Java之IO(四)DataInputStream和DataOutputStream
转载请注明源出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/lighten/p/6986155.html
1.前言
DataInputStream和DataOutputStream分别继承了FilterInputStream和FilterOutputStream,这块内容在第二节介绍BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream的时候介绍过了,这里不再介绍。Java中针对于IO有许多现有的封装类可以使用,但是每个封装类都有各自的特点,使用场景不一样。本章介绍的这对IO还实现了其它的接口,DataInput和DataOutput。之前所讲到的流都是字节流,但是实际上对我们而言,字节流是没有什么太大的意义,单个字节人是无法知道含义的,所以通常需要对字节进行解析,获取真正有价值的意义。而这对流就完成了一个对基本数据类型(boolean,byte,unsignedByte,short,unsignedShort,char,int,long,float,double)的写入和读取和一些常用的读一行,读取UTF格式等方法,不需要我们自己重复写。当然Java的IO体系针对字符流有专门的Reader和Writer进行操作字符流。这在之后的章节进行介绍。
2.DataInputStream

DataInputStream需要接受一个输入源流。

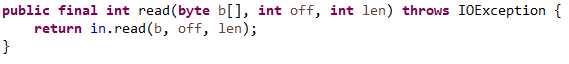
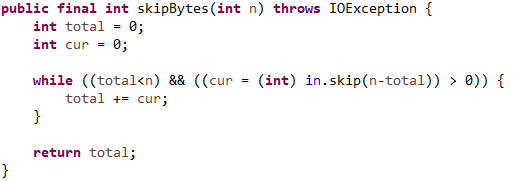
这些基础的InputStream的方法都是使用输入源的基本方法。
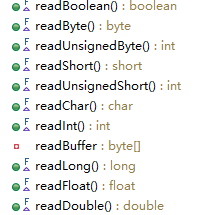
这些方法其实也十分的简单,都是针对每个类型的特点,将其读取出来,当然写入流的时候也要这样才行。
// 读取一个整形,根据是否为0返回boolean值
public final boolean readBoolean() throws IOException {
int ch = in.read();
if (ch < 0)
throw new EOFException();
return (ch != 0);
} // 读取一个整形,转成byte类型(实际上存的就是byte类型)
public final byte readByte() throws IOException {
int ch = in.read();
if (ch < 0)
throw new EOFException();
return (byte)(ch);
} // 读取一个整形,直接返回就是无符号的byte类型值了
public final int readUnsignedByte() throws IOException {
int ch = in.read();
if (ch < 0)
throw new EOFException();
return ch;
} // 读取两个字节,short是占两个字节,把第一读出来的左移8位到高8位。最后强转成short
public final short readShort() throws IOException {
int ch1 = in.read();
int ch2 = in.read();
if ((ch1 | ch2) < 0)
throw new EOFException();
return (short)((ch1 << 8) + (ch2 << 0));
} // 和short的方式一样,不进行强转就是无符合short
public final int readUnsignedShort() throws IOException {
int ch1 = in.read();
int ch2 = in.read();
if ((ch1 | ch2) < 0)
throw new EOFException();
return (ch1 << 8) + (ch2 << 0);
} // char也是两个字节,方法和short一样,最后强转成char
public final char readChar() throws IOException {
int ch1 = in.read();
int ch2 = in.read();
if ((ch1 | ch2) < 0)
throw new EOFException();
return (char)((ch1 << 8) + (ch2 << 0));
} // int是4个字节,第一个左移24位到最高8位,之后的依次就是最后的结果
public final int readInt() throws IOException {
int ch1 = in.read();
int ch2 = in.read();
int ch3 = in.read();
int ch4 = in.read();
if ((ch1 | ch2 | ch3 | ch4) < 0)
throw new EOFException();
return ((ch1 << 24) + (ch2 << 16) + (ch3 << 8) + (ch4 << 0));
} // long是8个字节,读入一个数组,然后按照一定的转换方式进行转换
public final long readLong() throws IOException {
readFully(readBuffer, 0, 8);
return (((long)readBuffer[0] << 56) +
((long)(readBuffer[1] & 255) << 48) +
((long)(readBuffer[2] & 255) << 40) +
((long)(readBuffer[3] & 255) << 32) +
((long)(readBuffer[4] & 255) << 24) +
((readBuffer[5] & 255) << 16) +
((readBuffer[6] & 255) << 8) +
((readBuffer[7] & 255) << 0));
} // float是调用readInt再通过Float的方法来转成float
public final float readFloat() throws IOException {
return Float.intBitsToFloat(readInt());
} // double与float类似,不过是8位所以用readLong()
public final double readDouble() throws IOException {
return Double.longBitsToDouble(readLong());
}
最后的readline()方法已经被废弃了。不过可以看看源代码,比较有意思:
public final String readLine() throws IOException {
char buf[] = lineBuffer;
if (buf == null) {
buf = lineBuffer = new char[128];
}
int room = buf.length;
int offset = 0;
int c;
loop: while (true) {
switch (c = in.read()) {
case -1:
case '\n':
break loop;
case '\r':
int c2 = in.read();
if ((c2 != '\n') && (c2 != -1)) {
if (!(in instanceof PushbackInputStream)) {
this.in = new PushbackInputStream(in);
}
((PushbackInputStream)in).unread(c2);
}
break loop;
default:
if (--room < 0) {
buf = new char[offset + 128];
room = buf.length - offset - 1;
System.arraycopy(lineBuffer, 0, buf, 0, offset);
lineBuffer = buf;
}
buf[offset++] = (char) c;
break;
}
}
if ((c == -1) && (offset == 0)) {
return null;
}
return String.copyValueOf(buf, 0, offset);
}
用了一个无限循环,读取到换行符才进行break,因为换行符根据操作系统不同,有两种'\r\n'和'\n'。所以'\r'的时候还判断了一下后面的字符是不是\n。不是的话使用了一个PushbackInputStream,这个很有意思,一般流读取了是无法反悔的(不能再次读取),但是专门有了个反悔的输入流。这个其实也简单,和BufferedInputStream原理类似,就是里面有个数组,不同的是BufferedInputStream是为了存从流中取得的字节,PushbackInputStream是放入反悔的字节,pos计数还是从缓存大小倒数的,这也是个不同点。最后是将流读取成UTF格式的字符串。但是只限于DataOutputStream输出的,其解析有固定的格式,前一个Int是字符串长度。
3.DataOutputStream

DataOutputStream也需要一个输出源,里面有一个计数字段written,计算写入了多少字节的数据,是int类型。如果长度超多了int类型的最大值,就会使用Integer.MAX_VALUE来标记。

超过了就会变成负数,就是变成了Integer.MAX_VALUE。接下来就是与DataInputStream解析方法对应的写入方法了。
public final void writeBoolean(boolean v) throws IOException {
out.write(v ? 1 : 0);
incCount(1);
}
public final void writeByte(int v) throws IOException {
out.write(v);
incCount(1);
}
public final void writeShort(int v) throws IOException {
out.write((v >>> 8) & 0xFF);
out.write((v >>> 0) & 0xFF);
incCount(2);
}
public final void writeChar(int v) throws IOException {
out.write((v >>> 8) & 0xFF);
out.write((v >>> 0) & 0xFF);
incCount(2);
}
public final void writeInt(int v) throws IOException {
out.write((v >>> 24) & 0xFF);
out.write((v >>> 16) & 0xFF);
out.write((v >>> 8) & 0xFF);
out.write((v >>> 0) & 0xFF);
incCount(4);
}
public final void writeLong(long v) throws IOException {
writeBuffer[0] = (byte)(v >>> 56);
writeBuffer[1] = (byte)(v >>> 48);
writeBuffer[2] = (byte)(v >>> 40);
writeBuffer[3] = (byte)(v >>> 32);
writeBuffer[4] = (byte)(v >>> 24);
writeBuffer[5] = (byte)(v >>> 16);
writeBuffer[6] = (byte)(v >>> 8);
writeBuffer[7] = (byte)(v >>> 0);
out.write(writeBuffer, 0, 8);
incCount(8);
}
public final void writeFloat(float v) throws IOException {
writeInt(Float.floatToIntBits(v));
}
public final void writeDouble(double v) throws IOException {
writeLong(Double.doubleToLongBits(v));
}
还有一些方法比如writeBytes(String)和writeUTF方法就不介绍了。
4.例子与结语
@Test
public void test() throws IOException {
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(1024);
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(baos);
dos.writeByte(1);
dos.writeInt(234);
dos.writeShort(56);
dos.writeLong(789L);
dos.writeDouble(11.11);
dos.writeFloat(22.22f);
dos.writeChar('a');
dos.writeBoolean(false);
dos.writeUTF("你好!");
dos.close();
ByteArrayInputStream bais = new ByteArrayInputStream(baos.toByteArray());
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(bais);
System.out.println(dis.readByte());
System.out.println(dis.readInt());
System.out.println(dis.readShort());
System.out.println(dis.readLong());
System.out.println(dis.readDouble());
System.out.println(dis.readFloat());
System.out.println(dis.readChar());
System.out.println(dis.readBoolean());
System.out.println(dis.readUTF());
dis.close();
}

上述就是一个简单的例子了。这里还需要说明的是:这对流是线程不安全的,如果你要在多线程下使用,需要自己保证线程安全。
Java之IO(四)DataInputStream和DataOutputStream的更多相关文章
- java代码----------实现创建DataInputStream和DataOutputStream进行读写
总结: 主要是 捕获异常 package com.a.b; import java.io.*; public class testData { public static void main(Stri ...
- Java之IO(零)总结
转载请注明原出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/lighten/p/7274378.html 1.前言 本章是对之前所讲述的整个Java的IO包的一个总结,抽出个人认为比较重要的知识点 ...
- Java IO(十一) DataInputStream 和 DataOutputStream
Java IO(十一) DataInputStream 和 DataOutputStream 一.介绍 DataInputStream 和 DataOutputStream 是数据字节流,分别继承自 ...
- Java基础-IO流对象之数据流(DataOutputStream与DataInputStream)
Java基础-IO流对象之数据流(DataOutputStream与DataInputStream) 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 一.数据流特点 操作基本数据类型 ...
- Java面向对象 IO (四)
Java面向对象 IO (四) 知识概要: (1)打印流 (2)序列流 SequenceInputStream (3)ObjectInputStream与Ob ...
- java io系列15之 DataOutputStream(数据输出流)的认知、源码和示例
本章介绍DataOutputStream.我们先对DataOutputStream有个大致认识,然后再深入学习它的源码,最后通过示例加深对它的了解. 转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblog ...
- java下DataInputStream与DataOutputStream写入数据的同时写入数据类型
package cn.stat.p2.demo; import java.io.DataInputStream; import java.io.DataOutputStream; import jav ...
- Java基础——IO流
今天刚刚看完java的io流操作,把主要的脉络看了一遍,不能保证以后使用时都能得心应手,但是最起码用到时知道有这么一个功能可以实现,下面对学习进行一下简单的总结: IO流主要用于硬板.内存.键盘等处理 ...
- 从Decorator,Adapter模式看Java的IO库
我想任何一本介绍模式的书在讲到Decorator模式的时候不能不提到它的实际应用--在Java/IO库里面的应用,<<Java与模式>>这本书也不例外,有点不一样的是,这本书在 ...
随机推荐
- Docker mysql启动自动按顺序导入sql
1.目录结构 -rw-r--r-- root root Jan : Dockerfile -rw-r--r-- root root Jan : initdb.sh drwxr-xr-x root ro ...
- BZOJ 1011 [HNOI2008]遥远的行星 (误差分析)
1011: [HNOI2008]遥远的行星 Time Limit: 10 Sec Memory Limit: 162 MBSec Special JudgeSubmit: 4974 Solved ...
- C/C++的Name Mangling
C语言 函数 1.void __CALLTYPE f();2.int __CALLTYPE f();3.int __CALLTYPE f(int);4.double __CALLTYPE f(int, ...
- 测试-LoadRunner
1录脚本 设置解析方式,html形式,会精炼成一个函数,此时找有用的url,写出函数:url方式,函数比较多. 参数化 两参数成对时,在脚本处选成对. 加上进程,加上返回值判断. 最后一段接口url, ...
- (最小生成树) Jungle Roads -- POJ -- 1251
链接: http://poj.org/problem?id=1251 Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 2177 ...
- HDU6024 Building Shops 2017-05-07 18:33 30人阅读 评论(0) 收藏
Building Shops Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS ...
- SQL 数据库开发一些精典的代码(转自 咏南工作室)
1.按姓氏笔画排序: Select * From TableName Order By CustomerName Collate Chinese_PRC_Stroke_ci_as 2.数据库加密: s ...
- Android-fragment-ListView展示-v4支持包
昨天写的这几篇博客,Android-fragment简介-fragment的简单使用,Activity-fragment-ListView展示,Android-fragment生命周期,Android ...
- Java位操作全面总结[ZZ]
Java位操作全面总结 在计算机中所有数据都是以二进制的形式储存的.位运算其实就是直接对在内存中的二进制数据进行操作,因此处理数据的速度非常快.在实际编程中,如果能巧妙运用位操作,完全可以达到四两拨千 ...
- Windows Phone 8.1 生命周期调试
之前重装了机子,今天调试时突然找不到调试生命周期的菜单栏了.最后找了5分钟,终于找回来了,特此记录以免以后重装后再出现这种状况. 项目启动调试后: 这样是没有显示调试生命周期的,接下来在工具栏右键: ...
