tcp 接收被动关闭 fin
void tcp_rcv_established(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb, const struct tcphdr *th, unsigned int len)
主要是处理已经连理连接的输入的tcp数据包。tcp_rcv_established实际上包含了两条路径用于处理不同目的的数据包。
- 快速路径 使用快速路径只进行最少的处理,如处理数据段、发生ACK、存储时间戳等。
- 慢速路径 使用慢速路径可以处理乱序数据段、PAWS、socket内存管理和紧急数据等。
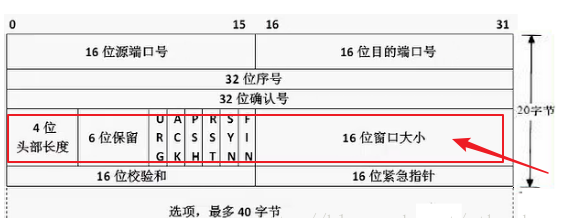
主要是:TCP首部中第4个32位字除去保留的bit位和预测标志一致,比如:skb包的序列号和sock结构下一个要接收到序号相等,并且skb包中的确认序列号是有效的,除了head_len,只有为1的bit位对应的是ACK标志其余为0,snd_wnd则是本端发送窗口的大小。就走快速路径;毕竟是预期的报文!!
但是如果设置了FIN标志的话,则检查预测标志时失败,所以会在慢速路径中处理FIN包。
其流程大约是:
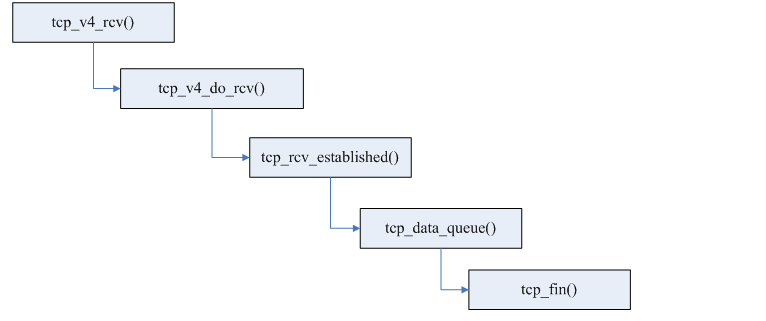
if (TCP_SKB_CB(skb)->tcp_flags & TCPHDR_FIN)
tcp_fin(sk);
/*
* Process the FIN bit. This now behaves as it is supposed to work
* and the FIN takes effect when it is validly part of sequence
* space. Not before when we get holes.
*
* If we are ESTABLISHED, a received fin moves us to CLOSE-WAIT
* (and thence onto LAST-ACK and finally, CLOSE, we never enter
* TIME-WAIT)
*
* If we are in FINWAIT-1, a received FIN indicates simultaneous
* close and we go into CLOSING (and later onto TIME-WAIT)
*
* If we are in FINWAIT-2, a received FIN moves us to TIME-WAIT.
*/
static void tcp_fin(struct sock *sk)TCP_FIN_TIM
{
struct tcp_sock *tp = tcp_sk(sk); inet_csk_schedule_ack(sk);//表明需要发送ack sk->sk_shutdown |= RCV_SHUTDOWN; //表明rcv 关闭 关闭接收通道
sock_set_flag(sk, SOCK_DONE);//sock结构的标志,表示连接将要结束 switch (sk->sk_state) {
case TCP_SYN_RECV:
case TCP_ESTABLISHED:
/* Move to CLOSE_WAIT */
tcp_set_state(sk, TCP_CLOSE_WAIT);//设置为 close_wait 状态
inet_csk(sk)->icsk_ack.pingpong = 1;//设置延迟发送ACK的标志----也就是进入延迟确认模式 -----期望发送数据或FIN时携带ACK确认
/*tcp_fin()中虽然设置了发送ACK的相关标志,但是要有一个引发ACK发送的操作,或者是给内核发送ACK的一个提示。
这个操作是在上层函数tcp_rcv_established()函数中进行的,通过间接调用__tcp_ack_snd_check()中完成
*/
break; case TCP_CLOSE_WAIT:
case TCP_CLOSING:
/* Received a retransmission of the FIN, do
* nothing.
*/
break;
case TCP_LAST_ACK:
/* RFC793: Remain in the LAST-ACK state. */
break; case TCP_FIN_WAIT1:
/* This case occurs when a simultaneous close
* happens, we must ack the received FIN and
* enter the CLOSING state.
*/
tcp_send_ack(sk);
tcp_set_state(sk, TCP_CLOSING);
break;
case TCP_FIN_WAIT2:
/* Received a FIN -- send ACK and enter TIME_WAIT. */
tcp_send_ack(sk);
tcp_time_wait(sk, TCP_TIME_WAIT, 0);
break;
default:
/* Only TCP_LISTEN and TCP_CLOSE are left, in these
* cases we should never reach this piece of code.
*/
pr_err("%s: Impossible, sk->sk_state=%d\n",
__func__, sk->sk_state);
break;
} /* It _is_ possible, that we have something out-of-order _after_ FIN.
* Probably, we should reset in this case. For now drop them.
清理乱序队列、状态更改时可能要唤醒相关进程 乱序队列数据直接干掉哦!!! 之前正常的序列还在 ----
*/
__skb_queue_purge(&tp->out_of_order_queue);
if (tcp_is_sack(tp))//开启了SACK选项
tcp_sack_reset(&tp->rx_opt);//清除SACK选项信息,因为对端已经不会再发送数据了
sk_mem_reclaim(sk); if (!sock_flag(sk, SOCK_DEAD)) {
sk->sk_state_change(sk);//状态更改时可能要唤醒相关进程 ---sock_def_wakeup /* Do not send POLL_HUP for half duplex close. */
if (sk->sk_shutdown == SHUTDOWN_MASK ||
sk->sk_state == TCP_CLOSE)
sk_wake_async(sk, SOCK_WAKE_WAITD, POLL_HUP);
else
sk_wake_async(sk, SOCK_WAKE_WAITD, POLL_IN);
}
}
如果收包队列中只有无数据的FIN包,则收包系统会调用返回0,这时应用进程就知道收到了FIN,对端关闭了连接。如果队列中有数据则系统调用会返回大于0的值 ;
然后 应用进程如果调用事件监听函数(如epoll_wait /poll)等待数据到来,这时会调用tcp_poll函数:
其实现如下:


/*
* Wait for a TCP event.
*
* Note that we don't need to lock the socket, as the upper poll layers
* take care of normal races (between the test and the event) and we don't
* go look at any of the socket buffers directly.
*/
unsigned int tcp_poll(struct file *file, struct socket *sock, poll_table *wait)
{
unsigned int mask;
struct sock *sk = sock->sk;
const struct tcp_sock *tp = tcp_sk(sk);
int state; sock_rps_record_flow(sk); sock_poll_wait(file, sk_sleep(sk), wait); state = sk_state_load(sk);
if (state == TCP_LISTEN)
return inet_csk_listen_poll(sk); /* Socket is not locked. We are protected from async events
* by poll logic and correct handling of state changes
* made by other threads is impossible in any case.
*/ mask = 0; /*
* POLLHUP is certainly not done right. But poll() doesn't
* have a notion of HUP in just one direction, and for a
* socket the read side is more interesting.
*
* Some poll() documentation says that POLLHUP is incompatible
* with the POLLOUT/POLLWR flags, so somebody should check this
* all. But careful, it tends to be safer to return too many
* bits than too few, and you can easily break real applications
* if you don't tell them that something has hung up!
*
* Check-me.
*
* Check number 1. POLLHUP is _UNMASKABLE_ event (see UNIX98 and
* our fs/select.c). It means that after we received EOF,
* poll always returns immediately, making impossible poll() on write()
* in state CLOSE_WAIT. One solution is evident --- to set POLLHUP
* if and only if shutdown has been made in both directions.
* Actually, it is interesting to look how Solaris and DUX
* solve this dilemma. I would prefer, if POLLHUP were maskable,
* then we could set it on SND_SHUTDOWN. BTW examples given
* in Stevens' books assume exactly this behaviour, it explains
* why POLLHUP is incompatible with POLLOUT. --ANK
*
* NOTE. Check for TCP_CLOSE is added. The goal is to prevent
* blocking on fresh not-connected or disconnected socket. --ANK
*/
if (sk->sk_shutdown == SHUTDOWN_MASK || state == TCP_CLOSE)
mask |= POLLHUP;
if (sk->sk_shutdown & RCV_SHUTDOWN)
mask |= POLLIN | POLLRDNORM | POLLRDHUP; /* Connected or passive Fast Open socket? */
if (state != TCP_SYN_SENT &&
(state != TCP_SYN_RECV || tp->fastopen_rsk)) {
int target = sock_rcvlowat(sk, 0, INT_MAX); if (tp->urg_seq == tp->copied_seq &&
!sock_flag(sk, SOCK_URGINLINE) &&
tp->urg_data)
target++; if (tp->rcv_nxt - tp->copied_seq >= target)
mask |= POLLIN | POLLRDNORM; if (!(sk->sk_shutdown & SEND_SHUTDOWN)) {
if (sk_stream_is_writeable(sk)) {
mask |= POLLOUT | POLLWRNORM;
} else { /* send SIGIO later */
sk_set_bit(SOCKWQ_ASYNC_NOSPACE, sk);
set_bit(SOCK_NOSPACE, &sk->sk_socket->flags); /* Race breaker. If space is freed after
* wspace test but before the flags are set,
* IO signal will be lost. Memory barrier
* pairs with the input side.
*/
smp_mb__after_atomic();
if (sk_stream_is_writeable(sk))
mask |= POLLOUT | POLLWRNORM;
}
} else
mask |= POLLOUT | POLLWRNORM; if (tp->urg_data & TCP_URG_VALID)
mask |= POLLPRI;
}
/* This barrier is coupled with smp_wmb() in tcp_reset() */
smp_rmb();
if (sk->sk_err || !skb_queue_empty(&sk->sk_error_queue))
mask |= POLLERR; return mask;
}
if (sk->sk_shutdown & RCV_SHUTDOWN)
mask |= POLLIN | POLLRDNORM | POLLRDHUP;
其代码中会判断 其 RCV_SHUTDOWN SEND_SHUTDOWN等状态 然后返回对应的掩码!!!
所以POLLRDHUP可以检测到文件是否挂起!!!-----也就是fd 是否被close
tcp 接收被动关闭 fin的更多相关文章
- TCP连接与关闭
1.建立连接协议(三次握手) (1)客户端发送一个带SYN标志的TCP报文到服务器.这是三次握手过程中的报文1. (2) 服务器端回应客户端的,这是三次握手中的第2个报文,这个报文同时带ACK标志和S ...
- TCP连接建立和关闭中的疑难点
TCP连接建立和关闭中的疑难点 作者:夏语岚 撰写日期:2011-10-29 近日在阅读<Unix网络编程>,以前在<计算机网络>课程中学到TCP,当时只是简单了解了TC ...
- Linux:TCP状态/半关闭/2MSL/端口复用
TCP状态 CLOSED:表示初始状态. LISTEN:该状态表示服务器端的某个SOCKET处于监听状态,可以接受连接. SYN_SENT:这个状态与SYN_RCVD遥相呼应,当客户端SOCKET执行 ...
- TCP连接建立与关闭
http://hi.baidu.com/psorqkxcsfbbghd/item/70f3bd91943b9248f14215cd TCP连接建立与关闭 TCP 是一个面向连接的协议,无论哪一方向另一 ...
- TCP连接的关闭
原文地址:http://lib.csdn.net/article/computernetworks/17264 TCP连接的关闭有两个方法close和shutdown,这篇文章将尽量精简的说明它们 ...
- 深入理解TCP建立和关闭连接
建立连接: 理解:窗口和滑动窗口TCP的流量控制TCP使用窗口机制进行流量控制什么是窗口?连接建立时,各端分配一块缓冲区用来存储接收的数据,并将缓冲区的尺寸发送给另一端 接收方发送的确认信息中包含了自 ...
- TCP中异常关闭链接的意义 异常关闭的情况
终止一个连接的正常方式是发送FIN. 在发送缓冲区中 所有排队数据都已发送之后才发送FIN,正常情况下没有任何数据丢失. 但我们有时也有可能发送一个RST报文段而不是F IN来中途关闭一个连接.这称为 ...
- TCP协议: SYN ACK FIN RST PSH URG 详解
TCP的三次握手是怎么进行的了:发送端发送一个SYN=1,ACK=0标志的数据包给接收端,请求进行连接,这是第一次握手:接收端收到请求并且允许连接的话,就会发送一个SYN=1,ACK=1标志的数据包给 ...
- 五十五、linux 编程——TCP 连接和关闭过程及服务器的并发处理
55.1 TCP 连接和关闭过程 55.1.1 介绍 建立连接的过程就是三次握手的过程:客户端发送 SYN 报文给服务器,服务器回复 SYN+ACK 报文,客户机再发送 ACK 报文. 关闭连接的过程 ...
随机推荐
- java高级&资深&专家面试题-行走江湖必备-持续更新ing
行走江湖必备一份面试题,这里给大家整理了一套.0面试官最喜欢问的问题或者出场率较高的面试题,助校招或者社招路上的你一臂之力! 首先我们需要明白一个事实,招聘的一个很关键的因素是在给自己找未来的同事,同 ...
- Springboot+Redis(发布订阅模式)跨多服务器实战
一:redis中发布订阅功能(http://www.redis.cn/commands.html#pubsub) PSUBSCRIBE pattern [pattern -]:订阅一个或者多个符合pa ...
- 异步编程新方式async/await
一.前言 实际上对async/await并不是很陌生,早在阮大大的ES6教程里面就接触到了,但是一直处于理解并不熟练使用的状态,于是决定重新学习并且总结一下,写了这篇博文.如果文中有错误的地方还请各位 ...
- pytest文档42-fixture参数化params
前言 参数化是自动化测试里面必须掌握的一个知识点,用过 unittest 框架的小伙伴都知道使用 ddt 来实现测试用例的参数化. pytest 测试用例里面对应的参数可以用 parametrize ...
- CentOS 7操作系统基础优化介绍
01 前言 操作系统部署完毕后,需要做一些基础的简单优化操作,可以为系统未来的使用过程带来更多便捷. 02 操作系统安全优化配置 系统安装完毕后,默认系统中会存在两个重要的安全服务程序,建议将其首先进 ...
- 如何获取前端提交来得json格式数据
composer.json { "require": { "guzzlehttp/guzzle": "~6.0" } } composer ...
- Django折腾日记(django2.0)
新建项目 django-admin startproject mysite 运行 python manage.py runserver 创建一个应用 python manage.py startapp ...
- 深入了解Redis(8)-高可用方案
生产环境中的redis基本都是多节点部署,本文只讨论redis高可用的三种方案,不涉及实际操作. 一.主从复制(一主一从,一主多从,级联结构) (图来源于网络) 一个Master,两个Slave,Sl ...
- Luogu P4234 最小差值生成树
题意 给定一个 \(n\) 个点 \(m\) 条边的有权无向图,求出原图的一棵生成树使得该树上最大边权与最小边权的差值最小. \(\texttt{Data Range:}1\leq n\leq 5\t ...
- 4G DTU模块带有MQTT协议吗?
DTU作为一种通讯设备,其应用场合十分广泛.从广义上讲,在进行通信时,传输数据链路两端负责发送数据信息的模块单元都称之为DTU,在它的作用下对所传信息格式转换和数据整理校验.在狭义上的定义,DTU一般 ...
