java的多线程是如何实现的?和操作系统有什么关系?
本文是作者原创,版权归作者所有.若要转载,请注明出处.本文只贴我觉得比较重要的源码,其他不重要非关键的就不贴了
本文操作系统是centos7
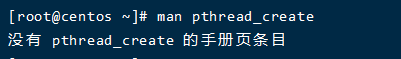
1.查看 pthread_create 函数显示及其示例
man pthread_create
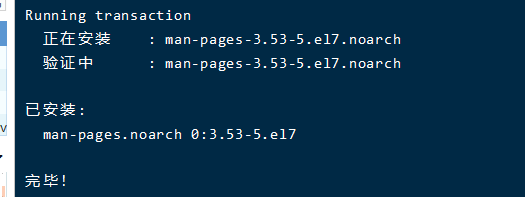
2.cengos下安装man手册命令:
yum install man-pages -y
3.重新查看 pthread_create 函数显示及其示例
man pthread_create
如下图
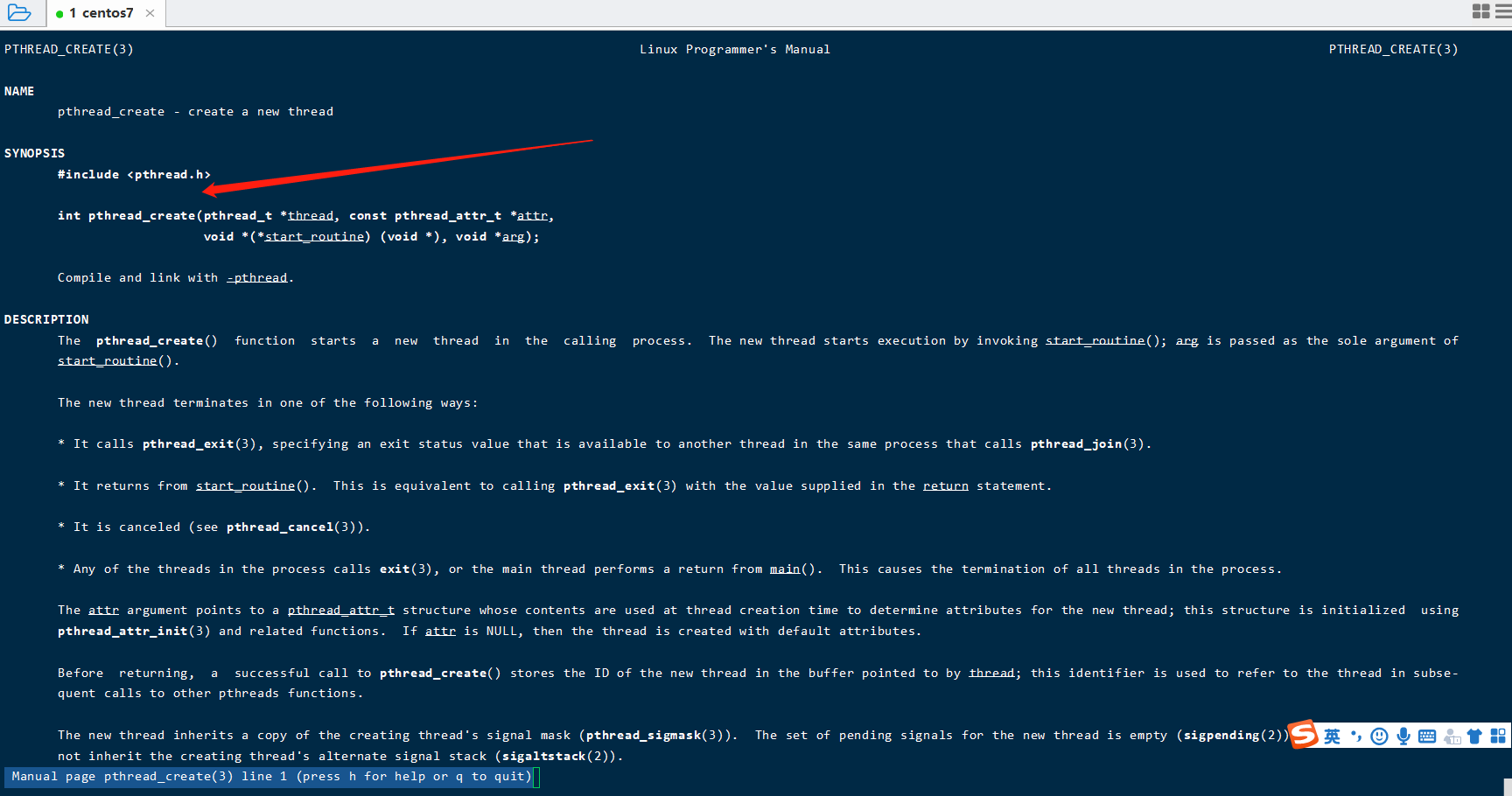
根据man配置的信息可以得出pthread_create会创建一个线程,这个函数是linux系统的函 数,可以用C或者C++直接调用,
上面信息也告诉程序员这个函数在pthread.h, 这个函数 有四个参数

一个小demo
#include <pthread.h>//头文件
#include <stdio.h>
pthread_t pid;//定义一个变量,接受创建线程后的线程id
//定义线程的主体函数
void* thread_entity(void* arg)
{
printf("i am new Thread!");
}
//main方法,程序入口,main和java的main一样会产生一个进程,继而产生一个main线程
int main()
{
//调用操作系统的函数创建线程,注意四个参数
pthread_create(&pid,NULL,thread_entity,NULL);
//usleep是睡眠的意思,那么这里的睡眠是让谁睡眠呢?
//为什么需要睡眠?如果不睡眠会出现什么情况
usleep(100);
printf("main\n");
}
4.那么java当中的线程和操作系统的线程是什么关系呢?,我们看下例子
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(){
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("i am new Thread!");
}
};
thread.start();
}
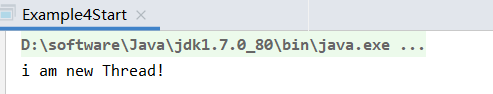
上述例子可以看出:我们启用线程是调用start方法,而非直接调用run方法
5.我们追踪start方法的源码:
public synchronized void start() {
/**
* This method is not invoked for the main method thread or "system"
* group threads created/set up by the VM. Any new functionality added
* to this method in the future may have to also be added to the VM.
*
* A zero status value corresponds to state "NEW".
*/
if (threadStatus != 0)
throw new IllegalThreadStateException();
/* Notify the group that this thread is about to be started
* so that it can be added to the group's list of threads
* and the group's unstarted count can be decremented. */
group.add(this);
boolean started = false;
try {
start0();//这行是关键代码
started = true;
} finally {
try {
if (!started) {
group.threadStartFailed(this);
}
} catch (Throwable ignore) {
/* do nothing. If start0 threw a Throwable then
it will be passed up the call stack */
}
}
}
6.继续追踪我注释的这行关键代码start0()
private native void start0();
这个是native方法,具体实现需要查看openjdk的源码
7.openjdk的写jni一般是一一对应的,Thread.java对应的就是Thread.c
static JNINativeMethod methods[] = {
{"start0", "()V", (void *)&JVM_StartThread},
{"stop0", "(" OBJ ")V", (void *)&JVM_StopThread},
{"isAlive", "()Z", (void *)&JVM_IsThreadAlive},
{"suspend0", "()V", (void *)&JVM_SuspendThread},
{"resume0", "()V", (void *)&JVM_ResumeThread},
{"setPriority0", "(I)V", (void *)&JVM_SetThreadPriority},
{"yield", "()V", (void *)&JVM_Yield},
{"sleep", "(J)V", (void *)&JVM_Sleep},
{"currentThread", "()" THD, (void *)&JVM_CurrentThread},
{"countStackFrames", "()I", (void *)&JVM_CountStackFrames},
{"interrupt0", "()V", (void *)&JVM_Interrupt},
{"isInterrupted", "(Z)Z", (void *)&JVM_IsInterrupted},
{"holdsLock", "(" OBJ ")Z", (void *)&JVM_HoldsLock},
{"getThreads", "()[" THD, (void *)&JVM_GetAllThreads},
{"dumpThreads", "([" THD ")[[" STE, (void *)&JVM_DumpThreads},
{"setNativeName", "(" STR ")V", (void *)&JVM_SetNativeThreadName},
};
8.start0其实就是JVM_StartThread。在jvm.h中找到了声明
/*
* java.lang.Thread
*/
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL
JVM_StartThread(JNIEnv *env, jobject thread);
9.在jvm.cpp中有实现,如下
JVM_ENTRY(void, JVM_StartThread(JNIEnv* env, jobject jthread))
JVMWrapper("JVM_StartThread");
JavaThread *native_thread = NULL; // We cannot hold the Threads_lock when we throw an exception,
// due to rank ordering issues. Example: we might need to grab the
// Heap_lock while we construct the exception.
bool throw_illegal_thread_state = false; // We must release the Threads_lock before we can post a jvmti event
// in Thread::start.
{
// Ensure that the C++ Thread and OSThread structures aren't freed before
// we operate.
MutexLocker mu(Threads_lock); // Since JDK 5 the java.lang.Thread threadStatus is used to prevent
// re-starting an already started thread, so we should usually find
// that the JavaThread is null. However for a JNI attached thread
// there is a small window between the Thread object being created
// (with its JavaThread set) and the update to its threadStatus, so we
// have to check for this
if (java_lang_Thread::thread(JNIHandles::resolve_non_null(jthread)) != NULL) {
throw_illegal_thread_state = true;
} else {
// We could also check the stillborn flag to see if this thread was already stopped, but
// for historical reasons we let the thread detect that itself when it starts running jlong size =
java_lang_Thread::stackSize(JNIHandles::resolve_non_null(jthread));
// Allocate the C++ Thread structure and create the native thread. The
// stack size retrieved from java is signed, but the constructor takes
// size_t (an unsigned type), so avoid passing negative values which would
// result in really large stacks.
size_t sz = size > 0 ? (size_t) size : 0;
native_thread = new JavaThread(&thread_entry, sz);//关键代码 // At this point it may be possible that no osthread was created for the
// JavaThread due to lack of memory. Check for this situation and throw
// an exception if necessary. Eventually we may want to change this so
// that we only grab the lock if the thread was created successfully -
// then we can also do this check and throw the exception in the
// JavaThread constructor.
if (native_thread->osthread() != NULL) {
// Note: the current thread is not being used within "prepare".
native_thread->prepare(jthread);
}
}
} if (throw_illegal_thread_state) {
THROW(vmSymbols::java_lang_IllegalThreadStateException());
} assert(native_thread != NULL, "Starting null thread?"); if (native_thread->osthread() == NULL) {
// No one should hold a reference to the 'native_thread'.
delete native_thread;
if (JvmtiExport::should_post_resource_exhausted()) {
JvmtiExport::post_resource_exhausted(
JVMTI_RESOURCE_EXHAUSTED_OOM_ERROR | JVMTI_RESOURCE_EXHAUSTED_THREADS,
"unable to create new native thread");
}
THROW_MSG(vmSymbols::java_lang_OutOfMemoryError(),
"unable to create new native thread");
} Thread::start(native_thread); JVM_END
10.大概浏览上下文,native_thread的构造应该是在JavaThread的构造中完成的.再看new JavaThread(...)这步
JavaThread::JavaThread(ThreadFunction entry_point, size_t stack_sz) :
Thread()
#if INCLUDE_ALL_GCS
, _satb_mark_queue(&_satb_mark_queue_set),
_dirty_card_queue(&_dirty_card_queue_set)
#endif // INCLUDE_ALL_GCS
{
if (TraceThreadEvents) {
tty->print_cr("creating thread %p", this);
}
initialize();
_jni_attach_state = _not_attaching_via_jni;
set_entry_point(entry_point);
os::ThreadType thr_type = os::java_thread;
thr_type = entry_point == &compiler_thread_entry ? os::compiler_thread :
os::java_thread;
os::create_thread(this, thr_type, stack_sz);//这里创建线程
_safepoint_visible = false; }
11.到了os::create_thread这步,具体实现在os_linux.cpp中(这里我们只说linux的,其他系统的实现就不在这里了)
bool os::create_thread(Thread* thread, ThreadType thr_type, size_t stack_size) {
assert(thread->osthread() == NULL, "caller responsible");
// Allocate the OSThread object
OSThread* osthread = new OSThread(NULL, NULL);
if (osthread == NULL) {
return false;
}
// set the correct thread state
osthread->set_thread_type(thr_type);
// Initial state is ALLOCATED but not INITIALIZED
osthread->set_state(ALLOCATED);
thread->set_osthread(osthread);
// init thread attributes
pthread_attr_t attr;
pthread_attr_init(&attr);
pthread_attr_setdetachstate(&attr, PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED);
// stack size
if (os::Linux::supports_variable_stack_size()) {
// calculate stack size if it's not specified by caller
if (stack_size == 0) {
stack_size = os::Linux::default_stack_size(thr_type);
switch (thr_type) {
case os::java_thread:
// Java threads use ThreadStackSize which default value can be
// changed with the flag -Xss
assert (JavaThread::stack_size_at_create() > 0, "this should be set");
stack_size = JavaThread::stack_size_at_create();
break;
case os::compiler_thread:
if (CompilerThreadStackSize > 0) {
stack_size = (size_t)(CompilerThreadStackSize * K);
break;
} // else fall through:
// use VMThreadStackSize if CompilerThreadStackSize is not defined
case os::vm_thread:
case os::pgc_thread:
case os::cgc_thread:
case os::watcher_thread:
if (VMThreadStackSize > 0) stack_size = (size_t)(VMThreadStackSize * K);
break;
}
}
stack_size = MAX2(stack_size, os::Linux::min_stack_allowed);
pthread_attr_setstacksize(&attr, stack_size);
} else {
// let pthread_create() pick the default value.
}
// glibc guard page
pthread_attr_setguardsize(&attr, os::Linux::default_guard_size(thr_type));
ThreadState state;
{
// Serialize thread creation if we are running with fixed stack LinuxThreads
bool lock = os::Linux::is_LinuxThreads() && !os::Linux::is_floating_stack();
if (lock) {
os::Linux::createThread_lock()->lock_without_safepoint_check();
}
pthread_t tid;
int ret = pthread_create(&tid, &attr, (void* (*)(void*)) java_start, thread);//看这行代码,是不是就是linux系统的线程调用函数
pthread_attr_destroy(&attr);
if (ret != 0) {
if (PrintMiscellaneous && (Verbose || WizardMode)) {
perror("pthread_create()");
}
// Need to clean up stuff we've allocated so far
thread->set_osthread(NULL);
delete osthread;
if (lock) os::Linux::createThread_lock()->unlock();
return false;
}
// Store pthread info into the OSThread
osthread->set_pthread_id(tid);
// Wait until child thread is either initialized or aborted
{
Monitor* sync_with_child = osthread->startThread_lock();
MutexLockerEx ml(sync_with_child, Mutex::_no_safepoint_check_flag);
while ((state = osthread->get_state()) == ALLOCATED) {
sync_with_child->wait(Mutex::_no_safepoint_check_flag);
}
}
if (lock) {
os::Linux::createThread_lock()->unlock();
}
}
// Aborted due to thread limit being reached
if (state == ZOMBIE) {
thread->set_osthread(NULL);
delete osthread;
return false;
}
// The thread is returned suspended (in state INITIALIZED),
// and is started higher up in the call chain
assert(state == INITIALIZED, "race condition");
return true;
}
12.这里终于看到了系统库函数的调用。,看我注释的那行代码,是不是就是linux系统的线程调用函数pthread_create
调用线程执行的方法是java_start,参数是thread
看下源码
// Thread start routine for all newly created threads
static void *java_start(Thread *thread) {
// Try to randomize the cache line index of hot stack frames.
// This helps when threads of the same stack traces evict each other's
// cache lines. The threads can be either from the same JVM instance, or
// from different JVM instances. The benefit is especially true for
// processors with hyperthreading technology.
static int counter = 0;
int pid = os::current_process_id();
alloca(((pid ^ counter++) & 7) * 128); ThreadLocalStorage::set_thread(thread); OSThread* osthread = thread->osthread();
Monitor* sync = osthread->startThread_lock(); // non floating stack LinuxThreads needs extra check, see above
if (!_thread_safety_check(thread)) {
// notify parent thread
MutexLockerEx ml(sync, Mutex::_no_safepoint_check_flag);
osthread->set_state(ZOMBIE);
sync->notify_all();
return NULL;
} // thread_id is kernel thread id (similar to Solaris LWP id)
osthread->set_thread_id(os::Linux::gettid()); if (UseNUMA) {
int lgrp_id = os::numa_get_group_id();
if (lgrp_id != -1) {
thread->set_lgrp_id(lgrp_id);
}
}
// initialize signal mask for this thread
os::Linux::hotspot_sigmask(thread); // initialize floating point control register
os::Linux::init_thread_fpu_state(); // handshaking with parent thread
{
MutexLockerEx ml(sync, Mutex::_no_safepoint_check_flag); // notify parent thread
osthread->set_state(INITIALIZED);
sync->notify_all(); // wait until os::start_thread()
while (osthread->get_state() == INITIALIZED) {
sync->wait(Mutex::_no_safepoint_check_flag);
}
} // call one more level start routine
thread->run();//终于找到run方法了 return 0;
}
13.这个方法可以直接跳到最后一行,他执行的是传递过来对象的run方法
14.总结:由上面源码可以看到:Java的多线程是直接调用linux的多线程函数实现的
每个继承java.lang.Thread的类,调用start方法之后,都调用start0()的native方法;
start0()的native方法在openjdk里调用的是JVM_StartThread;
JVM_StartThread最终调用的是操作系统的pthread_create()函数,有四个参数,我们写的run方法就是该函数的第三个参数.
java的多线程是如何实现的?和操作系统有什么关系?的更多相关文章
- Java的多线程机制系列:不得不提的volatile及指令重排序(happen-before)
一.不得不提的volatile volatile是个很老的关键字,几乎伴随着JDK的诞生而诞生,我们都知道这个关键字,但又不太清楚什么时候会使用它:我们在JDK及开源框架中随处可见这个关键字,但并发专 ...
- java线程 - 多线程 - 守护线程
1.多线程执行者/处理类 都是Runnable的实现类(如自定义类实现Runnable 或 java原生的Thread.FutureTask),但最后都必须封装成Thread线程类由Thread.st ...
- java之多线程 二
线程的生命周期: 当线程被创建并被启动时,它既不是一启动就进入了执行状态,在线程的生命周期中,它要经过new(新建),就绪(Runnable),运行(Running),阻塞(Blocked),dead ...
- Java的多线程机制系列:(一)总述及基础概念
前言 这一系列多线程的文章,一方面是个人对Java现有的多线程机制的学习和记录,另一方面是希望能给不熟悉Java多线程机制.或有一定基础但理解还不够深的读者一个比较全面的介绍,旨在使读者对Java的多 ...
- Java Thread 多线程 介绍
1.线程概述 几乎所有的操作系统都支持同时运行多个任务,一个任务通常就是一个程序,每个运行中的程序就是一个进程. 当一个程序运行时,内部可能包含了多个顺序执行流,每个顺序执行流就是一个线程. 2.线程 ...
- Java:多线程<一>
程序运行时,其实是CPU在执行程序的进程,为了提高工作效率一个进程可以有多个线程. Java的多线程: 其实我们之前就见过Java的线程,main就是Java的一个线程,还有另一个条线程总是和main ...
- Java的多线程机制系列:(四)不得不提的volatile及指令重排序(happen-before)
一.不得不提的volatile volatile是个很老的关键字,几乎伴随着JDK的诞生而诞生,我们都知道这个关键字,但又不太清楚什么时候会使用它:我们在JDK及开源框架中随处可见这个关键字,但并发专 ...
- Java的多线程机制系列:(三)synchronized的同步原理
synchronized关键字是JDK5之实现锁(包括互斥性和可见性)的唯一途径(volatile关键字能保证可见性,但不能保证互斥性,详细参见后文关于vloatile的详述章节),其在字节码上编译为 ...
- Java基础——多线程
Java中多线程的应用是非常多的,我们在Java中又该如何去创建线程呢? http://www.jianshu.com/p/40d4c7aebd66 一.常用的有三种方法来创建多线程 新建一个类继承自 ...
随机推荐
- Journal of Proteome Research | 人类牙槽骨蛋白的蛋白质组学和n端分析:改进的蛋白质提取方法和LysargiNase消化策略增加了蛋白质组的覆盖率和缺失蛋白的识别 | (解读人:卜繁宇)
文献名:Proteomic and N-Terminomic TAILS Analyses of Human Alveolar Bone Proteins: Improved Protein Extr ...
- 遍历集合的常见方式,排序,用lambda表示是怎样的
Collection集合的功能: Object[] toArray() 将集合转成数组 Iterator iterator() 通过方法的调用 获取I ...
- tcp\udp 操作系统发展史
目录 为什么会出现粘包现象 socket发送大文件示例 UDP协议 基于UDP实现简易版本的qq 总结: SocketServer模块介绍(让tcp也能支持并发) 为什么会出现粘包现象 TCP 三次握 ...
- no parameterless constructor define for type 解决一例
在生成根据模型和上下文生成带增删查改操作的视图的控制器时,提示上述信息,网上查找了资料也没有解决,突然想起该项目是连接MSSQL数据库和Redis数据库的,并且已经依赖注入了,而Redis数据库的服务 ...
- Trie树的简单实现
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.TreeMap; import util.FileOperation; public class Trie { ...
- C#中的9个“黑魔法”与“骚操作”
C#中的9个"黑魔法"与"骚操作" 我们知道C#是非常先进的语言,因为是它很有远见的"语法糖".这些"语法糖"有时过于好 ...
- IO多路复用(IO Multiplexing)
什么是IO多路复用 为什么要有IO多路复用 作者总结 遵循学习新知识的三部曲:是什么?为什么?怎么用? 作者前言:IO多路复用本质上是网络通信过程中的一个技术名词. 什么是IO多路复用 一个用机场管理 ...
- pyplot 作图总结
折线图 下面是绘制折线图,设置图片的横轴纵轴标签,图片标题的API的用法. import matplotlib.pyplot as pyplot # init pyplot.figure() # ar ...
- 深度学习中正则化技术概述(附Python代码)
欢迎大家关注我们的网站和系列教程:http://www.tensorflownews.com/,学习更多的机器学习.深度学习的知识! 磐石 介绍 数据科学研究者们最常遇见的问题之一就是怎样避免过拟合. ...
- javascript中的符号 == 和 === 的区别
== 表示相等 即仅仅比较两边变量的数值是否相等. 相等运算符隐藏的类型转换,会带来一些违反直觉的结果. 这就是为什么建议尽量不要使用相等运算符. 至于使用相等运算符会不会对后续代码造成意外影响,答 ...
