二叉搜索树的结构(30 分) PTA 模拟+字符串处理 二叉搜索树的节点插入和非递归遍历
二叉搜索树的结构(30 分) PTA 模拟+字符串处理 二叉搜索树的节点插入和非递归遍历
二叉搜索树的结构(30 分)
二叉搜索树或者是一棵空树,或者是具有下列性质的二叉树: 若它的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值;若它的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值;它的左、右子树也分别为二叉搜索树。(摘自百度百科)
给定一系列互不相等的整数,将它们顺次插入一棵初始为空的二叉搜索树,然后对结果树的结构进行描述。你需要能判断给定的描述是否正确。例如将{ 2 4 1 3 0 }插入后,得到一棵二叉搜索树,则陈述句如“2是树的根”、“1和4是兄弟结点”、“3和0在同一层上”(指自顶向下的深度相同)、“2是4的双亲结点”、“3是4的左孩子”都是正确的;而“4是2的左孩子”、“1和3是兄弟结点”都是不正确的。
输入格式:
输入在第一行给出一个正整数N(≤100),随后一行给出N个互不相同的整数,数字间以空格分隔,要求将之顺次插入一棵初始为空的二叉搜索树。之后给出一个正整数M(≤100),随后M行,每行给出一句待判断的陈述句。陈述句有以下6种:
A is the root,即"A是树的根";A and B are siblings,即"A和B是兄弟结点";A is the parent of B,即"A是B的双亲结点";A is the left child of B,即"A是B的左孩子";A is the right child of B,即"A是B的右孩子";A and B are on the same level,即"A和B在同一层上"。
题目保证所有给定的整数都在整型范围内。
输出格式:
对每句陈述,如果正确则输出Yes,否则输出No,每句占一行。
输入样例:
5
2 4 1 3 0
8
2 is the root
1 and 4 are siblings
3 and 0 are on the same level
2 is the parent of 4
3 is the left child of 4
1 is the right child of 2
4 and 0 are on the same level
100 is the right child of 3
输出样例:
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
No
No 题目分析:
数据结构的一个题,因为数据结构老师要求用课本上的语法,故写的比较麻烦,但比较清晰易懂(基本上使用的都是C语言的语法)。
二叉搜索树的结点定义分别有节点值,左右孩子指针,父节点指针,本题由输入的结点依次插入二叉排序树,然后根据输入的几组语句,判断两个结点的关系;
输入的待判断语句的处理,然后保存有用的值须想明白;
坑点:输入的语句的结点值可能不在已构建好的树中,须判断一下。 测试点: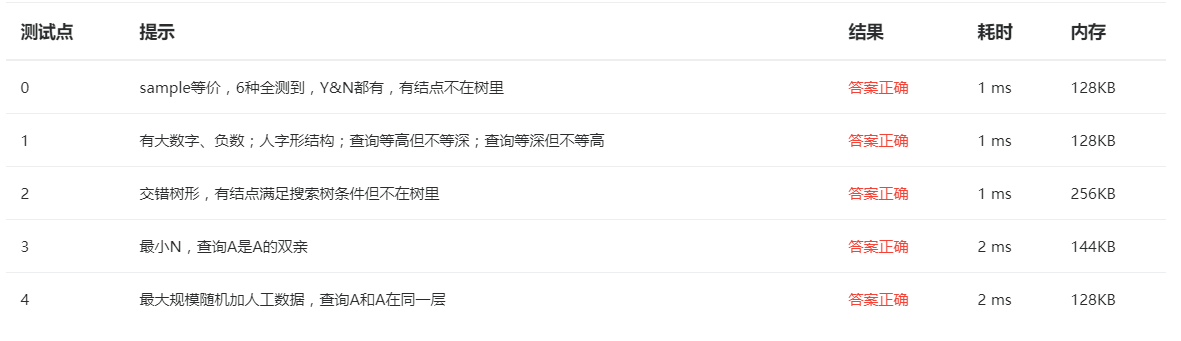
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm> using namespace std; const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
typedef int ElementType;
typedef struct TNode *Position;
typedef Position BinTree;
struct TNode
{
ElementType Data;
Position parent;
BinTree Left;
BinTree Right;
}; void InsertTree(BinTree &T,int k)
{
if(!T)
{
T=(BinTree)malloc(sizeof(TNode));
T->Data=k;
T->Left=T->Right=T->parent=NULL;
//printf("%d\n",T->Data);
}
else
{
//printf("1111111111111111\n");
Position p=T;
Position pre=NULL;
while(p)
{
pre=p;
if(p->Data<k)
p=p->Right;
else
p=p->Left;
}
p=(Position)malloc(sizeof(TNode));
p->Data=k;
p->Left=p->Right=NULL;
p->parent=pre;
if(pre->Data>k)
pre->Left=p;
else if(pre->Data<k)
pre->Right=p;
else
return ;
}
} Position Search(BinTree T,int k)
{
Position p=T;
while(p)
{
if(p->Data>k)
p=p->Left;
else if(p->Data<k)
p=p->Right;
else
return p;
}
return NULL;
}
int GetNumber(BinTree T,int k)
{
int sum=;
Position p=T;
while(p)
{
if(p->Data>k)
p=p->Left;
else if(p->Data<k)
p=p->Right;
else
return sum;
sum++;
}
return INF;
}
int main()
{
BinTree T=NULL;
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
int v;
for(int i=; i<n; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&v);
InsertTree(T,v);
}
int m;
scanf("%d",&m);
getchar();
char s[];
int v1,v2;
for(int i=; i<m; i++)
{
scanf("%d %s",&v1,s);
if(!strcmp(s,"is"))
{
scanf("%s",s);
scanf("%s",s); if(!strcmp(s,"root"))
{
if(T&&T->Data==v1)
printf("Yes\n");
else
printf("No\n");
continue;
}
else if(!strcmp(s,"left"))
{
Position p1=Search(T,v1);
scanf("%s",s);
scanf("%s %d",s,&v2);
Position p2=Search(T,v2);
if(p2&&p1&&p2->Left==p1)
printf("Yes\n");
else
printf("No\n");
}
else if(!strcmp(s,"right"))
{
Position p1=Search(T,v1);
scanf("%s",s);
scanf("%s %d",s,&v2);
Position p2=Search(T,v2);
if(p2&&p1&&p2->Right==p1)
printf("Yes\n");
else
printf("No\n");
}
else if(!strcmp(s,"parent"))
{
Position p1=Search(T,v1);
scanf("%s %d",s,&v2);
Position p2=Search(T,v2);
if(p2&&p1&&p2->parent==p1)
printf("Yes\n");
else
printf("No\n");
}
}
else if(!strcmp(s,"and"))
{
scanf("%d %s",&v2,s);
scanf("%s",s);
if(!strcmp(s,"siblings"))
{
Position p1=Search(T,v1);
Position p2=Search(T,v2);
if(p1&&p2&&p1->parent==p2->parent)
printf("Yes\n");
else
printf("No\n");
}
else if(!strcmp(s,"on"))
{
scanf("%s",s);
scanf("%s",s);
scanf("%s",s);
int n1=GetNumber(T,v1);
//printf("%d\n",n1);
int n2=GetNumber(T,v2);
if(n1==n2&&n1!=INF)
printf("Yes\n");
else
printf("No\n");
}
}
}
return ;
}
/* 5
2 4 1 3 0
8
10 is the root
10 and 100 are siblings
10 and 100 are on the same level
10 is the parent of 100
10 is the left child of 100
100 is the right child of 10
10 and 100 are on the same level
100 is the right child of 10
*/
我的0分代码
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<functional>
#include<cmath>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int a[];
int b[];
int insert(int root,int x)
{
if(a[root]==-)
{
a[root]=x;
return root;
}
else
{
if(x>a[root]) insert(*root+,x);
else insert(*root,x);
}
} int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
memset(a,-,sizeof a);
memset(b,-,sizeof b);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
int x;
cin>>x;
int f=insert(,x);
b[x]=f;
}
int m;
cin>>m;
for(int i=;i<=m;i++)
{
long long x;
cin>>x;//A char s[];
if(||x<||b[x]==-)
{
cin>>s; cout<<"No"<<endl;
continue;
} cin>>s;
if(s[]=='a')// and
{
int y;
cin>>y; cin>>s;//are cin>>s;//sil on if(s[]=='s')
{
if(b[x]/==b[y]/) cout<<"Yes"<<endl;
else cout<<"No"<<endl;
}
else
{
cin>>s; cin>>s; cin>>s; int x2=b[x]/;
int y2=b[y]/;
while(x2!=&&y2!=)
{
x2=x2/;
y2=y2/;
}
if(x2==&&y2==&&x!=y) cout<<"Yes"<<endl;
else cout<<"No"<<endl;
}
}
else
{
cin>>s; cin>>s; if(s[]=='r'&&s[]=='o')
{
if(b[x]==)cout<<"Yes"<<endl;
else cout<<"No"<<endl;
}
else if(s[]=='p')
{
cin>>s; int y;
cin>>y; if(b[y]/==b[x]) cout<<"Yes"<<endl;
else cout<<"No"<<endl;
}
else if(s[]=='l')
{
cin>>s; cin>>s; int y;
cin>>y;
;
if(b[y]*==b[x]) cout<<"Yes"<<endl;
else cout<<"No"<<endl;
}
else if(s[]=='r')
{
cin>>s; cin>>s; int y;
cin>>y; if(b[y]*+==b[x]) cout<<"Yes"<<endl;
else cout<<"No"<<endl;
}
}
}
}
二叉搜索树的结构(30 分) PTA 模拟+字符串处理 二叉搜索树的节点插入和非递归遍历的更多相关文章
- 二叉搜索树的结构(30 分) PTA 模拟+字符串处理 二叉搜索树的节点插入和非递归遍历
二叉搜索树的结构(30 分) 二叉搜索树或者是一棵空树,或者是具有下列性质的二叉树: 若它的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值:若它的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根 ...
- 天梯赛练习 L3-016 二叉搜索树的结构 (30分)
题目分析: 用数型结构先建树,一边输入一边建立,根节点的下标为1,所以左孩子为root*2,右孩子为root*2+1,输入的时候可用cin输入字符串也可用scanf不会超时,判断是否在同一层可以判断两 ...
- 家谱处理(30 分)(字符串的处理substr)
家谱处理(30 分) 人类学研究对于家族很感兴趣,于是研究人员搜集了一些家族的家谱进行研究.实验中,使用计算机处理家谱.为了实现这个目的,研究人员将家谱转换为文本文件.下面为家谱文本文件的实例: Jo ...
- PAT甲级 1155 Heap Paths (30分) 堆模拟
题意分析: 给出一个1000以内的整数N,以及N个整数,并且这N个数是按照完全二叉树的层序遍历输出的序列,输出所有的整条的先序遍历的序列(根 右 左),以及判断整棵树是否是符合堆排序的规则(判断是大顶 ...
- 【PAT甲级】1022 Digital Library (30 分)(模拟)
题意: 输入一个正整数N(<=10000),接下来输入N组数据,ID,书名,作者,关键词,出版社,出版年份. 然后输入一个正整数M(<=1000),接下来输入查询的数据,递增输出ID,若没 ...
- PTA二叉搜索树的操作集 (30分)
PTA二叉搜索树的操作集 (30分) 本题要求实现给定二叉搜索树的5种常用操作. 函数接口定义: BinTree Insert( BinTree BST, ElementType X ); BinTr ...
- PTA 7-2 二叉搜索树的结构(30 分)
7-2 二叉搜索树的结构(30 分) 二叉搜索树或者是一棵空树,或者是具有下列性质的二叉树: 若它的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值:若它的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大 ...
- PTA 7-1 是否完全二叉搜索树 (30分)
PTA 7-1 是否完全二叉搜索树 (30分) 将一系列给定数字顺序插入一个初始为空的二叉搜索树(定义为左子树键值大,右子树键值小),你需要判断最后的树是否一棵完全二叉树,并且给出其层序遍历的结果. ...
- 天梯赛练习 L3-010 是否完全二叉搜索树 (30分) 数组建树模拟
题目分析: 本题的要求是将n个数依次插入一个空的二叉搜索树(左大右小,且没有重复数字),最后需要输出其层次遍历以及判断是否是完全二叉搜索树,通过观察我们发现, 如果这个树是用数组建立的,那么最后输出的 ...
随机推荐
- 谈谈 cci 与 i2c
cci的名字叫, camera control interface, 他由两部分组成,一是i2c ,而另一个部分是 gpio.也就是说,cci 包含i2c.一般情况下,我们只是用到了i2c 部分,没有 ...
- javax.mail.MessagingException: Could not connect to SMTP host: smtp.xdf.cn
1.问题描述:关于使用Java Mail进行邮件发送,抛出Could not connect to SMTP host: xx@xxx.com, port: 25的异常可能: 当我们使用Java Ma ...
- log files of IIS
C:\inetpub\logs\LogFiles https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/iis/manage/provisioning-and-managing-iis/m ...
- Mysql -- SQL常用命令实例
sql: structured query language(结构化查询语言) 用户名和密码:root 创建一个名称为mydb1的数据库. create database mydb1; 查看所有数据库 ...
- java:IO:file 类
刷某一目录下的所有文件夹/文件 public class FileDemo2 { public static void main(String args[]) { File file = new Fi ...
- HYSBZ - 2038经典莫队算法题
无修改的莫队 emmm莫队的几条性质,必须是离线的,复杂度是n*sqrt(n) 就是通过预处理查询区间,然后从(l,r)转移到(ll,rr),这样的复杂度是曼哈顿距离,即abs(l-ll)+abs(r ...
- 如何显示u盘的隐藏的文件
方法/步骤 从U盘属性可以看出,U盘的大量空间被占用,U盘内有很多文件. 点击查看选项卡下的“选项”按钮 切换到中间的“查看”选项卡 取消勾选“隐藏受保护的操作系统文件” 在弹出的警告对话框, ...
- MYSQL 索引创建与使用
可能用到索引的地方: where 子句,order by,group by 不需要创建索引的情况: 1. 表比较小 2.赋值有限的列(枚举),不要创建索引.创建的索引返回的行越少越好,此时区分度大. ...
- tsne pca 自编码器 绘图(CC2)——一定记得做无量纲化处理使用standardscaler,数据聚类更明显
tsne 数据不做预处理: # coding: utf-8 import collections import numpy as np import os import pickle from skl ...
- mysql备份shell脚步
#!/bin/bash #Shell Command For Backup MySQL Database Everyday Automatically By Crontab USER=roo ...
