TensorFlow技术解析与实战学习笔记(13)------Mnist识别和卷积神经网络AlexNet
一、AlexNet:共8层:5个卷积层(卷积+池化)、3个全连接层,输出到softmax层,产生分类。
论文中lrn层推荐的参数:depth_radius = 4,bias = 1.0 , alpha = 0.001 / 9.0 , beta = 0.75
lrn现在仅在AlexNet中使用,主要是别的卷积神经网络模型效果不明显。而LRN在AlexNet中会让前向和后向速度下降,(下降1/3)。
【训练时耗时是预测的3倍】
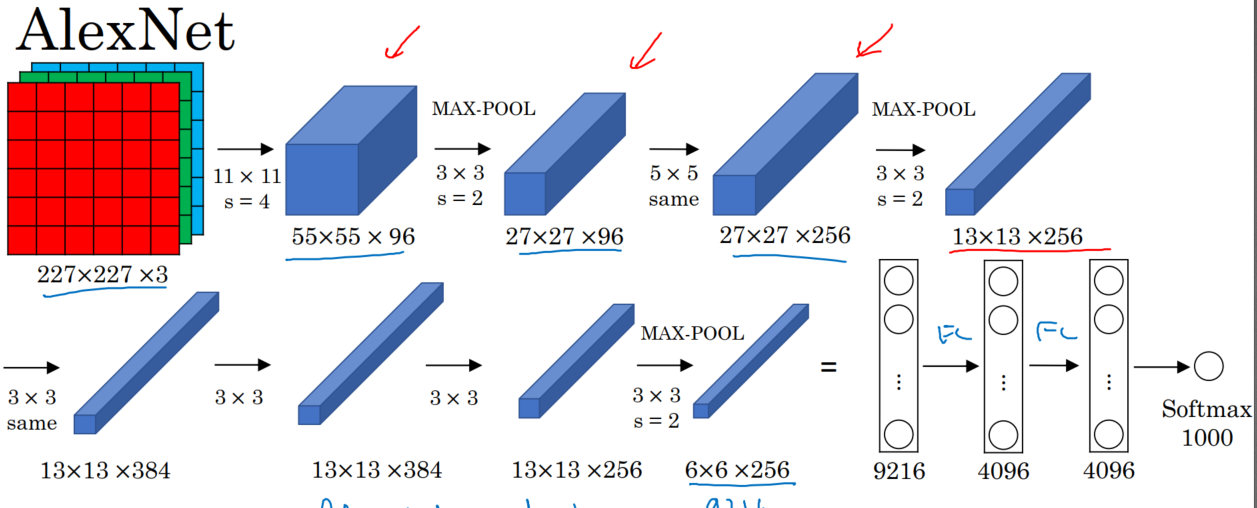
代码:
- #加载数据
- import tensorflow as tf
- from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
- mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/",one_hot = True)
- #定义卷积操作
- def conv2d(name , input_x , w , b , stride = 1,padding = 'SAME'):
- conv = tf.nn.conv2d(input_x,w,strides = [1,stride,stride,1],padding = padding , name = name)
- return tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(conv,b))
- def max_pool(name , input_x , k=2):
- return tf.nn.max_pool(input_x,ksize = [1,k,k,1],strides = [1,k,k,1],padding = 'SAME' , name = name)
- def norm(name , input_x , lsize = 4):
- return tf.nn.lrn(input_x , lsize , bias = 1.0 , alpha = 0.001 / 9.0 , beta = 0.75 , name = name)
- def buildGraph(x,learning_rate,weight,bias,dropout):
- #############前向传播##################
- #定义网络
- x = tf.reshape(x , [-1,28,28,1])
- #第一层卷积
- with tf.variable_scope('layer1'):
- conv1 = conv2d('conv1',x,weight['wc1'],bias['bc1'])
- pool1 = max_pool('pool1',conv1)
- norm1 = norm('norm1',pool1)
- with tf.variable_scope('layer2'):
- conv2 = conv2d('conv2',norm1,weight['wc2'],bias['bc2'])
- pool2 = max_pool('pool2',conv2)
- norm2 = norm('norm2',pool2)
- with tf.variable_scope('layer3'):
- conv3 = conv2d('conv3',norm2,weight['wc3'],bias['bc3'])
- pool3 = max_pool('pool3',conv3)
- norm3 = norm('norm3',pool3)
- with tf.variable_scope('layer4'):
- conv4 = conv2d('conv4',norm3,weight['wc4'],bias['bc4'])
- with tf.variable_scope('layer5'):
- conv5 = conv2d('conv5',conv4,weight['wc5'],bias['bc5'])
- pool5 = max_pool('pool5',conv5)
- norm5 = norm('norm5',pool5)
- with tf.variable_scope('func1'):
- norm5 = tf.reshape(norm5,[-1,4*4*256])
- fc1 = tf.add(tf.matmul(norm5,weight['wf1']) , bias['bf1'])
- fc1 = tf.nn.relu(fc1)
- #dropout
- fc1 = tf.nn.dropout(fc1,dropout)
- with tf.variable_scope('func2'):
- fc2 = tf.reshape(fc1,[-1,weight['wf1'].get_shape().as_list()[0]])
- fc2 = tf.add(tf.matmul(fc1,weight['wf2']),bias['bf2'])
- fc2 = tf.nn.relu(fc2)
- #dropout
- fc2 = tf.nn.dropout(fc2,dropout)
- with tf.variable_scope('outlayer'):
- out = tf.add(tf.matmul(fc2,weight['w_out']),bias['b_out'])
- return out
- def train(mnist):
- #定义网络的超参数
- learning_rate = 0.001
- training_step = 20000
- batch_size = 128
- #定义网络的参数
- n_input = 784
- n_output = 10
- dropout = 0.75
- #x、y的占位
- x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,784])
- y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,10])
- keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
- #权重和偏置的设置
- weight = {
- 'wc1':tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([11,11,1,96],stddev = 0.1)),
- 'wc2':tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([5,5,96,256],stddev = 0.1)),
- 'wc3':tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3,3,256,384],stddev = 0.1)),
- 'wc4':tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3,3,384,384],stddev = 0.1)),
- 'wc5':tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3,3,384,256],stddev = 0.1)),
- 'wf1':tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([4*4*256,4096])),
- 'wf2':tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([4096,4096])),
- 'w_out':tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([4096,10]))
- }
- bias = {
- 'bc1':tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1,shape = [96])),
- 'bc2':tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1,shape =[256])),
- 'bc3':tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1,shape =[384])),
- 'bc4':tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1,shape =[384])),
- 'bc5':tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1,shape =[256])),
- 'bf1':tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1,shape =[4096])),
- 'bf2':tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1,shape =[4096])),
- 'b_out':tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1,shape =[10]))
- }
- out = buildGraph(x,learning_rate,weight,bias,keep_prob)
- ####################后向传播####################
- #定义损失函数
- loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y, logits=out))
- optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(loss)
- #评估函数
- correction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(out,1),tf.argmax(y,1))
- acc = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correction,tf.float32))
- #####################################开始训练##############################
- init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
- with tf.Session() as sess:
- sess.run(init)
- step = 1
- while step <= training_step:
- batch_x , batch_y = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
- sess.run(out,feed_dict = {x:batch_x,y:batch_y,keep_prob:dropout})
- print(out.shape)
- sess.run(optimizer,feed_dict = {x:batch_x,y:batch_y,keep_prob:dropout})
- if step % 500 == 0:
- loss , acc = sess.run([loss,acc],feed_dict = {x:batch_x,y:batch_y,keep_prob:1})
- print(step,loss,acc)
- step += 1
- print(sess.run(acc,feed_dict = {x:mnist.test.images[:256],y:mnist.test.images[:256],keep_prob:1}))
- if __name__=='__main__':
- train(mnist)
TensorFlow技术解析与实战学习笔记(13)------Mnist识别和卷积神经网络AlexNet的更多相关文章
- TensorFlow技术解析与实战学习笔记(15)-----MNIST识别(LSTM)
一.任务:采用基本的LSTM识别MNIST图片,将其分类成10个数字. 为了使用RNN来分类图片,将每张图片的行看成一个像素序列,因为MNIST图片的大小是28*28像素,所以我们把每一个图像样本看成 ...
- 学习TF:《TensorFlow技术解析与实战》PDF+代码
TensorFlow 是谷歌公司开发的深度学习框架,也是目前深度学习的主流框架之一.<TensorFlow技术解析与实战>从深度学习的基础讲起,深入TensorFlow框架原理.模型构建. ...
- TensorFlow+实战Google深度学习框架学习笔记(12)------Mnist识别和卷积神经网络LeNet
一.卷积神经网络的简述 卷积神经网络将一个图像变窄变长.原本[长和宽较大,高较小]变成[长和宽较小,高增加] 卷积过程需要用到卷积核[二维的滑动窗口][过滤器],每个卷积核由n*m(长*宽)个小格组成 ...
- 《Tensorflow技术解析与实战》第四章
Tensorflow基础知识 Tensorflow设计理念 (1)将图的定义和图的运行完全分开,因此Tensorflow被认为是一个"符合主义"的库 (2)Tensorflow中涉 ...
- 学习笔记TF058:人脸识别
人脸识别,基于人脸部特征信息识别身份的生物识别技术.摄像机.摄像头采集人脸图像或视频流,自动检测.跟踪图像中人脸,做脸部相关技术处理,人脸检测.人脸关键点检测.人脸验证等.<麻省理工科技评论&g ...
- 机器学习实战 - 读书笔记(13) - 利用PCA来简化数据
前言 最近在看Peter Harrington写的"机器学习实战",这是我的学习心得,这次是第13章 - 利用PCA来简化数据. 这里介绍,机器学习中的降维技术,可简化样品数据. ...
- SQL反模式学习笔记13 使用索引
目标:优化性能 改善性能最好的技术就是在数据库中合理地使用索引. 索引也是数据结构,它能使数据库将指定列中的某个值快速定位在相应的行. 反模式:无规划的使用索引 1.不使用索引或索引不足 2.使用了 ...
- Elasticsearch技术解析与实战 PDF (内含目录)
Elasticsearch技术解析与实战 介绍: Elasticsearch是一个强[0大0]的搜索引擎,提供了近实时的索引.搜索.分 ...
- elasticsearch技术解析与实战ES
elasticsearch技术解析与实战ES 下载地址: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1NpPX05C0xKx_w9gBYaMJ5w 扫码下面二维码关注公众号回复100008 获取 ...
随机推荐
- jvm学习-垃圾回收算法(三)
垃圾回收算法 引用计数法 比较古老的一种垃圾回收算法.在java的GC并没有采用 增加一个引用 引用+1 减少一个引用引用减一 每次清除引用为0的的对象 缺点:不能回收循环引用的垃圾对象 标记清除 ...
- 暑假集训D13总结
考试 又炸掉了= = 本来看着题就一脸茫然,默默的打暴力骗分,然后就交了卷= = 重要的是,在本机跑的毫无障碍的T3程序竟然在评测机CE啊喂,35分就没了啊喂(这可是比我现在分还高= =) 内心几近崩 ...
- 洛谷 P1640 BZOJ 1854 [SCOI2010]连续攻击游戏
题目描述 lxhgww最近迷上了一款游戏,在游戏里,他拥有很多的装备,每种装备都有2个属性,这些属性的值用[1,10000]之间的数表示.当他使用某种装备时,他只能使用该装备的某一个属性.并且每种装备 ...
- 洛谷——P1910 L国的战斗之间谍
https://www.luogu.org/problem/show?pid=1910#sub 题目背景 L国即将与I国发动战争!! 题目描述 俗话说的好:“知己知彼,百战不殆”.L国的指挥官想派出间 ...
- Cloud Foundry中DEA与warden通信完毕应用port监听
在Cloud Foundry v2版本号中,DEA为一个用户应用执行的控制模块,而应用的真正执行都是依附于warden. 更详细的来说,是DEA接收到Cloud Controller的请求:DEA发送 ...
- ios weak和strong的差别
The difference is that an object will be deallocated as soon as there are no strong pointers to it. ...
- mybits 操作指南
第一.一对一: <resultMap type="com.zktx.platform.entity.tb.Module" id="BaseResultMap&quo ...
- VUEJS2.0源码理解--优
VUEJS2.0源码理解 http://jiongks.name/blog/vue-code-review/#pingback-112428
- k8s Job、Cronjob 的使用
Job负责处理任务,即仅执行一次的任务,它保证批处理任务的一个或多个Pod成功结束.而CronJob则就是在Job上加上了时间调度. Job 我们用Job这个资源对象来创建一个任务,我们定一个Job来 ...
- js设计模式-享元模式
享元模式实际上是一种优化模式,目的在于提高系统的性能和代码的效率. 使用享元模式的条件:最重要的条件是网页中必须使用了大量资源密集型对象,如果只会用到了少许这类对象,那么这种优化并不划算.第二个条件是 ...
