Python学习日记(九)—— 模块二(logging、json&pickle、xml、requests、configparser、shutil、subprocess)
logging模块
用于便捷记录日志且线程安全的模块(便捷的写文件的模块,不允许多个人同时操作文件)
1、单文件日志
import logging logging.basicConfig(filename='log.log', #指定往哪个文件里写
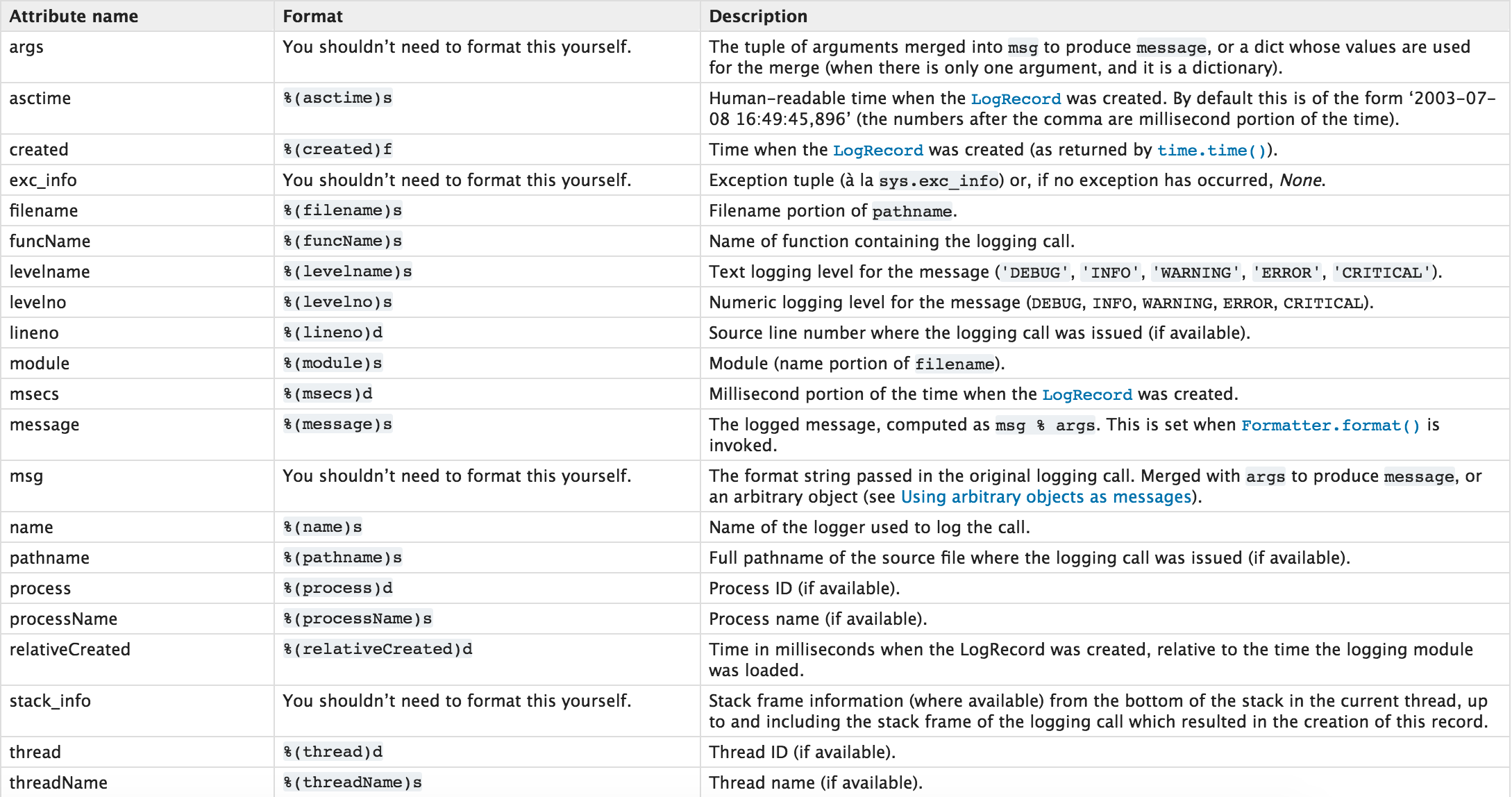
format='%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s -%(module)s: %(message)s',
datefmt='%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S %p',
level=10, #只记录level大于等于10的人
#level=logging.INFO 可以写数字也可以写单词,推荐些单词
) #写日志的时候都是小写的
logging.critical('critical')
logging.fatal("fatal")
logging.error("error")
logging.warning('warning')
logging.info('info')
logging.debug('debug') logging.log(2,'333') #可以用log设置level值
日志等级
CRITICAL =
FATAL = CRITICAL
ERROR =
WARNING =
WARN = WARNING
INFO =
DEBUG =
NOTSET =
注:只有【当前写等级】大于【日志等级】时,日志文件才被记录。
日志记录格式:

2、多文件日志
对于上述记录日志的功能,只能将日志记录在单文件中,如果想要设置多个日志文件,logging.basicConfig将无法完成,需要自定义文件和日志操作对象。
import logging
# 定义文件
# 创建文件
file_1_1 = logging.FileHandler('l1_1.log', 'a', encoding='utf-8')
# 创建格式
fmt = logging.Formatter(fmt="%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s -%(module)s: %(message)s")
# 让文件应用格式
file_1_1.setFormatter(fmt)
# 创建第二个文件
file_1_2 = logging.FileHandler('l1_2.log', 'a', encoding='utf-8')
# 创建格式
fmt = logging.Formatter()
# 让第二个文件应用格式
file_1_2.setFormatter(fmt) # 定义日志
logger1 = logging.Logger('s1', level=logging.ERROR)#定义一个阈值
logger1.addHandler(file_1_1)
logger1.addHandler(file_1_2) #把文件添加进去 # 写日志
logger1.critical('')
日志(一)
# 定义文件
file_2_1 = logging.FileHandler('l2_1.log', 'a')
fmt = logging.Formatter()
file_2_1.setFormatter(fmt) # 定义日志
logger2 = logging.Logger('s2', level=logging.INFO)
logger2.addHandler(file_2_1) # 写日志
logger1.critical('')
日志(二)
如上述创建的两个日志对象
- 当使用【logger1】写日志时,会将相应的内容写入 l1_1.log 和 l1_2.log 文件中
- 当使用【logger2】写日志时,会将相应的内容写入 l2_1.log 文件中
一、json&pickle
Python中用于序列化的两个模块
- json 用于【字符串】和 【python基本数据类型】 间进行转换
- pickle 用于【python特有的类型】 和 【python基本数据类型】间进行转换
Json模块提供了四个功能:loads、load、dumps、dump
import json #loads用于将字典,列表,元组形式的字符串,转换成相应的字典,列表,元组
s = '{"name1":"ciri","name2":"ellie"}'
l = "[11,22,33,44]" result = json.loads(s)
print(result,type(result)) result = json.loads(l)
print(result,type(result))
#loads —— 装载,把python的数据类型装载上去 # s = "{'name1':'ciri','name2':'ellie'}" #这样定义字符串时会报错
"""
在python中单引号和双引号都是字符串,但是在其他语言中只有双引号都是字符串
所以内部元素如果是字符串,必须是双引号,绝对不能是单引号,这就是为什么报错的原因
"""
#全用双引号就不知道哪个是开头哪个是结尾了
# s = "{"name1":"ciri","name2":"ellie"}"
loads
user_list = [11,22,33,44]
s = json.dumps(user_list)
print(s,type(s)) user_dic = {"name1":"ciri","name2":"ellie"}
s = json.dumps(user_dic)
print(s,type(s))
#将python的基本数据类型,转换成字符串
#dumps —— 卸货,把python的数据类型卸下来
dumps
#dump会做两件事
# 1.先发字典转换成字符串
# 2.把字符串写到db文件里去
user_dic = {"name1":"ciri","name2":"ellie"}
s = json.dump(user_dic , open('D:/db','w')) # load会先打开这个文件,然后读内容,再然后将读到的内容转换成字典
s = json.load(open('D:/db','r'))
print(s) #load:打开文件读取内容,然后把读取的 字符串 转换成 字典和列表
#dump:打开文件读取内容,然后把读取 字典和列表 转换成 字符串
load&dump
import json s = '(11,22,33,44,"alex")'
n = json.loads(s)
print(n)
#loads反解的时候会报错 n = (11,22,33,44,"alex")
s = json.dumps(n)
print(s)
#结果:[11, 22, 33, 44, "alex"] 变成列表了,并没有变成字符串 #把元素放进()里去是(元组类型),是python特有的,而{}[]是通用的
#其他语言中
#[] ——py 列表,其它 数组
#{}——py 字典,其它 字典
#因为json是通用的数据传输,所以自己有的数据类型转换了也没什么用
补充:元组为什么不能用json转换?
pickle模块提供了四个功能:dumps、dump、loads、load
import pickle
data = {'name': 'ciri'} #dumps把python的基本数据类型转换成python特有的数据类型
p_str = pickle.dumps(data)
print(p_str,type(p_str))
#b'\x80\x03}q\x00X\x04\x00\x00\x00nameq\x01X\x04\x00\x00\x00ciriq\x02s.' <class 'bytes'> #loads把python的特有数据类型转换成python基本的数据类型
new_p_str = pickle.loads(p_str)
print(new_p_str)
#结果:{'name': 'ciri'}
dumps&loads
import pickle #dump将基本数据类型 通过特殊形式 转换为只有python语言认识的字符串,并写入文件
data = {'name': 'ciri'} fp = open('ciri','wb') #用wb会报错
pickle.dump(data,fp)
fp.close() #load读取文件中只有python语言认识的字符串,转换成python的基本数据类型
file = open("ciri",'rb')
#account_db = pickle.loads(new_p_str.read())
new_data = pickle.load(file)
file.close() print(new_data) #ciri是文件名
dump&load
二、XML
XML是实现不同语言或程序之间进行数据交换的协议,XML文件格式如下:
<data>
<country name="Liechtenstein">
<rank updated="yes">2</rank>
<year>2023</year>
<gdppc>141100</gdppc>
<neighbor direction="E" name="Austria" />
<neighbor direction="W" name="Switzerland" />
</country>
<country name="Singapore">
<rank updated="yes">5</rank>
<year>2026</year>
<gdppc>59900</gdppc>
<neighbor direction="N" name="Malaysia" />
</country>
<country name="Panama">
<rank updated="yes">69</rank>
<year>2026</year>
<gdppc>13600</gdppc>
<neighbor direction="W" name="Costa Rica" />
<neighbor direction="E" name="Colombia" />
</country>
</data>
1、解析XML
from xml.etree import ElementTree as ET
"""
从xml文件夹下的etree文件夹,调用ElementTree.py文件,并命名为ET
为什么要改名为ET?
因为这个文件里面定义了一个和它自己同名的类
""" # 打开文件,读取XML内容
str_xml = open('xo.xml', 'r').read() # 将字符串解析成xml特殊对象,root代指xml文件的根节点
root = ET.XML(str_xml)
利用ElementTree.XML将字符串解析成xml对象
from xml.etree import ElementTree as ET # 直接解析xml文件
tree = ET.parse("xo.xml") # 获取xml文件的根节点
root = tree.getroot()
利用ElementTree.parse将文件直接解析成xml对象
2、操作XML
XML格式类型是节点嵌套节点,对于每一个节点均有以下功能,以便对当前节点进行操作:
class Element:
"""An XML element. This class is the reference implementation of the Element interface. An element's length is its number of subelements. That means if you
want to check if an element is truly empty, you should check BOTH
its length AND its text attribute. The element tag, attribute names, and attribute values can be either
bytes or strings. *tag* is the element name. *attrib* is an optional dictionary containing
element attributes. *extra* are additional element attributes given as
keyword arguments. Example form:
<tag attrib>text<child/>...</tag>tail """ 当前节点的标签名
tag = None
"""The element's name.""" 当前节点的属性 attrib = None
"""Dictionary of the element's attributes.""" 当前节点的内容
text = None
"""
Text before first subelement. This is either a string or the value None.
Note that if there is no text, this attribute may be either
None or the empty string, depending on the parser. """ tail = None
"""
Text after this element's end tag, but before the next sibling element's
start tag. This is either a string or the value None. Note that if there
was no text, this attribute may be either None or an empty string,
depending on the parser. """ def __init__(self, tag, attrib={}, **extra):
if not isinstance(attrib, dict):
raise TypeError("attrib must be dict, not %s" % (
attrib.__class__.__name__,))
attrib = attrib.copy()
attrib.update(extra)
self.tag = tag
self.attrib = attrib
self._children = [] def __repr__(self):
return "<%s %r at %#x>" % (self.__class__.__name__, self.tag, id(self)) def makeelement(self, tag, attrib):
创建一个新节点
"""Create a new element with the same type. *tag* is a string containing the element name.
*attrib* is a dictionary containing the element attributes. Do not call this method, use the SubElement factory function instead. """
return self.__class__(tag, attrib) def copy(self):
"""Return copy of current element. This creates a shallow copy. Subelements will be shared with the
original tree. """
elem = self.makeelement(self.tag, self.attrib)
elem.text = self.text
elem.tail = self.tail
elem[:] = self
return elem def __len__(self):
return len(self._children) def __bool__(self):
warnings.warn(
"The behavior of this method will change in future versions. "
"Use specific 'len(elem)' or 'elem is not None' test instead.",
FutureWarning, stacklevel=2
)
return len(self._children) != 0 # emulate old behaviour, for now def __getitem__(self, index):
return self._children[index] def __setitem__(self, index, element):
# if isinstance(index, slice):
# for elt in element:
# assert iselement(elt)
# else:
# assert iselement(element)
self._children[index] = element def __delitem__(self, index):
del self._children[index] def append(self, subelement):
为当前节点追加一个子节点
"""Add *subelement* to the end of this element. The new element will appear in document order after the last existing
subelement (or directly after the text, if it's the first subelement),
but before the end tag for this element. """
self._assert_is_element(subelement)
self._children.append(subelement) def extend(self, elements):
为当前节点扩展 n 个子节点
"""Append subelements from a sequence. *elements* is a sequence with zero or more elements. """
for element in elements:
self._assert_is_element(element)
self._children.extend(elements) def insert(self, index, subelement):
在当前节点的子节点中插入某个节点,即:为当前节点创建子节点,然后插入指定位置
"""Insert *subelement* at position *index*."""
self._assert_is_element(subelement)
self._children.insert(index, subelement) def _assert_is_element(self, e):
# Need to refer to the actual Python implementation, not the
# shadowing C implementation.
if not isinstance(e, _Element_Py):
raise TypeError('expected an Element, not %s' % type(e).__name__) def remove(self, subelement):
在当前节点在子节点中删除某个节点
"""Remove matching subelement. Unlike the find methods, this method compares elements based on
identity, NOT ON tag value or contents. To remove subelements by
other means, the easiest way is to use a list comprehension to
select what elements to keep, and then use slice assignment to update
the parent element. ValueError is raised if a matching element could not be found. """
# assert iselement(element)
self._children.remove(subelement) def getchildren(self):
获取所有的子节点(废弃)
"""(Deprecated) Return all subelements. Elements are returned in document order. """
warnings.warn(
"This method will be removed in future versions. "
"Use 'list(elem)' or iteration over elem instead.",
DeprecationWarning, stacklevel=2
)
return self._children def find(self, path, namespaces=None):
获取第一个寻找到的子节点
"""Find first matching element by tag name or path. *path* is a string having either an element tag or an XPath,
*namespaces* is an optional mapping from namespace prefix to full name. Return the first matching element, or None if no element was found. """
return ElementPath.find(self, path, namespaces) def findtext(self, path, default=None, namespaces=None):
获取第一个寻找到的子节点的内容
"""Find text for first matching element by tag name or path. *path* is a string having either an element tag or an XPath,
*default* is the value to return if the element was not found,
*namespaces* is an optional mapping from namespace prefix to full name. Return text content of first matching element, or default value if
none was found. Note that if an element is found having no text
content, the empty string is returned. """
return ElementPath.findtext(self, path, default, namespaces) def findall(self, path, namespaces=None):
获取所有的子节点
"""Find all matching subelements by tag name or path. *path* is a string having either an element tag or an XPath,
*namespaces* is an optional mapping from namespace prefix to full name. Returns list containing all matching elements in document order. """
return ElementPath.findall(self, path, namespaces) def iterfind(self, path, namespaces=None):
获取所有指定的节点,并创建一个迭代器(可以被for循环)
"""Find all matching subelements by tag name or path. *path* is a string having either an element tag or an XPath,
*namespaces* is an optional mapping from namespace prefix to full name. Return an iterable yielding all matching elements in document order. """
return ElementPath.iterfind(self, path, namespaces) def clear(self):
清空节点
"""Reset element. This function removes all subelements, clears all attributes, and sets
the text and tail attributes to None. """
self.attrib.clear()
self._children = []
self.text = self.tail = None def get(self, key, default=None):
获取当前节点的属性值
"""Get element attribute. Equivalent to attrib.get, but some implementations may handle this a
bit more efficiently. *key* is what attribute to look for, and
*default* is what to return if the attribute was not found. Returns a string containing the attribute value, or the default if
attribute was not found. """
return self.attrib.get(key, default) def set(self, key, value):
为当前节点设置属性值
"""Set element attribute. Equivalent to attrib[key] = value, but some implementations may handle
this a bit more efficiently. *key* is what attribute to set, and
*value* is the attribute value to set it to. """
self.attrib[key] = value def keys(self):
获取当前节点的所有属性的 key """Get list of attribute names. Names are returned in an arbitrary order, just like an ordinary
Python dict. Equivalent to attrib.keys() """
return self.attrib.keys() def items(self):
获取当前节点的所有属性值,每个属性都是一个键值对
"""Get element attributes as a sequence. The attributes are returned in arbitrary order. Equivalent to
attrib.items(). Return a list of (name, value) tuples. """
return self.attrib.items() def iter(self, tag=None):
在当前节点的子孙中根据节点名称寻找所有指定的节点,并返回一个迭代器(可以被for循环)。
"""Create tree iterator. The iterator loops over the element and all subelements in document
order, returning all elements with a matching tag. If the tree structure is modified during iteration, new or removed
elements may or may not be included. To get a stable set, use the
list() function on the iterator, and loop over the resulting list. *tag* is what tags to look for (default is to return all elements) Return an iterator containing all the matching elements. """
if tag == "*":
tag = None
if tag is None or self.tag == tag:
yield self
for e in self._children:
yield from e.iter(tag) # compatibility
def getiterator(self, tag=None):
# Change for a DeprecationWarning in 1.4
warnings.warn(
"This method will be removed in future versions. "
"Use 'elem.iter()' or 'list(elem.iter())' instead.",
PendingDeprecationWarning, stacklevel=2
)
return list(self.iter(tag)) def itertext(self):
在当前节点的子孙中根据节点名称寻找所有指定的节点的内容,并返回一个迭代器(可以被for循环)。
"""Create text iterator. The iterator loops over the element and all subelements in document
order, returning all inner text. """
tag = self.tag
if not isinstance(tag, str) and tag is not None:
return
if self.text:
yield self.text
for e in self:
yield from e.itertext()
if e.tail:
yield e.tail 节点功能一览表
节点功能一览表
由于 每个节点 都具有以上的方法,并且在上一步骤中解析时均得到了root(xml文件的根节点),so 可以利用以上方法进行操作xml文件。
a. 遍历XML文档的所有内容
from xml.etree import ElementTree as ET
############ 解析方式一 ############
"""
str_xml = open('xo.xml', 'r').read()
root = ET.XML(str_xml)
"""
############ 解析方式二 ############
tree = ET.parse("xo.xml")
root = tree.getroot() ### 操作
# 顶层标签
print(root.tag) # 遍历XML文档的第二层
for child in root:
# 第二层节点的标签名称和标签属性
print(child.tag, child.attrib)
# 遍历XML文档的第三层
for i in child:
# 第三层节点的标签名称和内容
print(i.tag,i.text)
查看所有的节点
b、遍历XML中指定的节点
from xml.etree import ElementTree as ET
############ 解析方式一 ############
"""
str_xml = open('xo.xml', 'r').read()
root = ET.XML(str_xml)
"""
############ 解析方式二 ############
tree = ET.parse("xo.xml")
root = tree.getroot() ### 操作 # 顶层标签
print(root.tag) # 遍历XML中所有的year节点
for node in root.iter('year'):
# 节点的标签名称和内容
print(node.tag, node.text)
查看所有的指定节点
c、修改节点内容
由于修改的节点时,均是在内存中进行,其不会影响文件中的内容。所以,如果想要修改,则需要重新将内存中的内容写到文件。
from xml.etree import ElementTree as ET ############ 解析方式一 ############ # 打开文件,读取XML内容
str_xml = open('xo.xml', 'r').read() # 将字符串解析成xml特殊对象,root代指xml文件的根节点
root = ET.XML(str_xml) ############ 操作 ############ # 顶层标签
print(root.tag) # 循环所有的year节点
for node in root.iter('year'):
# 将year节点中的内容自增一,和a,b互换值的原理相同
new_year = int(node.text) + 1
node.text = str(new_year) # 设置属性
node.set('name', 'alex')
node.set('age', '')
# 删除属性
del node.attrib['name'] ############ 保存文件 ############
tree = ET.ElementTree(root)
tree.write("newnew.xml", encoding='utf-8') #保存就是,把内存里的修改好的,重新写到文件里去 #tree是ElementTree的对象,root是element的对象,#ElementTree有write方法,element没有write方法,所以不能直接写入文件
解析字符串方式,修改,保存
from xml.etree import ElementTree as ET ############ 解析方式二 ############ # 直接解析xml文件
tree = ET.parse("xo.xml") # 获取xml文件的根节点
root = tree.getroot() ############ 操作 ############ # 顶层标签
print(root.tag) # 循环所有的year节点
for node in root.iter('year'):
# 将year节点中的内容自增一
new_year = int(node.text) + 1
node.text = str(new_year) # 设置属性
node.set('name', 'alex')
node.set('age', '')
# 删除属性
del node.attrib['name'] ############ 保存文件 ############
tree.write("newnew.xml", encoding='utf-8') #tree是ElementTree的对象,root是element的对象,#ElementTree有write方法,element没有write方法,所以不能直接写入文件
解析文件方式,修改,保存
d、删除节点
from xml.etree import ElementTree as ET ############ 解析字符串方式打开 ############ # 打开文件,读取XML内容
str_xml = open('xo.xml', 'r').read() # 将字符串解析成xml特殊对象,root代指xml文件的根节点
root = ET.XML(str_xml) ############ 操作 ############ # 顶层标签
print(root.tag) # 遍历data下的所有country节点
for country in root.findall('country'):
# 获取每一个country节点下rank节点的内容
rank = int(country.find('rank').text) if rank > 50:
# 删除指定country节点
root.remove(country) ############ 保存文件 ############
tree = ET.ElementTree(root)
tree.write("newnew.xml", encoding='utf-8')
解析字符串方式打开,删除,保存
from xml.etree import ElementTree as ET ############ 解析文件方式 ############ # 直接解析xml文件
tree = ET.parse("xo.xml") # 获取xml文件的根节点
root = tree.getroot() ############ 操作 ############ # 顶层标签
print(root.tag) # 遍历data下的所有country节点
for country in root.findall('country'):
# 获取每一个country节点下rank节点的内容
rank = int(country.find('rank').text) if rank > 50:
# 删除指定country节点
root.remove(country) ############ 保存文件 ############
tree.write("newnew.xml", encoding='utf-8')
解析文件方式打开,删除,保存
3、创建XML文档
from xml.etree import ElementTree as ET
#用ET文件中的Element功能直接创建节点 # 创建根节点
root = ET.Element("famliy")
# 创建儿子
son = ET.Element('son', {'name': '儿1'})
# 创建孙子
grandson = ET.Element('grandson', {'name': '儿11'}) #把孙子添加到儿子中去
son.append(grandson)
# 把儿子添加到根节点中
root.append(son) tree = ET.ElementTree(root)
tree.write('oooo.xml',encoding='utf-8', short_empty_elements=False)
创建方式(一)
from xml.etree import ElementTree as ET
#用节点自带的makeelement功能创建出子节点,但是也要自己进行节点的添加 # 创建根节点
root = ET.Element("famliy")
# 创建儿子
# son = ET.Element('son', {'name': '儿1'})
son = root.makeelement('son', {'name': '儿1'})
# 创建孙子
# grandson = ET.Element('grandson', {'name': '儿11'})
grandson = son.makeelement('grandson', {'name': '儿11'}) #把孙子添加到儿子节点中
son.append(grandson)
# 把儿子添加到根节点中
root.append(son) tree = ET.ElementTree(root)
tree.write('oooo.xml',encoding='utf-8', short_empty_elements=False)
创建方式(二)
from xml.etree import ElementTree as ET
#用ET文件内的SubElement函数,直接在儿子中创建孙子节点 # 创建根节点
root = ET.Element("famliy")
# 创建儿子
son = ET.SubElement(root, "son", attrib={'name': '儿1'}) # 直接在儿子中创建孙子节点
grandson = ET.SubElement(son, "age", attrib={'name': '儿11'})
grandson.text = '孙子' et = ET.ElementTree(root) #生成文档对象
et.write("test.xml", encoding="utf-8", xml_declaration=True, short_empty_elements=False)
#xml_declaration=True —— 自动加注释
创建方式(三)
由于原生保存的XML时默认无缩进,如果想要设置缩进的话, 需要修改保存方式:
from xml.etree import ElementTree as ET
from xml.dom import minidom
#minidom也能操作xml,但是功能少,效率低
#但是 提供了一个可以自动缩进的函数 def prettify(elem):
"""将节点转换成字符串,并添加缩进。
"""
rough_string = ET.tostring(elem, 'utf-8')
reparsed = minidom.parseString(rough_string)
return reparsed.toprettyxml(indent="\t") # 创建根节点
root = ET.Element("famliy")
# 创建儿子
son = ET.SubElement(root, "son", attrib={'name': '儿1'}) # 直接在儿子中创建孙子节点
grandson = ET.SubElement(son, "age", attrib={'name': '儿11'})
grandson.text = '孙子' raw_str = prettify(root)#prettify是之前定义函数 f = open("xxxoo.xml",'w',encoding='utf-8')
f.write(raw_str)
f.close()
缩进
4、命名空间
详细介绍,猛击这里
from xml.etree import ElementTree as ET
ET.register_namespace('h',"http://www.company.com") #some name
# build a tree structure
root = ET.Element("{http://www.company.com}deborah")#给http://www.company.com加个大括号,会把它变成h
body = ET.SubElement(root, "{http://www.company.com}CIRI", attrib={"{http://www.company.com}ellie": ""})
body.text = "STUFF EVERYWHERE!"
# wrap it in an ElementTree instance, and save as XML
tree = ET.ElementTree(root)
tree.write("page.xml",encoding='utf-8',method="xml")
命名空间
三、requests
Python标准库中提供了:urllib等模块以供Http请求,但是,它的 API 太渣了。它是为另一个时代、另一个互联网所创建的。它需要巨量的工作,甚至包括各种方法覆盖,来完成最简单的任务。
Requests 是使用 Apache2 Licensed 许可证的 基于Python开发的HTTP 库,其在Python内置模块的基础上进行了高度的封装,从而使得Pythoner进行网络请求时,变得美好了许多,使用Requests可以轻而易举的完成浏览器可有的任何操作。
1、安装模块
pip3 install requests
2、使用模块
# 1、无参数实例
import requests
ret = requests.get('https://github.com/timeline.json')
print(ret.url)
print(ret.text)
# 2、有参数实例
import requests
payload = {'key1': 'value1', 'key2': 'value2'}
ret = requests.get("http://httpbin.org/get", params=payload)
print(ret.url)
print(ret.text)
GET请求
# 1、基本POST实例
import requests
payload = {'key1': 'value1', 'key2': 'value2'}
ret = requests.post("http://httpbin.org/post", data=payload)
print(ret.text)
# 2、发送请求头和数据实例
import requests
import json
url = 'https://api.github.com/some/endpoint'
payload = {'some': 'data'}
headers = {'content-type': 'application/json'}
ret = requests.post(url, data=json.dumps(payload), headers=headers)
print(ret.text)
print(ret.cookies)
POST请求
requests.get(url, params=None, **kwargs)
requests.post(url, data=None, json=None, **kwargs)
requests.put(url, data=None, **kwargs)
requests.head(url, **kwargs)
requests.delete(url, **kwargs)
requests.patch(url, data=None, **kwargs)
requests.options(url, **kwargs) # 以上方法均是在此方法的基础上构建
requests.request(method, url, **kwargs)
其他请求
更多requests模块相关的文档见:http://cn.python-requests.org/zh_CN/latest/
3、Http请求和XML实例
实例:检测QQ账号是否在线
import urllib
import requests
from xml.etree import ElementTree as ET # 使用内置模块urllib发送HTTP请求,或者XML格式内容
"""
f = urllib.request.urlopen('http://www.webxml.com.cn//webservices/qqOnlineWebService.asmx/qqCheckOnline?qqCode=424662508')
result = f.read().decode('utf-8')
""" # 使用第三方模块requests发送HTTP请求,或者XML格式内容
r = requests.get('http://www.webxml.com.cn//webservices/qqOnlineWebService.asmx/qqCheckOnline?qqCode=424662508')
result = r.text # 解析XML格式内容
node = ET.XML(result) # 获取内容
if node.text == "Y":
print("在线")
else:
print("离线")
实例:查看火车停靠信息
import urllib
import requests
from xml.etree import ElementTree as ET # 使用内置模块urllib发送HTTP请求,或者XML格式内容
"""
f = urllib.request.urlopen('http://www.webxml.com.cn/WebServices/TrainTimeWebService.asmx/getDetailInfoByTrainCode?TrainCode=G666&UserID=')
result = f.read().decode('utf-8')
""" # 使用第三方模块requests发送HTTP请求,或者XML格式内容
r = requests.get('http://www.webxml.com.cn/WebServices/TrainTimeWebService.asmx/getDetailInfoByTrainCode?TrainCode=G666&UserID=')
result = r.text # 解析XML格式内容
root = ET.XML(result)
for node in root.iter('TrainDetailInfo'):
print(node.find('TrainStation').text,node.find('StartTime').text,node.tag,node.attrib)
注:更多接口猛击这里
四、configparse
configparser用于处理特定格式的文件,其本质上是利用open来操作文件。
该文件里不许需要加双引号和单引号来表示字符串,默认就全是字符串,例如文件中的 "ciri" 在Python中就相当于 ""ciri""
# 注释1
; 注释2 [section1] # 节点
k1 = v1 # 值
k2:v2 # 值 [section2] # 节点
k1 = v1 # 值
指定格式
下面的例子使用的文件名——ciri,内容:
[ellie]
love : joel
gender = 0 [ciri]
love = geralt
gender = 0
1、sections——获取所有节点
import configparser config = configparser.ConfigParser()
config.read('ciri', encoding='utf-8') #con对象的read功能,打开文件读取文件,放进内容
ret = config.sections() #con对象的sections,能在内存中寻找所有的[xxx]
print(ret) 结果:
['ellie', 'ciri']
2、items——获取指定节点下所有的键值对
import configparser config = configparser.ConfigParser()
config.read('ciri', encoding='utf-8')
ret = config.items('ellie')
print(ret)
结果:
[('love', 'joel'), ('gender', '0')]
3、options——获取指定节点下所有的建
import configparser config = configparser.ConfigParser()
config.read('ciri', encoding='utf-8')
ret = config.options('ellie')
print(ret) 结果:
['love', 'gender']
4、get——获取指定节点下指定key的值
import configparser config = configparser.ConfigParser()
config.read('ciri', encoding='utf-8')
v = config.get('ciri', 'love')
# v = config.getint('ciri', 'love')
# v = config.getfloat('ciri', 'love')
# v = config.getboolean('ciri', 'love')
print(v)
5、has_section,add_section,remove_section——检查、删除、添加节点
import configparser config = configparser.ConfigParser()
config.read('ciri', encoding='utf-8')
# 检查
has_sec = config.has_section('ellie')
print(has_sec)
结果:
True # 添加节点
config.add_section("deborah")
config.write(open('ciri', 'w')) # 删除节点
config.remove_section("deborah")
config.write(open('ciri', 'w'))
6、has_option,remove_option,set——检查、删除、设置指定组内的键值对
import configparser config = configparser.ConfigParser()
config.read('ciri', encoding='utf-8') # 检查
has_opt = config.has_option('ellie', 'love')
print(has_opt) # 删除
config.remove_option('ellie', 'joel')
config.write(open('ciri', 'w')) # 设置
config.set('ellie', 'love', "joel2")
config.write(open('ciri', 'w'))
五、shutil
高级的 文件、文件夹、压缩包 处理模块
shutil.copyfileobj(fsrc, fdst[, length])
将文件内容拷贝到另一个文件中
import shutil
shutil.copyfileobj(open('old.xml','r'), open('new.xml', 'w'))
shutil.copyfile(src, dst)
拷贝文件
shutil.copyfile('f1.log', 'f2.log')
shutil.copymode(src, dst)
仅拷贝权限。内容、组、用户均不变
shutil.copymode('f1.log', 'f2.log')
shutil.copystat(src, dst)
仅拷贝状态的信息,包括:mode bits, atime, mtime, flags
shutil.copystat('f1.log', 'f2.log')
shutil.copy(src, dst)
拷贝文件和权限
import shutil
shutil.copy('f1.log', 'f2.log')
shutil.copy2(src, dst)
拷贝文件和状态信息
import shutil
shutil.copy2('f1.log', 'f2.log')
shutil.ignore_patterns(*patterns)
shutil.copytree(src, dst, symlinks=False, ignore=None)
递归的去拷贝文件夹
import shutil
shutil.copytree('folder1', 'folder2', ignore=shutil.ignore_patterns('*.pyc', 'tmp*'))
#ignore=shutil.ignore_patterns('*.pyc', 'tmp*')忽略.pyc和.tmp文件
import shutil
shutil.copytree('f1', 'f2', symlinks=True)
#默认将内容复制到新文件,如果选项为true,会在目标中创建新的符号链接。
#windows里的快捷方式好像不是目录,没法用这条命令
文件or快捷方式
shutil.rmtree(path[, ignore_errors[, onerror]])
递归的去删除文件
import shutil
shutil.rmtree('folder1')
shutil.move(src, dst)
递归的去移动文件,它类似mv命令,其实就是重命名。
import shutil
shutil.move('folder1', 'folder3')
shutil.make_archive(base_name, format,...)
创建压缩包并返回文件路径,例如:zip、tar
- base_name: 压缩包的文件名,也可以是压缩包的路径。只是文件名时,则保存至当前目录,否则保存至指定路径,
如:www =>保存至当前路径
如:C:\python-practice\www =>保存至C:\python-practice - format: 压缩包种类,“zip”, “tar”, “bztar”,“gztar”
- root_dir: 要压缩的文件夹路径(默认当前目录)
- owner: 用户,默认当前用户
- group: 组,默认当前组
- logger: 用于记录日志,通常是logging.Logger对象
import shutil
# 将 C:\python-practice 下的文件打包放置当前程序目录
ret = shutil.make_archive("www", 'zip', root_dir='C:\python-practice') # 将 C:\python-practice 下的文件打包放置 D:\python-practice目录
ret = shutil.make_archive("D:\python-practice\www", 'zip', root_dir='C:\python-practice') 注:
# ret = shutil.make_archive("D:\python-practice\www", 'zip', root_dir='C:\python-practice')
# 这样会写一个死循环,不断的往压缩包里添加本文件,会越来越大
shutil 对压缩包的处理是调用 ZipFile 和 TarFile 两个模块来进行的,详细:
import zipfile # 压缩
z = zipfile.ZipFile('laxi.zip', 'w')
z.write('ciri')
z.write('ciri2')
z.close()
# 添加单一文件到压缩包中去
z = zipfile.ZipFile('laxi.zip', 'a')
z.write('ciri3')
# 解压
z = zipfile.ZipFile('laxi.zip', 'r')
z.extractall()
z.close()
zipfile解压缩
import tarfile # 压缩
tar = tarfile.open('your.tar','w')
tar.add('C:/Users/Sullivan/PycharmProjects/q1/pratice/ciri', arcname='bbs2.log')
tar.add('C:/Users/Sullivan/PycharmProjects/q1/pratice/ciri2', arcname='cmdb.log')
#把文件放到压缩包里去,并改名
tar.close() # 解压
tar = tarfile.open('your.tar','r')
tar.extractall('C:/Users/Sullivan/PycharmProjects/q1/pratice') # 可设置解压地址
tar.close()
tarfile解压缩
六、subprocess
可以执行shell命令的相关模块和函数有:
- os.system
- os.spawn*
- os.popen* --废弃
- popen2.* --废弃
- commands.* --废弃,3.x中被移除
以上执行shell命令的相关的模块和函数的功能均在 subprocess 模块中实现,并提供了更丰富的功能。
call
执行命令,返回状态码(命令会直接输出内容到屏幕,但是返回值是0,1)
#call就是执行系统命令,执行完了也拿不到结果,只能拿到返回码
ret = subprocess.call("ipconfig /all",shell=True)
#没有print也会出来结果
ret = subprocess.call(["ipconfig","/all"],shell=True)
print(ret)
#print输出的是命令执行成功与否的返回码
#shell=True或者是False,决定了输入命令的时候是字符串还是列表
#shell = True 表示命令形式是字符串
#shell = False表示命令形式是列表
check_call
执行命令,如果执行状态码是 0 ,则返回0,否则抛异常
subprocess.check_call("ipconfig /all")
subprocess.check_call(["ipconfig","/all"],shell=True)
check_output
执行命令,如果状态码是 0 ,则返回执行结果,否则抛异常
ret = subprocess.check_output("ipconfig")
print(ret)
#输出的是字节型的结果
new_ret = str(ret,encoding='gbk')
print(new_ret)
#输出转码后的结果
subprocess.Popen(...)
用于执行复杂的系统命令(以上名命令都是输入后直接返回结果,也有像python这样的shell命令,执行后会等待着用户继续输入,称之为复杂的shell命令)
参数:
- args:shell命令,可以是字符串或者序列类型(如:list,元组)
- bufsize:指定缓冲。0 无缓冲,1 行缓冲,其他 缓冲区大小,负值 系统缓冲
- stdin, stdout, stderr:分别表示程序的标准输入、输出、错误句柄
- preexec_fn:只在Unix平台下有效,用于指定一个可执行对象(callable object),它将在子进程运行之前被调用
- close_sfs:在windows平台下,如果close_fds被设置为True,则新创建的子进程将不会继承父进程的输入、输出、错误管道。
所以不能将close_fds设置为True同时重定向子进程的标准输入、输出与错误(stdin, stdout, stderr)。 - shell:同上
- cwd:用于设置子进程的当前目录
- env:用于指定子进程的环境变量。如果env = None,子进程的环境变量将从父进程中继承。
- universal_newlines:不同系统的换行符不同,True -> 同意使用 \n
- startupinfo与createionflags只在windows下有效
将被传递给底层的CreateProcess()函数,用于设置子进程的一些属性,如:主窗口的外观,进程的优先级等等
import subprocess
ret1 = subprocess.Popen(["mkdir","t1"])
ret2 = subprocess.Popen("mkdir t2", shell=True)
当然也可以执行简单的命令
终端输入的命令分为两种:
- 输入即可得到输出,如:ifconfig
- 输入进行某环境,依赖再输入,如:python
import subprocess
obj = subprocess.Popen("mkdir t3", shell=True, cwd='D:\\',)
#cwd后面只能加目录
#cwd的作用是执行前面的命令之前,先跳转到cwd后面的目录,并执行它
pwd
obj = subprocess.Popen(["python"], #后面相当于写了三个通道
stdin=subprocess.PIPE, #输入管道
stdout=subprocess.PIPE, #输出管道
stderr=subprocess.PIPE, #错误管道
universal_newlines=True) #新一行的换行符 obj.stdin.write("print(1)\n") #\n换行符
obj.stdin.write("print(2)") #在通道里写了两行数据
obj.stdin.close() cmd_out = obj.stdout.read() #去输出管道里读取东西
obj.stdout.close()
cmd_error = obj.stderr.read() #去错误管道里读取东西
obj.stderr.close() print(cmd_out,'===')
print(cmd_error) #管道会直接把你的输入内容,放到python解释器里去了
#所以直接操作管道就相当于,操作python解释器 #返回值会另外写到一个通道里
#如果出错,会把错误写到另外一个管道里 #参数Universal_newlines:不同操作系统下,文本的换行符是不一样的。
# 如:windows下用'/r/n'表示换,而Linux下用 '/n'。
# 如果将此参数设置为True,Python统一把这些换行符当作'/n'来处理
三个管道
import subprocess obj = subprocess.Popen(["python"],
stdin=subprocess.PIPE,
stdout=subprocess.PIPE,
stderr=subprocess.PIPE,
universal_newlines=True)
obj.stdin.write("print(1)\n")
obj.stdin.write("print(2)") out_error_list = obj.communicate()
"""
这一句话就相当于,上面读取的四行的代码,然后把读到的内容做个拼接
cmd_out = obj.stdout.read()
obj.stdout.close()
cmd_error = obj.stderr.read()
obj.stderr.close()
"""
print(out_error_list)
三个管道(简写,常用)
import subprocess obj = subprocess.Popen(["python"],
stdin=subprocess.PIPE,
stdout=subprocess.PIPE,
stderr=subprocess.PIPE,
universal_newlines=True) out_error_list = obj.communicate('print("hello")')
# 上面有print1和2两条命令,如果只写一条命令,可以把命令直接写到参数里
# obj.stdin.write("print(hello)")
# out_error_list = obj.communicate() print(out_error_list)
三个管道(单行命令)
Python学习日记(九)—— 模块二(logging、json&pickle、xml、requests、configparser、shutil、subprocess)的更多相关文章
- python学习日记(模块导入)
什么是模块? 常见的场景:一个模块就是一个包含了python定义和声明的文件,文件名就是模块名字加上.py的后缀. 但其实import加载的模块分为四个通用类别: 1 使用python编写的代码(.p ...
- python学习之路-day4-装饰器&json&pickle
本节内容 迭代器&生成器 装饰器 Json & pickle 数据序列化 一.生成器 1.列表生成式 >>> L = [x * x for x in range(10 ...
- json pickle xml shelve configparser
json:# 是一种跨平台的数据格式 也属于序列化的一种方式pickle和shevle 序列化后得到的数据 只有python才可以解析通常企业开发不可能做一个单机程序 都需要联网进行计算机间的交互 J ...
- Python学习第十二课——json&pickle&XML模块&OS模块
json模块 import json dic={'name':'hanhan'} i=8 s='hello' l=[11,22] data=json.dumps(dic) #json.dumps() ...
- Python学习日记(三十二) hmac检验客户端的合法性和socketsever模块
Hmac模块 其实这个模块类似hashlib模块,它能将一些重要的信息通过算法加密成密文,让信息更具有安全性. 关于hmac加密算法的了解:它的全名是哈希运算消息认证码(Hash-based Mess ...
- python 模块二(os,json,pickle)
#################################总结##################### os常用 os.makedirs('baby/安哥拉/特斯拉/黄晓明') os.mkd ...
- Python学习日记(四十二) Mysql数据库篇 十
前言 当我们自己去写SQL代码的时候有时候会因为不熟练会导致效率低,再之后要进行许多的优化,并且操作也较为繁琐.因此ORM框架就能够解决上面的问题,它能根据自身的一些规则来帮助开发者去生成SQL代码. ...
- Python学习日记(九) 装饰器函数
1.import time a.time.time() 获取到当前的时间,返回值为浮点型 import time print(time.time()) #1565422783.6497557 b.ti ...
- Python 学习日记(第三周)
知识回顾 在上一周的学习里,我学习了一些学习Python的基础知识下面先简短的回顾一些: 1Python的版本和和安装 Python的版本主要有2.x和3.x两个版本这两个版本在语法等方面有一定的区别 ...
- python学习之argparse模块
python学习之argparse模块 一.简介: argparse是python用于解析命令行参数和选项的标准模块,用于代替已经过时的optparse模块.argparse模块的作用是用于解析命令行 ...
随机推荐
- EF中DbContext的生命周期
/// <summary>/// 依赖注入系统中类的生命周期./// </summary>public enum DependencyLifeStyle{ /// < ...
- 听课笔记--DP--Authentication Failed
Authentication Failed https://www.codechef.com/problems/AUTHEN/ 从一个长为N+K的由小写字母组成的字符串中删去K个字符, 可以得到多少种 ...
- spring cloud Eureka 配置信息
Eureka instance 一个服务,如:订单系统,会部署多台服务器,而每台服务器上提供的服务就是instance; 负载配置. Eureka service 指的是服务,提供一种特定功能的服务, ...
- 六、TreeMap的使用 及其源码解析
TreeMap中的元素默认按照keys的自然排序排列 1. 构造函数TreeMap(): 创建一个空的TreeMap ,keys按照自然排序TreeMap(Comparator comparator) ...
- JS 百度地图 换地图主题颜色(自定义)
JS 百度地图 换地图主题颜色(自定义) 可通过这个在线编辑得到自己想要的主题:https://developer.baidu.com/map/custom/ <div id="all ...
- 使用jquery来完成AJAX操作
jQuery对Ajax操作进行了封装,在jQuery中最底层的方法是$.ajax(),第二个是load(),$.get()和$.post(),第三层是$.getscript()和$.getJSON() ...
- innodb是如何巧妙实现事务隔离级别-转载
原文地址:innodb是如何巧妙实现事务隔离级别 之前的文章mysql锁机制详解中我们详细讲解了innodb的锁机制,锁机制是用来保证在并发情况下数据的准确性,而要保证数据准确通常需要事务的支持,而m ...
- linux centos安装nginx1.7.4
原文转自 jerryhe326:https://www.cnblogs.com/jerrypro/p/7062101.html一.安装准备 首先由于nginx的一些模块依赖一些lib库,所以在安装ng ...
- Netty UDP 使用采坑
使用Netty搭建UDP服务收集日志,使用过程中发现,部分日志接收不到,排查发现,都是大日志记录不到,后查询相关文档进行如下修改 EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new Ni ...
- linux在线安装jdk,tomcat,Nginx
安装jdk yum search java 查看java的所有版本内容 yum install -y java版本 -openjdk 安装成功 安装tomcat yum search tomcat y ...
