Spring属性注入(set方式、构造函数方式、p名称空间、spel、复杂类型)
1、set注入方式
(1)注入的为值类型(八大数据类型)的数据
配置文件:
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
- <beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.2.xsd ">- <bean name="student" class="pers.zhb.domain.Student">
- <property name="sname" value="zhai"></property>
- <property name="snum" value="20200210"></property>
- <property name="sex" value="nan"></property>
- </bean>
- </beans>
也可以以子标签的方式配置:
- <property name="">
- <value>123</value>
- </property>
测试类:
- public class Test {
- public void test1(){
- ApplicationContext applicationContext=new
- ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");//创建容器对象
- Student student=(Student)applicationContext.getBean("student");
- System.out.println(student);
- }
- public static void main(String[] args){
- Test test=new Test();
- test.test1();
- }
- }

(2)注入的为引用数据类型的数据:
Student对象:
- package pers.zhb.domain;
- public class Student {
- private String snum;
- private String sname;
- private String sex;
- private Course course;
- public Course getCourse() {
- return course;
- }
- public void setCourse(Course course) {
- this.course = course;
- }
- public Student(){
- System.out.println("Student对象创建了!");
- }
- public String getSnum() {
- return snum;
- }
- public void setSnum(String snum) {
- this.snum = snum;
- }
- public String getSname() {
- return sname;
- }
- public void setSname(String sname) {
- this.sname = sname;
- }
- public String getSex() {
- return sex;
- }
- public void setSex(String sex) {
- this.sex = sex;
- }
- @Override
- public String toString() {
- return "Student{" +
- "snum='" + snum + '\'' +
- ", sname='" + sname + '\'' +
- ", sex='" + sex + '\'' +
- ", course=" + course +
- '}';
- }
- public void destory(){
- System.out.println("我是销毁的方法!");
- }
- public void init(){
- System.out.println("我是初始化的方法!");
- }
- }
Course对象:
- public class Course {
- private String cname;
- public String getCname() {
- return cname;
- }
- public void setCname(String cname) {
- this.cname = cname;
- }
- @Override
- public String toString() {
- return "Course{" +
- "cname='" + cname + '\'' +
- '}';
- }
- }
配置文件:
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
- <beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.2.xsd ">
- <bean name="student" class="pers.zhb.domain.Student">
- <property name="sname" value="zhai"></property>
- <property name="snum" value="20200210"></property>
- <property name="sex" value="nan"></property>
- <property name="course" ref="course"></property>
- </bean>
- <bean name="course" class="pers.zhb.domain.Course">
- <property name="cname" value="算法设计与分析"></property>
- </bean>
- </beans>
测试类:
- public class Test {
- public void test1(){
- ApplicationContext applicationContext=new
- ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");//创建容器对象
- Student student=(Student)applicationContext.getBean("student");
- System.out.println(student);
- }
- public static void main(String[] args){
- Test test=new Test();
- test.test1();
- }
- }
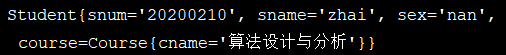
2、构造函数注入
创建Student对象:
- package pers.zhb.domain;
- public class Student {
- private String snum;
- private String sname;
- private String sex;
- private Course course;
- public Student(String snum, String sname, String sex, Course course) {
- this.snum = snum;
- this.sname = sname;
- this.sex = sex;
- this.course = course;
- }
- public Course getCourse() {
- return course;
- }
- public void setCourse(Course course) {
- this.course = course;
- }
- public Student(){
- System.out.println("Student对象创建了!");
- }
- public String getSnum() {
- return snum;
- }
- public void setSnum(String snum) {
- this.snum = snum;
- }
- public String getSname() {
- return sname;
- }
- public void setSname(String sname) {
- this.sname = sname;
- }
- public String getSex() {
- return sex;
- }
- public void setSex(String sex) {
- this.sex = sex;
- }
- @Override
- public String toString() {
- return "Student{" +
- "snum='" + snum + '\'' +
- ", sname='" + sname + '\'' +
- ", sex='" + sex + '\'' +
- ", course=" + course +
- '}';
- }
- public void destory(){
- System.out.println("我是销毁的方法!");
- }
- public void init(){
- System.out.println("我是初始化的方法!");
- }
- }
需要在Student类中创建一个构造函数。
配置文件:
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
- <beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.2.xsd ">
- <bean name="student" class="pers.zhb.domain.Student">
- <constructor-arg name="sname" value="zhai"></constructor-arg>
- <constructor-arg name="snum" value="123456"></constructor-arg>
- <constructor-arg name="sex" value="nan"></constructor-arg>
- <constructor-arg name="course" ref="course"></constructor-arg>
- </bean>
- <bean name="course" class="pers.zhb.domain.Course">
- <property name="cname" value="算法设计与分析"></property>
- </bean>
- </beans>
配置文件中的配置需要和构造函数中属性的配置一一对应。
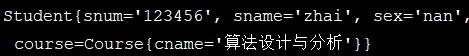
其他属性:
- index:指定构造函数的参数的索引
- type:指定构造函数参数的类型
3、p名称空间方式(对set方式注入进行简化)
(1)导入p名称空间(前提):
- xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
(2)配置文件:
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
- <beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
- xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
- xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
- xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.2.xsd ">
- <bean name="student" class="pers.zhb.domain.Student" p:sname="zhai"
- p:sex="nan" p:snum="1234" p:course-ref="course">
- </bean>
- <bean name="course" class="pers.zhb.domain.Course">
- <property name="cname" value="电子技术"></property>
- </bean>
- </beans>
测试:
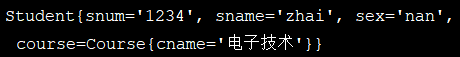
4、spel(Spring表达式语言)注入
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
- <beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
- xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
- xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.2.xsd ">
- <bean name="student" class="pers.zhb.domain.Student">
- <property name="sname" value="zhang"></property>
- <property name="snum" value="11111"></property>
- <property name="sex" value="nv"></property>
- </bean>
- <bean name="course" class="pers.zhb.domain.Course">
- <property name="cname" value="电子技术"></property>
- </bean>
- <bean name="student1" class="pers.zhb.domain.Student">
- <property name="sname" value="#{student.sname}"></property>
- <property name="snum" value="#{student.snum}"></property>
- <property name="sex" value="#{student.sex}"></property>
- <property name="course" ref="course"></property>
- </bean>
- </beans>
可以直接去取已经创建的对象的值。
5、复杂类型注入
(1)数组类型:
添加一个值:
- <bean name="arr" class="pers.zhb.domain.CollectionBean">
- <property name="arr" value="加油!!"></property>
- </bean>
添加多个值:
- <bean name="arr" class="pers.zhb.domain.CollectionBean">
- <property name="arr">
- <array>
- <value>你好</value>
- <value>加油</value>
- <value>努力</value>
- </array>
- </property>
- </bean>
值加对象:
- <bean name="arr" class="pers.zhb.domain.CollectionBean">
- <property name="arr">
- <array>
- <value>你好</value>
- <value>加油</value>
- <value>努力</value>
- <ref bean="student"></ref>
- </array>
- </property>
- </bean>
第四个值为一个Student对象。
(2)List类型:
- <bean name="cb" class="pers.zhb.domain.CollectionBean">
- <property name="li">
- <list>
- <value>你好</value>
- <value>加油</value>
- <value>努力</value>
- <ref bean="student"></ref>
- </list>
- </property>
- </bean>
(3)map类型:
- <bean name="map" class="pers.zhb.domain.CollectionBean">
- <property name="map">
- <map>
- <entry key="key" value="value"></entry>
- <entry key="student" value-ref="student"></entry>
- </map>
- </property>
- </bean>

(4)properties类型:
- <bean name="prop" class="pers.zhb.domain.CollectionBean">
- <property name="properties">
- <props>
- <prop key="key">key</prop>
- </props>
- </property>
- </bean>

Spring属性注入(set方式、构造函数方式、p名称空间、spel、复杂类型)的更多相关文章
- 六 Spring属性注入的四种方式:set方法、构造方法、P名称空间、SPEL表达式
Spring的属性注入: 构造方法的属性注入 set方法的属性注入
- Spring中属性注入的几种方式以及复杂属性的注入
在Spring框架中,属性的注入我们有多种方式,我们可以通过构造方法注入,可以通过set方法注入,也可以通过p名称空间注入,方式多种多样,对于复杂的数据类型比如对象.数组.List集合.map集合.P ...
- Spring中属性注入的几种方式以及复杂属性的注入详解
在spring框架中,属性的注入我们有多种方式,我们可以通过set方法注入,可以通过构造方法注入,也可以通过p名称空间注入,方式多种多样,对于复杂的数据类型比如对象.数组.List.Map.Prope ...
- Spring静态注入的三种方式
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载. https://blog.csdn.net/chen1403876161/article/details/53644024Spring静态注入的三 ...
- Spring 属性注入(一)JavaBean 内省机制在 BeanWrapper 中的应用
Spring 属性注入(一)JavaBean 内省机制在 BeanWrapper 中的应用 Spring 系列目录(https://www.cnblogs.com/binarylei/p/101174 ...
- Spring 属性注入(二)BeanWrapper 结构
Spring 属性注入(二)BeanWrapper 结构 Spring 系列目录(https://www.cnblogs.com/binarylei/p/10117436.html) BeanWrap ...
- Spring 属性注入(三)AbstractNestablePropertyAccessor
Spring 属性注入(三)AbstractNestablePropertyAccessor Spring 系列目录(https://www.cnblogs.com/binarylei/p/10117 ...
- Spring 属性注入(四)属性键值对 - PropertyValue
Spring 属性注入(四)属性键值对 - PropertyValue Spring 系列目录(https://www.cnblogs.com/binarylei/p/10117436.html) P ...
- SSH深度历险记(八) 剖析SSH核心原则+Spring依赖注入的三种方式
于java发育.一类程序猿必须依靠类的其他方法,它是通常new依赖类的方法,然后调用类的实例,这样的发展问题new良好的班统一管理的例子.spring提出了依赖注入的思想,即依赖类不由程 ...
随机推荐
- pandas 数据表中的字符与日期数据的处理
前面我们有学习过有关字符串的处理和正在表达式,但那都是基于单个字符串或字符串列表的操作.下面将学习如何基于数据框操作字符型变量. 同时介绍一下如何从日期型变量中取出年份,月份,星期几等,如何计算两个日 ...
- python的各种包安装地址
http://www.lfd.uci.edu/~gohlke/pythonlibs/#scipy-stack 这个网页里有python的所有包,whl的后缀是python压缩包的意思.在windows ...
- Java多线程_ReentrantLock
ReentrantLock是重入锁,它与synchronized很像,它是synchronized的加强版,因为它具有一些synchronized没有的功能.下面我们看看两者的区别:synchroni ...
- 《Head First 设计模式》:外观模式
正文 一.定义 外观模式提供了一个统一的接口,用来访问子系统中的一群接口.外观定义了一个高层接口,让子系统更容易使用. 要点: 外观模式将一个或数个类的复杂的一切都隐藏在背后,只显露出一个干净美好的外 ...
- 关于函数式接口, printable 自定义
这段代码在jdk1.8可以使用, 由于我是jdk14, 会报错. 这里可以优化, lambda表达式进一步优化写为: printString(System.Out::println); 注意案例版 ...
- Docker 镜像构建之 docker commit
我们可以通过公共仓库拉取镜像使用,但是,有些时候公共仓库拉取的镜像并不符合我们的需求.尽管已经从繁琐的部署工作中解放出来,但是实际开发时,我们可能希望镜像包含整个项目的完整环境,在其他机器上拉取打包完 ...
- FormData格式的数据
向服务器提交的是FormData格式的数据 || 必须添加以下两个配置项 contentType:false, processData:false,
- UI自动化测试、接口测试等自动化测试策略
今天跟大家介绍UI测试.接口测试.单元测试主要内容,以及每种测试花费时间讨论.UI测试[Selenium]UI测试是最接近软件真实用户使用行为的测试类型.通常是模拟真实用户使用软件的行为,即模拟用户在 ...
- 原生 JavaScript30 练习 Day 1 (原生JS控制键盘模拟击鼓)
代码如下 <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset=&qu ...
- Ubuntu 16.04 安装CP210x,CH340驱动
CH340 https://github.com/juliagoda/CH341SER CP210x 因为源码版本不是linux-source-4.15.0-91-generic,导致error,一个 ...
