MapReduce编程之Semi Join多种应用场景与使用
Map Join 实现方式一
● 使用场景:一个大表(整张表内存放不下,但表中的key内存放得下),一个超大表
● 实现方式:分布式缓存
● 用法:
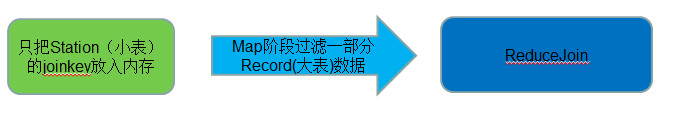
SemiJoin就是所谓的半连接,其实仔细一看就是reduce join的一个变种,就是在map端过滤掉一些数据,在网络中只传输参与连接的数据不参与连接的数据不必在网络中进行传输,从而减少了shuffle的网络传输量,使整体效率得到提高,其他思想和reduce join是一模一样的。说得更加接地气一点就是将小表中参与join的key单独抽出来通过DistributedCach分发到相关节点,然后将其取出放到内存中(可以放到HashSet中),在map阶段扫描连接表,将join key不在内存HashSet中的记录过滤掉,让那些参与join的记录通过shuffle传输到reduce端进行join操作,其他的和reduce join都是一样的。
代码实现
package com.hadoop.reducejoin.test; import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set; import org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FSDataInputStream;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileSplit;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.GenericOptionsParser;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.bloom.Key; /*
* 一个大表,一个小表(也很大,内存中放不下)
* map 阶段:Semi Join解决小表整个记录内存放不下的场景,那么就取出来一小部分关键字段放入内存,过滤大表
* 提前过滤,提前提取出小表中的连接字段放入内存中,在map阶段就仅留下大表中那些小表中存在的连接字段key
* reduce 阶段:reduce side join
*/
public class SemiJoin {
/**
* 为来自不同表(文件)的key/value对打标签以区别不同来源的记录。
* 然后用连接字段作为key,其余部分和新加的标志作为value,最后进行输出。
*/
public static class SemiJoinMapper extends
Mapper<Object, Text, Text, Text> {
// 定义Set集合保存小表中的key
private Set<String> joinKeys = new HashSet<String>();
private Text joinKey = new Text();
private Text combineValue = new Text(); /**
* 获取分布式缓存文件
*/
protected void setup(Context context) throws IOException,
InterruptedException {
BufferedReader br;
String infoAddr = null;
// 返回缓存文件路径
Path[] cacheFilesPaths = context.getLocalCacheFiles();
for (Path path : cacheFilesPaths) {
String pathStr = path.toString();
br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(pathStr));
while (null != (infoAddr = br.readLine())) {
// 按行读取并解析气象站数据
String[] records = StringUtils.split(infoAddr.toString(),
"\t");
if (null != records)// key为stationID
joinKeys.add(records[0]);
}
}
} @Override
protected void map(Object key, Text value, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String pathName = ((FileSplit) context.getInputSplit()).getPath()
.toString();
// 如果数据来自于records,加一个records的标记
if (pathName.endsWith("records-semi.txt")) {
String[] valueItems = StringUtils.split(value.toString(),
"\t");
// 过滤掉脏数据
if (valueItems.length != 3) {
return;
}
// 提前过滤,提前提取出小表中的连接字段,在map阶段就仅留下大表中那些小表中存在的连接字段key
if (joinKeys.contains(valueItems[0])) {
joinKey.set(valueItems[0]);
combineValue.set("records-semi.txt" + valueItems[1] + "\t"
+ valueItems[2]);
context.write(joinKey, combineValue);
} } else if (pathName.endsWith("station.txt")) {
// 如果数据来自于station,加一个station的标记
String[] valueItems = StringUtils.split(value.toString(),
"\t");
// 过滤掉脏数据
if (valueItems.length != 2) {
return;
}
joinKey.set(valueItems[0]);
combineValue.set("station.txt" + valueItems[1]);
context.write(joinKey, combineValue); }
}
}
/*
* reduce 端做笛卡尔积
*/
public static class SemiJoinReducer extends
Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text> {
private List<String> leftTable = new ArrayList<String>();
private List<String> rightTable = new ArrayList<String>();
private Text result = new Text(); @Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// 一定要清空数据
leftTable.clear();
rightTable.clear();
// 相同key的记录会分组到一起,我们需要把相同key下来自于不同表的数据分开,然后做笛卡尔积
for (Text value : values) {
String val = value.toString();
System.out.println("value=" + val);
if (val.startsWith("station.txt")) {
leftTable.add(val.replaceFirst("station.txt", ""));
} else if (val.startsWith("records-semi.txt")) {
rightTable.add(val.replaceFirst("records-semi.txt", ""));
}
}
// 笛卡尔积
for (String leftPart : leftTable) {
for (String rightPart : rightTable) {
result.set(leftPart + "\t" + rightPart);
context.write(key, result);
}
}
}
} public static void main(String[] arg0) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
String[] args = { "hdfs://sparks:9000/middle/reduceJoin/station.txt",
"hdfs://sparks:9000/middle/reduceJoin/station.txt",
"hdfs://sparks:9000/middle/reduceJoin/records-semi.txt",
"hdfs://sparks:9000/middle/reduceJoin/SemiJoin-out" };
String[] otherArgs = new GenericOptionsParser(conf, args)
.getRemainingArgs();
if (otherArgs.length < 2) {
System.err.println("Usage: semijoin <in> [<in>...] <out>");
System.exit(2);
} //输出路径
Path mypath = new Path(otherArgs[otherArgs.length - 1]);
FileSystem hdfs = mypath.getFileSystem(conf);// 创建输出路径
if (hdfs.isDirectory(mypath)) {
hdfs.delete(mypath, true);
}
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "SemiJoin"); //添加缓存文件
job.addCacheFile(new Path(otherArgs[0]).toUri());
job.setJarByClass(SemiJoin.class);
job.setMapperClass(SemiJoinMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(SemiJoinReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
//添加输入路径
for (int i = 1; i < otherArgs.length - 1; ++i) {
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[i]));
}
//添加输出路径
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(
otherArgs[otherArgs.length - 1]));
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
}
}
SemiJoin
Reduce join + BloomFilter
● 使用场景:一个大表(表中的key内存仍然放不下),一个超大表
在某些情况下,SemiJoin抽取出来的小表的key集合在内存中仍然存放不下,这时候可以使用BloomFiler以节省空间。
BloomFilter最常见的作用是:判断某个元素是否在一个集合里面。它最重要的两个方法是:add() 和membershipTest ()。
因而可将小表中的key保存到BloomFilter中,在map阶段过滤大表,可能有一些不在小表中的记录没有过滤掉(但是在小表中的记录一定不会过滤掉),这没关系,只不过增加了少量的网络IO而已。
● BloomFilter参数计算方式:
n:小表中的记录数。
m:位数组大小,一般m是n的倍数,倍数越大误判率就越小,但是也有内存限制,不能太大,这个值需要反复测试得出。
k:hash个数,最优hash个数值为:k = ln2 * (m/n)
代码实现
package com.hadoop.reducejoin.test; import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List; import org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileSplit;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.GenericOptionsParser;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.bloom.BloomFilter;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.bloom.Key;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.hash.Hash;
/*
* 一个大表,一个小表
* map 阶段:BloomFilter 解决小表的key集合在内存中仍然存放不下的场景,过滤大表
* reduce 阶段:reduce side join
*/
public class BloomFilteringDriver {
/**
* 为来自不同表(文件)的key/value对打标签以区别不同来源的记录。
* 然后用连接字段作为key,其余部分和新加的标志作为value,最后进行输出。
*/
public static class BloomFilteringMapper extends
Mapper<Object, Text, Text, Text> {
// 第一个参数是vector的大小,这个值尽量给的大,可以避免hash对象的时候出现索引重复
// 第二个参数是散列函数的个数
// 第三个是hash的类型,虽然是int型,但是只有默认两个值
// 哈希函数个数k、位数组大小m及字符串数量n之间存在相互关系
//n 为小表记录数,给定允许的错误率E,可以确定合适的位数组大小,即m >= log2(e) * (n * log2(1/E))
// 给定m和n,可以确定最优hash个数,即k = ln2 * (m/n),此时错误率最小
private BloomFilter filter = new BloomFilter(10000, 6, Hash.MURMUR_HASH);
private Text joinKey = new Text();
private Text combineValue = new Text(); /**
* 获取分布式缓存文件
*/
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
protected void setup(Context context) throws IOException,
InterruptedException {
BufferedReader br;
String infoAddr = null;
// 返回缓存文件路径
Path[] cacheFilesPaths = context.getLocalCacheFiles();
for (Path path : cacheFilesPaths) {
String pathStr = path.toString();
br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(pathStr));
while (null != (infoAddr = br.readLine())) {
// 按行读取并解析气象站数据
String[] records = StringUtils.split(infoAddr.toString(),
"\t");
if (null != records)// key为stationID
filter.add(new Key(records[0].getBytes()));
}
} } @Override
protected void map(Object key, Text value, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String pathName = ((FileSplit) context.getInputSplit()).getPath()
.toString();
// 如果数据来自于records,加一个records的标记
if (pathName.endsWith("records-semi.txt")) {
String[] valueItems = StringUtils.split(value.toString(),
"\t");
// 过滤掉脏数据
if (valueItems.length != 3) {
return;
}
//通过filter 过滤大表中的数据
if (filter.membershipTest(new Key(valueItems[0].getBytes()))) {
joinKey.set(valueItems[0]);
combineValue.set("records-semi.txt" + valueItems[1] + "\t"
+ valueItems[2]);
context.write(joinKey, combineValue);
} } else if (pathName.endsWith("station.txt")) {
// 如果数据来自于station,加一个station的标记
String[] valueItems = StringUtils.split(value.toString(),
"\t");
// 过滤掉脏数据
if (valueItems.length != 2) {
return;
}
joinKey.set(valueItems[0]);
combineValue.set("station.txt" + valueItems[1]);
context.write(joinKey, combineValue);
} }
}
/*
* reduce 端做笛卡尔积
*/
public static class BloomFilteringReducer extends
Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text> {
private List<String> leftTable = new ArrayList<String>();
private List<String> rightTable = new ArrayList<String>();
private Text result = new Text(); @Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// 一定要清空数据
leftTable.clear();
rightTable.clear();
// 相同key的记录会分组到一起,我们需要把相同key下来自于不同表的数据分开,然后做笛卡尔积
for (Text value : values) {
String val = value.toString();
System.out.println("value=" + val);
if (val.startsWith("station.txt")) {
leftTable.add(val.replaceFirst("station.txt", ""));
} else if (val.startsWith("records-semi.txt")) {
rightTable.add(val.replaceFirst("records-semi.txt", ""));
}
}
// 笛卡尔积
for (String leftPart : leftTable) {
for (String rightPart : rightTable) {
result.set(leftPart + "\t" + rightPart);
context.write(key, result);
}
}
}
} public static void main(String[] arg0) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
String[] args = { "hdfs://sparks:9000/middle/reduceJoin/station.txt",
"hdfs://sparks:9000/middle/reduceJoin/station.txt",
"hdfs://sparks:9000/middle/reduceJoin/records-semi.txt",
"hdfs://sparks:9000/middle/reduceJoin/BloomFilte-out" };
String[] otherArgs = new GenericOptionsParser(conf, args)
.getRemainingArgs();
if (otherArgs.length < 2) {
System.err.println("Usage: BloomFilter <in> [<in>...] <out>");
System.exit(2);
} //输出路径
Path mypath = new Path(otherArgs[otherArgs.length - 1]);
FileSystem hdfs = mypath.getFileSystem(conf);// 创建输出路径
if (hdfs.isDirectory(mypath)) {
hdfs.delete(mypath, true);
}
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "bloomfilter"); //添加缓存文件
job.addCacheFile(new Path(otherArgs[0]).toUri());
job.setJarByClass(BloomFilteringDriver.class);
job.setMapperClass(BloomFilteringMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(BloomFilteringReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
//添加输入文件
for (int i = 1; i < otherArgs.length - 1; ++i) {
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[i]));
}
//设置输出路径
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(
otherArgs[otherArgs.length - 1]));
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
}
}
BloomFilteringDriver
总结
三种join方式适用于不同的场景,其处理效率上相差很大,其主要导致因素是网络传输。Map join效率最高,其次是SemiJoin,最低的是reduce join。另外,写分布式大数据处理程序的时最好要对整体要处理的数据分布情况作一个了解,这可以提高我们代码的效率,使数据的倾斜度降到最低,使我们的代码倾向性更好。
MapReduce编程之Semi Join多种应用场景与使用的更多相关文章
- MapReduce编程之Reduce Join多种应用场景与使用
在关系型数据库中 Join 是非常常见的操作,各种优化手段已经到了极致.在海量数据的环境下,不可避免的也会碰到这种类型的需求, 例如在数据分析时需要连接从不同的数据源中获取到数据.不同于传统的单机模式 ...
- MapReduce编程之Map Join多种应用场景与使用
Map Join 实现方式一:分布式缓存 ● 使用场景:一张表十分小.一张表很大. ● 用法: 在提交作业的时候先将小表文件放到该作业的DistributedCache中,然后从DistributeC ...
- MapReduce编程之wordcount
实践 MapReduce编程之wordcount import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Fi ...
- mapReduce编程之Recommender System
1 协同过滤算法 协同过滤算法是现在推荐系统的一种常用算法.分为user-CF和item-CF. 本文的电影推荐系统使用的是item-CF,主要是由于用户数远远大于电影数,构建矩阵的代价更小:另外,电 ...
- 并发编程之Fork/Join
并发与并行 并发:多个进程交替执行. 并行:多个进程同时进行,不存在线程的上下文切换. 并发与并行的目的都是使CPU的利用率达到最大.Fork/Join就是为了尽可能提高硬件的使用率而应运而生的. 计 ...
- 并发编程之fork/join(分而治之)
1.什么是分而治之 分而治之就是将一个大任务层层拆分成一个个的小任务,直到不可拆分,拆分依据定义的阈值划分任务规模. fork/join通过fork将大任务拆分成小任务,在将小任务的结果join汇总 ...
- mapReduce编程之auto complete
1 n-gram模型与auto complete n-gram模型是假设文本中一个词出现的概率只与它前面的N-1个词相关.auto complete的原理就是,根据用户输入的词,将后续出现概率较大的词 ...
- mapReduce编程之google pageRank
1 pagerank算法介绍 1.1 pagerank的假设 数量假设:每个网页都会给它的链接网页投票,假设这个网页有n个链接,则该网页给每个链接平分投1/n票. 质量假设:一个网页的pagerank ...
- c++并发编程之thread::join()和thread::detach()
thread::join(): 阻塞当前线程,直至 *this 所标识的线程完成其执行.*this 所标识的线程的完成同步于从 join() 的成功返回. 该方法简单暴力,主线程等待子进程期间什么都不 ...
随机推荐
- 大数据入门第二天——基础部分之zookeeper(下)
一.集群自启动脚本 1.关闭zk [root@localhost bin]# jps Jps QuorumPeerMain [root@localhost bin]# //kill或者stop都是可以 ...
- matplotlib绑定到PyQt5(无菜单)
很简单的实现matplotlib绑定到PyQt5 [知识点] import matplotlib matplotlib.use("Qt5Agg") from matplotlib. ...
- 5289: [Hnoi2018]排列
5289: [Hnoi2018]排列 链接 分析: 首先将题意转化一下:每个点向a[i]连一条边,构成了一个以0为根节点的树,要求选一个拓扑序,点x是拓扑序中的第i个,那么价值是i*w[x].让价值最 ...
- COGS1871 [国家集训队2011]排队(魏铭)
bzoj:http://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=2141 cogs:http://cogs.pro:8080/cogs/problem/pro ...
- python爬虫之requests库介绍(二)
一.requests基于cookie操作 引言:有些时候,我们在使用爬虫程序去爬取一些用户相关信息的数据(爬取张三“人人网”个人主页数据)时,如果使用之前requests模块常规操作时,往往达不到我们 ...
- js中for循环的多种方式
For/In 循环 JavaScript for/in 语句循环遍历对象的属性: 实例 var person={fname:"John",lname:"Doe" ...
- 一个导致MGR数据混乱Bug的分析和修复
1.背景 MGR是个好东西,因为他从本质上解决了数据不一致的问题.不光是解决了问题,而且出自名门正派(Oracle的MySQL团队),对品质和后续的维护,我们是可以期待的. 但是在调研的过程中,发现有 ...
- virtualBox linux centos 挂载u盘 解决乱码
linux 挂载u盘 环境:虚拟机virtualBox5.2.8 linux centos6.5 64bit 第一步:插入u盘 第二步:virtualBox 设置启用u盘 提示:如果不知道哪个是你u盘 ...
- C++模板的实现(模板函数和模板类,附带模板实现顺序表和链表代码)
文章链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38646470/article/details/80209469
- Jmeter+ant+jenkins接口自动化测试 平台搭建(一)
平台简介 一个完整的接口自动化测试平台需要支持接口的自动执行,自动生成测试报告,以及持续集成.Jmeter 支持接口的测试,Ant 支持自动构建,而 Jenkins 支持持续集成,所以三者组合在一起可 ...
