySmartPtr2<int> ms2(ms1);
cout << "RefCount=" << ms1.getRefCount() << endl;
MySmartPtr2<int> ms3(ms1);
cout << "RefCount=" << ms1.getRefCount() << endl;
}
cout << "RefCount=" << ms1.getRefCount() << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
share_ptr: 强智能指针,可以改变资源的引用计数
weak_ptr: 弱智能指针,不会改变资源的引用计数
强智能指针:循环引用(交叉引用)是什么问题?什么结果?怎么解决?
交叉引用代码
class A{
pubic:
A(){cout<<"A()"<<endl;}
~A(){cou<<"~A()"<<endl;}
share_ptr<B> _ptrb;
}
class B{
pubic:
B(){cout<<"B()"<<endl;}
~B(){cou<<"~B()"<<endl;}
share_ptr<A> _ptrb;
}
int main(){
share_ptr<A> pa(new A());
share_ptr<B> pb(new B());
pa->_ptrb=pb;
pb->_ptra=pa;
cout<<pa.use_count()<<endl;// 2
cout<<pb.use_count()<<endl;// 2
}
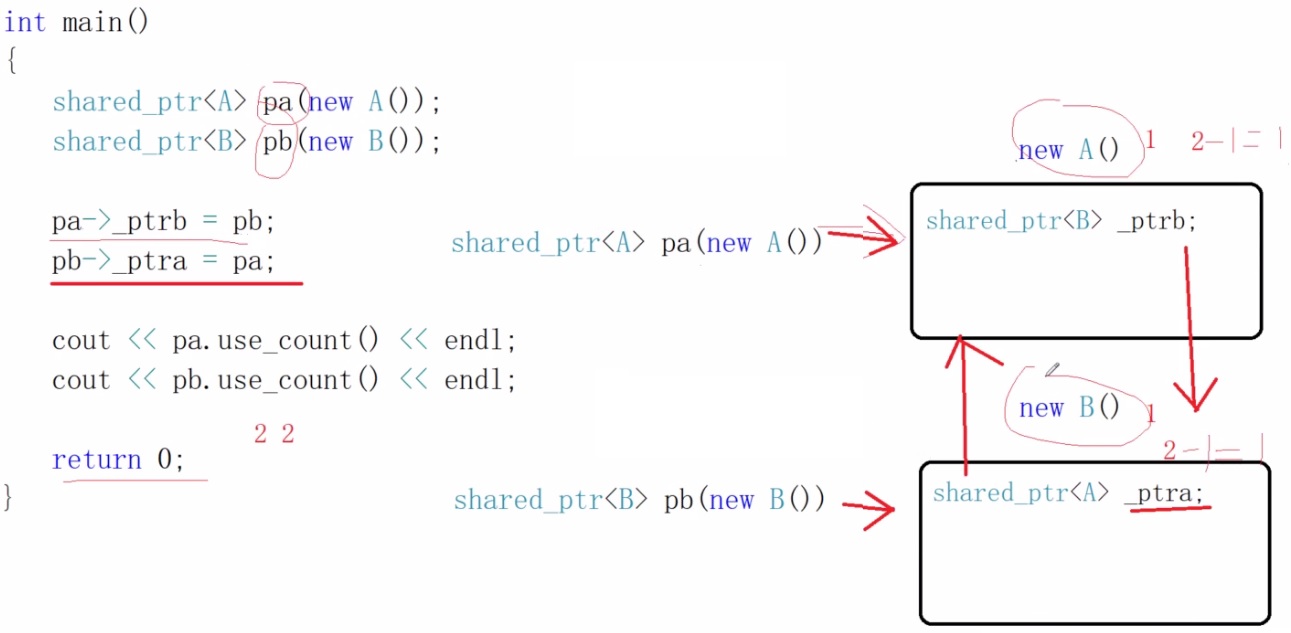
上面代码造成new出来的资源无法释放!!资源泄漏问题
解决:
定义对象的时候,用强智能指针,引用对象的地方用弱智能指针
class A{
pubic:
A(){cout<<"A()"<<endl;}
~A(){cou<<"~A()"<<endl;}
void testA(){
cout<<"A testA() Function"<<endl;
}
weak_ptr<B> _ptrb;
}
class B{
pubic:
B(){cout<<"B()"<<endl;}
~B(){cou<<"~B()"<<endl;}
void function(){
share_ptr<A> _tp=_ptrb.lock();//提升方法
if(_tp!=nullptr){
_tp->testA();
}
}
weak_ptr<A> _ptrb; //weak_ptr 弱智能指针,不会改变引用计数
}
int main(){
share_ptr<A> pa(new A());
share_ptr<B> pb(new B());
pa->_ptrb=pb;
pb->_ptra=pa;
pb.function();
cout<<pa.use_count()<<endl;// 2
cout<<pb.use_count()<<endl;// 2
}
share_ptr 和 weak_ptr 是线程安全的.
<一>智能指针基础的更多相关文章
- Boost智能指针-基础知识
简单介绍 内存管理一直是 C++ 一个比較繁琐的问题,而智能指针却能够非常好的解决问题,在初始化时就已经预定了删除.排解了后顾之忧.1998年修订的第一版C++标准仅仅提供了一种智能指针:std::a ...
- C++ 中的智能指针-基础
简介 在现代 C++ 编程中,标准库包含了智能指针(Smart pointers). 智能指针用来确保程序不会出现内存和资源的泄漏,并且是"异常安全"(exception-safe ...
- C++ 基础知识回顾(string基础、智能指针、迭代器、容器类)
[1] string基础 [1.1] string 的构造 #include <iostream> #include <string> int main() { using n ...
- [易学易懂系列|rustlang语言|零基础|快速入门|(21)|智能指针]
[易学易懂系列|rustlang语言|零基础|快速入门|(21)|智能指针] 实用知识 智能指针 我们今天来讲讲Rust中的智能指针. 什么是指针? 在Rust,指针(普通指针),就是保存内存地址的值 ...
- c++基础 使用智能指针
三个智能指针模板(auto_ptr.unique_ptr和shard_ptr)都定义了类似指针的对象(c++11已将auto_ptr摒弃),可以将new获得(直接或间接) 的地址赋给这种对象.当智能指 ...
- ndk学习之c++语言基础复习----C++线程与智能指针
线程 线程,有时被称为轻量进程,是程序执行的最小单元. C++11线程: 我们知道平常谈C++线程相关的东东基本都是基于之后要学习的posix相关的,其实在C++11有自己新式创建线程的方法,所以先来 ...
- C++基础--智能指针
智能指针其实也不是完全的指针,应该说是像指针一样的类对象,智能指针通常有指针的功能,当然同时也包含了一些额外的功能.目前比较常见的智能指针有auto_ptr.unique_ptr和shared_ptr ...
- 【UE4 C++ 基础知识】<15> 智能指针 TSharedPtr、UniquePtr、TWeakPtr、TSharedRef
基本概念 UE4 对 UObject 对象提供垃圾回收 UE4 对原生对象不提供垃圾回收,需要手动进行清理 方式 malloc / free new / delete new与malloc的区别在于, ...
- C++智能指针
引用计数技术及智能指针的简单实现 基础对象类 class Point { public: Point(int xVal = 0, int yVal = 0) : x(xVal), y(yVal) { ...
- C++ 引用计数技术及智能指针的简单实现
一直以来都对智能指针一知半解,看C++Primer中也讲的不够清晰明白(大概是我功力不够吧).最近花了点时间认真看了智能指针,特地来写这篇文章. 1.智能指针是什么 简单来说,智能指针是一个类,它对普 ...
随机推荐
- 我的Vue之旅、04 CSS媒体查询完全指南(Media Quires)
什么是SCSS Sass: Sass Basics (sass-lang.com) SCSS 是 CSS 的预处理器,它比常规 CSS 更强大. 可以嵌套选择器,更好维护.管理代码. 可以将各种值存储 ...
- 基于electron+vue+element构建项目模板之【创建项目篇】
1.概述 electron:使用javascript.css.html构建跨平台的桌面应用程序 vue:数据驱动视图中的一款渐进式的javascript框架 element:基于vue的桌面端UI组件 ...
- k8s日志架构和基本日志
如果一个容器崩溃了.一个Pod被驱逐了.或者一个节点停机了,您通常仍然需要访问您应用程序的日志.为此,您需要一个生命周期与节点.Pod.容器相对独立的存储空间来存储应用程序日志和系统日志. 此时,我们 ...
- Elasticsearch启动https访问
Elasticsearch上操作 前提:已设置密码访问 ./bin/elasticsearch-certutil ca # 生成elastic-stack-ca.p12文件 ./bin/elastic ...
- SpringCloud组件编写Dockerfile文件模板
在组件根目录下的Dockerfile文件 # Dockerfile文件内容 FROM idocker.io/jre:1.8.0_212 #自定义的基础镜像 VOLUME /tmp # 挂载目录 ADD ...
- Fluentd采集示例
Fluentd通过读取配置文件来加载各插件,日志经由各插件的处理完成输入到输出的整个路由. 本文通过一个最简单的示例来说明配置文件的结构.td-agent.conf默认位于/etc/td-agent/ ...
- 1_Linux
一. Linux介绍 1.1 引言 在学习Linux之前, 大家先了解开发环境,生产,测试环境 开发环境: 平时大家大多是在Windows或者Mac操作系统下去编写代码进行开发,在开发环境中安装大量的 ...
- Jquery封装的ajax的使用过程发生的问题
Jquery封装的ajax的使用过程发生的问题 今天在做项目的时候使用到了ajax来完成项目前后端数据交互,在之后发现在前端没有数据显示,而后端数据确实存在,在多次检查代码之后,发现代码并不存在问题, ...
- PHP全栈开发(六):PHP与HTML页面交互
之前我们在HTML表单学习这篇文章里面创建了一个HTML页面下的表单. 这个表单是用户用来输入数据的 具体代码如下 <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <hea ...
- 6.ElasticSearch系列之倒排索引
1. 倒排索引简介 对于书通过目录查找对应章节内容的方式属于正排索引,而对于想查询文本,如我爱中国在书籍中出现的次数与具体位置,则是倒排索引的范畴. 2. 倒排索引核心组成 单词词典(Term Dic ...
