第19章 Redis的一些常用技术
19.1 Redis的基础事务
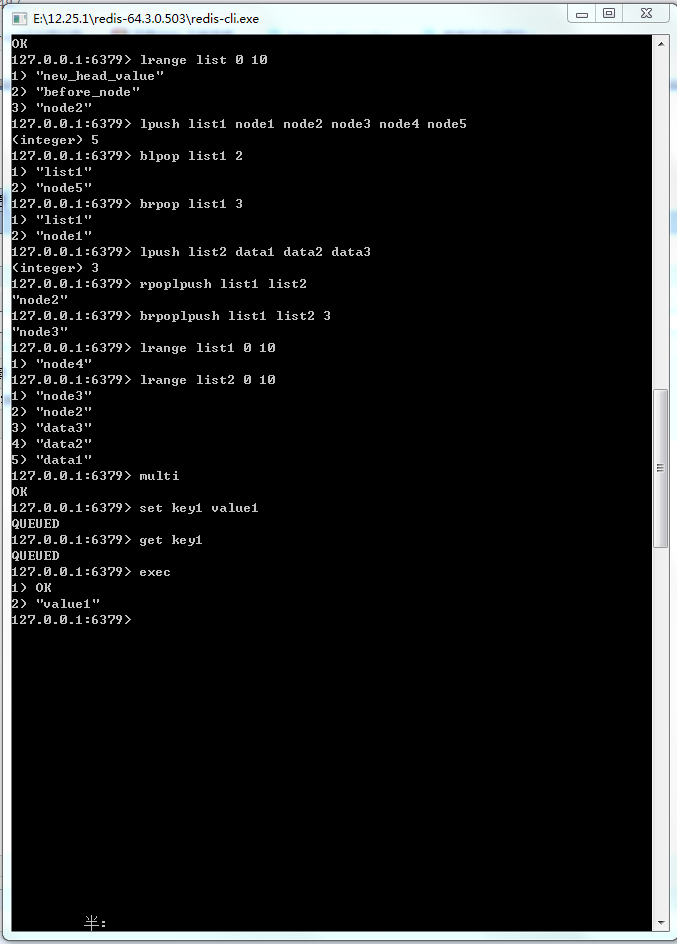
图19-1 Redis命令执行事务的过程
19-1:在Spring中使用Redis事务命令
public static void testTransaction(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
RedisTemplate redisTemplate = applicationContext.getBean(RedisTemplate.class);
SessionCallback callBack = (SessionCallback)(RedisOperations ops) -> {
ops.multi();
ops.boundValueOps("key1").set("value1");
// 注意由于命令只是进入队列,而没有被执行,所以此处采用get命令,而value却返回为null
String value = (String) ops.boundValueOps("key1").get();
System.out.println("事务执行过程中,命令入队列,而没有被执行,所以value为空:value=" + value);
// 此时list会保存之前进入队列的所有命令的结果
ops.exec();// 执行事务
// 事务结束后,获取value1
value = (String) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("key1");
return value;
};
// 执行Redis的命令
String value = (String) redisTemplate.execute(callBack);
System.out.println(value);
}
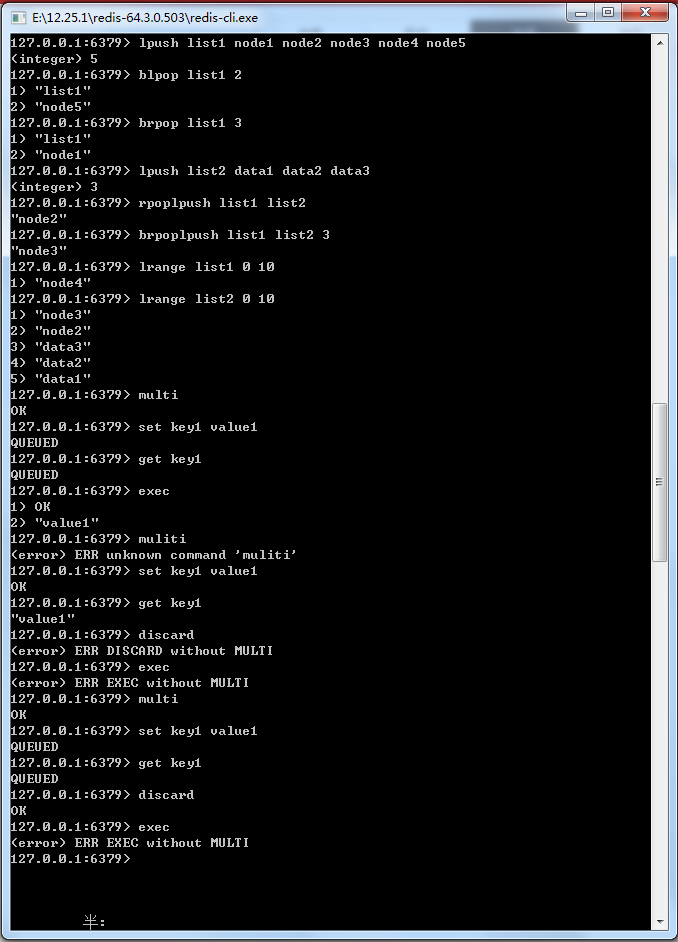
图19-2 使用discard命令取消事务
19.2 探索Redis事务回滚
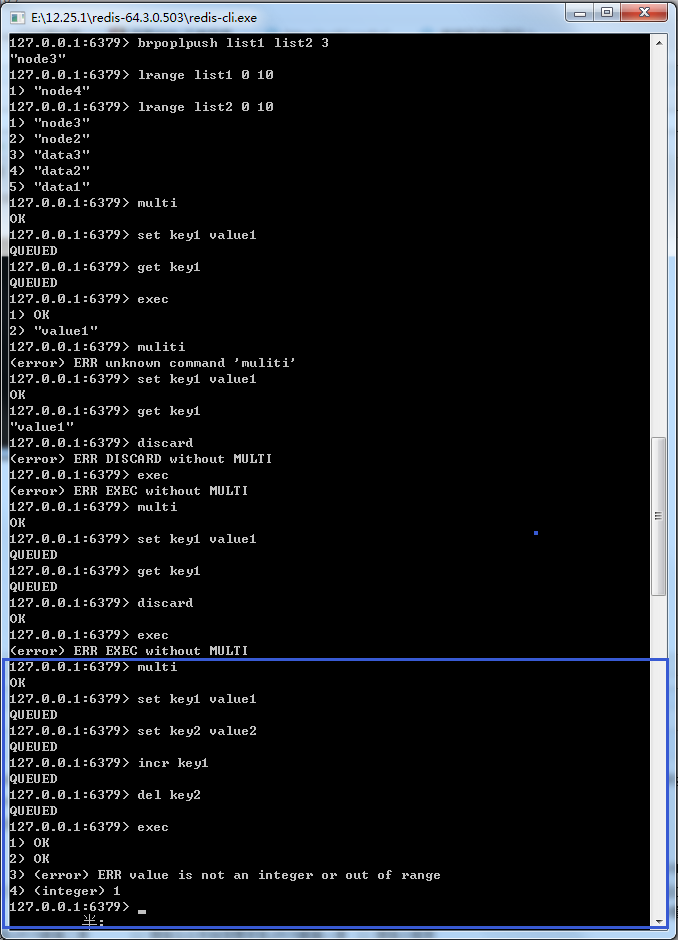
图19-3 Redis事务遇到命令格式正确而数据类型不符合
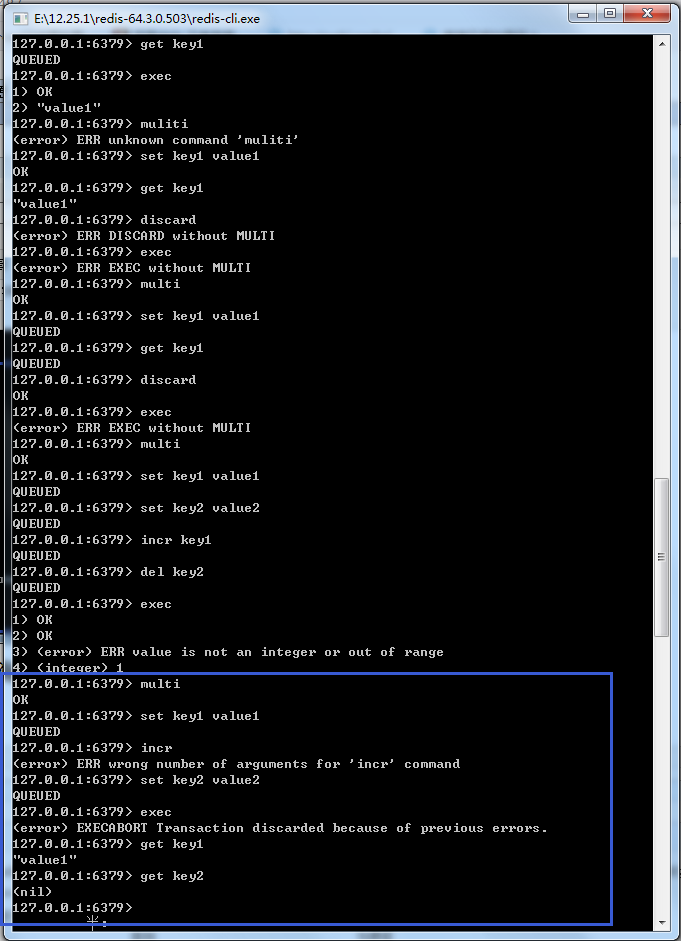
图19-4 Redis事务遇到命令格式错误的
19.3 使用watch命令监控事务
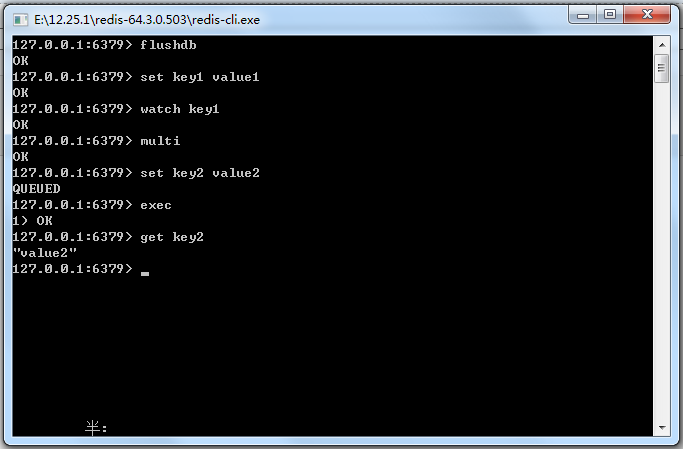
图19-6 Redis执行事务


图19-7 测试Redis事务回滚
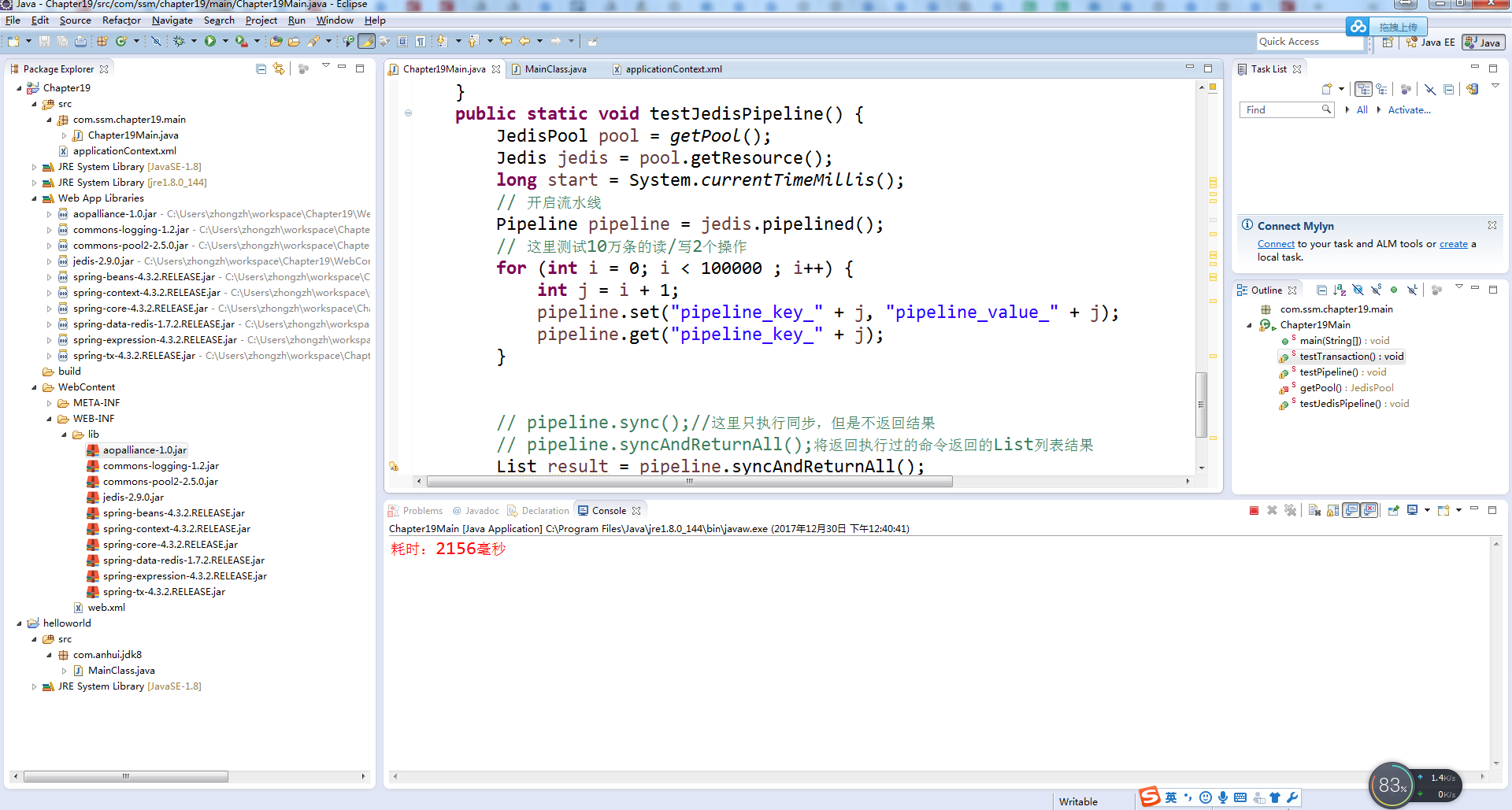
19.4 流水线(pipelined)
19-2:使用流水线操作Redis命令
public static void testJedisPipeline() {
JedisPool pool = getPool();
Jedis jedis = pool.getResource();
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 开启流水线
Pipeline pipeline = jedis.pipelined();
// 这里测试10万条的读/写2个操作
for (int i = 0; i < 100000 ; i++) {
int j = i + 1;
pipeline.set("pipeline_key_" + j, "pipeline_value_" + j);
pipeline.get("pipeline_key_" + j);
}
// pipeline.sync();//这里只执行同步,但是不返回结果
// pipeline.syncAndReturnAll();将返回执行过的命令返回的List列表结果
List result = pipeline.syncAndReturnAll();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 计算耗时
System.err.println("耗时:" + (end - start) + "毫秒");
}
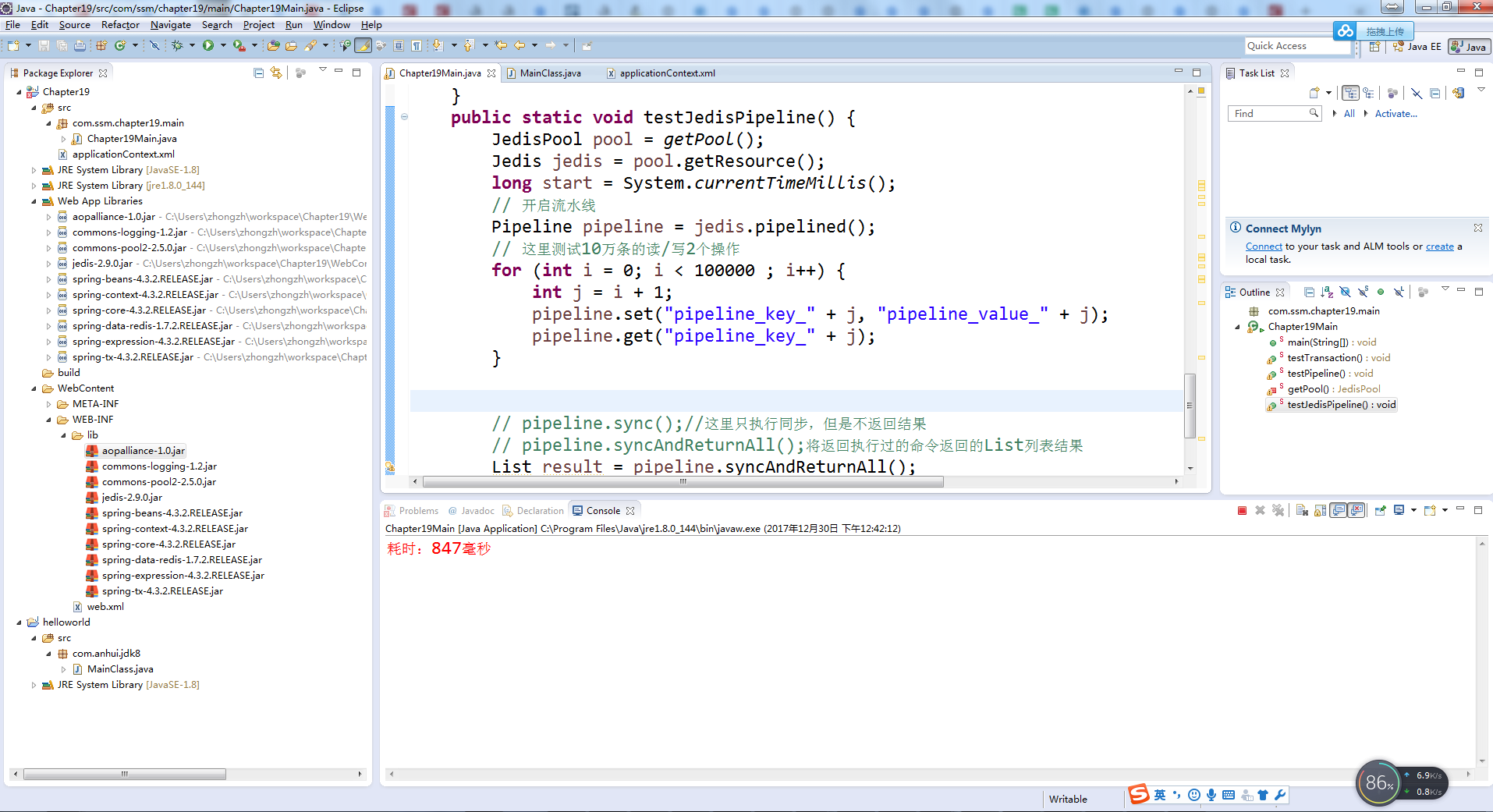
19-3:使用Spring操作Redis流水线
public static void testPipeline(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
RedisTemplate redisTemplate = applicationContext.getBean(RedisTemplate.class);
// 使用Java8的Lambda表达式
SessionCallback callBack = (SessionCallback) (RedisOperations ops) -> {
for(int i = 0; i < 100000; i++){
int j = i + 1;
ops.boundValueOps("pipeline_key_" + j).set("pipeline_value_" + j);
ops.boundValueOps("pipeline_key_" + j).get();
}
return null;
};
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 执行Redis的流水线命令
List resultList = redisTemplate.executePipelined(callBack);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.err.println(end-start);
}
19-5 发布订阅



图19-10 Redis的发布订阅过程
代码清单19-4:Redis发布订阅监听类
package com.ssm.chapter19.redis.listener; import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.Message;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.MessageListener;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.SerializationException; /*** imports ***/
public class RedisMessageListener implements MessageListener{
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
/*** 此处省略redisTemplate的setter和getter方法 ***/ @Override
public void onMessage(Message message, byte[] bytes) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
// 获取消息
byte[] body = message.getBody();
// 使用值序列化器转换
String msgBody;
String channelStr = null;
try {
msgBody = (String)
getRedisTemplate().getValueSerializer().deserialize(body); System.err.println(msgBody);
// 获取channel
byte[] channel = message.getChannel();
// 使用字符串序列化器转换
channelStr = (String)
getRedisTemplate().getStringSerializer().deserialize(channel);
} catch (SerializationException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.err.println(channelStr);
// 渠道名称转换
String bytesStr = new String(bytes);
System.err.println(bytesStr);
} public RedisTemplate getRedisTemplate() {
return redisTemplate;
} public void setRedisTemplate(RedisTemplate redisTemplate) {
this.redisTemplate = redisTemplate;
}
}
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8' ?>
<!-- was: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> -->
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd">
<bean id="poolConfig" class="redis.clients.jedis.JedisPoolConfig">
<property name="maxIdle" value="50" />
<property name="maxTotal" value="100" />
<property name="maxWaitMillis" value="20000" />
</bean> <bean id="stringRedisSerializer"
class="org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer" /> <bean id="connectionFactory"
class="org.springframework.data.redis.connection.jedis.JedisConnectionFactory">
<property name="hostName" value="localhost" />
<property name="port" value="6379" />
<property name="poolConfig" ref="poolConfig" />
</bean> <bean id="redisTemplate" class="org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate">
<property name="connectionFactory" ref="connectionFactory" />
<property name="defaultSerializer" ref="stringRedisSerializer" />
<property name="keySerializer" ref="stringRedisSerializer" />
<property name="valueSerializer" ref="stringRedisSerializer" />
</bean> <bean id="redisMsgListener"
class="com.ssm.chapter19.redis.listener.RedisMessageListener">
<property name="redisTemplate" ref="redisTemplate" />
</bean> <bean id="topicContainer"
class="org.springframework.data.redis.listener.RedisMessageListenerContainer"
destroy-method="destroy">
<!--Redis连接工厂 -->
<property name="connectionFactory" ref="connectionFactory" />
<!--连接池,这里只要线程池生存,才能继续监听 -->
<property name="taskExecutor">
<bean
class="org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskScheduler">
<property name="poolSize" value="2" />
</bean>
</property>
<!--消息监听Map -->
<property name="messageListeners">
<map>
<!--配置监听者,key-ref和bean id定义一致 -->
<entry key-ref="redisMsgListener">
<!--监听类 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.listener.ChannelTopic">
<constructor-arg value="chat" />
</bean>
</entry>
</map>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
代码清单19-5:测试Redis发布订阅
package com.ssm.chapter19.main; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate; public class Chapter19Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext
= new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
RedisTemplate redisTemplate = applicationContext.getBean(RedisTemplate.class);
String channel = "chat";
redisTemplate.convertAndSend(channel, "I am lazy!!");
} }
public static void testPubSub(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext
= new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
RedisTemplate redisTemplate = applicationContext.getBean(RedisTemplate.class);
String channel = "chat";
redisTemplate.convertAndSend(channel, "I am lazy!!");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
/* ApplicationContext applicationContext
= new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
RedisTemplate redisTemplate = applicationContext.getBean(RedisTemplate.class);
String channel = "chat";
redisTemplate.convertAndSend(channel, "I am lazy!!");*/
testPubSub();
}

19.6 超时命令
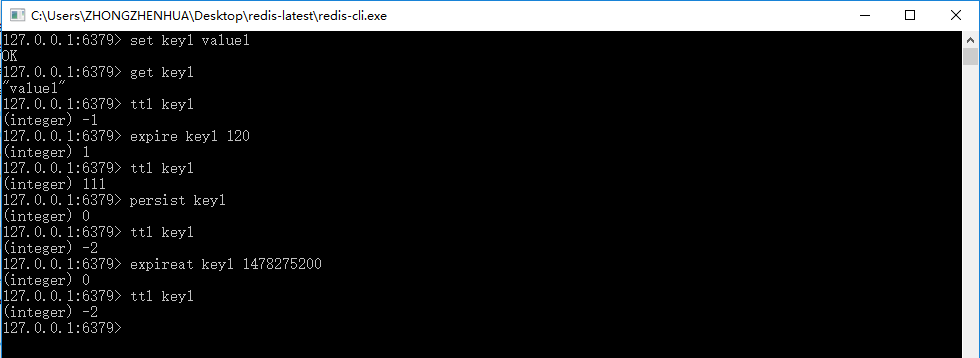
图19-11 Redis超时命令

代码清单19-6:使用Spring操作Redis超时命令
public static void testExpire() {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
RedisTemplate redisTemplate = applicationContext.getBean(RedisTemplate.class);
redisTemplate.execute((RedisOperations ops) -> {
ops.boundValueOps("key1").set("value1");
String keyValue = (String) ops.boundValueOps("key1").get();
Long expSecond = ops.getExpire("key1");
System.err.println(expSecond);
boolean b = false;
b = ops.expire("key1", 120L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
b = ops.persist("key1");
Long l = 0L;
l = ops.getExpire("key1");
Long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
Date date = new Date();
date.setTime(now + 120000);
ops.expireAt("key", date);
return null;
});
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
/* ApplicationContext applicationContext
= new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
RedisTemplate redisTemplate = applicationContext.getBean(RedisTemplate.class);
String channel = "chat";
redisTemplate.convertAndSend(channel, "I am lazy!!");*/
//testPubSub();
testExpire();
}
19.7 使用Lua语言
19.7.1 执行输入Lua程序代码
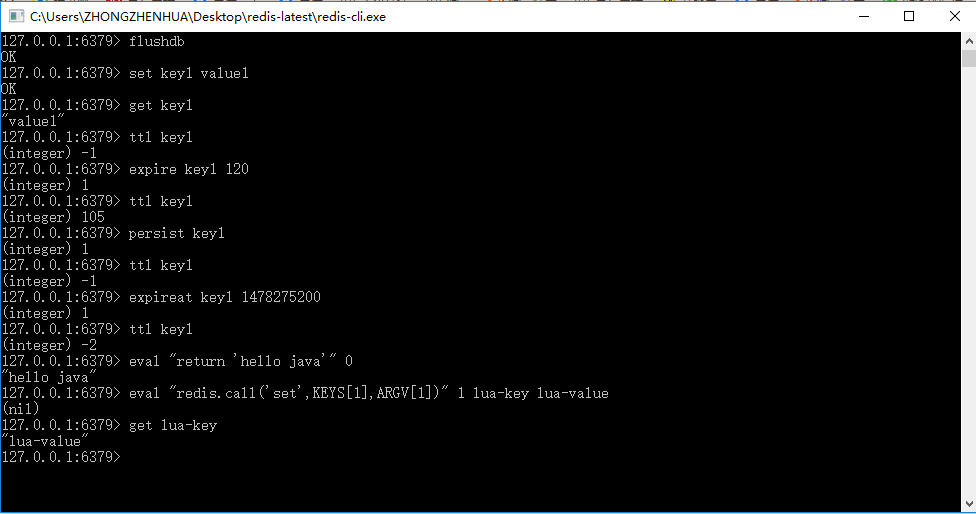
图19-12 Redis执行Lua语言脚本

图19-13 使用签名运行Lua脚本
代码清单19-7:在Java中使用Lua脚本
public static void testLuaScript(){
// 如果是简单的对象,使用原来的封装会简易些
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
RedisTemplate redisTemplate = applicationContext.getBean(RedisTemplate.class);
// 如果是简单的操作,使用原来的Jedis会简易些
Jedis jedis = (Jedis) redisTemplate.getConnectionFactory().getConnection().getNativeConnection();
// 执行简单的脚本
String helloJava = (String) jedis.eval("return 'hello java'");
System.out.println(helloJava);
// 执行带参数的脚本
jedis.eval("redis.call('set',KEYS[1],ARGV[1])",1,"lua-key","lua-value");
String luaKey = (String) jedis.get("lua-key");
System.out.println(luaKey);
// 缓存脚本,返回sha1签名标识
String sha1 = jedis.scriptLoad("redis.call('set',KEYS[1],ARGV[1])");
// 通过标识执行脚本
jedis.evalsha(sha1, 1, new String[]{ "sha-key", "sha-val"});
// 获取执行脚本后的数据
String shaVal = jedis.get("sha-key");
System.out.println(shaVal);
// 关闭连接
jedis.close();
}
代码清单19-8:可序列化的Role对象
public class Role implements Serializable{
/**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 5334128099542779325L;
private Long id;
private String roleName;
private String note;
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getRoleName() {
return roleName;
}
public void setRoleName(String roleName) {
this.roleName = roleName;
}
public String getNote() {
return note;
}
public void setNote(String note) {
this.note = note;
}
}
代码清单19-9:使用RedisScript接口对象通过Lua脚本操作对象
public static void testRedisScript() {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
RedisTemplate redisTemplate = applicationContext.getBean(RedisTemplate.class);
// 定义默认脚本封装类
DefaultRedisScript<Role> redisScript = new DefaultRedisScript<Role>();
// 设置脚本
redisScript.setScriptText("redis.call('set', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]) return redis.call('get', KEYS[1])");
// 定义操作的key列表
List<String> keyList = new ArrayList<String>();
keyList.add("role1");
// 需要序列化保存和读取的对象
Role role = new Role();
role.setId(1L);
role.setRoleName("role_name_1");
role.setNote("note_1");
// 获得标识字符串
String sha1 = redisScript.getSha1();
System.out.println(sha1);
// 设置返回结果类型,如果没有这句话,结果返回为空
redisScript.setResultType(Role.class);
// 定义序列化器
JdkSerializationRedisSerializer serializer = new JdkSerializationRedisSerializer();
// 执行脚本
// 第一个是RedisScript接口对象,第二个是参数序列化器
// 第三个是结果序列化器,第四个是Redis的key列表,最后是参数列表
Role obj = (Role) redisTemplate.execute(redisScript, serializer, serializer, keyList, role);
// 打印结果
System.out.println(obj);
}
19.7.2 执行Lua文件
代码清单19-10:test.lua
redis.call('set', KEYS[], ARGV[])
redis.call('set', KEYS[], ARGV[])
local n1 = tonumber(redis.call('get' ,KEYS[]))
local n2 = tonumber(redis.call('get' ,KEYS[]))
if n1 > n2 then
return
end
if n1 == n2 then
return
end
if n1 < n2 then
return
end

图19-14 redis-cli的命令执行
代码清单19-11:使用Java执行Redis脚本
public static void testLuaFile(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
RedisTemplate redisTemplate = applicationContext.getBean(RedisTemplate.class);
// 读入文件流
File file = new File("C:\\Users\\ZHONGZHENHUA\\Desktop\\redis-latest\\test.lua");
byte[] bytes = getFileToByte(file);
Jedis jedis = (Jedis) redisTemplate.getConnectionFactory().getConnection().getNativeConnection();
// 发送文件二进制给Redis,这样Redis就会返回sha1标识
byte[] sha1 = jedis.scriptLoad(bytes);
// 使用返回的标识执行,其中第二个参数2,表示使用2个键
// 而后面的字符串都转化为了二进制字节进行传输
Object obj = jedis.evalsha(sha1, 2, "key1".getBytes(),"key2".getBytes(),"2".getBytes(),"4".getBytes());
System.out.println(obj);
}
/**
* 把文件转化为二进制数组
*
* @param file
* 文件
* @return 二进制数组
*
*/
public static byte[] getFileToByte(File file) {
byte[] by = new byte[(int) file.length()];
try {
InputStream is = new FileInputStream(file);
ByteArrayOutputStream bytestream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] bb = new byte[2048];
int ch;
ch = is.read(bb);
while(ch != -1) {
bytestream.write(bb, 0, ch);
ch = is.read(bb);
}
by = bytestream.toByteArray();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return by;
}
第19章 Redis的一些常用技术的更多相关文章
- Redis | 第5章 Redis 中的持久化技术《Redis设计与实现》
目录 前言 1. RDB 持久化 1.1 RDB 文件的创建与载入 1.2 自动间隔性保存 1.2.1 设置保存条件 1.2.2 dirty 计数器和 lastsave 属性 1.2.3 检查保存条件 ...
- Redis(十五)Redis 的一些常用技术(Spring 环境下)
一.Redis 事务与锁机制 1.Redis的基础事务 在Redis中开启事务的命令是 multi 命令, 而执行事务的命令是 exec 命令.multi 到 exec 命令之间的 Redis 命令将 ...
- 第19章 通讯的基本概念—零死角玩转STM32-F429系列
第19章 通讯的基本概念 全套200集视频教程和1000页PDF教程请到秉火论坛下载:www.firebbs.cn 野火视频教程优酷观看网址:http://i.youku.com/firege ...
- 第19章 集合框架(3)-Map接口
第19章 集合框架(3)-Map接口 1.Map接口概述 Map是一种映射关系,那么什么是映射关系呢? 映射的数学解释 设A,B是两个非空集合,如果存在一个法则,使得对A中的每一个元素a,按法则f,在 ...
- 第19章 queue队列容器
/* 第19章 queue队列容器 19.1 queue技术原理 19.2 queue应用基础 19.3 本章小结 */ // 第19章 queue队列容器 // 19.1 queue技术原理 // ...
- Linux就这个范儿 第19章 团结就是力量 LSB是Linux标准化基地(Linux Standards Base)的简称
Linux就这个范儿 第19章 团结就是力量 LSB是Linux标准化基地(Linux Standards Base)的简称 这个图片好可爱,它是LSB组织的图标.你肯定会问:“图标这么设计一定有说 ...
- OC中另外的一个常用技术:通知(Notification)
OC中另外的一个常用技术:通知(Nofitication)其实这里的通知和之前说到的KVO功能很想,也是用于监听操作的,但是和KVO不同的是,KVO只用来监听属性值的变化,这个发送监听的操作是系统控制 ...
- $.ajax()方法详解 ajax之async属性 【原创】详细案例解剖——浅谈Redis缓存的常用5种方式(String,Hash,List,set,SetSorted )
$.ajax()方法详解 jquery中的ajax方法参数总是记不住,这里记录一下. 1.url: 要求为String类型的参数,(默认为当前页地址)发送请求的地址. 2.type: 要求为Str ...
- redis实战笔记(3)-第3章 Redis命令
第3章 Redis命令 本章主要内容 字符串命令. 列表命令和集合命令 散列命令和有序集合命令 发布命令与订阅命令 其他命令 在每个不同的数据类型的章节里, 展示的都是该数据类型所独有的. 最 ...
随机推荐
- 课上练习 script
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/ ...
- CodeForces 356A_(set应用,线段树)
A. Knight Tournament time limit per test 3 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standar ...
- coredata示意图
NSPersistentStoreCoordinator(Persistent Store Coordinator),缩写为PSC:存储信息+结构信息(MOM) NSManagedObjectMode ...
- vue向数组中动态添加数据
vue中数据更新通过v-model实现,向数组中添加数据通过push()实现,向shortcuts数组中动态添加newShortcut对象中的title和action this.shortcuts.p ...
- BZOJ 4259: 残缺的字符串 FFT_多项式
Code: #include<bits/stdc++.h> #define maxn 1200000 using namespace std; void setIO(string s) { ...
- 【剑指Offer】52、正则表达式匹配
题目描述: 请实现一个函数用来匹配包括'.'和'*'的正则表达式.模式中的字符'.'表示任意一个字符,而'*'表示它前面的字符可以出现任意次(包含0次). 在本题中,匹配是指字符串的所有字符匹 ...
- MySQL7.5.15数据库配置主从服务器实现双机热备实例教程
环境说明 程序在:Web服务器192.168.0.57上面 数据库在:MySQL服务器192.168.0.67上面 实现目的:增加一台MySQL备份服务器(192.168.0.68),做为MySQL服 ...
- Linux系统学习之 二:新手必须掌握的Linux命令2
2018-10-03 22:20:48 一.文件目录管理命令 1.touch 命令 用于创建空白文件或设置文件的时间,格式为“touch [选项] [文件]”. 参数: -a :仅修改“读取时间(at ...
- 2.1 SVN的安装
一.SVN客户端安装 运行TortoiseSVN-1.6.6.17493-win32-svn-1.6.6.msi程序, 开始安装 点击Next, 下一步 选择 I accept 接受, 点击Next ...
- (34)Spring Boot的启动器Starter详解【从零开始学Spring Boot】
Spring Boot应用启动器基本的一共有N(现知道的是44)种:具体如下: 1)spring-boot-starter 这是Spring Boot的核心启动器,包含了自动配置.日志和YAML. 2 ...
