Kubernetes K8S之Service服务详解与示例
K8S之Service概述与代理说明,并详解所有的service服务类型与示例
主机配置规划
| 服务器名称(hostname) | 系统版本 | 配置 | 内网IP | 外网IP(模拟) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| k8s-master | CentOS7.7 | 2C/4G/20G | 172.16.1.110 | 10.0.0.110 |
| k8s-node01 | CentOS7.7 | 2C/4G/20G | 172.16.1.111 | 10.0.0.111 |
| k8s-node02 | CentOS7.7 | 2C/4G/20G | 172.16.1.112 | 10.0.0.112 |
Service概述
Kubernetes Service定义了这样一种抽象:逻辑上的一组 Pod,一种可以访问它们的策略 —— 通常被称为微服务。这一组 Pod 能够被 Service 访问到,通常是通过 selector实现的。
举例:考虑一个图片处理 backend,它运行了3个副本。这些副本是可互换的 —— frontend 不需要关心它们调用了哪个 backend 副本。 然而组成这一组 backend 程序的 Pod 实际上可能会发生变化,frontend 客户端不应该也没必要知道,而且也不需要跟踪这一组 backend 的状态。Service 定义的抽象能够解耦这种关联。
Service可以提供负载均衡的能力,但是使用上存在如下限制:
- 只能提供4层负载均衡能力,而没有7层功能。有时我们可能需要更多的匹配规则来转发请求,这点上4层负载均衡是不支持的、
如web访问的service服务示例图:
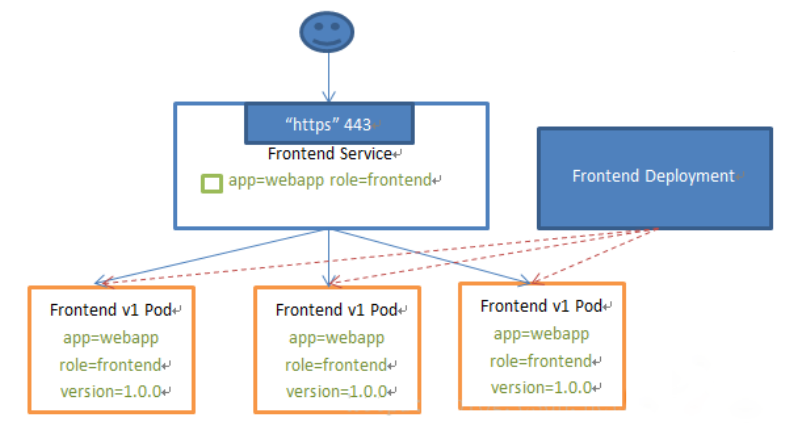
VIP和Service代理
在 Kubernetes 集群中,每个 Node 运行一个 kube-proxy 进程。kube-proxy 负责为 Service 实现了一种 VIP(虚拟 IP)的形式,而不是 ExternalName 的形式。
从Kubernetes v1.0开始,已经可以使用 userspace代理模式。Kubernetes v1.1添加了 iptables 代理模式,在 Kubernetes v1.2 中kube-proxy 的 iptables 模式成为默认设置。Kubernetes v1.8添加了 ipvs 代理模式。
原因如下:
- DNS 实现的历史由来已久,它不遵守记录 TTL,并且在名称查找到结果后会对其进行缓存。
- 有些应用程序仅执行一次 DNS 查找,并无限期地缓存结果。
- 即使应用和库进行了适当的重新解析,DNS 记录上的 TTL 值低或为零也可能会给 DNS 带来高负载,从而使管理变得困难。
总之就是因为有缓存,因此不合适。
userspace代理模式
这种模式,kube-proxy 会监视 Kubernetes master 对 Service 对象和 Endpoints 对象的添加和移除。 对每个 Service,它会在本地 Node 上打开一个端口(随机选择)。 任何连接到“代理端口”的请求,都会被代理到 Service 的backend Pods 中的某个上面(如 Endpoints 所报告的一样)。 使用哪个 backend Pod,是 kube-proxy 基于 SessionAffinity 来确定的。
最后,它配置 iptables 规则,捕获到达该 Service 的 clusterIP(是虚拟 IP)和 Port 的请求,并重定向到代理端口,代理端口再代理请求到 backend Pod。
默认情况下,userspace模式下的kube-proxy通过循环算法选择后端。
默认的策略是,通过 round-robin 算法来选择 backend Pod。

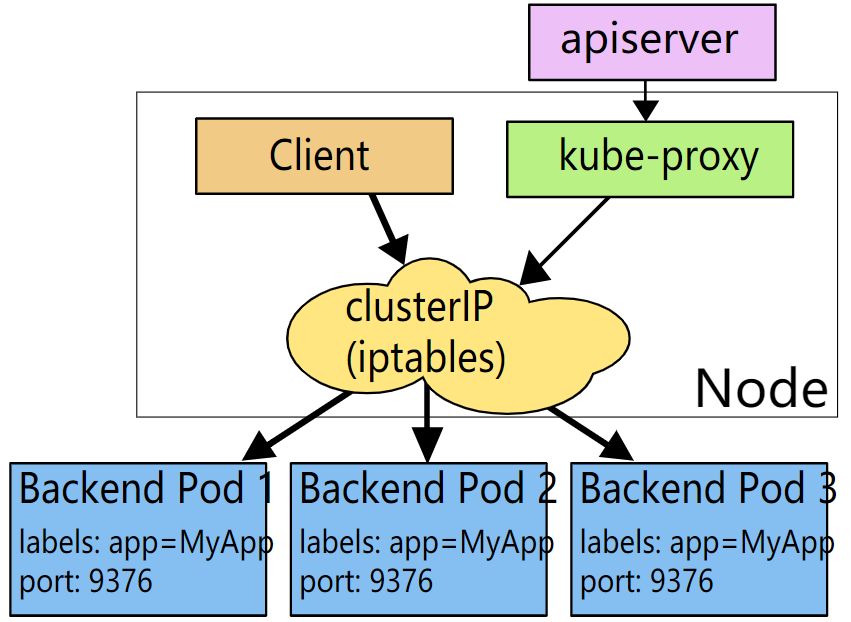
iptables 代理模式
这种模式,kube-proxy 会监视 Kubernetes 控制节点对 Service 对象和 Endpoints 对象的添加和移除。 对每个 Service,它会配置 iptables 规则,从而捕获到达该 Service 的 clusterIP 和端口的请求,进而将请求重定向到 Service 的一组 backend 中的某个上面。对于每个 Endpoints 对象,它也会配置 iptables 规则,这个规则会选择一个 backend 组合。
默认的策略是,kube-proxy 在 iptables 模式下随机选择一个 backend。
使用 iptables 处理流量具有较低的系统开销,因为流量由 Linux netfilter 处理,而无需在用户空间和内核空间之间切换。 这种方法也可能更可靠。
如果 kube-proxy 在 iptables模式下运行,并且所选的第一个 Pod 没有响应,则连接失败。 这与userspace模式不同:在这种情况下,kube-proxy 将检测到与第一个 Pod 的连接已失败,并会自动使用其他后端 Pod 重试。
我们可以使用 Pod readiness 探测器 验证后端 Pod 是否可以正常工作,以便 iptables 模式下的 kube-proxy 仅看到测试正常的后端。这样做意味着可以避免将流量通过 kube-proxy 发送到已知已失败的Pod。
IPVS 代理模式
在 ipvs 模式下,kube-proxy监视Kubernetes服务(Service)和端点(Endpoints),调用 netlink 接口相应地创建 IPVS 规则, 并定期将 IPVS 规则与 Kubernetes服务(Service)和端点(Endpoints)同步。该控制循环可确保 IPVS 状态与所需状态匹配。访问服务(Service)时,IPVS 将流量定向到后端Pod之一。
IPVS代理模式基于类似于 iptables 模式的 netfilter 挂钩函数,但是使用哈希表作为基础数据结构,并且在内核空间中工作。 这意味着,与 iptables 模式下的 kube-proxy 相比,IPVS 模式下的 kube-proxy 重定向通信的延迟要短,并且在同步代理规则时具有更好的性能。与其他代理模式相比,IPVS 模式还支持更高的网络流量吞吐量。
IPVS提供了更多选项来平衡后端Pod的流量。这些是:
- rr: round-robin
- lc: least connection (smallest number of open connections)
- dh: destination hashing
- sh: source hashing
- sed: shortest expected delay
- nq: never queue
注意:要在 IPVS 模式下运行 kube-proxy,必须在启动 kube-proxy 之前使 IPVS Linux 在节点上可用。 当 kube-proxy 以 IPVS 代理模式启动时,它将验证 IPVS 内核模块是否可用。 如果未检测到 IPVS 内核模块,则 kube-proxy 将退回到以 iptables 代理模式运行。

Service服务类型
Kubernetes 中Service有以下4中类型:
- ClusterIP:默认类型,自动分配一个仅Cluster内部可以访问的虚拟IP
- NodePort:通过每个 Node 上的 IP 和静态端口(NodePort)暴露服务。以ClusterIP为基础,NodePort 服务会路由到 ClusterIP 服务。通过请求
<NodeIP>:<NodePort>,可以从集群的外部访问一个集群内部的 NodePort 服务。 - LoadBalancer:使用云提供商的负载均衡器,可以向外部暴露服务。外部的负载均衡器可以路由到 NodePort 服务和 ClusterIP 服务。
- ExternalName:通过返回 CNAME 和它的值,可以将服务映射到 externalName 字段的内容(例如,foo.bar.example.com)。没有任何类型代理被创建。
需要注意的是:Service 能够将一个接收 port 映射到任意的 targetPort。默认情况下,targetPort 将被设置为与 port 字段相同的值。
Service域名格式:$(service name).$(namespace).svc.cluster.local,其中 cluster.local 为指定的集群的域名
Deployment的yaml信息
yaml文件
[root@k8s-master service]# pwd
/root/k8s_practice/service
[root@k8s-master service]# cat myapp-deploy.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: myapp-deploy
namespace: default
spec:
replicas:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: myapp
release: v1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: myapp
release: v1
env: test
spec:
containers:
- name: myapp
image: registry.cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/google_registry/myapp:v1
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
ports:
- name: http
containerPort:
启动Deployment并查看状态
[root@k8s-master service]# kubectl apply -f myapp-deploy.yaml
deployment.apps/myapp-deploy created
[root@k8s-master service]#
[root@k8s-master service]# kubectl get deploy -o wide
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE CONTAINERS IMAGES SELECTOR
myapp-deploy / 31h myapp registry.cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/google_registry/myapp:v1 app=myapp,release=v1
[root@k8s-master service]#
[root@k8s-master service]# kubectl get rs -o wide
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE CONTAINERS IMAGES SELECTOR
myapp-deploy-5695bb5658 31h myapp registry.cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/google_registry/myapp:v1 app=myapp,pod-template-hash=5695bb5658,release=v1
[root@k8s-master service]#
[root@k8s-master service]# kubectl get pod -o wide --show-labels
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES LABELS
myapp-deploy-5695bb5658-2866m / Running 31h 10.244.2.116 k8s-node02 <none> <none> app=myapp,env=test,pod-template-hash=5695bb5658,release=v1
myapp-deploy-5695bb5658-dcfw7 / Running 31h 10.244.4.105 k8s-node01 <none> <none> app=myapp,env=test,pod-template-hash=5695bb5658,release=v1
myapp-deploy-5695bb5658-n2b5w / Running 31h 10.244.2.115 k8s-node02 <none> <none> app=myapp,env=test,pod-template-hash=5695bb5658,release=v1
curl访问
[root@k8s-master service]# curl 10.244.2.116
Hello MyApp | Version: v1 | <a href="hostname.html">Pod Name</a>
[root@k8s-master service]#
[root@k8s-master service]# curl 10.244.2.116/hostname.html
myapp-deploy-5695bb5658-2866m
[root@k8s-master service]#
[root@k8s-master service]# curl 10.244.4.105
Hello MyApp | Version: v1 | <a href="hostname.html">Pod Name</a>
[root@k8s-master service]#
[root@k8s-master service]# curl 10.244.4.105/hostname.html
myapp-deploy-5695bb5658-dcfw7
[root@k8s-master service]#
[root@k8s-master service]# curl 10.244.2.115
Hello MyApp | Version: v1 | <a href="hostname.html">Pod Name</a>
[root@k8s-master service]#
[root@k8s-master service]# curl 10.244.2.115/hostname.html
myapp-deploy-5695bb5658-n2b5w
ClusterIP类型示例
yaml文件
[root@k8s-master service]# pwd
/root/k8s_practice/service
[root@k8s-master service]# cat myapp-svc-ClusterIP.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: myapp-clusterip
namespace: default
spec:
type: ClusterIP # 可以不写,为默认类型
selector:
app: myapp
release: v1
ports:
- name: http
port:
targetPort:
启动Service并查看状态
[root@k8s-master service]# kubectl apply -f myapp-svc-ClusterIP.yaml
service/myapp-clusterip created
[root@k8s-master service]#
[root@k8s-master service]# kubectl get svc -o wide
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE SELECTOR
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> /TCP 22d <none>
myapp-clusterip ClusterIP 10.106.66.120 <none> /TCP 15s app=myapp,release=v1
查看pod信息
[root@k8s-master service]# kubectl get pod -o wide --show-labels
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES LABELS
myapp-deploy-5695bb5658-2866m / Running 31h 10.244.2.116 k8s-node02 <none> <none> app=myapp,env=test,pod-template-hash=5695bb5658,release=v1
myapp-deploy-5695bb5658-dcfw7 / Running 31h 10.244.4.105 k8s-node01 <none> <none> app=myapp,env=test,pod-template-hash=5695bb5658,release=v1
myapp-deploy-5695bb5658-n2b5w / Running 31h 10.244.2.115 k8s-node02 <none> <none> app=myapp,env=test,pod-template-hash=5695bb5658,release=v1
查看ipvs信息
[root@k8s-master service]# ipvsadm -Ln
IP Virtual Server version 1.2. (size=)
Prot LocalAddress:Port Scheduler Flags
-> RemoteAddress:Port Forward Weight ActiveConn InActConn
………………
TCP 10.106.66.120: rr
-> 10.244.2.115: Masq
-> 10.244.2.116: Masq
-> 10.244.4.105: Masq
curl访问
[root@k8s-master service]# curl 10.106.66.120
Hello MyApp | Version: v1 | <a href="hostname.html">Pod Name</a>
[root@k8s-master service]#
[root@k8s-master service]# curl 10.106.66.120/hostname.html
myapp-deploy-5695bb5658-2866m
[root@k8s-master service]#
[root@k8s-master service]# curl 10.106.66.120/hostname.html
myapp-deploy-5695bb5658-n2b5w
[root@k8s-master service]#
[root@k8s-master service]# curl 10.106.66.120/hostname.html
myapp-deploy-5695bb5658-dcfw7
[root@k8s-master service]#
[root@k8s-master service]# curl 10.106.66.120/hostname.html
myapp-deploy-5695bb5658-2866m
备注:如果访问失败,请参考如下文章:
「Kubernetes K8S在IPVS代理模式下svc服务的ClusterIP类型访问失败处理」
Headless Services
有时不需要或不想要负载均衡,以及单独的 Service IP。遇到这种情况,可以通过指定 Cluster IP(spec.clusterIP)的值为 “None” 来创建 Headless Service。
这对headless Service 并不会分配 Cluster IP,kube-proxy 不会处理它们,而且平台也不会为它们进行负载均衡和路由。
- 第一种:自主选择权,有时候client想自己来决定使用哪个Real Server,可以通过查询DNS来获取Real Server的信息。
- 第二种:Headless Services还有一个用处(PS:也就是我们需要的那个特性)。Headless Service对应的每一个Endpoints,即每一个Pod,都会有对应的DNS域名;这样Pod之间就可以互相访问。【结合statefulset有状态服务使用,如Web、MySQL集群】
yaml文件
[root@k8s-master service]# pwd
/root/k8s_practice/service
[root@k8s-master service]# cat myapp-svc-headless.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: myapp-headless
namespace: default
spec:
selector:
app: myapp
release: v1
clusterIP: "None"
ports:
- port:
targetPort:
启动Service并查看状态和详情
[root@k8s-master service]# kubectl apply -f myapp-svc-headless.yaml
service/myapp-headless created
[root@k8s-master service]#
[root@k8s-master service]# kubectl get svc -o wide
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE SELECTOR
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> /TCP 22d <none>
myapp-headless ClusterIP None <none> /TCP 6s app=myapp,release=v1
[root@k8s-master service]#
[root@k8s-master service]# kubectl describe svc/myapp-headless
Name: myapp-headless
Namespace: default
Labels: <none>
Annotations: kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration:
{"apiVersion":"v1","kind":"Service","metadata":{"annotations":{},"name":"myapp-headless","namespace":"default"},"spec":{"clusterIP":"None"...
Selector: app=myapp,release=v1
Type: ClusterIP
IP: None
Port: <unset> /TCP
TargetPort: /TCP
Endpoints: 10.244.2.115:,10.244.2.116:,10.244.4.105: # 后端的Pod信息
Session Affinity: None
Events: <none>
service只要创建成功就会写入到coredns。我们得到coredns IP的命令如下:
[root@k8s-master service]# kubectl get pod -o wide -A | grep 'coredns'
kube-system coredns-6955765f44-c9zfh / Running 22d 10.244.0.62 k8s-master <none> <none>
kube-system coredns-6955765f44-lrz5q / Running 22d 10.244.0.61 k8s-master <none> <none>
在宿主机安装nslookup、dig命令安装
yum install -y bind-utils
coredns记录信息如下
# 其中 10.244.0.61 为 coredns IP
# myapp-headless.default.svc.cluster.local 为Headless Service域名。格式为:$(service name).$(namespace).svc.cluster.local,其中 cluster.local 指定的集群的域名
[root@k8s-master service]# nslookup myapp-headless.default.svc.cluster.local 10.244.0.61
Server: 10.244.0.61
Address: 10.244.0.61# Name: myapp-headless.default.svc.cluster.local
Address: 10.244.2.116
Name: myapp-headless.default.svc.cluster.local
Address: 10.244.4.105
Name: myapp-headless.default.svc.cluster.local
Address: 10.244.2.115 [root@k8s-master service]#
### 或使用如下命令
[root@k8s-master service]# dig -t A myapp-headless.default.svc.cluster.local. @10.244.0.61 ; <<>> DiG 9.11.-P2-RedHat-9.11.-.P2.el7_8. <<>> -t A myapp-headless.default.svc.cluster.local. @10.244.0.61
;; global options: +cmd
;; Got answer:
;; WARNING: .local is reserved for Multicast DNS
;; You are currently testing what happens when an mDNS query is leaked to DNS
;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id:
;; flags: qr aa rd; QUERY: , ANSWER: , AUTHORITY: , ADDITIONAL:
;; WARNING: recursion requested but not available ;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION:
; EDNS: version: , flags:; udp:
;; QUESTION SECTION:
;myapp-headless.default.svc.cluster.local. IN A ;; ANSWER SECTION:
myapp-headless.default.svc.cluster.local. IN A 10.244.2.116
myapp-headless.default.svc.cluster.local. IN A 10.244.4.105
myapp-headless.default.svc.cluster.local. IN A 10.244.2.115 ;; Query time: msec
;; SERVER: 10.244.0.61#(10.244.0.61)
;; WHEN: Wed Jun :: CST
;; MSG SIZE rcvd:
NodePort类型示例
如果将 type 字段设置为 NodePort,则 Kubernetes 控制层面将在 --service-node-port-range 标志指定的范围内分配端口(默认值:30000-32767)。
yaml文件
[root@k8s-master service]# pwd
/root/k8s_practice/service
[root@k8s-master service]# cat myapp-svc-NodePort.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: myapp-nodeport
namespace: default
spec:
type: NodePort
selector:
app: myapp
release: v1
ports:
- name: http
# 默认情况下,为了方便起见,`targetPort` 被设置为与 `port` 字段相同的值。
port: # Service对外提供服务端口
targetPort: # 请求转发后端Pod使用的端口
nodePort: # 可选字段,默认情况下,为了方便起见,Kubernetes 控制层面会从某个范围内分配一个端口号(默认:-)
启动Service并查看状态
[root@k8s-master service]# kubectl apply -f myapp-svc-NodePort.yaml
service/myapp-nodeport created
[root@k8s-master service]#
[root@k8s-master service]# kubectl get svc -o wide
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE SELECTOR
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> /TCP 22d <none>
myapp-nodeport NodePort 10.99.50.81 <none> :/TCP 6s app=myapp,release=v1
由上可见,类型变为了NodePort
查看ipvs信息
[root@k8s-master service]# ipvsadm -Ln
IP Virtual Server version 1.2. (size=)
Prot LocalAddress:Port Scheduler Flags
-> RemoteAddress:Port Forward Weight ActiveConn InActConn
………………
TCP 10.99.50.81: rr
-> 10.244.2.115: Masq
-> 10.244.2.116: Masq
-> 10.244.4.105: Masq
端口查看,可见在本地宿主机监听了相应的端口(备注:集群所有机器都监听了该端口)
# 集群所有机器都可以执行查看
[root@k8s-master service]# netstat -lntp | grep ''
tcp6 ::: :::* LISTEN /kube-proxy
curl通过ClusterIP访问
# 通过ClusterIP访问
[root@k8s-master service]# curl 10.99.50.81
Hello MyApp | Version: v1 | <a href="hostname.html">Pod Name</a>
[root@k8s-master service]#
[root@k8s-master service]# curl 10.99.50.81/hostname.html
myapp-deploy-5695bb5658-2866m
[root@k8s-master service]#
[root@k8s-master service]# curl 10.99.50.81/hostname.html
myapp-deploy-5695bb5658-n2b5w
[root@k8s-master service]#
[root@k8s-master service]# curl 10.99.50.81/hostname.html
myapp-deploy-5695bb5658-dcfw7
curl通过节点IP访问
# 通过集群节点IP访问
[root@k8s-master service]# curl 172.16.1.110:
Hello MyApp | Version: v1 | <a href="hostname.html">Pod Name</a>
[root@k8s-master service]#
[root@k8s-master service]# curl 172.16.1.110:/hostname.html
myapp-deploy-5695bb5658-2866m
[root@k8s-master service]#
[root@k8s-master service]# curl 172.16.1.110:/hostname.html
myapp-deploy-5695bb5658-n2b5w
[root@k8s-master service]#
[root@k8s-master service]# curl 172.16.1.110:/hostname.html
myapp-deploy-5695bb5658-dcfw7
# 访问集群其他节点。每台机器都有LVS,和相关调度
[root@k8s-master service]# curl 172.16.1.111:/hostname.html
myapp-deploy-5695bb5658-dcfw7
[root@k8s-master service]#
[root@k8s-master service]# curl 172.16.1.112:/hostname.html
myapp-deploy-5695bb5658-dcfw7
访问日志查看
kubectl logs -f svc/myapp-nodeport
LoadBalancer类型示例
需要相关云厂商服务支持,这里就不表述了。
ExternalName类型示例
这种类型的Service通过返回CNAME和它的值,可以将服务映射到externalName字段的内容(例如:my.k8s.example.com;可以实现跨namespace名称空间访问)。ExternalName Service是Service的特例,它没有selector,也没有定义任何的端口和Endpoint。相反的,对于运行在集群外部的服务,它通过返回该外部服务的别名这种方式提供服务。
具体使用参见:「Kubernetes K8S之Pod跨namespace名称空间访问Service服务」
yaml文件
[root@k8s-master service]# pwd
/root/k8s_practice/service
[root@k8s-master service]# cat myapp-svc-ExternalName.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: myapp-externalname
namespace: default
spec:
type: ExternalName
externalName: my.k8s.example.com
启动Service并查看状态
[root@k8s-master service]# kubectl apply -f myapp-svc-ExternalName.yaml
service/myapp-externalname created
[root@k8s-master service]#
[root@k8s-master service]# kubectl get svc -o wide
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE SELECTOR
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> /TCP 21d <none>
myapp-externalname ExternalName <none> my.k8s.example.com <none> 21s <none>
由上可见,类型变为了ExternalName
宿主机dig命令安装
yum install -y bind-utils
coredns记录信息如下
# 其中 10.244.0.61 为 coredns IP
# myapp-externalname.default.svc.cluster.local 为Service域名。格式为:$(service name).$(namespace).svc.cluster.local,其中 cluster.local 指定的集群的域名
##### 通过 nslookup 访问
[root@k8s-master service]# nslookup myapp-externalname.default.svc.cluster.local 10.244.0.61
Server: 10.244.0.61
Address: 10.244.0.61# myapp-externalname.default.svc.cluster.local canonical name = my.k8s.example.com.
** server can't find my.k8s.example.com: NXDOMAIN [root@k8s-master service]#
##### 通过 dig 访问
[root@k8s-master service]# dig -t A myapp-externalname.default.svc.cluster.local. @10.244.0.61 ; <<>> DiG 9.11.-P2-RedHat-9.11.-.P2.el7_8. <<>> -t A myapp-externalname.default.svc.cluster.local. @10.244.0.61
;; global options: +cmd
;; Got answer:
;; WARNING: .local is reserved for Multicast DNS
;; You are currently testing what happens when an mDNS query is leaked to DNS
;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id:
;; flags: qr aa rd; QUERY: , ANSWER: , AUTHORITY: , ADDITIONAL:
;; WARNING: recursion requested but not available ;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION:
; EDNS: version: , flags:; udp:
;; QUESTION SECTION:
;myapp-externalname.default.svc.cluster.local. IN A ;; ANSWER SECTION:
myapp-externalname.default.svc.cluster.local. IN CNAME my.k8s.example.com. ;; Query time: msec
;; SERVER: 10.244.0.61#(10.244.0.61)
;; WHEN: Wed Jun :: CST
;; MSG SIZE rcvd:
ExternalIP示例
如果外部的 IP 路由到集群中一个或多个 Node 上,Kubernetes Service 会被暴露给这些 externalIPs。通过外部 IP(作为目的 IP 地址)进入到集群,打到 Service 端口上的流量,将会被路由到 Service 的 Endpoint 上。
externalIPs 不会被 Kubernetes 管理,它属于集群管理员的职责范畴。
根据 Service 的规定,externalIPs 可以同任意的 ServiceType 来一起指定。在下面的例子中,my-service 可以在【模拟外网IP】“10.0.0.240”(externalIP:port) 上被客户端访问。
yaml文件
[root@k8s-master service]# pwd
/root/k8s_practice/service
[root@k8s-master service]# cat myapp-svc-externalIP.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: myapp-externalip
namespace: default
spec:
selector:
app: myapp
release: v1
ports:
- name: http
port:
targetPort:
externalIPs:
- 10.0.0.240
启动Service并查看状态
[root@k8s-master service]# kubectl apply -f myapp-svc-externalIP.yaml
service/myapp-externalip created
[root@k8s-master service]#
[root@k8s-master service]# kubectl get svc -o wide
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE SELECTOR
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> /TCP 22d <none>
myapp-externalip ClusterIP 10.107.186.167 10.0.0.240 /TCP 8s app=myapp,release=v1
查看ipvs信息
[root@k8s-master service]# ipvsadm -Ln
IP Virtual Server version 1.2. (size=)
Prot LocalAddress:Port Scheduler Flags
-> RemoteAddress:Port Forward Weight ActiveConn InActConn
………………
TCP 10.107.186.167: rr
-> 10.244.2.115: Masq
-> 10.244.2.116: Masq
-> 10.244.4.105: Masq
………………
TCP 10.0.0.240: rr
-> 10.244.2.115: Masq
-> 10.244.2.116: Masq
-> 10.244.4.105: Masq
curl访问,通过ClusterIP
[root@k8s-master service]# curl 10.107.186.167
Hello MyApp | Version: v1 | <a href="hostname.html">Pod Name</a>
[root@k8s-master service]#
[root@k8s-master service]# curl 10.107.186.167/hostname.html
myapp-deploy-5695bb5658-n2b5w
[root@k8s-master service]#
[root@k8s-master service]# curl 10.107.186.167/hostname.html
myapp-deploy-5695bb5658-2866m
[root@k8s-master service]#
[root@k8s-master service]# curl 10.107.186.167/hostname.html
myapp-deploy-5695bb5658-dcfw7
curl访问,通过ExternalIP
[root@k8s-master service]# curl 10.0.0.240
Hello MyApp | Version: v1 | <a href="hostname.html">Pod Name</a>
[root@k8s-master service]#
[root@k8s-master service]# curl 10.0.0.240/hostname.html
myapp-deploy-5695bb5658-2866m
[root@k8s-master service]#
[root@k8s-master service]# curl 10.0.0.240/hostname.html
myapp-deploy-5695bb5658-dcfw7
[root@k8s-master service]#
[root@k8s-master service]# curl 10.0.0.240/hostname.html
myapp-deploy-5695bb5658-n2b5w
相关阅读
1、Kubernetes K8S在IPVS代理模式下svc服务的ClusterIP类型访问失败处理
2、Kubernetes K8S之Pod跨namespace名称空间访问Service服务
3、kubernetes学习Service之headless和statefulSet结合
4、linuxea:kubernetes Headless Service无头服务
———END———
如果觉得不错就关注下呗 (-^O^-) !

Kubernetes K8S之Service服务详解与示例的更多相关文章
- 【K8S】Service服务详解,看这一篇就够了!!
k8s用命名空间namespace把资源进行隔离,默认情况下,相同的命名空间里的服务可以相互通讯,反之进行隔离. 1.1 Service Kubernetes中一个应用服务会有一个或多个实例(Pod, ...
- Kubernetes K8S之存储Volume详解
K8S之存储Volume概述与说明,并详解常用Volume示例 主机配置规划 服务器名称(hostname) 系统版本 配置 内网IP 外网IP(模拟) k8s-master CentOS7.7 2C ...
- Android中Service(服务)详解
http://blog.csdn.net/ryantang03/article/details/7770939 Android中Service(服务)详解 标签: serviceandroidappl ...
- Kubernetes K8S之存储ConfigMap详解
K8S之存储ConfigMap概述与说明,并详解常用ConfigMap示例 主机配置规划 服务器名称(hostname) 系统版本 配置 内网IP 外网IP(模拟) k8s-master CentOS ...
- Kubernetes K8S之存储Secret详解
K8S之存储Secret概述与类型说明,并详解常用Secret示例 主机配置规划 服务器名称(hostname) 系统版本 配置 内网IP 外网IP(模拟) k8s-master CentOS7.7 ...
- kubernetes系列08—service资源详解
本文收录在容器技术学习系列文章总目录 1.认识service 1.1 为什么要使用service Kubernetes Pod 是有生命周期的,它们可以被创建,也可以被销毁,然而一旦被销毁生命就永远结 ...
- [Android] Service服务详解以及如何使service服务不被杀死
排版上的细节有些不好看,主要是我用的MarkDown编辑器预览和这里的不一样,在那个上面的样式很舒服.这里要改的地方太多就不想改了,将就看吧.下次写的时候注意.还有看到错误给我提啊. 本文链接:htt ...
- Kubernetes K8S之affinity亲和性与反亲和性详解与示例
Kubernetes K8S之Node节点亲和性与反亲和性以及Pod亲和性与反亲和性详解与示例 主机配置规划 服务器名称(hostname) 系统版本 配置 内网IP 外网IP(模拟) k8s-mas ...
- k8s之yaml文件详解
k8s之yaml文件详解 目录 k8s之yaml文件详解 1. k8s支持的文件格式 2. YAML语言格式 3. 查看api资源版本标签 4. 编写nginx-test.yaml资源配置清单 4.1 ...
随机推荐
- Git使用之submodule
入职第一周,就因为clone项目而产生了很大的障碍,花了差不多三四个小时才定位问题并解决,记录一下. 一.问题 当我们在使用Git克隆项目的时候,无法克隆下来一个文件夹.记该文件夹为A,A在远程仓库是 ...
- 【算法•日更•第四十三期】QQ for linux
废话不多说,直接看一张图: 没错,这是QQ,但是这有什么稀奇的?但是在Linux上使用QQ就很稀奇了. 众所周知,腾讯早就已经对Linux下的QQ和微信停止了服务,即便是网页版也不能用,通信这一直是小 ...
- DataNode(面试开发重点)
1 DataNode工作机制 DataNode工作机制,如图所示. 1)一个数据块在DataNode上以文件形式存储在磁盘上,包括两个文件,一个是数据本身,一个是元数据包括数据块的长度,块数据的校验和 ...
- golang方法
1.方法声明 在函数声明时,在其名字之前放上一个变量,即是一个方法.这个附加的参数会将该函数附加到这种类型上,即相当于为这种类型定义了一个独占的方法. package main import &quo ...
- Centos7 KVM启用嵌套虚拟化
[root@kvm-hypervisor ~]# cat /etc/modprobe.d/kvm-nested.conf options kvm-intel nested= options kvm-i ...
- 第3篇scrum冲刺(5.23)
一.站立会议 1.照片 2.工作安排 成员 昨天已完成的工作 今天的工作安排 困难 陈芝敏 调用小程序接口获取用户微信登录权限,初始化 完成云开发配置,初始化数据库: 进度较慢,后面可能会有点困难 ...
- Four Fundamental Operations(JS) --结对项目
一.Github地址:https://github.com/BayardM/Four-Fundamental-Operations (本项目由鲍鱼铭3118004995 和 许铭楷3118005023 ...
- 如何运用excel或spss等软件统计大量纸质问卷?
在用纸质问卷进行数据收集时,总是避不开一个问题,就是如何把数据快速准确的进行统计分析.这里提供一个方法,包括以下几个步骤: 一.录入数据 二.上传数据 三.分析数据 一.录入数据 首先把纸质问卷 ...
- muduo源码解析11-logger类
logger: class logger { }; 在说这个logger类之前,先看1个关键的内部类 Impl private: //logger内部数据实现类Impl,内部含有以下成员变量 //时间 ...
- asp.net Core3.1自定义权限体系-菜单和操作按钮权限
我们在做项目项目,经常会碰到权限体系,权限体系属于系统架构的一个最底层的功能,也是非常重要的功能,几乎在每个项目都会用到.那么我们该如何设计一个比较合理的且扩展性较强的权限体系呢? 经过多天的摸索,参 ...
