POJ 1330 Nearest Common Ancestors / UVALive 2525 Nearest Common Ancestors (最近公共祖先LCA)
POJ 1330 Nearest Common Ancestors / UVALive 2525 Nearest Common Ancestors (最近公共祖先LCA)
Description
A rooted tree is a well-known data structure in computer science and engineering. An example is shown below:
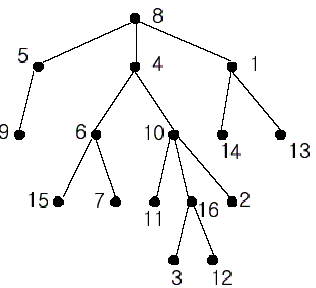
In the figure, each node is labeled with an integer from {1, 2,...,16}. Node 8 is the root of the tree. Node x is an ancestor of node y if node x is in the path between the root and node y. For example, node 4 is an ancestor of node 16. Node 10 is also an ancestor of node 16. As a matter of fact, nodes 8, 4, 10, and 16 are the ancestors of node 16. Remember that a node is an ancestor of itself. Nodes 8, 4, 6, and 7 are the ancestors of node 7. A node x is called a common ancestor of two different nodes y and z if node x is an ancestor of node y and an ancestor of node z. Thus, nodes 8 and 4 are the common ancestors of nodes 16 and 7. A node x is called the nearest common ancestor of nodes y and z if x is a common ancestor of y and z and nearest to y and z among their common ancestors. Hence, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 16 and 7 is node 4. Node 4 is nearer to nodes 16 and 7 than node 8 is.
For other examples, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 2 and 3 is node 10, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 6 and 13 is node 8, and the nearest common ancestor of nodes 4 and 12 is node 4. In the last example, if y is an ancestor of z, then the nearest common ancestor of y and z is y.
Write a program that finds the nearest common ancestor of two distinct nodes in a tree.
Input
The input consists of T test cases. The number of test cases (T) is given in the first line of the input file. Each test case starts with a line containing an integer N , the number of nodes in a tree, 2<=N<=10,000. The nodes are labeled with integers 1, 2,..., N. Each of the next N -1 lines contains a pair of integers that represent an edge --the first integer is the parent node of the second integer. Note that a tree with N nodes has exactly N - 1 edges. The last line of each test case contains two distinct integers whose nearest common ancestor is to be computed.
Output
Print exactly one line for each test case. The line should contain the integer that is the nearest common ancestor.
Sample Input
2
16
1 14
8 5
10 16
5 9
4 6
8 4
4 10
1 13
6 15
10 11
6 7
10 2
16 3
8 1
16 12
16 7
5
2 3
3 4
3 1
1 5
3 5
Sample Output
4
3
Http
POJ:https://vjudge.net/problem/POJ-1330
UVAlive:https://vjudge.net/problem/UVALive-2525
Source
最近公共祖先,LCA
题目大意
给出一棵树,求两点之间的公共祖先。
解决思路
求LCA有多种方法,那么本题我们用在线的倍增算法。
倍增算法基于的是非常高效的二分思想,即二分两个点的祖先,看是否是共同祖先,若是,则寻找更近的,若不是,则寻找更远的。
那么为了实现这个二分,我们定义一个Parent数组,Parent[u][i]表示u的(1 << i)祖先(即2i祖先),为什么要选择2i呢,因为我们用的是二分嘛。
另外,为了方便后面倍增,我们再定义一个Depth[u]数组表示u的深度。
那么首先我们用一个dfs求出Depth[u]和parent[u][0](即u的父亲,这是可以在dfs中求出来的)
然后,我们求出Parent的其他数组,Parent[u][i]=Parent[Parent[u][i-1]][i-1],这个很显然,u的2i祖先就是u的2(i-1)祖先的2^(i-1)祖先(自己可以手动模拟一下)
有了上面求出来的两组信息,我们就可以在线地求LCA啦。
现在假设我们要求LCA的是两个点a和b,并且Depth[a]>Depth[b](如果不是怎么办,swap(a,b)就可以了)。
那么,我们的第一步是把a与b提升到同一高度,这个较好理解。让k从大(一般是20)到小(0)循环,每次判断Depth[Parent[a][k]]与Depth[b]的大小关系,若Depth[Parent[a][k]]==Deptf[b],则a=Parent[a][k],相当于把a向上翻。
在a与b到达同一高度后,若此时ab说明已经找到了a,b的公共祖先,直接输出即可。若还不是,则把二者同时向上翻。注意,为了保证求得的是最近的公共祖先,这里的if判断不能写Parent[a][k]Parent[b][k],而要写Parent[a][k]!=Parent[b][k](自己想一想,为什么)
最后求得的解就是Parent[a][0](或者是Parent[b][0],两者是一样的)
LCA还有一些细节的地方需要注意,具体请看代码(都用注释标记出来了)
代码
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
const int maxN=10011;
const int inf=2147483647;
int n;
int root;
vector<int> E[maxN];
int Parent[maxN][25];
int Depth[maxN];
bool vis[maxN];
int read();//读入优化
void LCA_init();
void dfs(int u);
int LCA(int a,int b);
int main()
{
int TT;
TT=read();
for (int ti=1;ti<=TT;ti++)
{
n=read();
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
E[i].clear();
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
for (int i=1;i<n;i++)
{
int x=read(),y=read();
E[x].push_back(y);
vis[y]=1;
}
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
if (vis[i]==0)
root=i;
//cout<<root<<endl;
LCA_init();//LCA的初始化,即计算Depth和Parent数组
cout<<LCA(read(),read())<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
int read()
{
int x=0;
int k=1;
char ch=getchar();
while (((ch>'9')||(ch<'0'))&&(ch!='-'))
ch=getchar();
if (ch=='-')
{
k=-1;
ch=getchar();
}
while ((ch<='9')&&(ch>='0'))
{
x=x*10+ch-48;
ch=getchar();
}
return x*k;
}
void LCA_init()
{
memset(Depth,0,sizeof(Depth));
Depth[root]=0;
memset(Parent,0,sizeof(Parent));
dfs(root);//首先用dfs计算出Depth和Parent[u][0]
int kk=0;
for (int j=1;j<=20;j++)//注意这里必须是j的循环在外面,i在里面,这是为了保证要计算某个值时它所需要的值已经计算出来了。
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
Parent[i][j]=Parent[Parent[i][j-1]][j-1];
/*for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for (int j=0;j<=kk;j++)
cout<<Parent[i][j]<<' ';
cout<<endl;
}
*/
}
void dfs(int u)
{
for (int i=0;i<E[u].size();i++)
{
int v=E[u][i];
Depth[v]=Depth[u]+1;
Parent[v][0]=u;
dfs(v);
}
return;
}
int LCA(int a,int b)
{
if (Depth[b]>Depth[a])//保证a的深度>=b的深度
swap(a,b);
for (int i=20;i>=0;i--)//把a提到与b高度一致
if ((Parent[a][i]!=0)&&(Depth[Parent[a][i]]>=Depth[b]))
a=Parent[a][i];
if (a==b)
return a;
for (int i=20;i>=0;i--)//把a和b同时向上提
if ((Parent[a][i]!=0)&&(Parent[b][i]!=0)&&(Parent[a][i]!=Parent[b][i]))
{
a=Parent[a][i];
b=Parent[b][i];
}
return Parent[a][0];注意返回值
}
POJ 1330 Nearest Common Ancestors / UVALive 2525 Nearest Common Ancestors (最近公共祖先LCA)的更多相关文章
- POJ 1470 Closest Common Ancestors(最近公共祖先 LCA)
POJ 1470 Closest Common Ancestors(最近公共祖先 LCA) Description Write a program that takes as input a root ...
- POJ 1330 Nearest Common Ancestors 【最近公共祖先LCA算法+Tarjan离线算法】
Nearest Common Ancestors Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 20715 Accept ...
- POJ 1470 Closest Common Ancestors【近期公共祖先LCA】
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主同意不得转载. https://blog.csdn.net/u013912596/article/details/35311489 题目链接:http://poj ...
- [leetcode]236. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree二叉树最近公共祖先
Given a binary tree, find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two given nodes in the tree. Accordi ...
- 236. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree(最低公共祖先,难理解)
Given a binary tree, find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two given nodes in the tree. According ...
- LeetCode OJ:Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree(最近公共祖先)
Given a binary tree, find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two given nodes in the tree. According ...
- POJ 1330 Nearest Common Ancestors (最近公共祖先LCA + 详解博客)
LCA问题的tarjan解法模板 LCA问题 详细 1.二叉搜索树上找两个节点LCA public int query(Node t, Node u, Node v) { int left = u.v ...
- HDU 1330 Nearest Common Ancestors(求两个点的近期公共祖先)
题目链接:id=1330">传送门 在线算法: #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstri ...
- POJ 1470 Closest Common Ancestors (最近公共祖先LCA 的离线算法Tarjan)
Tarjan算法的详细介绍,请戳: http://www.cnblogs.com/chenxiwenruo/p/3529533.html #include <iostream> #incl ...
随机推荐
- node async基础1
async的基础使用 1 async each 语法格式each(collection, iteratee, [callback]) 用途:遍历集合中的元素,并行对每个元素执行一定的操作,但是 ...
- 移动前端meta
<!-- 页面描述 --> <meta name="description" content="不超过150个字符"/> <!-- ...
- Hadoop之WordCount详解
花了好长时间查找资料理解.学习.总结 这应该是一篇比较全面的MapReduce之WordCount文章了 耐心看下去 1,创建本地文件 在hadoop-2.6.0文件夹下创建一个文件夹data,在其中 ...
- Ionic3新特性--页面懒加载1
Ionic3新的懒加载机制给我带来了如下新特性: 避免在每一个使用到某Page的Module或其他Page中重复的import这个类(需要写一堆路径) 允许我们通过字符串key在任何想使用的地方获取某 ...
- 一天搞定CSS:支持IE的Layout布局--16
1.BFC和Layout区别: BFC和Layout的作用是一样的,只是对浏览器的支持不同而已. BFC- -标准浏览器所具有的 Layout- -IE浏览器所具有的 BFC详解地址:http://b ...
- linux升级openssh7.4sp1
1.准备相关的包 openssh下载地址:http://mirror.internode.on.net/pub/OpenBSD/OpenSSH/portable/ openssl相关包下载:http: ...
- TypeScript 零基础入门
前言 2015 年末看过一篇文章<ES2015 & babel 实战:开发 npm 模块>,那时刚接触 ES6 不久,发觉新的 ES6 语法大大简化了 JavaScript 程序的 ...
- CentOS上安装redis记录
下载稳定版 curl -O http://download.redis.io/releases/redis-stable.tar.gz tar -zxvf redis-stable.tar.gz cd ...
- javascript中 __proto__与prorotype的理解
我们先看看这样一段代码: <script type="text/javascript"> var Person = function () { }; var p = n ...
- Java线程间通信之wait/notify
Java中的wait/notify/notifyAll可用来实现线程间通信,是Object类的方法,这三个方法都是native方法,是平台相关的,常用来实现生产者/消费者模式.我们来看下相关定义: w ...
