Android 7.1 屏幕旋转流程分析
Android 7.1 屏幕旋转流程分析
一、概述
Android屏幕的旋转在framework主要涉及到三个类,结构如图
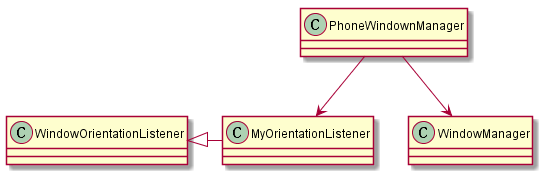
PhoneWindowManager:为屏幕的横竖屏转换的管理类。
WindowOrientationListener: 是一个传感器的listener的基类,PhoneWindowManager的MyOrientationListener继承自该基类。
WindowManagerService:是具体实施屏幕旋转的工作。
代码路径:
PhoneWindowManager:
路径:/frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/policy/PhoneWindowManager.java
WindowOrientationListener:
路径:
/frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/policy/WindowOrientationListener.java
WindowManagerService:
路径:
/fram eworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowManagerService.java
总的流程大致如下:
PhoneWindowManager实现一个MyOrientationListener用来注册和监听传感器(屏幕)变化,根据用户设置情况(是否允许屏幕旋转)来启动和关闭监听。当屏幕方向变化时PhoneWindowManager通过调用 WindowManagerService具体来完成屏幕的旋转。
二、流程分析
1)PhoneWindownManager 开启监听
A: 监听用户设置的变化
PhoneWindownManager 通过注册一个ContentObserver来监听用户设置的变化,当用户设置变化后调用updateSettings()函数,做设置变化的更新和做相应的动作。
class SettingsObserver extends ContentObserver {
SettingsObserver(Handler handler) {
super(handler);
}
void observe() {
// Observe all users' changes
ContentResolver resolver = mContext.getContentResolver();
resolver.registerContentObserver(Settings.System.getUriFor(
Settings.System.END_BUTTON_BEHAVIOR), false, this,
UserHandle.USER_ALL);
resolver.registerContentObserver(Settings.Secure.getUriFor(
Settings.Secure.INCALL_POWER_BUTTON_BEHAVIOR), false, this,
UserHandle.USER_ALL);
resolver.registerContentObserver(Settings.Secure.getUriFor(
Settings.Secure.INCALL_BACK_BUTTON_BEHAVIOR), false, this,
UserHandle.USER_ALL);
resolver.registerContentObserver(Settings.Secure.getUriFor(
Settings.Secure.WAKE_GESTURE_ENABLED), false, this,
UserHandle.USER_ALL);
resolver.registerContentObserver(Settings.System.getUriFor(
Settings.System.ACCELEROMETER_ROTATION), false, this,
UserHandle.USER_ALL);
resolver.registerContentObserver(Settings.System.getUriFor(
Settings.System.USER_ROTATION), false, this,
UserHandle.USER_ALL);
resolver.registerContentObserver(Settings.System.getUriFor(
Settings.System.SCREEN_OFF_TIMEOUT), false, this,
UserHandle.USER_ALL);
resolver.registerContentObserver(Settings.System.getUriFor(
Settings.System.POINTER_LOCATION), false, this,
UserHandle.USER_ALL);
resolver.registerContentObserver(Settings.Secure.getUriFor(
Settings.Secure.DEFAULT_INPUT_METHOD), false, this,
UserHandle.USER_ALL);
resolver.registerContentObserver(Settings.Secure.getUriFor(
Settings.Secure.IMMERSIVE_MODE_CONFIRMATIONS), false, this,
UserHandle.USER_ALL);
resolver.registerContentObserver(Settings.Global.getUriFor(
Settings.Global.POLICY_CONTROL), false, this,
UserHandle.USER_ALL);
updateSettings();
}
@Override public void onChange(boolean selfChange) {
updateSettings();
updateRotation(false);
}
}
B:监听传感器(设备方向)的变化
PhoneWindownManager是通过其中的updateSettings()函数来更新用户的设定来判断是否需要启动方向监听(即设置中的屏幕锁定按钮),如果允许屏幕旋转则去注册传感器的监听。
public void updateSettings() {
ContentResolver resolver = mContext.getContentResolver();
boolean updateRotation = false;
synchronized (mLock) {
。。。。。。。。。
// Configure rotation lock.
int userRotation = Settings.System.getIntForUser(resolver,
Settings.System.USER_ROTATION, Surface.ROTATION_0,
UserHandle.USER_CURRENT);
if (mUserRotation != userRotation) {
mUserRotation = userRotation;
updateRotation = true;
}
int userRotationMode = Settings.System.getIntForUser(resolver,
Settings.System.ACCELEROMETER_ROTATION, 0, UserHandle.USER_CURRENT) != 0 ?
WindowManagerPolicy.USER_ROTATION_FREE :
WindowManagerPolicy.USER_ROTATION_LOCKED;
if (mUserRotationMode != userRotationMode) {
mUserRotationMode = userRotationMode;
updateRotation = true;
updateOrientationListenerLp();
}
if (mSystemReady) {
int pointerLocation = Settings.System.getIntForUser(resolver,
Settings.System.POINTER_LOCATION, 0, UserHandle.USER_CURRENT);
if (mPointerLocationMode != pointerLocation) {
mPointerLocationMode = pointerLocation;
mHandler.sendEmptyMessage(pointerLocation != 0 ?
MSG_ENABLE_POINTER_LOCATION : MSG_DISABLE_POINTER_LOCATION);
}
}
// use screen off timeout setting as the timeout for the lockscreen
mLockScreenTimeout = Settings.System.getIntForUser(resolver,
Settings.System.SCREEN_OFF_TIMEOUT, 0, UserHandle.USER_CURRENT);
String imId = Settings.Secure.getStringForUser(resolver,
Settings.Secure.DEFAULT_INPUT_METHOD, UserHandle.USER_CURRENT);
boolean hasSoftInput = imId != null && imId.length() > 0;
if (mHasSoftInput != hasSoftInput) {
mHasSoftInput = hasSoftInput;
updateRotation = true;
}
if (mImmersiveModeConfirmation != null) {
mImmersiveModeConfirmation.loadSetting(mCurrentUserId);
}
}
synchronized (mWindowManagerFuncs.getWindowManagerLock()) {
PolicyControl.reloadFromSetting(mContext);
}
if (updateRotation) {
updateRotation(true);
}
}
C: updateOrientationListenerLp()函数多种场景下都会被调用:(注释很清楚无需解释)
(1) screen turning off, should always disable listeners if already enabled
(2) screen turned on and current app has sensor based orientation, enable listeners if not already enabled
(3) screen turned on and current app does not have sensor orientation, disable listeners if already enabled
(4) screen turning on and current app has sensor based orientation, enable listeners if needed
(5) screen turning on and current app has nosensor based orientation, do nothing
void updateOrientationListenerLp() {
if (!mOrientationListener.canDetectOrientation()) {
// If sensor is turned off or nonexistent for some reason
return;
}
// Could have been invoked due to screen turning on or off or
// change of the currently visible window's orientation.
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, "mScreenOnEarly=" + mScreenOnEarly
+ ", mAwake=" + mAwake + ", mCurrentAppOrientation=" + mCurrentAppOrientation
+ ", mOrientationSensorEnabled=" + mOrientationSensorEnabled
+ ", mKeyguardDrawComplete=" + mKeyguardDrawComplete
+ ", mWindowManagerDrawComplete=" + mWindowManagerDrawComplete);
boolean disable = true;
// Note: We postpone the rotating of the screen until the keyguard as well as the
// window manager have reported a draw complete.
if (mScreenOnEarly && mAwake &&
mKeyguardDrawComplete && mWindowManagerDrawComplete) {
if (needSensorRunningLp()) {
disable = false;
//enable listener if not already enabled
if (!mOrientationSensorEnabled) {
mOrientationListener.enable();
if(localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, "Enabling listeners");
mOrientationSensorEnabled = true;
}
}
}
//check if sensors need to be disabled
if (disable && mOrientationSensorEnabled) {
mOrientationListener.disable();
if(localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, "Disabling listeners");
mOrientationSensorEnabled = false;
}
}
D: WindowOrientationListener的enable()和disable()
启动和取消传感器事件的监听,是通过调 SensorManager.registerListener()和SensorManager.unregisterListener()函数来完成的,与APP 的传感器事件的监听和取消监听用法没有区别。
/**
* Enables the WindowOrientationListener so it will monitor the sensor and call
* {@link #onProposedRotationChanged(int)} when the device orientation changes.
*/
public void enable() {
synchronized (mLock) {
if (mSensor == null) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Cannot detect sensors. Not enabled");
return;
}
if (mEnabled == false) {
if (LOG) {
Slog.d(TAG, "WindowOrientationListener enabled");
}
mOrientationJudge.resetLocked();
if (mSensor.getType() == Sensor.TYPE_ACCELEROMETER) {
mSensorManager.registerListener(
mOrientationJudge, mSensor, mRate, DEFAULT_BATCH_LATENCY, mHandler);
} else {
mSensorManager.registerListener(mOrientationJudge, mSensor, mRate, mHandler);
}
mEnabled = true;
}
}
} /**
* Disables the WindowOrientationListener.
*/
public void disable() {
synchronized (mLock) {
if (mSensor == null) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Cannot detect sensors. Invalid disable");
return;
}
if (mEnabled == true) {
if (LOG) {
Slog.d(TAG, "WindowOrientationListener disabled");
}
mSensorManager.unregisterListener(mOrientationJudge);
mEnabled = false;
}
}
}
2)sensor事件回调
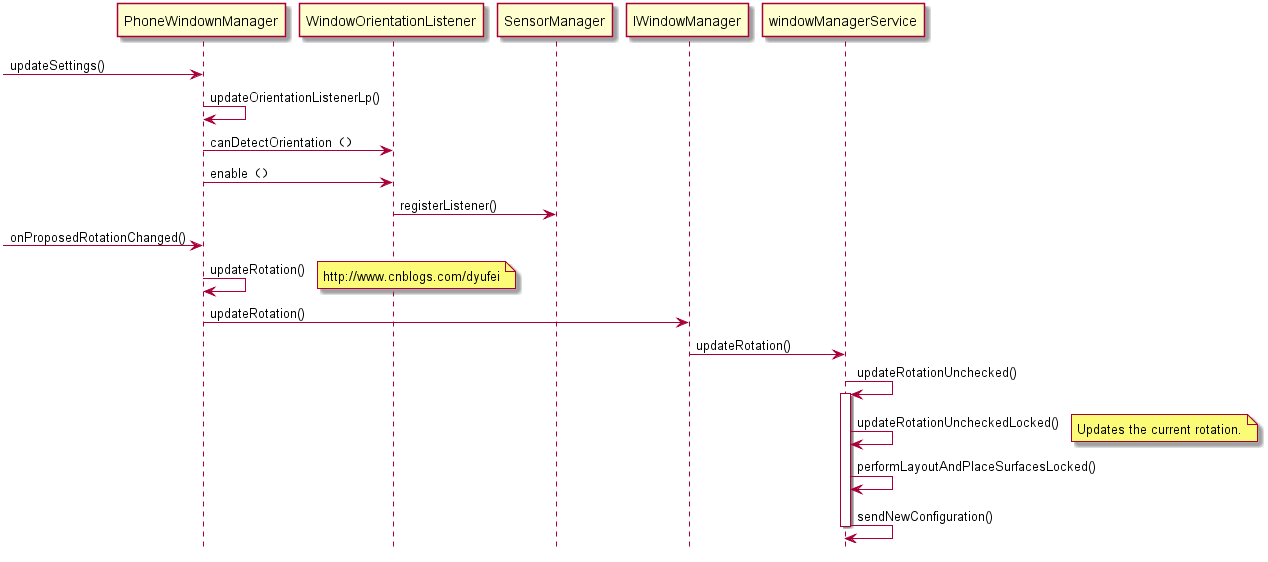
传感器事件是通过WindowOrientationListener 的onProposedRotationChanged()接口回调到PhoneWindownManager中的,然后通过updateRotation()调用windowManagerService的updateRotation()做屏幕旋转。
首先调用PowerManagerInternal.powerHint()来提升cpu的频率来提高屏幕旋转时候的性能,然后调用WindowManager.updateRotation()做屏幕旋转,屏幕旋转的实际操作是由WindowManagerService实际来完成的。
class MyOrientationListener extends WindowOrientationListener {
private final Runnable mUpdateRotationRunnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// send interaction hint to improve redraw performance
mPowerManagerInternal.powerHint(PowerManagerInternal.POWER_HINT_INTERACTION, 0);
updateRotation(false);
}
};
MyOrientationListener(Context context, Handler handler) {
super(context, handler);
}
@Override
public void onProposedRotationChanged(int rotation) {
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, "onProposedRotationChanged, rotation=" + rotation);
mHandler.post(mUpdateRotationRunnable);
}
}
void updateRotation(boolean alwaysSendConfiguration) {
try {
//set orientation on WindowManager
mWindowManager.updateRotation(alwaysSendConfiguration, false);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// Ignore
}
}
3)WindowManagerService做屏幕旋转
WindowManagerService 大致完成三件事,首先更新屏幕方向,然后具体实施屏幕旋转,最后通知AMS configuration变更。
具体实施屏幕旋转的函数是updateRotationUncheckedLocked()这部分详细旋转过程单独详细分析。
@Override
public void updateRotation(boolean alwaysSendConfiguration, boolean forceRelayout) {
updateRotationUnchecked(alwaysSendConfiguration, forceRelayout);
}
public void updateRotationUnchecked(boolean alwaysSendConfiguration, boolean forceRelayout) {
if(DEBUG_ORIENTATION) Slog.v(TAG_WM, "updateRotationUnchecked("
+ "alwaysSendConfiguration=" + alwaysSendConfiguration + ")");
long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
boolean changed;
synchronized(mWindowMap) {
changed = updateRotationUncheckedLocked(false);
if (!changed || forceRelayout) {
getDefaultDisplayContentLocked().layoutNeeded = true;
mWindowPlacerLocked.performSurfacePlacement();
}
}
if (changed || alwaysSendConfiguration) {
sendNewConfiguration();
}
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
public boolean updateRotationUncheckedLocked(boolean inTransaction) {
if (mDeferredRotationPauseCount > 0) {
// Rotation updates have been paused temporarily. Defer the update until
// updates have been resumed.
if (DEBUG_ORIENTATION) Slog.v(TAG_WM, "Deferring rotation, rotation is paused.");
return false;
}
ScreenRotationAnimation screenRotationAnimation =
mAnimator.getScreenRotationAnimationLocked(Display.DEFAULT_DISPLAY);
if (screenRotationAnimation != null && screenRotationAnimation.isAnimating()) {
// Rotation updates cannot be performed while the previous rotation change
// animation is still in progress. Skip this update. We will try updating
// again after the animation is finished and the display is unfrozen.
if (DEBUG_ORIENTATION) Slog.v(TAG_WM, "Deferring rotation, animation in progress.");
return false;
}
if (mDisplayFrozen) {
// Even if the screen rotation animation has finished (e.g. isAnimating
// returns false), there is still some time where we haven't yet unfrozen
// the display. We also need to abort rotation here.
if (DEBUG_ORIENTATION) Slog.v(TAG_WM, "Deferring rotation, still finishing previous rotation");
return false;
}
if (!mDisplayEnabled) {
// No point choosing a rotation if the display is not enabled.
if (DEBUG_ORIENTATION) Slog.v(TAG_WM, "Deferring rotation, display is not enabled.");
return false;
}
final DisplayContent displayContent = getDefaultDisplayContentLocked();
final WindowList windows = displayContent.getWindowList();
final int oldRotation = mRotation;
int rotation = mPolicy.rotationForOrientationLw(mLastOrientation, mRotation);
boolean rotateSeamlessly = mPolicy.shouldRotateSeamlessly(oldRotation, rotation);
if (rotateSeamlessly) {
for (int i = windows.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
WindowState w = windows.get(i);
// We can't rotate (seamlessly or not) while waiting for the last seamless rotation
// to complete (that is, waiting for windows to redraw). It's tempting to check
// w.mSeamlessRotationCount but that could be incorrect in the case of window-removal.
if (w.mSeamlesslyRotated) {
return false;
}
// In what can only be called an unfortunate workaround we require
// seamlessly rotated child windows to have the TRANSFORM_TO_DISPLAY_INVERSE
// flag. Due to limitations in the client API, there is no way for
// the client to set this flag in a race free fashion. If we seamlessly rotate
// a window which does not have this flag, but then gains it, we will get
// an incorrect visual result (rotated viewfinder). This means if we want to
// support seamlessly rotating windows which could gain this flag, we can't
// rotate windows without it. This limits seamless rotation in N to camera framework
// users, windows without children, and native code. This is unfortunate but
// having the camera work is our primary goal.
if (w.isChildWindow() & w.isVisibleNow() &&
!w.mWinAnimator.mSurfaceController.getTransformToDisplayInverse()) {
rotateSeamlessly = false;
}
}
}
// TODO: Implement forced rotation changes.
// Set mAltOrientation to indicate that the application is receiving
// an orientation that has different metrics than it expected.
// eg. Portrait instead of Landscape.
boolean altOrientation = !mPolicy.rotationHasCompatibleMetricsLw(
mLastOrientation, rotation);
if (DEBUG_ORIENTATION) {
Slog.v(TAG_WM, "Selected orientation "
+ mLastOrientation + ", got rotation " + rotation
+ " which has " + (altOrientation ? "incompatible" : "compatible")
+ " metrics");
}
if (mRotation == rotation && mAltOrientation == altOrientation) {
// No change.
return false;
}
if (DEBUG_ORIENTATION) {
Slog.v(TAG_WM,
"Rotation changed to " + rotation + (altOrientation ? " (alt)" : "")
+ " from " + mRotation + (mAltOrientation ? " (alt)" : "")
+ ", lastOrientation=" + mLastOrientation);
}
mRotation = rotation;
mAltOrientation = altOrientation;
mPolicy.setRotationLw(mRotation);
mWindowsFreezingScreen = WINDOWS_FREEZING_SCREENS_ACTIVE;
mH.removeMessages(H.WINDOW_FREEZE_TIMEOUT);
mH.sendEmptyMessageDelayed(H.WINDOW_FREEZE_TIMEOUT, WINDOW_FREEZE_TIMEOUT_DURATION);
mWaitingForConfig = true;
displayContent.layoutNeeded = true;
final int[] anim = new int[2];
if (displayContent.isDimming()) {
anim[0] = anim[1] = 0;
} else {
mPolicy.selectRotationAnimationLw(anim);
}
if (!rotateSeamlessly) {
startFreezingDisplayLocked(inTransaction, anim[0], anim[1]);
// startFreezingDisplayLocked can reset the ScreenRotationAnimation.
screenRotationAnimation =
mAnimator.getScreenRotationAnimationLocked(Display.DEFAULT_DISPLAY);
} else {
// The screen rotation animation uses a screenshot to freeze the screen
// while windows resize underneath.
// When we are rotating seamlessly, we allow the elements to transition
// to their rotated state independently and without a freeze required.
screenRotationAnimation = null;
// We have to reset this in case a window was removed before it
// finished seamless rotation.
mSeamlessRotationCount = 0;
}
// We need to update our screen size information to match the new rotation. If the rotation
// has actually changed then this method will return true and, according to the comment at
// the top of the method, the caller is obligated to call computeNewConfigurationLocked().
// By updating the Display info here it will be available to
// computeScreenConfigurationLocked later.
updateDisplayAndOrientationLocked(mCurConfiguration.uiMode);
final DisplayInfo displayInfo = displayContent.getDisplayInfo();
if (!inTransaction) {
if (SHOW_TRANSACTIONS) {
Slog.i(TAG_WM, ">>> OPEN TRANSACTION setRotationUnchecked");
}
SurfaceControl.openTransaction();
}
try {
// NOTE: We disable the rotation in the emulator because
// it doesn't support hardware OpenGL emulation yet.
if (CUSTOM_SCREEN_ROTATION && screenRotationAnimation != null
&& screenRotationAnimation.hasScreenshot()) {
if (screenRotationAnimation.setRotationInTransaction(
rotation, mFxSession,
MAX_ANIMATION_DURATION, getTransitionAnimationScaleLocked(),
displayInfo.logicalWidth, displayInfo.logicalHeight)) {
scheduleAnimationLocked();
}
}
if (rotateSeamlessly) {
for (int i = windows.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
WindowState w = windows.get(i);
w.mWinAnimator.seamlesslyRotateWindow(oldRotation, mRotation);
}
}
mDisplayManagerInternal.performTraversalInTransactionFromWindowManager();
} finally {
if (!inTransaction) {
SurfaceControl.closeTransaction();
if (SHOW_LIGHT_TRANSACTIONS) {
Slog.i(TAG_WM, "<<< CLOSE TRANSACTION setRotationUnchecked");
}
}
}
for (int i = windows.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
WindowState w = windows.get(i);
// Discard surface after orientation change, these can't be reused.
if (w.mAppToken != null) {
w.mAppToken.destroySavedSurfaces();
}
if (w.mHasSurface && !rotateSeamlessly) {
if (DEBUG_ORIENTATION) Slog.v(TAG_WM, "Set mOrientationChanging of " + w);
w.mOrientationChanging = true;
mWindowPlacerLocked.mOrientationChangeComplete = false;
w.mLastFreezeDuration = 0;
}
}
if (rotateSeamlessly) {
mH.removeMessages(H.SEAMLESS_ROTATION_TIMEOUT);
mH.sendEmptyMessageDelayed(H.SEAMLESS_ROTATION_TIMEOUT, SEAMLESS_ROTATION_TIMEOUT_DURATION);
}
for (int i=mRotationWatchers.size()-1; i>=0; i--) {
try {
mRotationWatchers.get(i).watcher.onRotationChanged(rotation);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
}
// TODO (multidisplay): Magnification is supported only for the default display.
// Announce rotation only if we will not animate as we already have the
// windows in final state. Otherwise, we make this call at the rotation end.
if (screenRotationAnimation == null && mAccessibilityController != null
&& displayContent.getDisplayId() == Display.DEFAULT_DISPLAY) {
mAccessibilityController.onRotationChangedLocked(getDefaultDisplayContentLocked(),
rotation);
}
return true;
}
Android 7.1 屏幕旋转流程分析的更多相关文章
- Android 7.1 WindowManagerService 屏幕旋转流程分析 (二)
一.概述 从上篇[Android 7.1 屏幕旋转流程分析]知道实际的旋转由WindowManagerService来完成,这里接着上面具体详细展开. 调了三个函数完成了三件事,即首先调用update ...
- Android 7.1 WindowManagerService 屏幕旋转流程分析 (三)
三.屏幕的绘制 performSurfacePlacement()函数来触发window的绘制,这里最大的循环次数是6,当然一般不会到最大次数就会被Scheduled. final void perf ...
- Android 7.1 ActivityManagerService 屏幕旋转流程分析 (四)
四.Activity的更新(旋转) sendNewConfiguration()会调用到ActivityManagerService的updateConfiguration()来update Conf ...
- Qt for Android 程序禁止屏幕旋转
有时候我们希望让一个程序的界面始终保持在一个方向,不随手机(平板)方向旋转而变化:在AndroidManifest.xml的每一个需要禁止转向的Activity配置中加入 android:screen ...
- 设置Android默认锁定屏幕旋转
/********************************************************************************** * 设置Android默认锁定屏 ...
- Android 4.4 音量调节流程分析(二)
之前在Android 4.4 音量调节流程分析(一)里已经有简单的分析音量控制的流程,今天想接着继续分析下音量大小计算的方法.对于任一播放文件而言其本身都有着固定大小的音量Volume_Max,而在A ...
- Android之 MTP框架和流程分析
概要 本文的目的是介绍Android系统中MTP的一些相关知识.主要的内容包括:第1部分 MTP简介 对Mtp协议进行简单的介绍.第2部分 MTP框架 介绍 ...
- Android系统之LK启动流程分析(一)
1.前言 LK是Little Kernel的缩写,在Qualcomm平台的Android系统中普遍采用LK作为bootloader,它是一个开源项目,LK是整个系统的引导部分,所以不是独立存在的,但是 ...
- Android视图状态及重绘流程分析,带你一步步深入了解View(三)
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/guolin_blog/article/details/17045157 在前面一篇文章中,我带着大家一起从源码的层面上分析了视图的绘制流程, ...
随机推荐
- 数据结构--汉诺塔递归Java实现
/*汉诺塔递归 * 1.将编号0-N-1个圆盘,从A塔座移动到B上面 * 2.将编号N的1个圆盘,从A移动到C上面 * 3.最后将B上面的N-1个圆盘移动到C上面 * 注意:盘子的编号从上到下1-N ...
- IDEA搭建SSMM框架(详细过程)
IDEA搭建SSMM框架(详细过程) 相关环境 Intellij IDEA Ultimate Tomcat JDK MySql 5.6(win32/win64) Maven (可使用Intellij ...
- 实现基于Keepalived高可用集群网站架构的多种方法
实现基于Keepalived高可用集群网站架构 随着业务的发展,网站的访问量越来越大,网站访问量已经从原来的1000QPS,变为3000QPS,目前业务已经通过集群LVS架构可做到随时拓展,后端节点已 ...
- canvas图表(1) - 柱状图
原文地址:canvas图表(1) - 柱状图 前几天用到了图表库,其中百度的ECharts,感觉做得最好,看它默认用的是canva,canvas图表在处理大数据方面比svg要好.那我也用canvas来 ...
- 免费好用的阿里云云盾证书服务(https证书)申请步骤
推荐一个免费的阿里云产品:云盾证书(https证书) 为了能让非专业人士看懂,同样尽量用直白的话,一般来说:当你个人需要建立网站,或者公司要建立官网.商城,通常需要先购买服务器或云主机,虚拟空间,然后 ...
- windows服务启动有界面的程序
大家写windows服务守护进程的时候,肯定会遇到启动的程序看不到界面,只能在任务管理器里面看到xxx.exe问题. 发现可能有如下情况 a.无论是开机,还是程序被关掉后,守护服务启动的程序只能看到任 ...
- Dev控件 galleryControl
发现一个规律,不会的控件先拖到界面上,右上角需要add 的就对应add一个.然后就是找属性和集合手动添加几个. 然后把XXXForm.Designer.cs 里面的代码提取到逻辑代码中,就把常量换成变 ...
- Google Python编程规范
http://pan.baidu.com/s/1dD1Ra7J 其他语言的编程风格: http://zh-google-styleguide.readthedocs.org/en/latest/
- 使用dropwizard(3)-加入DI-dagger2
前言 习惯了Spring全家桶,对spring的容器爱不释手.使用dropwizard,看起来确实很轻,然而,真正使用的时候不得不面临一个问题.我们不可能一个resource就能把所有的业务逻辑囊括! ...
- JavaScript数据可视化编程学习(二)Flotr2,雷达图
一.雷达图 使用雷达图显示多维数据. 如果你有多维的数据要展示,那么雷达图就是一种非常有效的可视化方法. 由于雷达图不常用,比较陌生,所以向用户解释的时候有一些难度.注意使用雷达图会增加用户认知负担. ...
