Selenium 2自动化测试实战29(组织单元测试用例和discover更多测试用例)
一、组织单元测试用例
看看unittest单元测试框架是如何扩展和组织新增的测试用例
以之前的calculator.py文件为例,为其扩展sub()方法,用来计算两个数相减的结果。
#coding:utf-8
#计算器类
class Count():
def __init__(self,a,b):
self.a=int(a)
self.b=int(b) #计算加法
def sum(self):
return self.a+self.b #计算减法
def sub(self):
return self.a-self.b
因为对计算器类又新增了减法功能(sub),所以需要针对新功能编写测试用例,扩展后的test.py如下
#coding:utf-8
from Demo1 import Count
import unittest class TestSum(unittest.TestCase): def setUp(self):
a = input("please input the date:")
self.a = int(a)
b = input("please input the other date:")
self.b = int(b) def testSum(self):
self.assertEqual((Count(self.a,self.b).sum()),5,msg="the date is not Equal") def testSum2(self):
self.assertEqual((Count(self.a,self.b).sum()),15,msg="the date is not Equal") def tearDown(self):
print"test sum end" class TestSub(unittest.TestCase):
def setUp(self): a = input("please input the date:")
self.a=int(a)
b = input("please input the other date:")
self.b = int(b) def testSub(self):
self.assertEqual((Count(self.a,self.b).sub()), 5, msg="the date is not Equal") def testSub2(self):
self.assertEqual((Count(self.a,self.b).sub()), 15, msg="the date is not Equal") def tearDown(self):
print"test sub end" if __name__=="__main__":
#构造测试集
suite=unittest.TestSuite()
suite.addTest(TestSum("testSum"))
suite.addTest(TestSum("testSum2"))
suite.addTest(TestSub("testSub"))
suite.addTest(TestSub("testSub2")) #运行测试集
runner=unittest.TextTestRunner()
runner.run(suite)
上例中创建了TestAdd()和TestSub()两个测试类,分别测试calculator.py文件中的add()和sub()两个功能。通过TestSuite类的addTest()方法把不同测试类中的测试方法组装到测试套件中。
运行结果如下所示:
D:\Python27\python.exe F:/study/Demo2/testDemo1/test.py
please input the date:2
please input the other date:3
test sum end
.please input the date:4
please input the other date:5
Ftest sum end
please input the date:6
please input the other date:1
.test sub end
please input the date:20
please input the other date:10
test sub end
F
======================================================================
FAIL: testSum2 (__main__.TestSum)
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "F:/study/Demo2/testDemo1/test.py", line 18, in testSum2
self.assertEqual((Count(self.a,self.b).sum()),15,msg="the date is not Equal")
AssertionError: the date is not Equal ======================================================================
FAIL: testSub2 (__main__.TestSub)
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "F:/study/Demo2/testDemo1/test.py", line 35, in testSub2
self.assertEqual((Count(self.a,self.b).sub()), 15, msg="the date is not Equal")
AssertionError: the date is not Equal ----------------------------------------------------------------------
Ran 4 tests in 21.417s FAILED (failures=2) Process finished with exit code 0
通过测试结果看到,setUp()和tearDown()方法分别作用于每个测试用例的开始与结束。尝试着封装一个自己的测试类。
#test.py
#coding:utf-8
import unittest
from Demo1 import Count class Mytest(unittest.TestCase): def setUp(self):
a = input("please input the date:")
self.a = int(a)
b = input("please input the other date:")
self.b = int(b) def tearDown(self):
print"test sum end" class TestSum(Mytest): def testSum(self):
self.assertEqual((Count(self.a,self.b).sum()),5,msg="the date is not Equal") def testSum2(self):
self.assertEqual((Count(self.a,self.b).sum()),15,msg="the date is not Equal") class TestSub(Mytest):
def testSub(self):
self.assertEqual((Count(self.a,self.b).sub()), 5, msg="the date is not Equal") def testSub2(self):
self.assertEqual((Count(self.a,self.b).sub()), 15, msg="the date is not Equal") if __name__=="__main__":
# 构造测试集
suite = unittest.TestSuite()
suite.addTest(TestSum("testSum"))
suite.addTest(TestSum("testSum2"))
suite.addTest(TestSub("testSub"))
suite.addTest(TestSub("testSub2")) # 运行测试集
runner = unittest.TextTestRunner()
runner.run(suite)
创建MyTest()类的好处显而易见,对于测试类和测试方法来说,应将注意力放在具体用例的编写上,不需要关心setUp()和tearDown()所做的事情,不过,前提条件是setUp()和tearDown()所做的事情是每个用例都需要的。
二、discover更多测试用例
对上例中test.py文件的测试用例进行拆分,拆分后的目录结果如下:
Testpro/
--count.py
--testsum.py
--testsub.py
--runtest.py
文件拆分后的代码如下:
#count.py
#coding:utf-8
#计算器类
class Count():
def __init__(self,a,b):
self.a=int(a)
self.b=int(b) #计算加法
def sum(self):
return self.a+self.b #计算减法
def sub(self):
return self.a-self.b
#testsum.py
#coding:utf-8
from Demo1 import Count
import unittest class TestSum(unittest.TestCase):
def setUp(self):
a = input("please input the date:")
self.a = int(a)
b = input("please input the other date:")
self.b = int(b) def tearDown(self):
print"test sum end" def testSum(self):
self.assertEqual((Count(self.a,self.b).sum()),5,msg="the date is not Equal") def testSum2(self):
self.assertEqual((Count(self.a, self.b).sum()),15, msg="the date is not Equal") if __name__=="__main__":
unittest.main()
#testsub.py
#coding:utf-8
from Demo1 import Count
import unittest class TestSub(unittest.TestCase):
def setUp(self):
a = input("please input the date:")
self.a = int(a)
b = input("please input the other date:")
self.b = int(b) def tearDown(self):
print"test sum end" def testSub(self):
self.assertEqual((Count(self.a,self.b).sub()),5,msg="the date is not Equal") def testSub2(self):
self.assertEqual((Count(self.a, self.b).sub()),15, msg="the date is not Equal") if __name__=="__main__":
unittest.main()
#runtest.py
#coding:utf-8
import unittest
#加载测试文件
import testsum
import testsub #构造测试集
suite=unittest.TestSuite()
suite.addTest(testsum.TestSum("testSum"))
suite.addTest(testsum.TestSum("testSum2"))
suite.addTest(testsub.TestSub("testSub"))
suite.addTest(testsub.TestSub("testSub2")) #执行测试
if __name__=="__main__":
runner=unittest.TextTestRunner()
runner.run(suite)
运行结果如下:
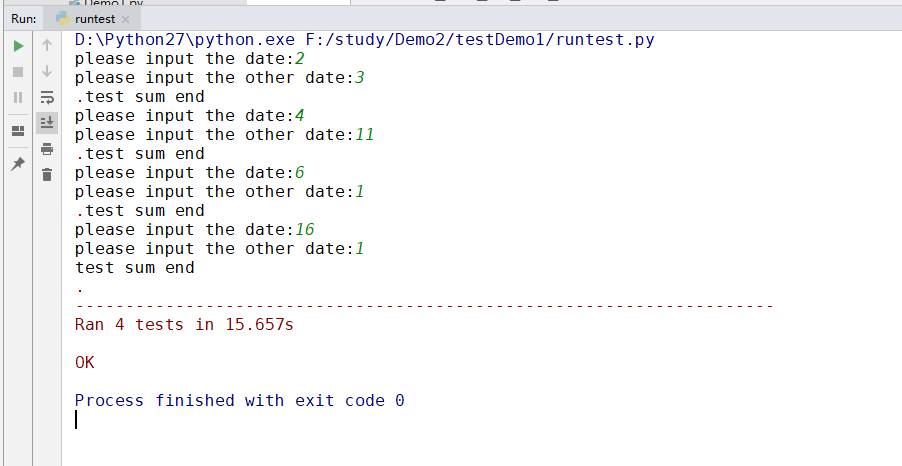
这样的拆分带来了好处,可以根据不同的功能创建不同的测试用例,甚至是不同的测试目录,测试文件中还可以将不同的小功能划分为不同的测试类,在类下编写测试用例,整体结构更清晰。
但是这样还是没有解决添加用例的问题,此时使用TestLoader类中提供的discover()方法可以解决这个问题。
TestLoader
该类负责根据各种标准加载测试用例,并将它们返回给测试套件,正常情况下,不需要创建这个类的实例。unittest提供了可以共享的defaultTestLoader类,可以使用其子类和方法创建实例,discover()方法就是其中之一。 discover(start_dir,pattern=‘test*.py’,top_level_dir=None)
找到指定目录下所有测试模块,并可递归查到子目录下的测试模块,只有匹配到文件名才能加载。如果启动的不是顶层目录,那么顶层目录必须单独指定。 start_dir:要测试的模块名或测试用例目录。 pattern=‘test*.py’:表示用例文件名的匹配原则。此处匹配文件名以“test”开头的“.py"类型的文件,星号“*”表示任意多个字符。 top_level_dir=None:测试模块的顶层目录,如果没有顶层目录,默认为None。
现在通过discover()方法重新实现runtest.py文件的功能。
#runtest.py
#coding:utf-8
import unittest #定义测试用例的目录为当前目录
test_dir='./'
discover=unittest.defaultTestLoader.discover(test_dir,pattern='test*.py') if __name__=="__main__":
runner=unittest.TextTestRunner()
runner.run(discover)
Discover()方法会自动根据测试目录(test_dir)匹配查找测试用例文件(test*.py),并将查找到的测试用例组装到测试套件中,因此,可以直接通过run()方法执行discover,大大简化了测试用例的查找与执行。
Selenium 2自动化测试实战29(组织单元测试用例和discover更多测试用例)的更多相关文章
- Selenium 2自动化测试实战
Selenium 2自动化测试实战 百度网盘 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1aiP3d8Y1QlcHD3fAlEj4sg 提取码:jp8e 复制这段内容后打开百度网盘手机Ap ...
- Selenium 2自动化测试实战3(函数、类和方法)
一.函数.类和方法1.函数在python中通过def关键字来定义函数 创建一个add()函数,此函数接收两个参数a,b,通过print()打印a+b的结果.调用add()函数,并且上传两个参数3,5给 ...
- 《Selenium 2自动化测试实战 基于Python语言》中发送最新邮件无内容问题的解决方法
虫师的<Selenium 2自动化测试实战 基于Python语言>是我自动化测试的启蒙书 也是我推荐的自动化测试入门必备书,但是书中有一处明显的错误,会误导很多读者,这处错误就是第8章自动 ...
- Selenium 2自动化测试实战34(编写Web测试用例)
编写Web测试用例 1.介绍了unittest单元测试框架,其主要是来运行Web自动化测试脚本.简单的规划一下测试目录:web_demo1/------test_case/------------te ...
- Selenium 与自动化测试 —— 《Selenium 2 自动化测试实战》读书笔记
背景 最近在弄 appium,然后顺便发现了 Selenium 框架和这本书,恰好这本书也介绍了一些软件测试&自动化测试的理论知识,遂拿过来学习学习.所以本文几乎没有实践内容,大多都是概念和工 ...
- Selenium 2自动化测试实战39(Page Object设计模式)
Page Object设计模式 Page object是selenium自动化测试项目开发时间的最佳设计模式之一,主要体现在对界面交互细节的封装. 1.认识page object优点如下:1.减少代码 ...
- Selenium 2自动化测试实战35(HTML测试报告)
HTML测试报告 显然,一份漂亮的测试报告展示自动化测试成果只有一个简单的log文件是不够的.HTMLTestRunner是python标准库unittest单元测试框架的一个扩展,它生成易于使用的H ...
- Selenium+Python自动化测试实战(2)元素定位
1.Selenium2 的原理 第一篇分享简单介绍了基于Python开发的Selenium2的环境配置,这篇主要讲一下基本用法.首先讲一下Selenium2的基本原理.基本上知道了这个东西是怎么回事, ...
- Selenium 2自动化测试实战38(整合自动发邮件功能)
整合自动发邮件功能 解决了前面的问题后,现在就可以将自动发邮件功能集成到自动化测试项目中了.下面重新编辑runtest.py文件 #runtest.py #coding:utf-8 from HTML ...
随机推荐
- Windows Server 2016分层式存储,使用PowerShell修改底层介质类型
新部署的备份服务器,需要做分层式存储,按照网上最常见一个作者叫刘兵的文档,名叫<Windows Server2016分层存储技术详细拆解手册>,做到使用PowerShell修改磁盘的Med ...
- CTAP: Complementary Temporal Action Proposal Generation论文笔记
主要观点:基于sliding window(SW)类的方法,如TURN,可以达到很高的AR,但定位不准:基于Group的方法,如TAG,AR有明显的上界,但定位准.所以结合两者的特长,加入Comple ...
- 简单混合锁(HybridLock)
internal sealed class SimpleHybridLock : IDisposable { //基元用户模式构造使用 ; //基元内核模式构造 private AutoResetEv ...
- Tomcat基础知识
介绍Tomcat之前先介绍下Java相关的知识. 各常见组件: 1.服务器(server):Tomcat的一个实例,通常一个JVM只能包含一个Tomcat实例:因此,一台物理服务器上可以在启动多个JV ...
- 初识LVS和LVS_NAT
如果一台服务器承受过多的压力,那么服务可能会崩溃,所以,我们应该让一台服务器承受的压力在合理范围内,但是如果服务端必须要承受较大的压力,那么一台服务器可能无法满足我们的要求,所以我们可以使用多台服务器 ...
- Python numpy.ZIP 安装问题
今天在python上安装numpy,按照网上教程,安装pip,然后命令行直接:pip install numpy .但是一直因为资源问题下载失败. 后来下载了一个numpy-1.11.2.zip 安 ...
- js中for..of..和迭代器
for..of是ES6中引入的新特性,它主要的作用是:循环一个可迭代的对象. 它可以循环遍历,数组.字符串.Set对象等等 示例一: let str = 'hello' for (item of st ...
- numpy常用矩阵操作
1.删除列 column_to_delete = [0, 1, 2] arr = np.delete(arr, [0, 1, 2], axis=1) 2.归一化 arr = normalize(arr ...
- Prism框架实战——订餐软件
参考B站刘铁猛老师的订餐软件https://www.bilibili.com/video/av29782724?from=search&seid=6787438911056306128 环境: ...
- php+提高大文件上传速度
PHP用超级全局变量数组$_FILES来记录文件上传相关信息的. 1.file_uploads=on/off 是否允许通过http方式上传文件 2.max_execution_time=30 允许脚本 ...
