Vue-router插件使用
单页面原理
Vue是单页面开发,即页面不刷新。
页面不刷新,而又要根据用户选择完成内容的更新该怎么做?Vue中采用锚点来完成。
如访问http://127.0.0.1#/index就是主页,而访问http://127.0.0.1#/home就是家目录。
手动分析url组成与处理视图的切换非常麻烦,所以Vue提供插件Vue-router,它能够根据用户在地址栏中输入的不同链接展示不同的内容,十分的方便。
Vue-router
打开Vue.js官网,在生态系统中找到vue-router。
然后根据它的官方文档进行安装即可:
示例演示
使用<router-view>当作组件的显示容器。
使用<router-link>与属性to让Vue切换显示的组件。
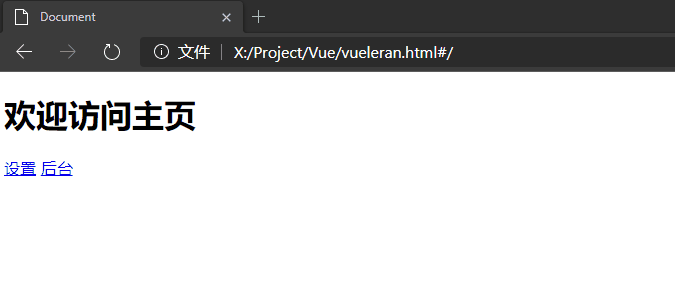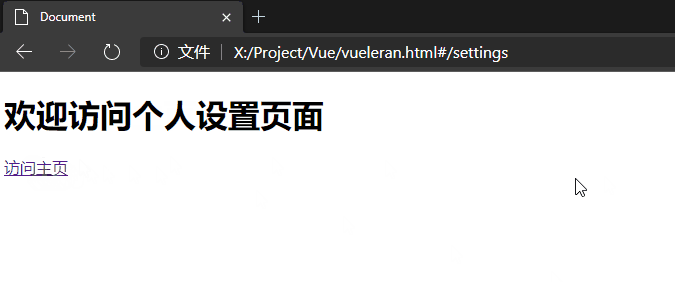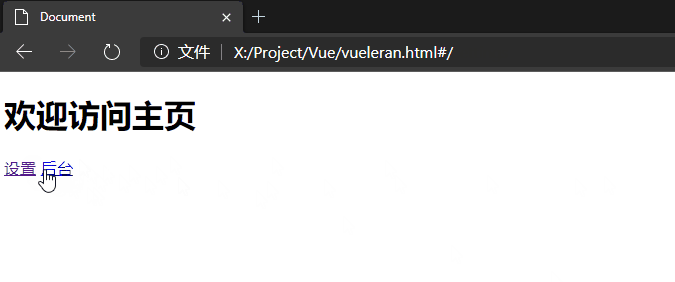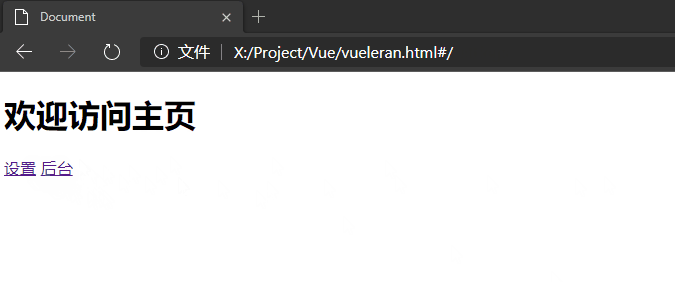
注意查看下图中url的变化,它确实没有刷新。
<body>
<div id="app">
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<script src="./vue-router.js"></script>
<script>
// 第一步:书写组件
const index = {
template: `
<div>
<h1>欢迎访问主页</h1>
<router-link to="/settings">设置</router-link>
<router-link to="/backend">后台</router-link>
</div>
`
}
const backend = {
template: `
<div>
<h1>欢迎访问后台</h1>
<router-link to="/">访问主页</router-link>
</div>
`
}
const settings = {
template: `
<div>
<h1>欢迎访问个人设置页面</h1>
<router-link to="/">访问主页</router-link>
</div>
`
}
// 第二步:配置路由
// 根据资源请求来展示或隐藏对应的组件
const routes = [
// 主页,/
{path: "/", component: index},
{path: "/backend", component: backend},
{path: "/settings", component: settings},
]
// 第三步:实例化路由对象
// {routes:routes}
const router = new VueRouter({routes,})
// 第四步:根组件中添加路由信息
// {router:router}
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
router,
})
</script>
</body>
参数相关
参数传递
在很多情况下,我们都需要用户的请求地址携带一些参数,然后通过这个参数再进行查询。
比如查询某一本书时,地址栏通常是这样的:
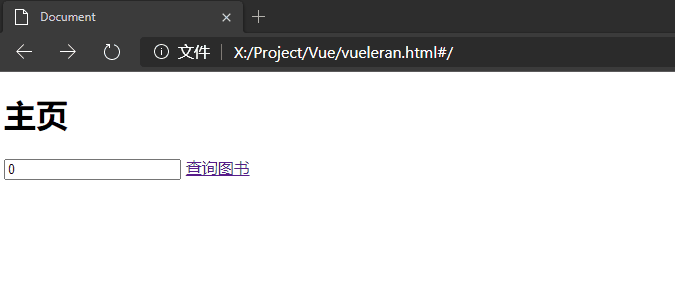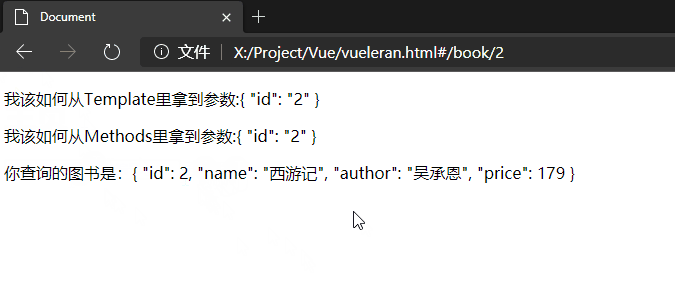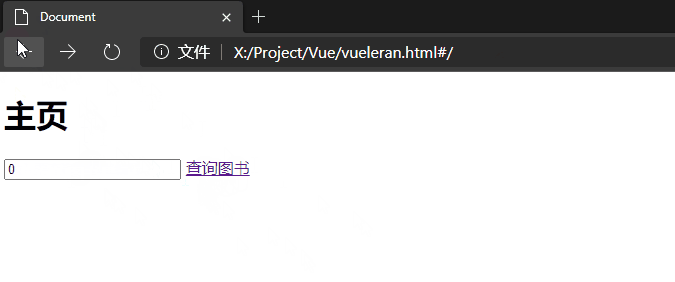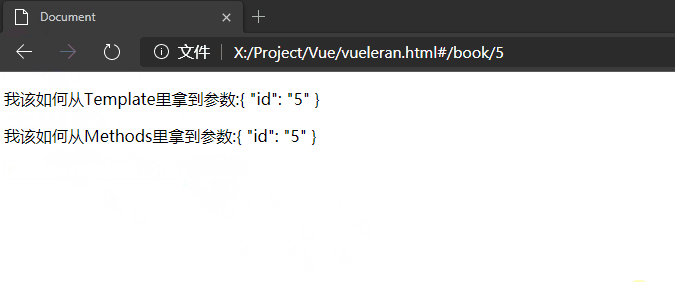
#/book/2
而且很有可能在今后的<router-link>以及methods中都要使用这个参数,如何操作?
{path: "/book/:id(\\d+)", component: book}, // 转义 \d+
我该如何从Template里拿到参数:{{ $route.params }}
我该如何从Methods里拿到参数:this.$route.params
示例如下:
<body>
<div id="app">
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<script src="./vue-router.js"></script>
<script>
// 第一步:书写组件
const index = {
template: `
<div>
<h1>主页</h1>
<input type="text" v-model="book_id" placeholder="输入要查询的图书编号">
<router-link :to="'/book/'+book_id">查询图书</router-link>
</div>
`,
data() {
return {
book_id: 0,
};
}
}
const book = {
// 在模板以及方法中,你都可以拿到查询的参数
template: `
<div>
<p>我该如何从Template里拿到参数:{{ $route.params }}</p>
<p>我该如何从Methods里拿到参数:{{ show() }}</p>
<p v-for="item in books" v-if="item.id==$route.params.id">你查询的图书是:{{ item }}</p>
</div>
`,
data() {
return {
books: [
{id: 1, name: "红楼梦", author: "曹雪芹", price: 199,},
{id: 2, name: "西游记", author: "吴承恩", price: 179,},
{id: 3, name: "三国演义", author: "罗贯中", price: 158,},
{id: 4, name: "水浒传", author: "施耐庵", price: 128,},
]
}
},
methods:{
show(){
return this.$route.params
}
}
}
// 第二步:配置路由
const routes = [
// 主页,/
{path: "/", component: index},
{path: "/book/:id(\\d+)", component: book}, // 转义 \d+
]
// 第三步:实例化路由对象
// {routes:routes}
const router = new VueRouter({routes,})
// 第四步:根组件中添加路由信息
// {router:router}
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
router,
})
</script>
</body>
默认参数
根据RestAPI规范,如果没有携带参数则代表查询所有。
如果按照上面的示例,直接不带参数进行请求路由将匹配不上,所以我们还需要做一个查询所有的功能。
其实对上面路由进行改进即可,设置为默认参数:
{path: "/book/:id?", component: book}, // ?代表可以有也可以没有
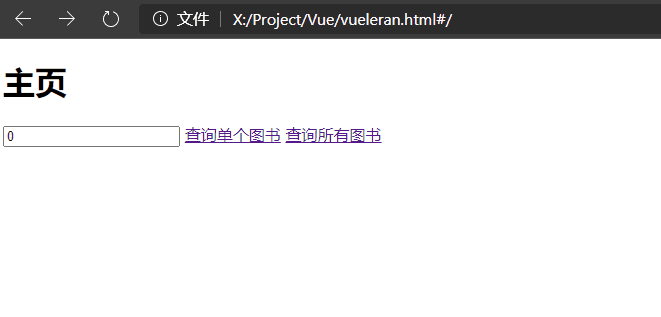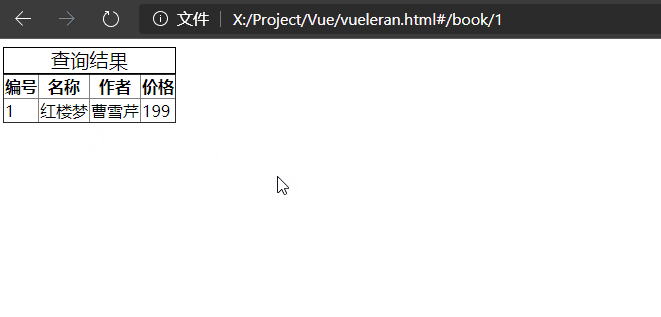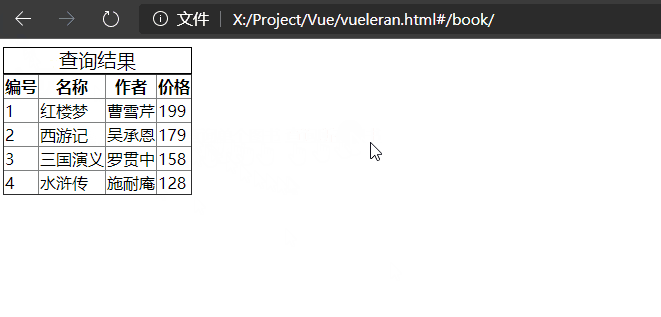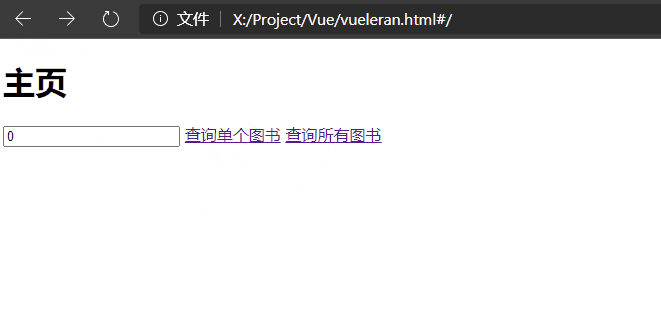
示例如下:
<body>
<div id="app">
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
<!--查询模板-->
<template id="result">
<div>
<table border="1" :style="{borderCollapse:'collapse'}">
<caption :style="{border:'1px solid #000',fontSize:'1.2rem'}">查询结果</caption>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>编号</th>
<th>名称</th>
<th>作者</th>
<th>价格</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<!-- 查询一本 -->
<tbody v-if="$route.params.id">
<tr v-for="item in books" v-if="item.id == $route.params.id">
<td>{{ item.id }}</td>
<td>{{ item.name }}</td>
<td>{{ item.author }}</td>
<td>{{ item.price }}</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
<!-- 查询所有 -->
<tbody v-else>
<tr v-for="item in books">
<td>{{ item.id }}</td>
<td>{{ item.name }}</td>
<td>{{ item.author }}</td>
<td>{{ item.price }}</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
</template>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<script src="./vue-router.js"></script>
<script>
// 第一步:书写组件
const index = {
template: `
<div>
<h1>主页</h1>
<input type="text" v-model="book_id" placeholder="输入要查询的图书编号">
<router-link :to="'/book/'+book_id">查询单个图书</router-link>
<router-link to="/book/">查询所有图书</router-link>
</div>
`,
data() {
return {
book_id: 0,
};
}
}
const book = {
// 在模板以及方法中,你都可以拿到查询的参数
template: `#result`,
data() {
return {
books: [
{id: 1, name: "红楼梦", author: "曹雪芹", price: 199,},
{id: 2, name: "西游记", author: "吴承恩", price: 179,},
{id: 3, name: "三国演义", author: "罗贯中", price: 158,},
{id: 4, name: "水浒传", author: "施耐庵", price: 128,},
]
}
},
}
// 第二步:配置路由
const routes = [
// 主页,/
{path: "/", component: index},
{path: "/book/:id?", component: book}, // 转义 \d+,?可以有也可以没有
]
// 第三步:实例化路由对象
// {routes:routes}
const router = new VueRouter({routes,})
// 第四步:根组件中添加路由信息
// {router:router}
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
router,
})
</script>
</body>
路由别名
路由name
为每一个路由匹配规则添加name属性,使其更方便的在模板以及Js代码中进行跳转:
如下所示:
const routes = [
{path: "/", component: index, name: "index"},
{path: "/book/:id?", component: book, name: "query_book"},
]
router-link
模板中使用router-link与路由的别名name进行跳转时,格式如下:
<!-- 有参数就传递,没有就不传递。注意在to前添加: -->
<router-link :to="{name:'query_book',params:{id:书籍编号}}">查询</router-link>
$route.push
Js代码中使用跳转时要用到this.$router.push()这个方法,如下所示:
// 模板中的按钮
<button @click="func(书籍编号)">查看详情</button>
// js
func(bookId){
// 使用url拼接跳转
let url = {path:"/book/"+bookId};
// 使用别名进行跳转跳转:
// {name:'book_query',params:{id:id}}
this.$router.push(url); // 使用$router.push(url)进行跳转
}
视图布局
视图嵌套
一个大的组件中可以包含很多小的组件。
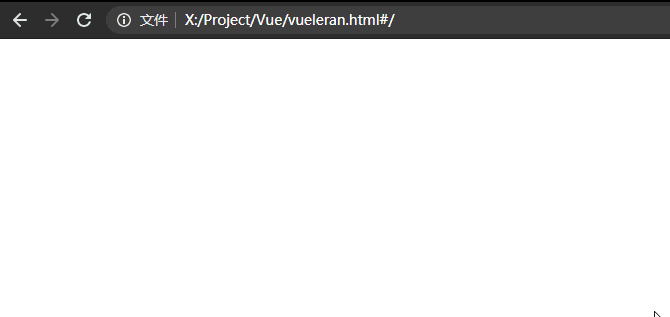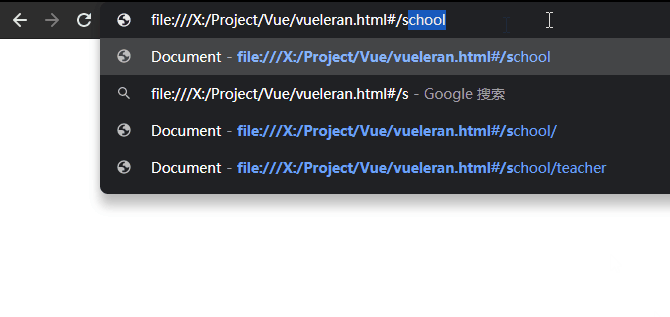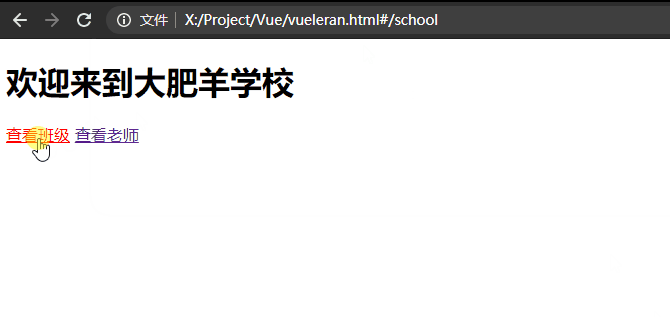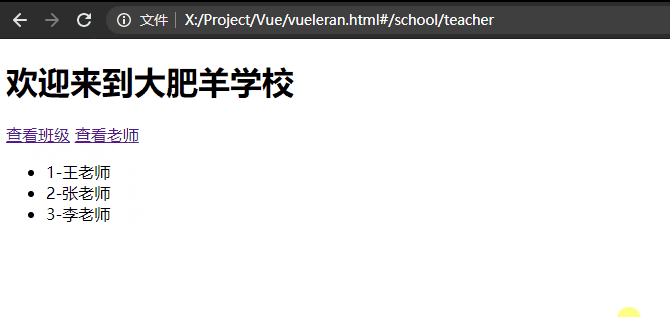
如下所示,有一个school组件,在school组件中你可以查看到当前的teacher和classes。
当然teacher与classes也都是两个组件。
换而言之,我在school组件中点击查看教师或者班级,我并不希望他跳转到新的页面而是在当前页面的其他位置进行显示其他组件就可以使用路由嵌套。
<div id="app">
<!-- 第一层,展示学校 -->
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
# 子组件中的关键代码
<router-view></router-view>
# 路由中的代码,第一层的路由匹配第一层的router-view,第二层的路由就在第二层的router-view中显示
path: "/school", component: school, name: "school", children: [
{path: "/school/teacher", component: teacher, name: "teacher"},
{path: "/school/classes", component: classes, name: "classes"},
]
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- 第一层,展示学校 -->
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<script src="./vue-router.js"></script>
<script>
// 第一步:书写组件
const school = {
template: `
<div>
<h1>欢迎来到大肥羊学校</h1>
<router-link :to="{name:'classes'}">查看班级</router-link>
<router-link :to="{name:'teacher'}">查看老师</router-link>
<!-- 第二层,展示班级或者教师 -->
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
`
}
const teacher = {
template: `
<div>
<ul>
<li v-for="item in teacherMessage">{{item.id}}-{{item.name}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
`,
data() {
return {
teacherMessage: [
{id: 1, name: "王老师",},
{id: 2, name: "张老师",},
{id: 3, name: "李老师",},
]
}
}
}
const classes = {
template: `
<div>
<ul>
<li v-for="item in classMessage">{{item.id}}-{{item.name}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
`,
data() {
return {
classMessage: [
{id: 1, name: "一年级一班",},
{id: 2, name: "一年级二班",},
{id: 3, name: "一年级三班",},
]
}
}
}
// 第二步:配置路由
const routes = [
{
path: "/school", component: school, name: "school", children: [
{path: "/school/teacher", component: teacher, name: "teacher"},
{path: "/school/classes", component: classes, name: "classes"},
]
},
]
// 第三步:实例化路由对象
// {routes:routes}
const router = new VueRouter({routes,})
// 第四步:根组件中添加路由信息
// {router:router}
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
router,
})
</script>
</body>
嵌套的问题
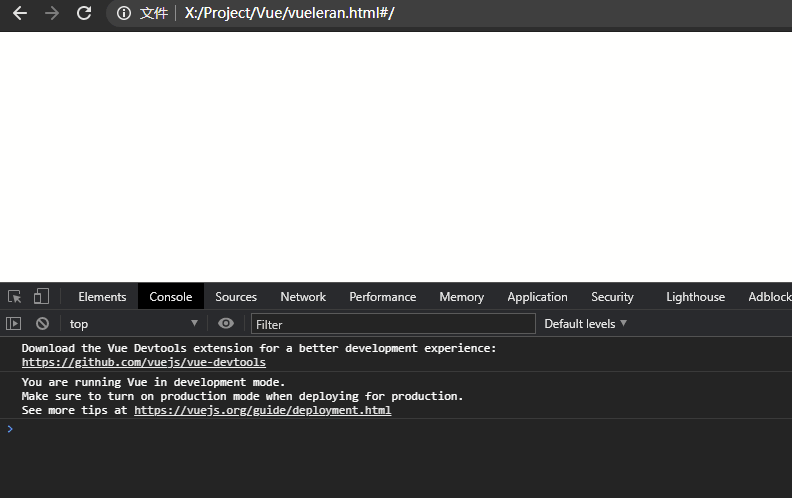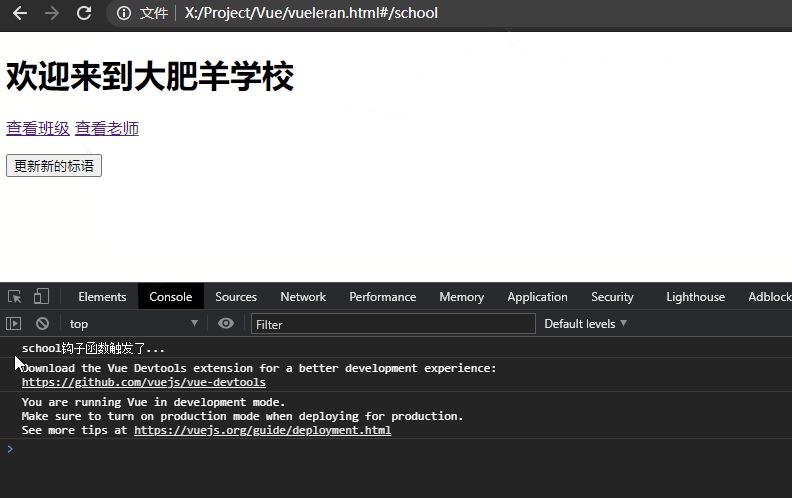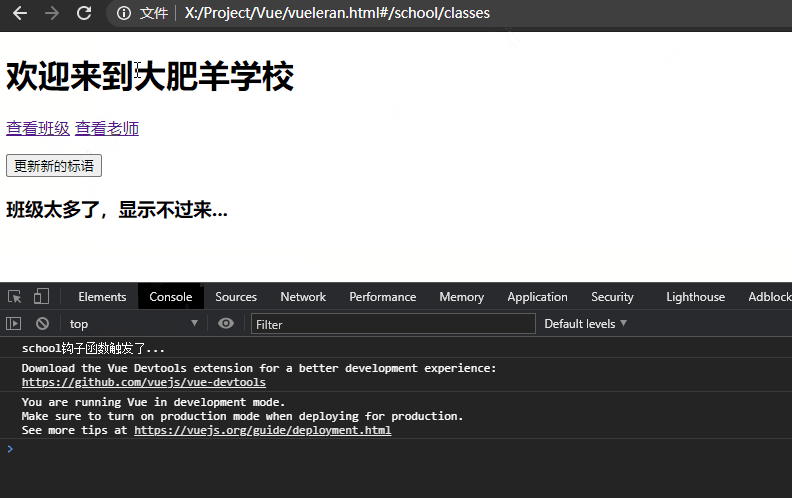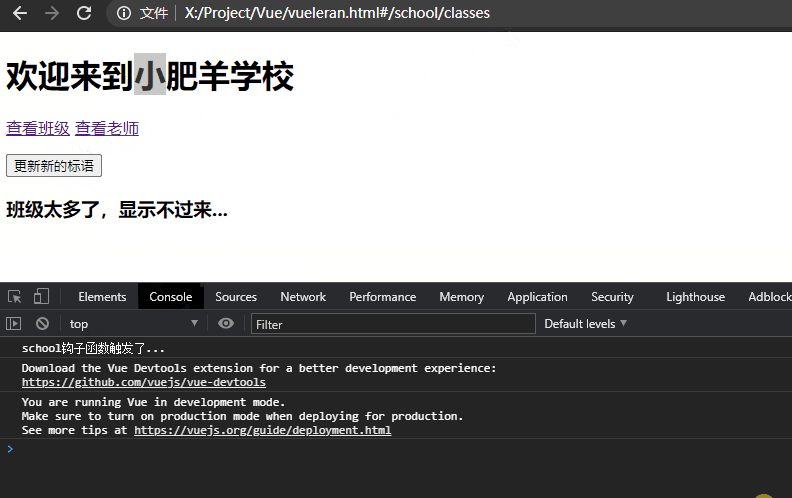
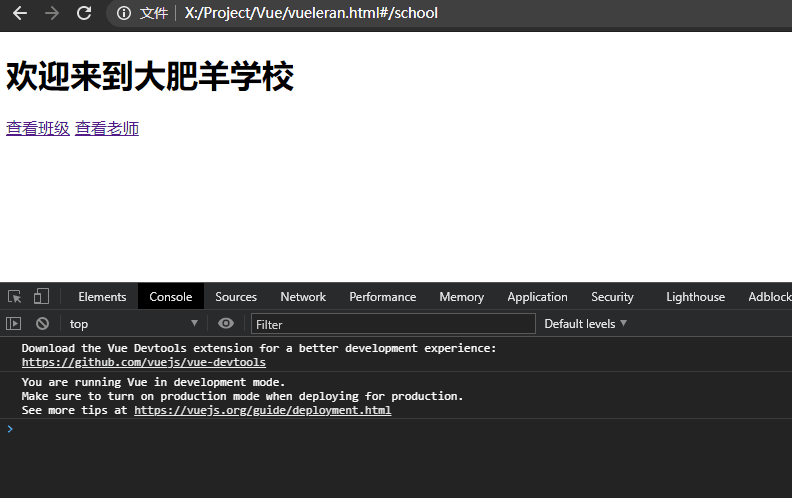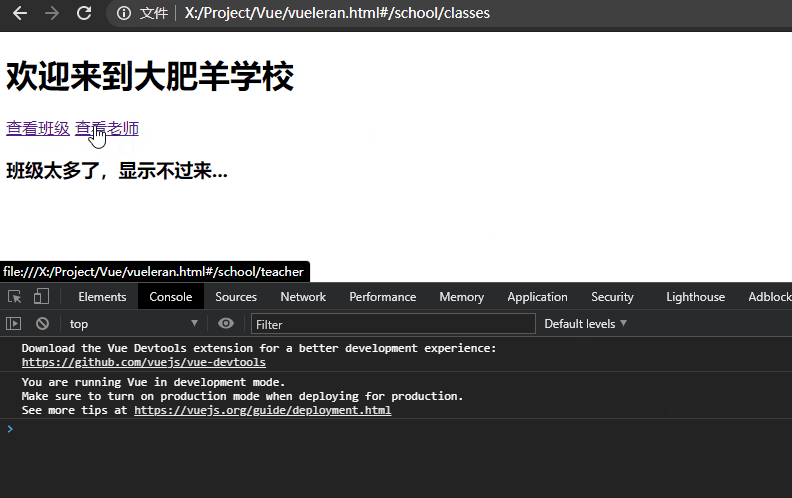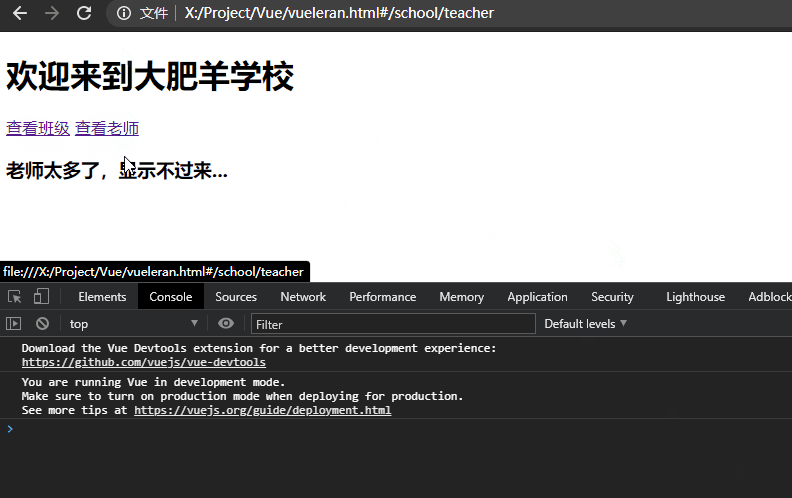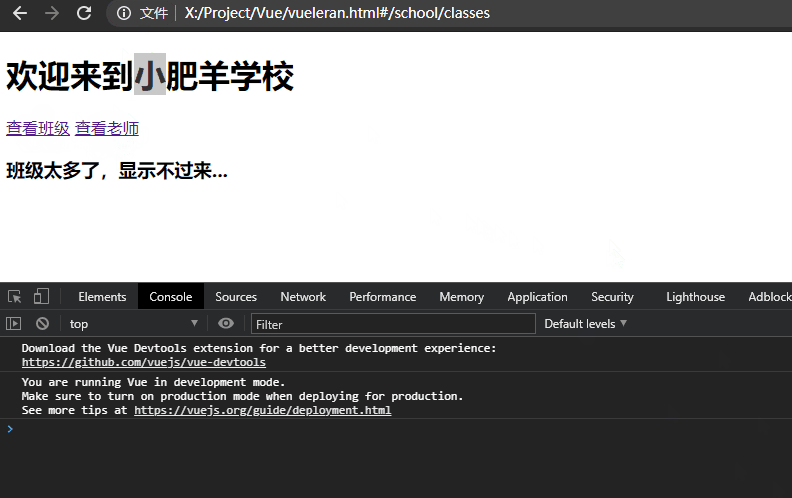
当页面发生变化,如#school/classes跳转到#school/teacher,school组件将会产生复用。
这代表school的组件声明周期钩子函数不会被重复调用,就可能造成数据更新不及时的问题。
举一个例子,上述示例中的school欢迎语是欢迎来到大肥羊学校,如果它是钩子函数created()从后端获取的数据,在用户查看#school/classes后跳转到#school/teacher这个时间点中间后端数据发生了改变,变成了欢迎来到小肥羊学校,由于组件复用问题不会再次执行created(),则代表用户依旧看到的是欢迎来到大肥羊学校。如下所示,我们只有手动更新标语才能执行更新,这显然是不符合常理的:
<body>
<div id="app">
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<script src="./vue-router.js"></script>
<script>
// 假设是从后端抓取数据
let schoolTitle = "欢迎来到大肥羊学校";
// 5s后发生改变
setTimeout(() => {
schoolTitle = "欢迎来到小肥羊学校";
}, 5000);
// 第一步:书写组件
const school = {
template: `
<div>
<h1>{{ title }}</h1>
<router-link :to="{name:'classes'}">查看班级</router-link>
<router-link :to="{name:'teacher'}">查看老师</router-link>
<p><button @click="updateTitle">更新新的标语</button></p>
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
`,
data(){
return {
title : "",
}
},
created(){
// 假设发送异步请求
console.log("school钩子函数触发了...")
this.title = schoolTitle;
},
methods:{
updateTitle(){
this.title = schoolTitle;
}
}
}
const teacher = {
template: `
<div>
<h3>老师太多了,显示不过来...</h3>
</div>
`,
}
const classes = {
template: `
<div>
<h3>班级太多了,显示不过来...</h3>
</div>
`,
}
// 第二步:配置路由
const routes = [
{
path: "/school", component: school, name: "school", children: [
{path: "/school/teacher", component: teacher, name: "teacher"},
{path: "/school/classes", component: classes, name: "classes"},
]
},
]
// 第三步:实例化路由对象
// {routes:routes}
const router = new VueRouter({routes,})
// 第四步:根组件中添加路由信息
// {router:router}
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
router,
})
</script>
</body>
解决问题
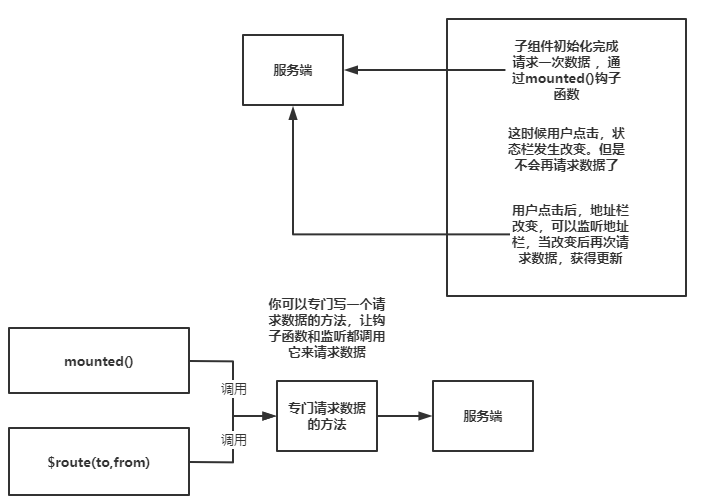
如果想解决组件复用钩子函数不执行的问题,我们可以使用watch来监听$route对象,也就是使用watch来监听地址栏变化,当发生变化时就重新获取数据。
或者使用 2.2 中引入的 beforeRouteUpdate 导航守卫,解决思路如下图所示:
代码如下,使用watch进行解决:
const school = {
template:"...",
data(){
return {
title : "",
}
},
created(){
// 假设发送异步请求
this.getTitle();
},
methods:{
getTitle(){
// 从后端获取数据
this.title = schoolTitle;
}
},
watch:{
$route(to,from){
// to 要跳转的页面
// from 从那个页面进行跳转
this.getTitle();
}
}
}
使用导航守卫进行解决的代码如下:
// 第一步:书写组件
const school = {
template:"...",
data(){
return {
title : "",
}
},
created(){
// 假设发送异步请求
this.getTitle();
},
methods:{
getTitle(){
// 从后端获取数据
this.title = schoolTitle;
}
},
beforeRouteUpdate (to, from, next) {
this.getTitle();
}
}
命名视图
命名视图就是说可以在一个页面上,使用多个<router-view>,相较于路由嵌套的层级关系,它是一种扁平化的设计。
如,头部导航栏,左侧菜单栏,右边内容块三个组件,都显示在一个页面上,就可以使用命名视图。
核心代码如下:
# 根组件模板
<div id="app">
<!-- 这里只放个人主页 -->
<router-view></router-view>
<router-view name="menu"></router-view>
<router-view name="show"></router-view>
</div>
# Js配置路由,/代表根目录。有三个视图,router-view
path: "/", components: {
default: header, // 如果 view-router没有name属性,则用default
menu: menu,
show: show,
}

<style>
*{
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
header{
height: 45px;
display: flex;
justify-content: space-evenly;
background-color: #ddd;
align-items: center;
}
body>div>div:nth-child(2){
display: inline-flex;
width: 15%;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
height: 1000px;
}
menu>ul{
list-style-type: none;
display: inline-flex;
flex-flow: column;
}
menu>ul>li{
margin: 10px 0 0 10px;
}
body>div>div:last-child{
display: inline-flex;
justify-content: center;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
width: 70%;
height: 1000px;
}
</style>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- 这里只放个人主页 -->
<router-view></router-view>
<router-view name="menu"></router-view>
<router-view name="show"></router-view>
</div>
<!-- 头部组件 -->
<template id="header">
<div>
<header><span>首页</span><span>新闻</span><span>关注</span><span>链接</span></header>
</div>
</template>
<!-- 左侧菜单 -->
<template id="menu">
<div>
<menu>
<ul>
<li>最新</li>
<li>最热</li>
<li>最多评论</li>
</ul>
</menu>
</div>
</template>
<!-- 内容区域 -->
<template id="show">
<div>
<section>
<h1>内容区域</h1>
</section>
</div>
</template>
<script src="vue.js"></script>
<script src="vue-router.js"></script>
<script>
// 第一步:书写组件
const header = {
template: "#header",
}
const menu = {
template: "#menu",
}
const show = {
template: "#show",
}
// 第二步:配置路由
const routes = [
{
// 当你访问主页时,有三个组件扁平显示
path: "/", components: {
default: header, // 如果 view-router没有name属性,则用default
menu: menu,
show: show,
}
}
]
// 第三步:实例化路由对象
const router = new VueRouter({
routes, // es6新语法
})
// 第四步:根组件中添加路由信息
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
router,
});
</script>
</body>
重定向
redirect
当你访问一个页面时,可以重定向至另一个页面,如下示例,使用redirect进行重定向。
访问/doc,重定向到/help中。但是地址栏中显示的还是/help:
const routes = [
// 当用户访问doc时,将会跳转到help中,地址栏中显示是help
{ path: "/help", component: help, name: "help"},
{ path: "/doc", redirect: { name: "help" } }
]
alias
如果你使用alias参数进行匹配,就方便许多了,并且地址栏中显示的是用户输入的值,但是当输入的路径不存在,则不会显示:
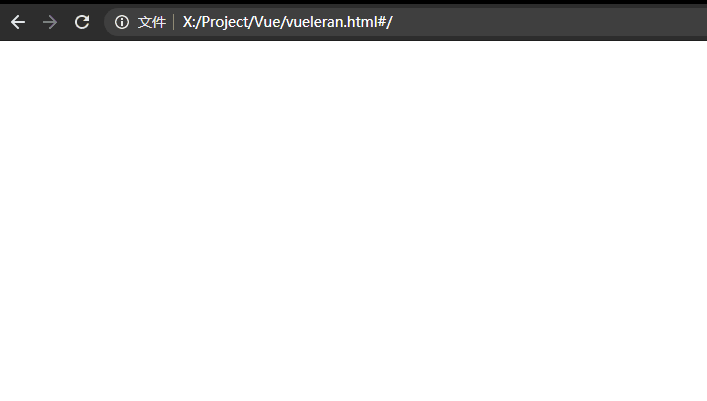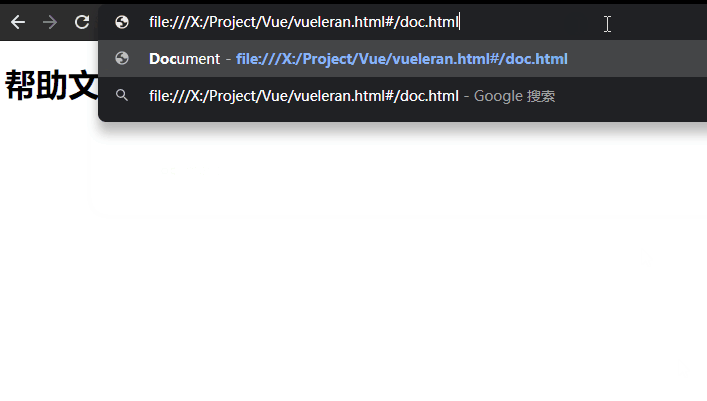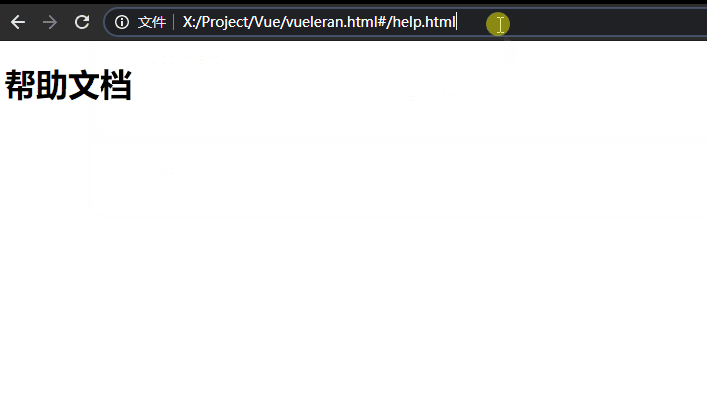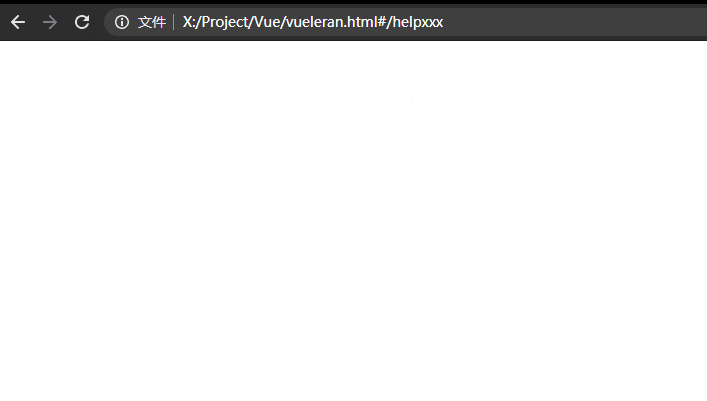
const routes = [
// 用户输入在alias中的所有路径,都会交给help组件进行处理
{ path: "/help", component: help, name: "help", alias: ["/doc", "/doc.html", "/help.html"] },
]
history模式
如果你的url中不想有#号的锚点,可开启history模式。
同时你还需要在后端做相应的配置,参见官方文档:
切换动画
相信现在你已经对单页面开发有所了解,单页面开发说白了就是根据url请求的#后的参数不停的更换要显示的组件。
所以我们可以为这一切换过程加上过渡动画,你可以在其他子组件模板中添加<transition>标签,并自己书写css类或者引用第三方库。
如下所示:
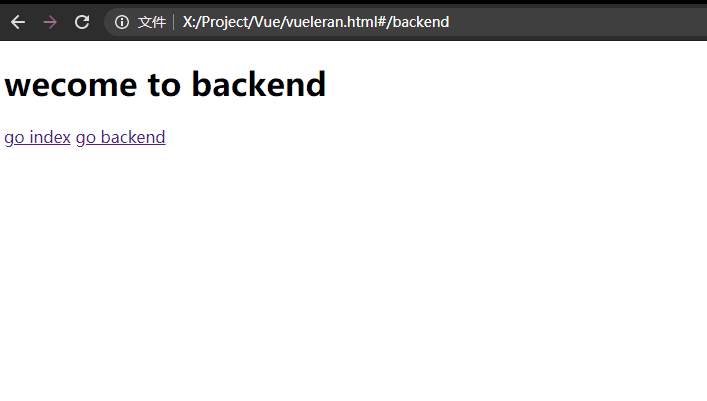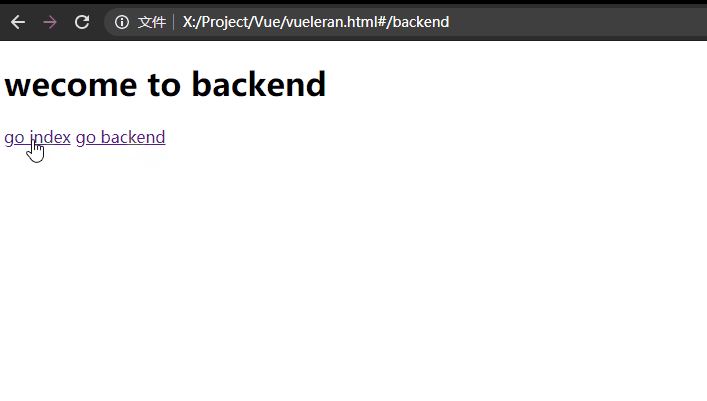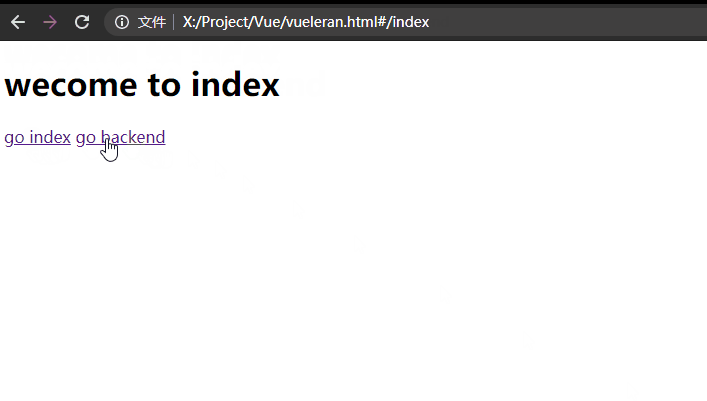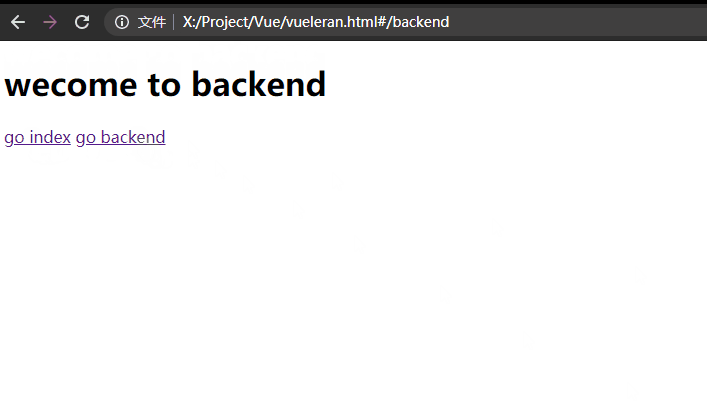
我这里是单独给每个子组件加的动画:
// 书写组件
const index = {
template:
`
<transition enter-active-class="animate__animated animate__bounce">
<h1>wecome to index</h1>
</transition>
`,
}
const backend = {
template: `
<transition enter-active-class="animate__animated animate__bounce">
<h1>wecome to backend</h1>
</transition>
`,
}
如想了解更多,请参考官方文档。
Vue-router插件使用的更多相关文章
- 「vue基础」一篇浅显易懂的 Vue 路由使用指南( Vue Router 上)
大家好,今天的内容,我将和大家一起聊聊 Vue 路由相关的知识,如果你以前做过服务端相关的开发,那你一定会对程序的URL结构有所了解,我没记错的话也是路由映射的概念,需要进行配置. 其实前端这些框架的 ...
- 「进阶篇」Vue Router 核心原理解析
前言 此篇为进阶篇,希望读者有 Vue.js,Vue Router 的使用经验,并对 Vue.js 核心原理有简单了解: 不会大篇幅手撕源码,会贴最核心的源码,对应的官方仓库源码地址会放到超上,可以配 ...
- vue.js插件使用(02) vue-router
概述 vue-router是Vue.js官方的路由插件,它和vue.js是深度集成的,适合用于构建单页面应用.vue的单页面应用是基于路由和组件的,路由用于设定访问路径,并将路径和组件映射起来.传统的 ...
- vue.js及项目实战[笔记]— 03 vue.js插件
一. vue补充 1. 获取DOM元素 救命稻草,document.querySelector 在template中标示元素`ref = "xxx" 在要获取的时候,this.$r ...
- 深入浅出的webpack构建工具--webpack4+vue+router项目架构(十四)
阅读目录 一:vue-router是什么? 二:vue-router的实现原理 三:vue-router使用及代码配置 四:理解vue设置路由导航的两种方法. 五:理解动态路由和命名视图 六:理解嵌套 ...
- Vue Router的入门以及简单使用
Vue Router 是Vue官方的路由管理器,是Vue用来实现SPA的插件.它和 Vue.js 的核心深度集成,让构建单页面应用(SPA)变得易如反掌. 基本概念: 路由:是一种映射关系,是 “pa ...
- Vue躬行记(8)——Vue Router
虽然Vue.js未提供路由功能,但是官方推出了Vue Router(即vue-router库),以插件的形式支持.它与Vue.js深度集成,可快速的创建单页应用(Single Page Applica ...
- 8. Vue - Router
一.Vue Router 的使用 JavaScript: 1.创建组件:创建单页面应用需要渲染的组件 2.创建路由:创建VueRouter实例 3.映射路由:调用VueRouter实例的map方法 4 ...
- vue Router——基础篇
vue--Router简介 vue-router是Vue.js官方的路由插件,它和vue.js是深度集成的,适合用于构建单页面应用. vue的单页面应用是基于路由和组件的,路由用于设定访问路径,并将路 ...
- vue使用插件的流程
1.引入vue 2.引入插件 3.通过vue.use()调用 例子:使用router插件 import Vue from "vue"; import VueRouter from ...
随机推荐
- 带你了解 MySQL Binlog 不为人知的秘密
MySQL 的 Binlog 日志是一种二进制格式的日志,Binlog 记录所有的 DDL 和 DML 语句(除了数据查询语句SELECT.SHOW等),以 Event 的形式记录,同时记录语句执行时 ...
- Linux文件元数据和节点表结构
文件元数据 一块硬盘的分区可以认为有两部分组成,保存元数据的成为节点表,用来保存属性等. 元数据中有个小指针,指向数据存放的实际空间. 元数据(Metadata) 又称中介数据.中继数据,为描述数据的 ...
- 经典剪枝算法的例题——Sticks详细注释版
这题听说是道十分经典的剪枝算的题目,不要问我剪枝是什么,我也不知道,反正我只知道用到了深度搜索 我参考了好多资料才悟懂,然后我发现网上的那些大神原理讲的很明白,但代码没多少注释,看的很懵X,于是我抄起 ...
- MySQL 主从复制原理不再难
上篇我们分析过 Binlog 日志的作用以及存储原理,感兴趣的可以翻阅: 一文带你了解 Binlog 日志 Binlog 日志主要作用是数据恢复和主从复制.本身就是二进制格式的日志文件,网络传输无需进 ...
- MongoDB 监控 --- MongoDB基础用法(八)
MongoDB 监控 在你已经安装部署并允许MongoDB服务后,你必须要了解MongoDB的运行情况,并查看MongoDB的性能.这样在大流量得情况下可以很好的应对并保证MongoDB正常运作. M ...
- STM32入门系列-学习STM32要掌握的内容
STM32芯片架构 STM32F103系列芯片的系统架构如下: STM32芯片基于ARM公司的Cortex-M3内核,由ST公司设计生产,内核与总线矩阵之间有I(指令).S(系统).D(数据)三条信号 ...
- 云服务器部署Python项目(nginx+uwsgi+mysql+项目)
python项目部署到云服务器 关注公众号"轻松学编程"了解更多. 一.硬件准备 云服务器,系统ubuntu_16_04 . 注意:要在安全组中开放Http的80端口. 二.软件准 ...
- 【快速因数分解】Pollard's Rho 算法
Pollard-Rho 是一个很神奇的算法,用于在 $O(n^{\frac{1}4}) $的期望时间复杂度内计算合数 n 的某个非平凡因子(除了1和它本身以外能整除它的数).事书上给出的复杂度是 \( ...
- 网络编程NIO:BIO和NIO
BIO BIO(Blocking I/O),同步阻塞,实现模式为一个连接一个线程,即当有客户端连接时,服务器端需为其单独分配一个线程,如果该连接不做任何操作就会造成不必要的线程开销.BIO是传统的Ja ...
- Luogu P3324 [SDOI2015]星际战争
二分+最大流 首先考虑二分答案 然后可以发现对于已知时间,判断是否可以将所有机器人摧毁可以用网络流 建立源点和汇点,源点向每一个激光武器连一条容量为$time*b[i]$的边,表示该激光武器在$tim ...
