c++详细学习——继承
通常讲父类(parrent)-子类(child)、基类(base)-派生类(derived)和超类(super)-子类(sub)
1 最基础的写法
以下例子为最基本的写法,默认构造
1 enum Gender {
2 MALE,
3 FEMALE,
4 };
5
6 class Person
7 {
8 private:
9 string name;
10 Gender gend;
11 int age;
12 public:
13 Person():name(""), gend(Gender::MALE), age(18)
14 {
15 cout << "Person::Person()" << endl;
16 }
17 ~Person()
18 {
19 cout << "Person::~Person()" << endl;
20 }
21 };
22
23 class Student : public Person
24 {
25 private:
26 int studentId;
27 int score;
28 public:
29 Student():studentId(10000), score(100)
30 {
31 cout << "Student::Student()" << endl;
32 }
33 ~Student()
34 {
35 cout << "Student::~Student()" << endl;
36 }
37 };
测试:
1 void TestAccess()
2 {
3 Student stu;
4 }
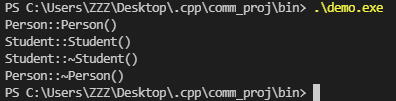
从运行结果来看,声明一个Student的对象之后,依次执行的是:Person的构造函数 --> Student的构造函数 --> Student的析构函数 --> Person的析构函数
2 访问权限
2.1 public
父类的所有public成员变量和函数都可以被子类访问、操作
Example
例子中父类Person的成员变量int age放在public中,不提供操作函数,测试函数中申明子类Student的对象后直接对age进行写和读,编译运行ok
1 enum Gender {
2 MALE,
3 FEMALE,
4 };
5
6 class Person
7 {
8 private:
9 string name;
10 Gender gend;
11 public:
12 Person():name(""), gend(Gender::MALE), age(18)
13 {
14 cout << "Person::Person()" << endl;
15 }
16 ~Person()
17 {
18 cout << "Person::~Person()" << endl;
19 }
20
21 void SetName(const string name_)
22 {
23 name = name_;
24 }
25 string GetName() const
26 {
27 return name;
28 }
29
30 int age;
31
32 void SetGender(const Gender gend_)
33 {
34 gend = gend_;
35 }
36 Gender GetGender() const
37 {
38 return gend;
39 }
40 };
41
42 class Student : public Person
43 {
44 private:
45 int studentId;
46 int score;
47 public:
48 Student():studentId(10000), score(100)
49 {
50 cout << "Student::Student()" << endl;
51 }
52 ~Student()
53 {
54 cout << "Student::~Student()" << endl;
55 }
56
57 void SetStudentId(const int id)
58 {
59 studentId = id;
60 }
61 int GetStudentId() const
62 {
63 return studentId;
64 }
65
66 void SetScore(const int score_)
67 {
68 score = score_;
69 }
70 int GetScore() const
71 {
72 return score;
73 }
74 };
测试函数:
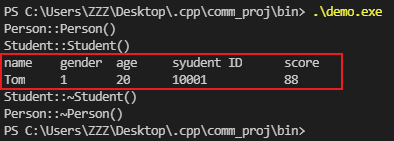
1 void TestAccess()
2 {
3 Student stu;
4 stu.SetName("Tom");
5 stu.SetGender(Gender::FEMALE);
6 stu.age = 20; /* 直接操作成员变量 */
7 stu.SetStudentId(10001);
8 stu.SetScore(88);
9
10 cout << "name\t" << "gender\t" << "age\t" << "syudent ID\t" << "score" << endl;
11 cout << stu.GetName() << "\t" << stu.GetGender() << "\t" << stu.age << "\t"
12 << stu.GetStudentId() << "\t\t" << stu.GetScore() << endl;
13 }
运行结果ok:
2.2 private
子类拥有父类的所有private成员变量,可以通过public中父类提供的操作函数进行访问,但是没有直接操作和访问权限
Example
例子中父类Person的private成员变量int age,不提供操作函数,测试函数中申明子类Student的对象后直接对age进行写和读,编译error
1 enum Gender {
2 MALE,
3 FEMALE,
4 };
5
6 class Person
7 {
8 private:
9 string name;
10 Gender gend;
11 int age;
12 public:
13 Person():name(""), gend(Gender::MALE), age(18)
14 {
15 cout << "Person::Person()" << endl;
16 }
17 ~Person()
18 {
19 cout << "Person::~Person()" << endl;
20 }
21
22 void SetName(const string name_)
23 {
24 name = name_;
25 }
26 string GetName() const
27 {
28 return name;
29 }
30
31 void SetGender(const Gender gend_)
32 {
33 gend = gend_;
34 }
35 Gender GetGender() const
36 {
37 return gend;
38 }
39 };
40
41 class Student : public Person
42 {
43 private:
44 int studentId;
45 int score;
46 public:
47 Student():studentId(10000), score(100)
48 {
49 cout << "Student::Student()" << endl;
50 }
51 ~Student()
52 {
53 cout << "Student::~Student()" << endl;
54 }
55
56 void SetStudentId(const int id)
57 {
58 studentId = id;
59 }
60 int GetStudentId() const
61 {
62 return studentId;
63 }
64
65 void SetScore(const int score_)
66 {
67 score = score_;
68 }
69 int GetScore() const
70 {
71 return score;
72 }
73 };
测试函数:
1 void TestAccess()
2 {
3 Student stu;
4 stu.SetName("Tom");
5 stu.SetGender(Gender::FEMALE);
6 stu.age = 20; /* 直接操作成员变量 */
7 stu.SetStudentId(10001);
8 stu.SetScore(88);
9
10 cout << "name\t" << "gender\t" << "age\t" << "syudent ID\t" << "score" << endl;
11 cout << stu.GetName() << "\t" << stu.GetGender() << "\t" << stu.age << "\t"
12 << stu.GetStudentId() << "\t\t" << stu.GetScore() << endl;
13 }
编译结果error

2.3 protected
父类protected成员变量和函数,子类可以当父类的private变量使用,但父类的对象不能不能使用
Example
例子中父类Person的protected成员函数PrintBaseInfo(),测试函数中Person的对象直接使用,编译error。但子类Student可以把它当父类的private成员函数一样使用。
1 enum Gender {
2 MALE,
3 FEMALE,
4 };
5
6 class Person
7 {
8 private:
9 string name;
10 Gender gend;
11 int age;
12 protected:
13 void PrintBaseInfo()
14 {
15 cout << "Person::PrintBaseInfo()\t";
16 cout << "name: " << name << "\tgend: " << gend << "\tage: " << age << endl;
17 }
18 public:
19 Person():name(""), gend(Gender::MALE), age(18)
20 {
21 cout << "Person::Person()" << endl;
22 }
23 ~Person()
24 {
25 cout << "Person::~Person()" << endl;
26 }
27
28 void SetName(const string name_)
29 {
30 name = name_;
31 }
32 string GetName() const
33 {
34 return name;
35 }
36
37 void SetGender(const Gender gend_)
38 {
39 gend = gend_;
40 }
41 Gender GetGender() const
42 {
43 return gend;
44 }
45
46 void SetAge(const int age_)
47 {
48 age = age_;
49 }
50 int GetAge() const
51 {
52 return age;
53 }
54 };
55
56 class Student : public Person
57 {
58 private:
59 int studentId;
60 int score;
61 public:
62 Student():studentId(10000), score(100)
63 {
64 cout << "Student::Student()" << endl;
65 }
66 ~Student()
67 {
68 cout << "Student::~Student()" << endl;
69 }
70
71 void SetStudentId(const int id)
72 {
73 studentId = id;
74 }
75 int GetStudentId() const
76 {
77 return studentId;
78 }
79
80 void SetScore(const int score_)
81 {
82 score = score_;
83 }
84 int GetScore() const
85 {
86 return score;
87 }
88
89 void Print()
90 {
91 PrintBaseInfo(); /* 子类使用父类的protected成员函数, ok */
92 }
93 };
测试函数:
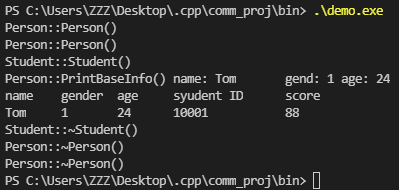
1 void TestAccess()
2 {
3 Person per;
4 // per.PrintBaseInfo(); /* error */
5
6 Student stu;
7 stu.SetName("Tom");
8 stu.SetGender(Gender::FEMALE);
9 stu.SetAge(24);
10 stu.SetStudentId(10001);
11 stu.SetScore(88);
12 stu.Print();
13
14 cout << "name\t" << "gender\t" << "age\t" << "syudent ID\t" << "score" << endl;
15 cout << stu.GetName() << "\t" << stu.GetGender() << "\t" << stu.GetAge() << "\t"
16 << stu.GetStudentId() << "\t\t" << stu.GetScore() << endl;
17 }
执行结果:
3 构造和析构
在第1章中已经介绍,依次执行的是:Person的构造函数 --> Student的构造函数 --> Student的析构函数 --> Person的析构函数

子类对父类的初始化必须放在子类构造函数的初始化列表中,这是初始化父类的唯一办法
1 enum Gender {
2 MALE,
3 FEMALE,
4 };
5
6 class Person
7 {
8 private:
9 string name;
10 Gender gend;
11 int age;
12 public:
13 Person(const string &_name, const Gender _gend, const int _age) : name(_name), gend(_gend), age(_age)
14 {
15 cout << "Person::Person()" << endl;
16 }
17 ~Person()
18 {
19 cout << "Person::~Person()" << endl;
20 }
21 };
22
23 class Student : public Person
24 {
25 private:
26 int studentId;
27 int score;
28 public:
29 Student(const int id, const int _score) : Person("", Gender::MALE, 18), studentId(id), score(_score)
30 {
31 cout << "Student::Student()" << endl;
32 }
33 ~Student()
34 {
35 cout << "Student::~Student()" << endl;
36 }
37 };
4 继承与重载
4.1 重载(overload)
在类中有多个函数类型和函数名相同,但参数列表不同的成员函数时,各个同名的函数之间形成重载,调用时根据调用者的参数去匹配这些重载函数
Example
Person类中4个Print之间构成重载的关系,Person的对象调用时根据传的实参参数类型或个数不同,执行不同的Print()。
1 enum Gender {
2 MALE,
3 FEMALE,
4 };
5
6 class Person
7 {
8 private:
9 string name;
10 Gender gend;
11 int age;
12 public:
13 Person(const string &_name, const Gender _gend, const int _age) : name(_name), gend(_gend), age(_age)
14 {
15 cout << "Person::Person()" << endl;
16 }
17 ~Person()
18 {
19 cout << "Person::~Person()" << endl;
20 }
21
22 void Print()
23 {
24 cout << "Person::Print 1" << endl;
25 }
26 void Print(const int num)
27 {
28 cout << "Person::Print 2" << endl;
29 }
30 void Print(const string str)
31 {
32 cout << "Person::Print 3" << endl;
33 }
34 void Print(const int num1, const int num2)
35 {
36 cout << "Person::Print 4" << endl;
37 }
38 };
测试函数:
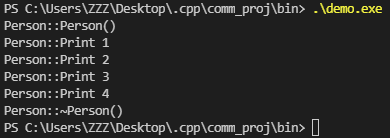
1 void TestAccess()
2 {
3 Person per("", Gender::MALE, 18);
4 per.Print();
5 per.Print(100);
6 per.Print("hello");
7 per.Print(100, 300);
8 }
测试结果:
4.2 继承与重载
(1)子类中没有与父类重载函数同名的成员函数
子类中没有与父类重载函数同名的成员函数时,子类依然可以根据传递的参数类型不同或个数不同,调用到父类不同的函数
Example
父类Person中4个Print()之间构成重载的关系,子类Student的对象调用Print()时,根据传的实参参数类型或个数不同,执行父类不同的Print()。
1 enum Gender {
2 MALE,
3 FEMALE,
4 };
5
6 class Person
7 {
8 private:
9 string name;
10 Gender gend;
11 int age;
12 public:
13 Person(const string &_name, const Gender _gend, const int _age) : name(_name), gend(_gend), age(_age)
14 {
15 cout << "Person::Person()" << endl;
16 }
17 ~Person()
18 {
19 cout << "Person::~Person()" << endl;
20 }
21
22 void Print()
23 {
24 cout << "Person::Print 1" << endl;
25 }
26 void Print(const int num)
27 {
28 cout << "Person::Print 2" << endl;
29 }
30 void Print(const string str)
31 {
32 cout << "Person::Print 3" << endl;
33 }
34 void Print(const int num1, const int num2)
35 {
36 cout << "Person::Print 4" << endl;
37 }
38 };
39
40 class Student : public Person
41 {
42 private:
43 int studentId;
44 int score;
45 public:
46 Student(const int id, const int _score) : Person("", Gender::MALE, 18), studentId(id), score(_score)
47 {
48 cout << "Student::Student()" << endl;
49 }
50 ~Student()
51 {
52 cout << "Student::~Student()" << endl;
53 }
54 };
测试函数:
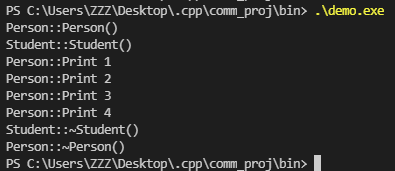
1 void TestAccess()
2 {
3 Student stu(10001, 100);
4
5 stu.Print();
6 stu.Print(100);
7 stu.Print("hello");
8 stu.Print(100, 300);
9 }
测试结果:
(2)子类中存在与父类重载函数同名的成员函数
子类中存在与父类重载函数相同函数名的成员函数时,子类的该函数与父类的重载函数没有关系,此在OOP语言中是C++独有的,称之为名字隐藏(name hidden)
Example
子类中也有Print()函数,此时子类的Print()把父类的Print()隐藏掉了
1 enum Gender {
2 MALE,
3 FEMALE,
4 };
5
6 class Person
7 {
8 private:
9 string name;
10 Gender gend;
11 int age;
12 public:
13 Person(const string &_name, const Gender _gend, const int _age) : name(_name), gend(_gend), age(_age)
14 {
15 cout << "Person::Person()" << endl;
16 }
17 ~Person()
18 {
19 cout << "Person::~Person()" << endl;
20 }
21
22 void Print()
23 {
24 cout << "Person::Print 1" << endl;
25 }
26 void Print(const int num)
27 {
28 cout << "Person::Print 2" << endl;
29 }
30 void Print(const string str)
31 {
32 cout << "Person::Print 3" << endl;
33 }
34 void Print(const int num1, const int num2)
35 {
36 cout << "Person::Print 4" << endl;
37 }
38 };
39
40 class Student : public Person
41 {
42 private:
43 int studentId;
44 int score;
45 public:
46 Student(const int id, const int _score) : Person("", Gender::MALE, 18), studentId(id), score(_score)
47 {
48 cout << "Student::Student()" << endl;
49 }
50 ~Student()
51 {
52 cout << "Student::~Student()" << endl;
53 }
54
55 void Print()
56 {
57 cout << "Student::Print()" << endl;
58 }
59 };
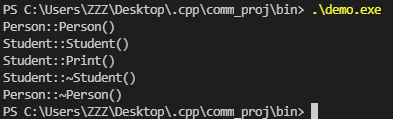
测试函数:
1 void TestAccess()
2 {
3 Student stu(10001, 100);
4
5 stu.Print();
6 // stu.Print(100); /* 编译error */
7 // stu.Print("hello"); /* 编译error */
8 // stu.Print(100, 300); /* 编译error */
9 }
测试结果:
c++详细学习——继承的更多相关文章
- Hbase技术详细学习笔记
注:转自 Hbase技术详细学习笔记 最近在逐步跟进Hbase的相关工作,由于之前对Hbase并不怎么了解,因此系统地学习了下Hbase,为了加深对Hbase的理解,对相关知识点做了笔记,并在组内进行 ...
- JavaScript 核心学习——继承
本篇博文讲述如何在 JavaScript 中实现继承,以及原型与原型链的知识,在附录中将会讲述 JavaScript 面向对象的常见错误. ##原型与原型链在 JavaScript 中,使用类将会付出 ...
- Java基础学习-- 继承 的简单总结
代码参考:Java基础学习小记--多态 为什么要引入继承? 还是做一个媒体库,里面可以放CD,可以放DVD.如果把CD和DVD做成两个没有联系的类的话,那么在管理这个媒体库的时候,要单独做一个添加CD ...
- 详细学习ORACLE JOBS
一点一点学习jobs的各个方面比较长,比较烦,但是应该看完后会对jobs比较好的应用 一.学习准备 开始dbms_job学习前,先认识一个参数job_queue_processes a.job_que ...
- Android 服务类Service 的详细学习
http://blog.csdn.net/vipzjyno1/article/details/26004831 Android服务类Service学习四大组建 目录(?)[+] 什么是服务 服务有 ...
- Spring Boot详细学习地址转载
阿里中间件牛人,学习榜样,源码分析: https://fangjian0423.github.io/ 基础.详细.全面的教程: https://gitee.com/roncoocom/spring-b ...
- 做出一个SwitchButton的效果,并详细学习一下onDraw(Canvas canvas)方法的使用
代码的灵感和原理主要来自于android自定义开关控件-SlideSwitch http://blog.csdn.net/singwhatiwanna/article/details/9254309这 ...
- python学习-继承
# 继承# 你的是我的,我的还是我的 class Animal: def __init__(self,name,private_v1): self.name = name self._private_ ...
- Git详细学习教程
作者:gafish https://github.com/gafish/gafish.github.com Git简介 Git 是一种分布式版本控制系统,它可以不受网络连接的限制,加上其它众多优点,目 ...
- 基于【 MySql 】二 || mysql详细学习笔记
mysql重点学习笔记 /* Windows服务 */ -- 启动MySQL net start mysql -- 创建Windows服务 sc create mysql binPath= mysql ...
随机推荐
- Winsw将jar包部署为windows服务
1. 下载Winsw https://github.com/winsw/winsw/releases 下载winsw官网上的xml文件和.exe文件 2. 编辑配置文件 创建一个文件夹demo,将所需 ...
- PPR的断管
1. 小管径PPR管的断管 2. 大管径PPR管的断管
- 「Tubian」Tubian0.41!支持Windows QQ微信!
Tubian 0.42已发布:https://www.cnblogs.com/tubentubentu/p/16745926.html Sourceforge.net下载:https://source ...
- 【博学谷学习记录】超强总结,用心分享|MySql连接查询超详细总结
一.概述 在实际开发中,大部分情况下都不是在单表中进行数据操作,一般都是多张表进行联合查询.通常一个业务就会对应的有好几张表.MySql中的连接查询分为交叉连接,内连接,外连接三部分.其中交叉连接也叫 ...
- Oracle导出和导入
导出 exp exp 用户名/密码@实例名 file=导出的dmp文件存放路径 l og=导出日志存放路径 exp hr/123456@orcl file= C:\Users\Administrato ...
- MyBatis获取参数值的两种方式
MyBatis获取参数值的两种方式:${}和#{} ${}的本质就是字符串拼接,#{}的本质就是占位符赋值 ${}使用字符串拼接的方式拼接sql,若为字符串类型或日期类型的字段进行赋值时,需要手动加单 ...
- CompareTest
一.说明:Java中的对象,正常情况下,只能进行比较:== 或 != .不能使用 > 或 < 的 但是在开发场景中,我们需要对多个对象进行排序,言外之意,就需要比较对象的大小. 如何实现? ...
- FJOI2007轮状病毒 行列式递推详细证明
题目链接 题目给了你一个奇怪的图,让你求它的生成树个数. 开始写了一个矩阵树: #include<cstdio> #include<cstdlib> #include<c ...
- 浅谈消息队列 Message Queue
消息队列:在消息传递的过程中暂时保存消息的容器,充当发送者和接受者的中间人 消息队列的基本操作 using System; using System.Messaging; namespace MQ { ...
- 支持向量机(SVM)公式整理
支持向量机可以分为三类: 线性可分的情况 ==> 硬间隔最大化 ==> 硬间隔SVM 近似线性可分的情况 ==> 软间隔最大化 ==> 线性支持向量机 线性不可分的情况 ==& ...
