C语言实现二叉树的基本操作
二叉树是一种非常重要的数据结构。本文总结了二叉树的常见操作:二叉树的构建,查找,删除,二叉树的遍历(包括前序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历、层次遍历),二叉搜索树的构造等。
1. 二叉树的构建
二叉树的基本构建方式为:添加一个节点,如果这是一棵空树,则将该节点作为根节点;否则按照从左到右、先左子树后右子树的顺序逐个添加节点。比如依次添加节点:1,6,10,2,7,11,则得到的二叉树为:
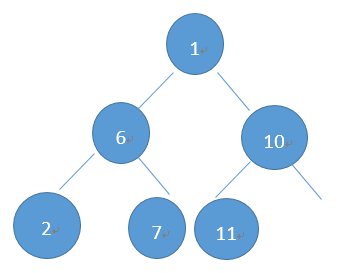
在这里,我们需要借助一个链表来保存节点,以实现二叉树的顺序插入,具体做法如下:
1.0 初始化一个用来保存二叉树节点的空链表;
1.1 插入一个节点,
①如果该树是一棵空树,则将该节点作为根节点,并且将该节点添加到链表中;
②如果该树不为空,取得链表第一个节点的值(注意不是链表的头节点)。如果该节点左子树为空,则将待插入节点添加到左子树,并且将左子树添加到链表;否则将待插入节点添加到右子树,将右子树添加到链表。此时,父节点的左右子树都不为空,将该父节点(即链表第一个节点)
弹出。
按照这样的顺序,我们就可以完成二叉树节点的顺序插入。
2. 二叉搜索树的构建
二叉搜索树是这样一棵树:对于任意一个节点,其左子树的值均小于父节点的值;右子树的值均大于父节点的值。从二叉树的根节点开始,对于其左右子树均按照这样的方式递归插入,即可以得到一棵二叉搜索树。二叉搜索树具有很好的性质,因为它的有序性,如果在二叉搜索树中查找一个元素可以按照类似二分查找的方式进行;对于二叉搜索树,如果采用中序遍历则可以得到按照值递增排列的节点。二叉搜索树的具体构建方式如下:
插入一个节点:
2.1如果当前节点本身值为空,则将插入节点直接作为当前节点;
2.2如果当前节点本身值不为空,
①比较插入节点的值与当前节点的值,如果插入节点值小于当前节点值,则将该节点递归插入左子树;
②比较插入节点的值与当前节点的值,如果插入节点值大于当前节点值,则将该节点递归插入右子树;
③ 如果插入节点的值等于当前节点的值,则直接返回(即二叉搜索树每个节点的值都是不同的)。
3.二叉搜索树的查找
二叉搜索树的查找类似于二分查找。具体步骤如下:
3.1 从根节点开始,比较查找值与当前节点值的大小:
① 如果当前节点值为空,则说明无法查找到该值,直接返回;
②如果当前节点值等于查找值,则查找成功;
③如果查找值小于当前节点的值,则递归查找左子树;
④如果查找值大于当前节点的值,则递归查找右子树。
4. 二叉搜索树的删除
二叉搜索树的删除与查找基本类似,不同之处在于如果查找到了待删除的节点,则将该节点直接删除之后,还要进行如下操作保证删除节点之后的二叉树仍是一棵二叉搜索树:
①如果该删除节点没有左右子树,则直接删除该节点;
②如果该删除节点只有左子树(右子树),则将删除节点的父节点直接指向其左子树(右子树);
③如果该删除节点既有左子树又有右子树,则有下面的三种处理方法:
4.3.1:找到按照中序遍历该删除节点的直接前驱节点,将该节点转移到删除节点,然后删除这个前驱节点;
4.3.2:找到按照中序遍历该删除节点的直接后续节点,将该节点转移到删除节点,然后删除这个后序节点;
4.3.3:找到按照中序遍历该删除节点的直接前驱节点,将删除节点的左子树接到父节点上,将删除节点的右子树接到该前序节点的右子树上,然后删除节点。
5. 二叉树的前序遍历
由于二叉树是递归定义的,所以二叉树的遍历一般也是采用递归的形式。前序遍历即采用先访问根节点,再访问左子树,最后访问右子树的顺序。前序遍历也是按照类似的方式递归遍历,具体操作如下:
① 如果当前节点值为空,返回;
②如果当前节点值不为空,打印当前节点值;递归遍历左子树;递归遍历右子树。
6. 二叉树的中序遍历
①如果当前节点值为空,返回;
②递归遍历左子树;打印当前节点的值;递归遍历右子树。
7. 二叉树的后序遍历
①如果当前节点值为空,返回;
②递归遍历左子树;递归遍历右子树;打印当前节点的值。
8. 二叉树的层次遍历
二叉树的层次遍历,即从根节点开始,逐层按照从左到右的顺序遍历。层次遍历比前中后序遍历要麻烦一点,它需要借助一个额外的链表来保存节点进行遍历。具体做法如下:
①初始化一个用来保存二叉树节点的空链表;
②如果这是一棵空二叉树,直接返回;否则将根节点添加到链表;
③while(当链表不为空时)
弹出链表第一个二叉树节点,打印该二叉树节点的值;
如果该二叉树节点的左子树不为空,则将该左子树添加到链表;
如果该二叉树节点的右子树不为空,则将该右子树添加到链表;
以上就是关于二叉树的基本操作,下面是C语言具体实现的代码,供大家参考:
/*
二叉树的基本操作:插入,删除,查找,前序遍历,中序遍历,后序遍历,层次遍历
*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define BLANK -1
#define LEFT -2
#define RIGHT -3
typedef struct BINARY_TREE
{
// 左子树
struct BINARY_TREE *left;
// 右子树
struct BINARY_TREE *right;
int value;
} Binary_tree;
typedef struct NODE
{
struct NODE *link;
Binary_tree *value;
} Node;
// 二叉树插入
int insert(Binary_tree *root,int value,Node *node_root);
// 二叉搜索树插入
int search_insert(Binary_tree *root,int value);
// 二叉树删除
int erase(Binary_tree *roote,int value);
// 二叉搜索树查找
int search_find(Binary_tree *root,int value);
// 二叉树前序遍历
void pre_print(Binary_tree *root);
// 二叉树中序遍历
void mid_print(Binary_tree *root);
// 二叉树后序遍历
void back_print(Binary_tree *root);
// 层次遍历
void level_print(Binary_tree *root);
// 弹出链表第一个元素
Binary_tree* top(Node *root);
// 将元素添加到链表末尾
int append(Node *current,Binary_tree* value);
int main(void)
{
Binary_tree *root = (Binary_tree*)malloc(sizeof(Binary_tree));
if(root == NULL)
{
printf("Malloc memory failed!\n");
exit(-1);
}
root->left = NULL;
root->right = NULL;
root->value = BLANK;
Node *node_root = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(node_root == NULL)
{
printf("Malloc memory failed!\n");
exit(-1);
}
node_root->link = NULL;
search_insert(root,10);
search_insert(root,2);
search_insert(root,2);
search_insert(root,3);
search_insert(root,4);
search_insert(root,15);
search_insert(root,6);
search_find(root,15);
/*
insert(root,10,node_root);
insert(root,2,node_root);
insert(root,2,node_root);
insert(root,3,node_root);
insert(root,4,node_root);
insert(root,15,node_root);
insert(root,6,node_root);
*/
printf("前序遍历: ");
pre_print(root);
puts("");
printf("中序遍历: ");
mid_print(root);
puts("");
printf("后序遍历: ");
back_print(root);
puts("");
printf("层次遍历: ");
level_print(root);
puts("");
free(root);
return 0;
}
// 二叉树插入
int insert(Binary_tree *root,int value,Node *node_root)
{
// 如果是空树
if(root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL && root->value == BLANK)
{
root->value = value;
append(node_root,root);
printf("Insert %d into an empty link list!\n",value);
}
else
{
// 构造一个新节点
Binary_tree *new_tree_node = (Binary_tree*)malloc(sizeof(Binary_tree));
new_tree_node->value = value;
new_tree_node->left = new_tree_node->right = NULL;
// 得到链表第一个节点的值
Binary_tree *current = node_root->link->value;
// 如果左子树为空
if(current->left == NULL)
{
current->left = new_tree_node;
append(node_root,current->left);
printf("Insert %d in parent's left node!\n",value);
}
// 左子树不为空
else
{
current->right = new_tree_node;
append(node_root,current->right);
printf("Insert %d in parent's right node!\n",value);
top(node_root);
}
}
return 0;
}
// 二叉搜索树插入
int search_insert(Binary_tree *root,int value)
{
// 如果左右子树都为空且根节点值为小于0(BLANK 或者 LEFT 或者 RIGHT)
if(root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL && root->value < 0)
{
if(root->value == BLANK)
printf("Insert %d into an empty binary tree succeed!\n",value);
else if(root->value == LEFT)
printf("Insert %d into parent's left node succeed!\n",value);
else
printf("Insert %d into parent's right node succeed!\n",value);
root->value = value;
return value;
}
if(value < root->value)
{
if(root->left == NULL)
{
root->left = (Binary_tree*)malloc(sizeof(Binary_tree));
if(root->left == NULL)
{
printf("Malloc memory failed!\n");
exit(-1);
}
root->left->value = LEFT;
root->left->left = root->left->right = NULL;
}
search_insert(root->left,value);
}
else if(value > root->value)
{
if(root->right == NULL)
{
root->right = (Binary_tree*)malloc(sizeof(Binary_tree));
if(root->right == NULL)
{
printf("Malloc memory failed!\n");
exit(-1);
}
root->right->value = RIGHT;
root->right->left = root->right->right = NULL;
}
search_insert(root->right,value);
}
else
{
printf("%d already exits in binary tree!\n");
return value;
}
}
// 二叉搜索树查找
int search_find(Binary_tree *root,int value)
{
if(root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL && root->value < 0)
{
printf("Can't find %d in binary tree!\n",value);
return -1;
}
if(root->value == value)
{
printf("Find %d in binary tree!\n",value);
return 0;
}
else if(value < root->value)
{
if(root->left == NULL)
{
printf("Can't find %d in binary tree!\n",value);
return -1;
}
search_find(root->left,value);
}
else
{
if(root->right == NULL)
{
printf("Can't find %d in binary tree!\n",value);
return -1;
}
search_find(root->right,value);
}
}
// 二叉树前序遍历
void pre_print(Binary_tree *root)
{
if(root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL && root->value < 0)
return;
printf("%d ",root->value);
if(root->left != NULL)
pre_print(root->left);
if(root->right != NULL)
pre_print(root->right);
}
// 二叉树中序遍历
void mid_print(Binary_tree *root)
{
if(root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL && root->value < 0)
return;
if(root->left != NULL)
pre_print(root->left);
printf("%d ",root->value);
if(root->right != NULL)
pre_print(root->right);
}
// 二叉树后序遍历
void back_print(Binary_tree *root)
{
if(root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL && root->value < 0)
return;
if(root->left != NULL)
pre_print(root->left);
if(root->right != NULL)
pre_print(root->right);
printf("%d ",root->value);
}
// 弹出链表第一个元素
Binary_tree* top(Node *root)
{
if(root->link == NULL)
{
printf("Can't get top value from empty link list!\n");
exit(-1);
}
Node *current = root->link;
root->link = current->link;
return current->value;
}
// 将元素添加到链表末尾
int append(Node *current,Binary_tree* value)
{
Node *new_node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
new_node->value = value;
while(current->link != NULL)
{
current = current->link;
}
current->link = new_node;
new_node->link = NULL;
return 0;
}
// 二叉树层次遍历
void level_print(Binary_tree* root)
{
if(root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL && root->value < 0)
return;
Node *node_root = (Node*)(malloc(sizeof(Node)));
node_root->link = NULL;
append(node_root,root);
Binary_tree* current;
while(node_root->link != NULL)
{
current = top(node_root);
printf("%d ",current->value);
if(current->left != NULL)
append(node_root,current->left);
if(current->right != NULL)
append(node_root,current->right);
}
}
运行结果如下:

C语言实现二叉树的基本操作的更多相关文章
- 二叉树的基本操作(C语言版)
今天走进数据结构之二叉树 二叉树的基本操作(C 语言版) 1 二叉树的定义 二叉树的图长这样: 二叉树是每个结点最多有两个子树的树结构,常被用于实现二叉查找树和二叉堆.二叉树是链式存储结构,用的是二叉 ...
- c语言描述的二叉树的基本操作(层序遍历,递归,非递归遍历)
#include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #define OK 1 #define ERROR 0 #define TRUE 1 #define ...
- 实现二叉树的基本操作(Java版)
近期研究了一下二叉树,试着用Java语言实现了二叉树的基本操作,下面分享一下实现代码: package com.sf.test; import java.util.ArrayDeque; import ...
- C语言实现二叉树-02版
---恢复内容开始--- 昨天,提交完我们的二叉树项目后,今天早上项目经理早早给我打电话: 他说,小伙子干的不错.但是为什么你上面的insert是recusive的呢? 你难道不知道万一数据量大啦!那 ...
- C语言实现二叉树-利用二叉树统计单词数目
昨天刚参加了腾讯2015年在线模拟考: 四道大题的第一题就是单词统计程序的设计思想: 为了记住这一天,我打算今天通过代码实现一下: 我将用到的核心数据结构是二叉树: (要是想了解简单二叉树的实现,可以 ...
- <二叉树的基本操作(有层次遍历)>
#include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<string.h> #define num 100 #define OK ...
- <二叉树的基本操作>
#include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<string.h> #define num 100 #define OK ...
- C语言实现二叉树
二叉树的重要性就不用多说啦: 我以前也学习过,但是一直没有总结: 网上找到的例子,要么是理论一大堆,然后是伪代码实现: 要么是复杂的代码,没有什么解释: 最终,还是靠FQ找到一些好的文章,参考地址我会 ...
- C语言描述二叉树的实现及操作(链表实现)
概述 二叉树为每个节点最多有两个儿子节点(左儿子节点和右儿子节点)的树. 前序遍历:根结点 ---> 左子树 ---> 右子树. 中序遍历:左子树---> 根结点 ---&g ...
随机推荐
- 关于逆元的概念、用途和可行性的思考(附51nod 1013 和 51nod 1256)
[逆元的概念] 逆元和单位元这个概念在群中的解释是: 逆元是指数学领域群G中任意一个元素a,都在G中有唯一的逆元a',具有性质a×a'=a'×a=e,其中e为该群的单位元. 群的概念是: 如果独异 ...
- Jenkins 在声明式 pipeline 中并行执行任务
在持续集成的过程中,并行的执行那些没有依赖关系的任务可以缩短整个执行过程.Jenkins 的 pipeline 功能支持我们用代码来配置持续集成的过程.本文将介绍在 Jenkins 中使用声明式 pi ...
- Linux系统centOS7在虚拟机下的安装及XShell软件的配置
前面的话 本文将详细介绍Linux系统centOS7在虚拟机下的安装 准备工作 [系统下载] 在安装centOS7之前,首先在官网下载合适的版本 然后,选择一个链接下载即可 [虚拟机配置] 接下来,需 ...
- 用html+css+js做打地鼠小游戏
html 代码 first.html <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta char ...
- javascript正则表达式入门
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/ ...
- EditPlus行首行尾批量添加字符 以及其它常用正则
打开EditPlus,输入多行数据,快捷键ctrl+h 打开替换窗口,选择"正则表达式"替换 行首批量添加 查找"^" 替换为"我是行首aaa&q ...
- Hadoop(五)搭建Hadoop与Java访问HDFS集群
前言 上一篇详细介绍了HDFS集群,还有操作HDFS集群的一些命令,常用的命令: hdfs dfs -ls xxx hdfs dfs -mkdir -p /xxx/xxx hdfs dfs -cat ...
- Android模拟器检测常用方法
在Android开发过程中,防作弊一直是老生常谈的问题,而模拟器的检测往往是防作弊中的重要一环,接下来有关于模拟器的检测方法,和大家进行一个简单的分享. 1.传统的检测方法. 传统的检测方法主要是对模 ...
- Ubuntu 16.04 LTS 下安装MATLAB2015b 以及Matlab system error解决办法
下载MATLAB2015b破解版 操作系统:Ubuntu 16.o4 LTS 程序文件:Matlab2015b-glnxa64破解版 解压提取文件:在ubuntu系统下可以直接提取压缩文件,得到三个文 ...
- PE格式第九讲,资源表解析
PE格式第九讲,资源表解析 一丶熟悉Windows管理文件的方法 首先,为什么标题是这个,主要是为了下边讲解资源方便,因为资源结构体很乱.如果直接拿出来讲解,那么就会很晕. 1.windows管理文件 ...
