Round 1A 2020 - Code Jam 2020
Problem A. Pattern Matching
把每个字符串分成第一个之前,最后一个之后,中间的部分 三个部分
每个字符串的中间的部分可以直接拼接
前后两个部分需要判断下是否合法
#include <algorithm>
#include <bitset>
#include <cassert>
#include <cmath>
#include <complex>
#include <cstring>
#include <ctime>
#include <deque>
#include <fstream>
#include <functional>
#include <iomanip>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <numeric>
#include <queue>
#include <random>
#include <set>
#include <stack>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <vector>
#define MP make_pair
#define ll long long
#define ld long double
#define null NULL
#define all(a) a.begin(), a.last()
#define forn(i, n) for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
#define sz(a) (int)a.size()
#define lson l , m , rt << 1
#define rson m + 1 , r , rt << 1 | 1
#define bitCount(a) __builtin_popcount(a)
template<class T> int gmax(T &a, T b) { if (b > a) { a = b; return 1; } return 0; }
template<class T> int gmin(T &a, T b) { if (b < a) { a = b; return 1; } return 0; }
using namespace std;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
string to_string(string s) { return '"' + s + '"'; }
string to_string(const char* s) { return to_string((string) s); }
string to_string(bool b) { return (b ? "true" : "false"); }
template <typename A, typename B>
string to_string(pair<A, B> p) { return "(" + to_string(p.first) + ", " + to_string(p.second) + ")"; }
template <typename A>
string to_string(A v) { bool first = true; string res = "{"; for (const auto &x : v) { if (!first) { res += ", "; } first = false; res += to_string(x); } res += "}"; return res; }
void debug_out() { cerr << endl; }
template <typename Head, typename... Tail>
void debug_out(Head H, Tail... T) { cerr << " " << to_string(H); debug_out(T...); }
#ifdef LOCAL
#define debug(...) cerr << "[" << #__VA_ARGS__ << "]:", debug_out(__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define debug(...) 42
#endif
char seq[55][105];
int main() {
int T;
scanf("%d", &T);
for(int cas = 1; cas <= T; ++cas) {
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
scanf("%s", seq[i]);
}
vector<string> front, last;
string mid_result;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int len = strlen(seq[i]);
vector<string> split;
string tmp;
if(seq[i][0] == '*') split.push_back("");
for(int j = 0; j < len; ++j) {
// cout << seq[i][j] << endl;
if(seq[i][j] == '*') {
if((int)tmp.size() != 0) split.push_back(tmp);
tmp.clear();
} else tmp += seq[i][j];
}
if((int)tmp.size() != 0) split.push_back(tmp);
// debug(split);
if(seq[i][len - 1] == '*') split.push_back("");
front.push_back(split[0]); last.push_back(split.back());
if(split.size() > 2) {
for(int j = 1, split_len = split.size(); j < split_len - 1; ++j) {
mid_result += split[j];
}
}
}
auto cmp = [](string &A, string &B) { return A.size() < B.size(); };
sort(front.begin(), front.end(), cmp);
sort(last.begin(), last.end(), cmp);
// debug(front, last, mid_result);
bool suc = true;
for(int i = 0, len = front.size(); i < len - 1 && suc; ++i) {
string &now = front[i]; string &tem = front.back();
for(int j = 0, len_now = now.size(); j < len_now && suc; ++j) {
if(now[j] != tem[j]) { suc = false; }
}
}
// debug(suc);
for(int i = 0, len = last.size(); i < len - 1 && suc; ++i) {
string &now = last[i]; string &tem = last.back(); int len_tem = tem.size();
for(int j = 0, len_now = now.size(); j < len_now && suc; ++j) {
if(now[j] != tem[len_tem + j - len_now]) {
// debug(now, tem, j);
suc = false;
}
}
}
string result = front.back() + mid_result + last.back();
printf("Case #%d: ", cas);
if(suc == false) printf("*\n");
else printf("%s\n", result.c_str());
}
return 0;
}
/*
2
5
*CONUTS
*COCONUTS
*OCONUTS
*CONUTS
*S
2
*XZ
*XYZ
*/
problem B. Pascal Walk
这是一个 非常巧妙的构造题
首先想到一个杨辉三角的每一个层的和是 2^i ,如果我们可以跳跃就好了,直接按照N的二进制表示,使用对应层的和
问题在于我们无法跳跃,怎么办
通过构造可以发现我们可以将两个很远的两层连在一起,下面举例5,19的情况,具体的逻辑可以去代码里面体会
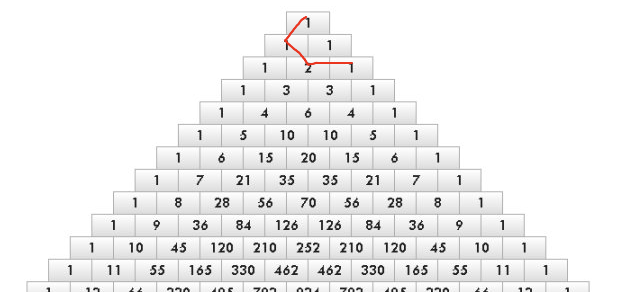
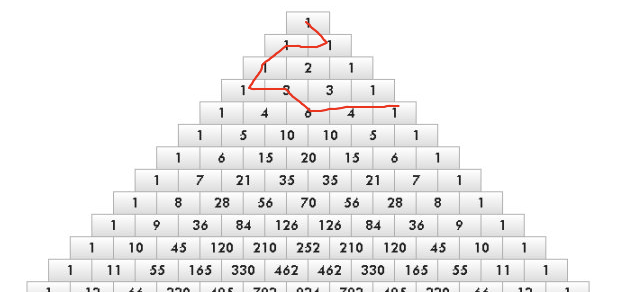
#include <algorithm>
#include <bitset>
#include <cassert>
#include <cmath>
#include <complex>
#include <cstring>
#include <ctime>
#include <deque>
#include <fstream>
#include <functional>
#include <iomanip>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <numeric>
#include <queue>
#include <random>
#include <set>
#include <stack>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <vector>
#define MP make_pair
#define ll long long
#define ld long double
#define null NULL
#define all(a) a.begin(), a.last()
#define forn(i, n) for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
#define sz(a) (int)a.size()
#define lson l , m , rt << 1
#define rson m + 1 , r , rt << 1 | 1
#define bitCount(a) __builtin_popcount(a)
template<class T> int gmax(T &a, T b) { if (b > a) { a = b; return 1; } return 0; }
template<class T> int gmin(T &a, T b) { if (b < a) { a = b; return 1; } return 0; }
using namespace std;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
string to_string(string s) { return '"' + s + '"'; }
string to_string(const char* s) { return to_string((string) s); }
string to_string(bool b) { return (b ? "true" : "false"); }
template <typename A, typename B>
string to_string(pair<A, B> p) { return "(" + to_string(p.first) + ", " + to_string(p.second) + ")"; }
template <typename A>
string to_string(A v) { bool first = true; string res = "{"; for (const auto &x : v) { if (!first) { res += ", "; } first = false; res += to_string(x); } res += "}"; return res; }
void debug_out() { cerr << endl; }
template <typename Head, typename... Tail>
void debug_out(Head H, Tail... T) { cerr << " " << to_string(H); debug_out(T...); }
#ifdef LOCAL
#define debug(...) cerr << "[" << #__VA_ARGS__ << "]:", debug_out(__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define debug(...) 42
#endif
void add(vector<pair<int, int> >& vc, int pre, int target, int times) {
// debug(pre, target, vc);
int dir = 0;
if( times % 2 == 0) dir = 0; else dir = 1;
int preX = -1, preY = 0;
if(vc.size() != 0) {
preX = vc.back().first; preY = vc.back().second;
}
int needFloor = target - pre - 1;
if(needFloor == 0) {
vc.push_back(dir ? MP(preX + 1, preY + 1) : MP(preX + 1, preY));
for(int i = 0; i < target; ++i) {
vc.push_back(dir ? MP(vc.back().first, vc.back().second - 1) : MP(vc.back().first, vc.back().second + 1));
}
} else {
vc.push_back(dir ? MP(preX + 1, preY + 1) : MP(preX + 1, preY));
int count = 2;
for(int i = 0; i < needFloor - 1; ++i) {
int tmp_count = count - 1; int now_dir = (i & 1) ^ (needFloor & 1) ^ dir;
vc.push_back(now_dir ? MP(vc.back().first + 1, vc.back().second + 1) : MP(vc.back().first + 1, vc.back().second));
while(tmp_count --) {
vc.push_back(now_dir ? MP(vc.back().first, vc.back().second - 1) : MP(vc.back().first, vc.back().second + 1));
}
count ++;
}
vc.push_back(dir ? MP(vc.back().first + 1, vc.back().second) : MP(vc.back().first + 1, vc.back().second + 1));
for(int i = 0; i < target - count + 1; ++i) {
vc.push_back(dir ? MP(vc.back().first, vc.back().second - 1) : MP(vc.back().first, vc.back().second + 1));
}
}
}
int main() {
int T;
scanf("%d", &T);
for(int cas = 1; cas <= T; ++cas) {
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
vector<pair<int, int> > vc;
int floor = -1; int cnt = 0; int times = 0;
while(n) {
if(n & 1) {
add(vc, floor, cnt, times);
times ++;
floor = cnt;
}
cnt ++;
n /= 2;
}
assert((int)vc.size() < 500);
printf("Case #%d: \n", cas);
for(int i = 0, len = vc.size(); i < len; ++i) {
printf("%d %d\n", vc[i].first + 1, vc[i].second + 1);
}
}
return 0;
}
Problem C: Square Dance
这题看起来就是暴力,能过小数据
有个显而易见的优化,就是每次删除一个点之后,下一轮潜在的可能删除点一定是上轮被删点的邻居
复杂度不太会算,题解说这样优化后能到O(R * C)
找邻居这种数据结构 我用十字链表维护的
#include <algorithm>
#include <bitset>
#include <cassert>
#include <cmath>
#include <complex>
#include <cstring>
#include <ctime>
#include <deque>
#include <fstream>
#include <functional>
#include <iomanip>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <numeric>
#include <queue>
#include <random>
#include <set>
#include <stack>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <vector>
#define MP make_pair
#define ll long long
#define ld long double
#define null NULL
#define all(a) a.begin(), a.last()
#define forn(i, n) for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
#define sz(a) (int)a.size()
#define lson l , m , rt << 1
#define rson m + 1 , r , rt << 1 | 1
#define bitCount(a) __builtin_popcount(a)
template<class T> int gmax(T &a, T b) { if (b > a) { a = b; return 1; } return 0; }
template<class T> int gmin(T &a, T b) { if (b < a) { a = b; return 1; } return 0; }
using namespace std;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
string to_string(string s) { return '"' + s + '"'; }
string to_string(const char* s) { return to_string((string) s); }
string to_string(bool b) { return (b ? "true" : "false"); }
template <typename A, typename B>
string to_string(pair<A, B> p) { return "(" + to_string(p.first) + ", " + to_string(p.second) + ")"; }
template <typename A>
string to_string(A v) { bool first = true; string res = "{"; for (const auto &x : v) { if (!first) { res += ", "; } first = false; res += to_string(x); } res += "}"; return res; }
void debug_out() { cerr << endl; }
template <typename Head, typename... Tail>
void debug_out(Head H, Tail... T) { cerr << " " << to_string(H); debug_out(T...); }
#ifdef LOCAL
#define debug(...) cerr << "[" << #__VA_ARGS__ << "]:", debug_out(__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define debug(...) 42
#endif
struct Node{
int u, d, l, r;
int val;
Node() {
u = d = l = r = -1; val = 0;
}
};
vector<Node> mp;
int R, C;
int getId(int x, int y) { return x * (C + 2) + y; }
void erase(int x) {
mp[mp[x].l].r = mp[x].r;
mp[mp[x].r].l = mp[x].l;
mp[mp[x].u].d = mp[x].d;
mp[mp[x].d].u = mp[x].u;
mp[x].val = 0;
}
vector<int> update(vector<int> &choosList, ll &ans, ll &origin) {
// debug(origin);
vector<int> needErase;
vector<int> newList, _newList;
ans += origin;
for(int i = 0, len = choosList.size(); i < len; ++i) {
int x = choosList[i];
int neiNum = 0; int neiVal = 0;
if(mp[mp[x].r].val != 0) { neiNum ++; neiVal += mp[mp[x].r].val; }
if(mp[mp[x].l].val != 0) { neiNum ++; neiVal += mp[mp[x].l].val; }
if(mp[mp[x].u].val != 0) { neiNum ++; neiVal += mp[mp[x].u].val; }
if(mp[mp[x].d].val != 0) { neiNum ++; neiVal += mp[mp[x].d].val; }
// debug(x / (C + 2), x % (C + 2), neiVal, neiNum, mp[x].val);
if(neiVal > mp[x].val * neiNum) {
// debug("erase", x / (C + 2), x % (C + 2));
origin -= mp[x].val;
needErase.push_back(x);
}
}
for(auto x : needErase) {
assert(mp[x].r != -1); assert(mp[x].l != -1); assert(mp[x].u != -1); assert(mp[x].d != -1);
if(mp[mp[x].r].val != 0) { _newList.push_back(mp[x].r); }
if(mp[mp[x].l].val != 0) { _newList.push_back(mp[x].l); }
if(mp[mp[x].u].val != 0) { _newList.push_back(mp[x].u); }
if(mp[mp[x].d].val != 0) { _newList.push_back(mp[x].d); }
erase(x);
}
for(auto it : _newList) {
if(mp[it].val != 0) newList.push_back(it);
}
sort(newList.begin(), newList.end());
newList.erase(unique(newList.begin(), newList.end()), newList.end());
// for(int i = 0, len = newList.size(); i < len; ++i) printf("%d %d: ", newList[i] / (C + 2), newList[i] % (C + 2)); printf("\n");
return newList;
}
int main() {
int T;
scanf("%d", &T);
for(int cas = 1; cas <= T; ++cas) {
mp.clear();
scanf("%d %d", &R, &C);
mp.resize( (R + 5) * (C + 5), Node());
ll origin = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= R; ++i) {
for(int j = 1; j <= C; ++j) {
scanf("%d", &mp[getId(i , j)].val);
origin += mp[getId(i , j)].val;
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= R; ++i) {
mp[getId(i , 1)].l = getId(i, 0);
for(int j = 1; j <= C; ++j) {
mp[getId(i , j - 1)].r = getId(i, j);
mp[getId(i , j + 1)].l = getId(i, j);
}
mp[getId(i , C)].r = getId(i, C + 1);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= C; ++i) {
mp[getId(1 , i)].u = getId(0, i);
for(int j = 1; j <= R; ++j) {
mp[getId(j - 1, i)].d = getId(j, i);
mp[getId(j + 1, i)].u = getId(j, i);
}
mp[getId(R, i)].d = getId(R + 1, i);
}
vector<int> choosList;
for(int i = 1; i <= R; ++i) {
for(int j = 1; j <= C; ++j) {
choosList.push_back(getId(i, j));
}
}
ll ans = 0;
while(1) {
choosList = update(choosList, ans, origin);
if(choosList.size() == 0) break;
}
printf("Case #%d: %lld\n", cas, ans);
}
return 0;
}
/*
4
1 1
15
3 3
1 1 1
1 2 1
1 1 1
1 3
3 1 2
1 3
1 2 3
3 3
1 100 1
1 2 2
1000 1 1
1 3
1 1
*/
Round 1A 2020 - Code Jam 2020的更多相关文章
- Google Code Jam 2020 Round1B Expogo
题意 你初始位于\((0,0)\),然后你想要到\((x,y)\)去,第\(i\)步的步长是\(2^{i-1}\),要求用最少的步数走到\((x,y)\). 解题思路 首先可以推出,走\(i\)步可以 ...
- Google Code Jam 2020 Round1B Join the Ranks
题意 给你一个形如\(1,2,\cdots,R,1,2,\cdots,R,1\cdots\)的序列,共重复\(C\)次.你每次可以选择一个区间\([L,R]\)将其平移到序列首部,最终使得序列具有\( ...
- Google Code Jam 2020 Round1B Blindfolded Bullseye
总结 这一题是道交互题,平时写的不多,没啥调试经验,GYM上遇到了少说交个十几发.一开始很快的想出了恰烂分的方法,但是没有着急写,果然很快就又把Test Set3的方法想到了,但是想到归想到,调了快一 ...
- [C++]Store Credit——Google Code Jam Qualification Round Africa 2010
Google Code Jam Qualification Round Africa 2010 的第一题,很简单. Problem You receive a credit C at a local ...
- Google Code Jam Africa 2010 Qualification Round Problem B. Reverse Words
Google Code Jam Africa 2010 Qualification Round Problem B. Reverse Words https://code.google.com/cod ...
- Google Code Jam Africa 2010 Qualification Round Problem A. Store Credit
Google Code Jam Qualification Round Africa 2010 Problem A. Store Credit https://code.google.com/code ...
- Google Code Jam 2010 Round 1C Problem A. Rope Intranet
Google Code Jam 2010 Round 1C Problem A. Rope Intranet https://code.google.com/codejam/contest/61910 ...
- ural 2020 Traffic Jam in Flower Town(模拟)
2020. Traffic Jam in Flower Town Time limit: 1.0 secondMemory limit: 64 MB Having returned from Sun ...
- Google Code Jam 2010 Round 1C Problem B. Load Testing
https://code.google.com/codejam/contest/619102/dashboard#s=p1&a=1 Problem Now that you have won ...
随机推荐
- vs code开发python时找不到当前目录下的文件、UnicodeDecodeError: 'gbk'
一.vs code开发python时找不到当前目录下的文件, file = open("readme.txt")一直报错,找不到目录下面的文件 原来vscode 默认都是以打开的项 ...
- C语言程序设计(一) 为什么要学C语言
第一章 为什么要学C语言 学编程的过程,其实就是学习怎样用编程语言说话,让编译器听懂的过程. 汇编语言缺少“可移植性” 除了机器语言和汇编语言以外,几乎所有的编程语言都被统称为高级语言,它的特点是更接 ...
- Python面向对象之:类空间问题以及类之间的关系
一. 类的空间问题 1.1 何处可以添加对象属性 class A: def __init__(self,name): self.name = name def func(self,sex): se ...
- MySQL 【优化宝典】
概述 为什么要优化 系统的吞吐量瓶颈往往出现在数据库的访问速度上 随着应用程序的运行,数据库的中的数据会越来越多,处理时间会相应变慢 数据是存放在磁盘上的,读写速度无法和内存相比 如何优化 设计数据库 ...
- .net webapi 接收保存图片到服务器,并居中剪裁压缩图片
原文链接:https:////www.cnblogs.com/Jackyye/p/12510943.html 每天解决一些c#小问题,在写微信小程序,或者一些手机软件接口,我们经常要用到上传图片到服务 ...
- failed to open directory
解决方法: 解决方案的路径不要包含中文!
- Python习题集(十三)
每天一习题,提升Python不是问题!!有更简洁的写法请评论告知我! https://www.cnblogs.com/poloyy/category/1676599.html 题目 写一个函数,该函数 ...
- 150多个Flutter组件详细介绍送给你
迷茫是什么,迷茫就是大事干不了,小事不想干,能力配不上欲望,才华配不上梦想. 150+Flutter组件详细介绍地址:http://laomengit.com/ 前言 我在Flutter未正式发布之前 ...
- angualrjs 总结 随记(二)
表单控制变量form 控制变量 //字段是否未更改 fromName.inputFieldName.$pristine //字段是否更改 fromName.inputFieldName.$dirty ...
- 前端html学习笔记
一 HTML介绍 1. Web服务的本质 import socket sk = socket.socket() sk.bind(("127.0.0.1", 8080)) sk.li ...
