mina写入数据的过程
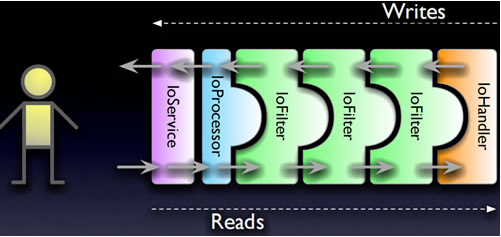
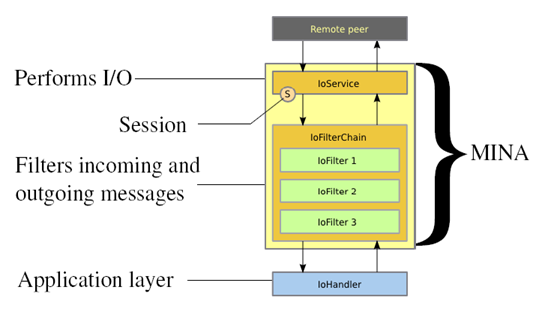
mina架构图
写数据、读数据触发点:
写数据:
1、写操作很简单,是调用session的write方法,进行写数据的,写数据的最终结果保存在一个缓存队列里面,等待发送,并把当前session放入flushSession队列里面。
2、发数据其实和读数据是差不多的,都在Processor中的触发的,在process()完新消息后,会调用flush()方法,把flushSession队列里面的session取出来,并把缓存的消息发送到客户端。
读数据:
读操作是在Processor中的触发的,Processor是AbstractPollingIoProcessor的内部私有类。
Processor中有一个死循环,循环调用Selector的select方法,若有新消息,则进行process()。
写数据过程
MINA数据类型
ByteBuffer、IoBuffer、Object。ByteBuffer是Java的NIO接口从channel读取数据的数据类型;IoBuffer是MINA自定义的数据类型,它封装了ByteBuffer;Object是用户自定义类型,通过用户自定义的codec与IoBuffer进行互相转换。
MINA数据类型转换流程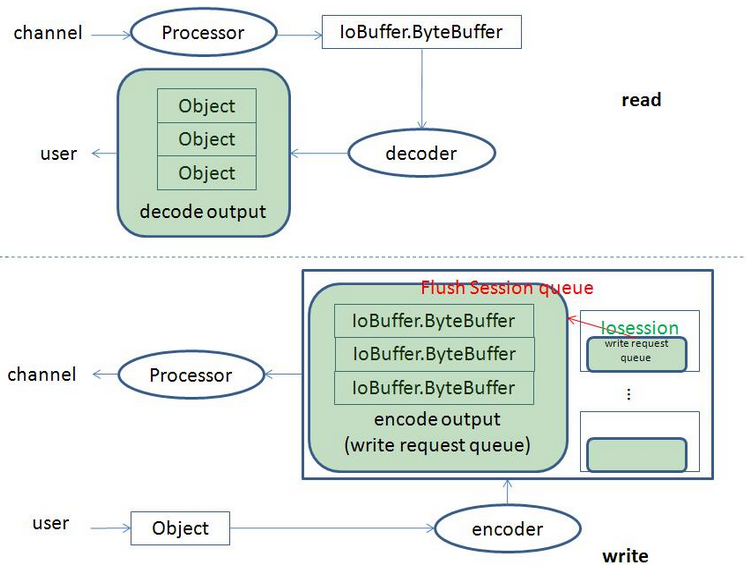
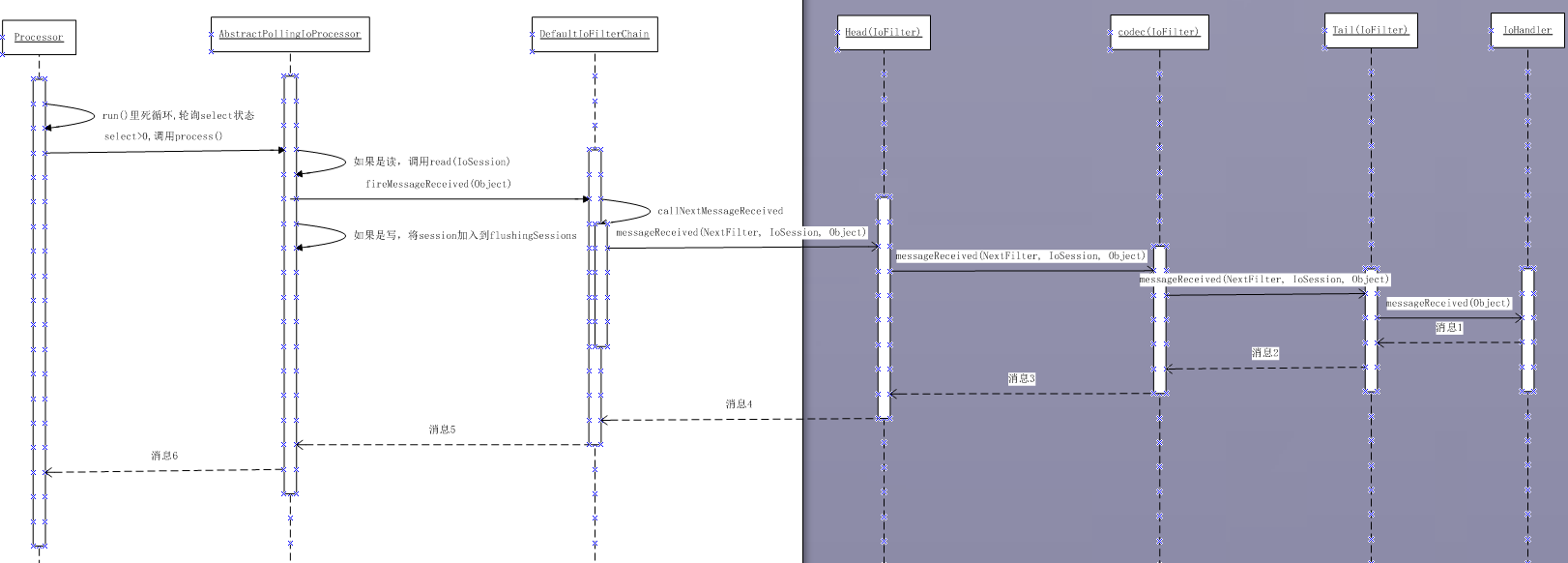
读数据过程
Processor从channel读取ByteBuffer数据,经MINA封装成IoBuffer提交给用户设置的decoder,decoder把解码结果放到一个解码输出队列(decode output queue)中,最后把队列元素按顺序提交给用户。如果设置了线程池来处理IO事件,那么Processor解码ByteBuffer数据以后的操作都由线程池执行,不然所有的操作都由Processor所在的线程执行。使用解码输出队列的原因是processor可能会收到的数据量超过decode成一个Object的所需要数据量,同时该队列是一个线程安全的,目的是防止在使用线程池运行IO事件时带来的数据竞争。
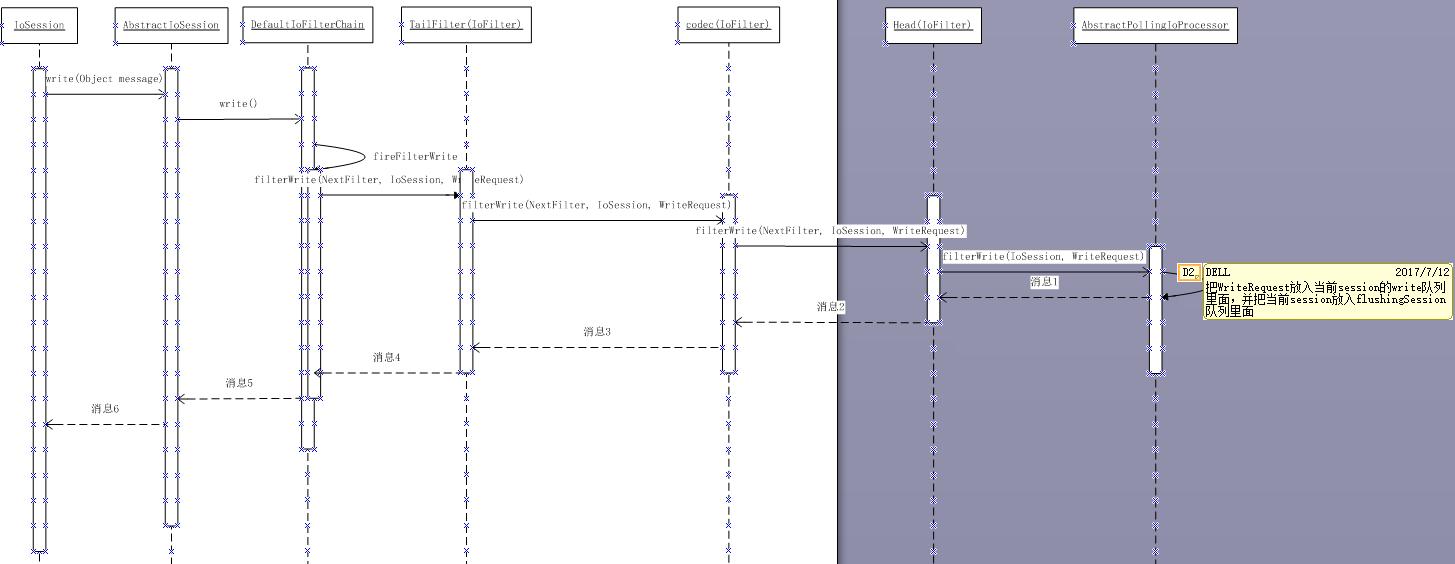
写数据过程
用户往IoSession中写入数据,通过encoder把用户类型的数据编码成IoBuffer并把它放入编码输出队列(写请求队列WriteRequestQueue),并把当前的IoSession放入Processor的刷新队列,最后Processor把每个IoSession中的写请求队列(WriteRequestQueue)中的数据写入channel。可以设置了运行IO事件的线程池执行在Processor处理之前的操作,不然这些操作都在用户写入IoSession的当前线程中执行。因为Processor所在线程跟用户往IoSession写数据的线程并不是同一个线程,所以需要一个线程安全的写请求队列(WriteRequestQueue)。
写数据:
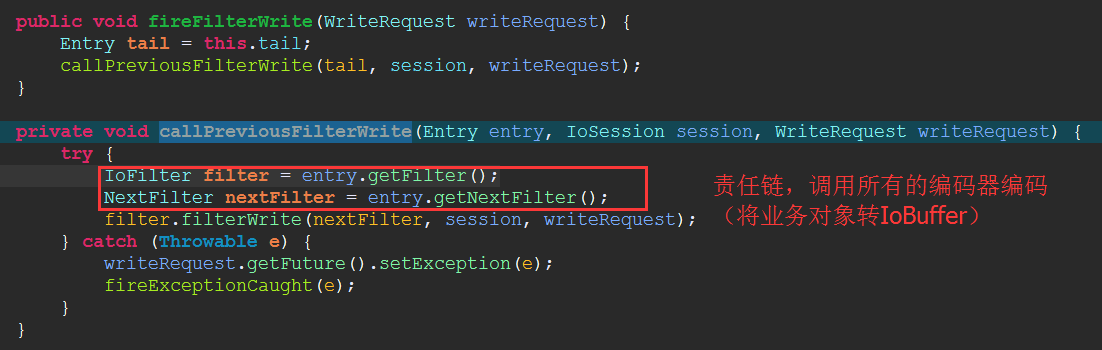
通过eclipse的单步调试:session.write()-->AbsructIoSession.write()-->DefaultIoFilterChain.fireFilterWrite()-->DefaultIoFilterChain.callPreviousFilterWrite()-->HeadFilter.filterWrite()-->SimpleIoProcessorPool-->IoProcessor(线程).write()
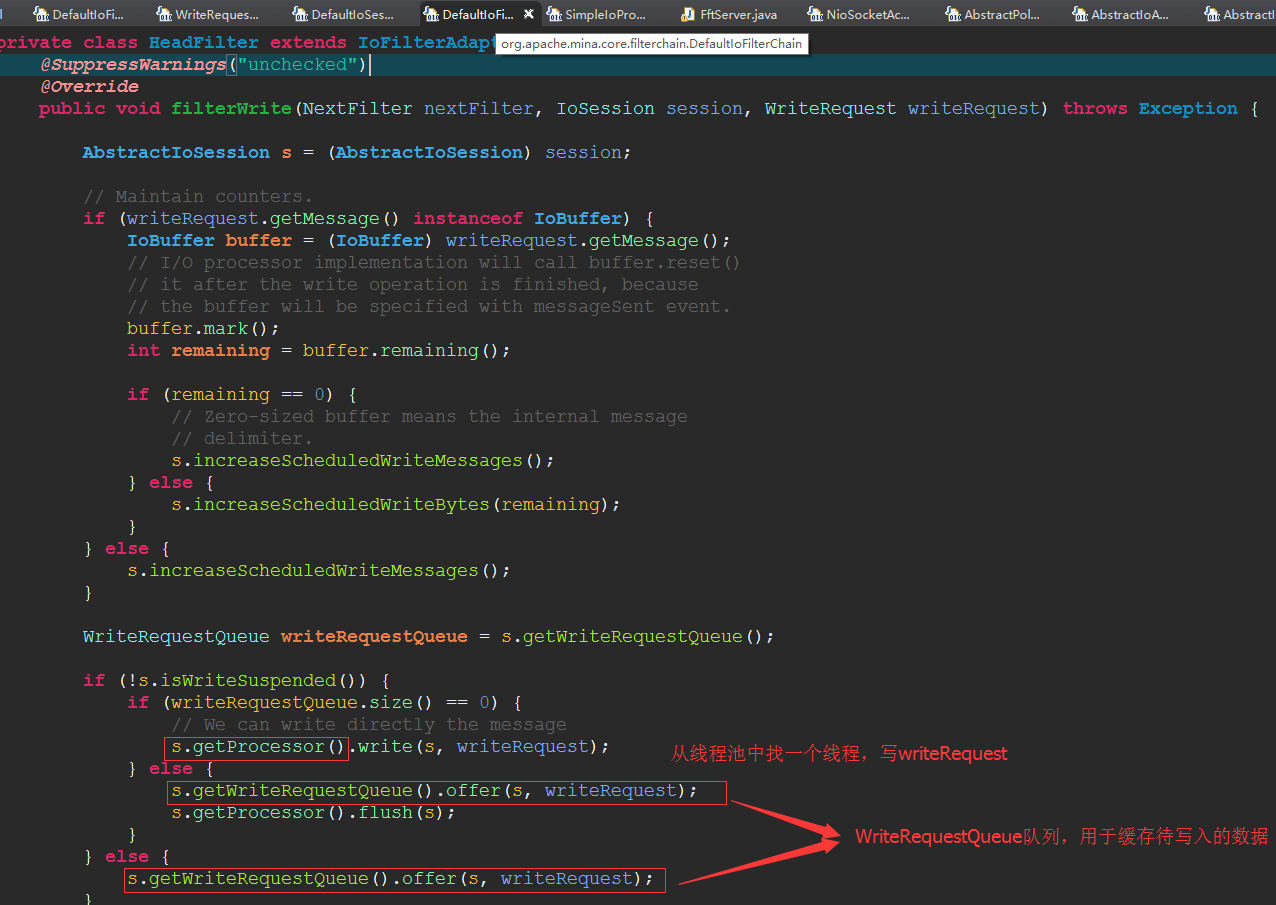
在最后一个Filter也就是HeadFilter中,会获取IoSession与之相关的 WriteRequestQueue 队列,作为应用层写出数据缓冲区。 把写出的WriteRequest放到写出缓冲区队列中。
因为apache mina 是按照SEDA架构设计,同时把要写出数据的IoSession放在 WriteRequestQueue队列中等待写出数据。
再看HeadFilter:
再来看 WriteRequestQueue中的数据是怎么处理的。
然后在Processor线程的run()方法中,来轮询flushIoSession队列。
AbstractPollingIoProcessor$Processor.run()-->AbstractPollingIoProcessor.flush(currentTime)-->AbstractPollingIoProcessor.flushNow(session, currentTime)-->
在NioProcessor(AbstractPollingIoProcessor<S>).flushNow(S, long) 方法中,依次把同一个IoSession中的writeRequest 请求写入到系统缓冲区。
private boolean flushNow(S session, long currentTime) {
if (!session.isConnected()) {
scheduleRemove(session);
return false;
}
final boolean hasFragmentation = session.getTransportMetadata().hasFragmentation();
final WriteRequestQueue writeRequestQueue = session.getWriteRequestQueue();
// Set limitation for the number of written bytes for read-write
// fairness. I used maxReadBufferSize * 3 / 2, which yields best
// performance in my experience while not breaking fairness much.
final int maxWrittenBytes = session.getConfig().getMaxReadBufferSize()
+ (session.getConfig().getMaxReadBufferSize() >>> 1);
int writtenBytes = 0;
WriteRequest req = null;
try {
// Clear OP_WRITE
setInterestedInWrite(session, false);
do {
// Check for pending writes.
req = session.getCurrentWriteRequest();
if (req == null) {
req = writeRequestQueue.poll(session);
if (req == null) {
break;
}
session.setCurrentWriteRequest(req);
}
int localWrittenBytes = 0;
Object message = req.getMessage();
if (message instanceof IoBuffer) {
localWrittenBytes = writeBuffer(session, req, hasFragmentation, maxWrittenBytes - writtenBytes,
currentTime);
if ((localWrittenBytes > 0) && ((IoBuffer) message).hasRemaining()) {
// the buffer isn't empty, we re-interest it in writing
writtenBytes += localWrittenBytes;
setInterestedInWrite(session, true);
return false;
}
} else if (message instanceof FileRegion) {
localWrittenBytes = writeFile(session, req, hasFragmentation, maxWrittenBytes - writtenBytes,
currentTime);
// Fix for Java bug on Linux
// http://bugs.sun.com/bugdatabase/view_bug.do?bug_id=5103988
// If there's still data to be written in the FileRegion,
// return 0 indicating that we need
// to pause until writing may resume.
if ((localWrittenBytes > 0) && (((FileRegion) message).getRemainingBytes() > 0)) {
writtenBytes += localWrittenBytes;
setInterestedInWrite(session, true);
return false;
}
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException("Don't know how to handle message of type '"
+ message.getClass().getName() + "'. Are you missing a protocol encoder?");
}
if (localWrittenBytes == 0) {
// Kernel buffer is full.
setInterestedInWrite(session, true);
return false;
}
writtenBytes += localWrittenBytes;
if (writtenBytes >= maxWrittenBytes) {
// Wrote too much
scheduleFlush(session);
return false;
}
} while (writtenBytes < maxWrittenBytes);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (req != null) {
req.getFuture().setException(e);
}
IoFilterChain filterChain = session.getFilterChain();
filterChain.fireExceptionCaught(e);
return false;
}
return true;
}
如何在应用层缓冲区的写出数据全部写入到系统缓冲区后才关闭socket
关闭socket,从IoSession开始:IoSession(boolean immediately)-->AstractIoSession.close(boolean rightNow)
如果参数是true:-->AstractIoSession.close()
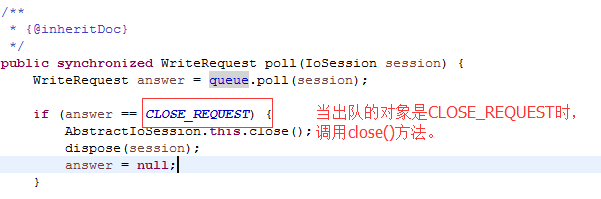
如果参数是false:-->AstractIoSession.closeOnFlush():创建了一个CLOSE_Request请求,当轮询flushIosession时,调用了close()方法。因为IoSession.close(flase) 也是一个写请求队列,所以在处理CLOSE_REQUEST请求时,之前的应用层缓冲区数据已经写入到系统缓冲区中。
CloseFuture close(boolean immediately);
IoSession的默认实现类AstractIoSession:
public final CloseFuture close(boolean rightNow) {
if (!isClosing()) {
if (rightNow) {
return close();
}
return closeOnFlush();
} else {
return closeFuture;
}
}
private final CloseFuture closeOnFlush() {
getWriteRequestQueue().offer(this, CLOSE_REQUEST);
getProcessor().flush(this);
return closeFuture;
}
CLOSE_REQUEST:(AbstractIoSession)
/**
* An internal write request object that triggers session close.
*
* @see #writeRequestQueue
*/
private static final WriteRequest CLOSE_REQUEST = new DefaultWriteRequest(new Object());
AbstractIoSession里的writeRequestQueue是CloseAwareWriteQueue
/**
* Create a new close aware write queue, based on the given write queue.
*
* @param writeRequestQueue
* The write request queue
*/
public final void setWriteRequestQueue(WriteRequestQueue writeRequestQueue) {
this.writeRequestQueue = new CloseAwareWriteQueue(writeRequestQueue);
}

NioProcessor(AbstractPollingIoProcessor<S>)
AbstractPollingIoProcessor
/** A queue used to store the sessions to be removed */
private final Queue<S> removingSessions = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<S>();
AbstractPollingIoProcessor$Processor.run()-->NioProcessor(AbstractPollingIoProcessor<S>).removeSessions()
private class Processor implements Runnable {
public void run() {
assert (processorRef.get() == this);
int nSessions = 0;
lastIdleCheckTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (;;) {
try {
// This select has a timeout so that we can manage
// idle session when we get out of the select every
// second. (note : this is a hack to avoid creating
// a dedicated thread).
long t0 = System.currentTimeMillis();
int selected = select(SELECT_TIMEOUT);
long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
long delta = (t1 - t0);
if ((selected == 0) && !wakeupCalled.get() && (delta < 100)) {
// Last chance : the select() may have been
// interrupted because we have had an closed channel.
if (isBrokenConnection()) {
LOG.warn("Broken connection");
// we can reselect immediately
// set back the flag to false
wakeupCalled.getAndSet(false);
continue;
} else {
LOG.warn("Create a new selector. Selected is 0, delta = " + (t1 - t0));
// Ok, we are hit by the nasty epoll
// spinning.
// Basically, there is a race condition
// which causes a closing file descriptor not to be
// considered as available as a selected channel, but
// it stopped the select. The next time we will
// call select(), it will exit immediately for the same
// reason, and do so forever, consuming 100%
// CPU.
// We have to destroy the selector, and
// register all the socket on a new one.
registerNewSelector();
}
// Set back the flag to false
wakeupCalled.getAndSet(false);
// and continue the loop
continue;
}
// Manage newly created session first
nSessions += handleNewSessions();
updateTrafficMask();
// Now, if we have had some incoming or outgoing events,
// deal with them
if (selected > 0) {
//LOG.debug("Processing ..."); // This log hurts one of the MDCFilter test...
process();
}
// Write the pending requests
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
flush(currentTime);
// And manage removed sessions
nSessions -= removeSessions();
// Last, not least, send Idle events to the idle sessions
notifyIdleSessions(currentTime);
// Get a chance to exit the infinite loop if there are no
// more sessions on this Processor
if (nSessions == 0) {
processorRef.set(null);
if (newSessions.isEmpty() && isSelectorEmpty()) {
// newSessions.add() precedes startupProcessor
assert (processorRef.get() != this);
break;
}
assert (processorRef.get() != this);
if (!processorRef.compareAndSet(null, this)) {
// startupProcessor won race, so must exit processor
assert (processorRef.get() != this);
break;
}
assert (processorRef.get() == this);
}
// Disconnect all sessions immediately if disposal has been
// requested so that we exit this loop eventually.
if (isDisposing()) {
for (Iterator<S> i = allSessions(); i.hasNext();) {
scheduleRemove(i.next());
}
wakeup();
}
} catch (ClosedSelectorException cse) {
// If the selector has been closed, we can exit the loop
break;
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionMonitor.getInstance().exceptionCaught(t);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e1) {
ExceptionMonitor.getInstance().exceptionCaught(e1);
}
}
}
try {
synchronized (disposalLock) {
if (disposing) {
doDispose();
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionMonitor.getInstance().exceptionCaught(t);
} finally {
disposalFuture.setValue(true);
}
}
}
可以看到这个类实现了Runnable接口, run方法中的for循环一直在处理IOSession的数据读取和写入。
int selected = select(SELECT_TIMEOUT); SELECT_TIMEOUT 的默认值为1000L 所以超时时间设置为1S 如果有数据可写或者数据可读 则返回值大于0
if ((selected == 0) && !wakeupCalled.get() && (delta < 100)) 这个地方主要是处理判断是已经断开的连接还是新建立的连接 对于delta 为什么小于100
这个暂时还不知道 哦,这个是个nio的bug 链接可以看下 http://maoyidao.iteye.com/blog/1739282
selected大于0 则开始处理IOSession的读写。
如果可读
IoFilterChain filterChain = session.getFilterChain();
filterChain.fireMessageReceived(buf);
DefaultIoFilterChain实现fireMessageReceived的方法来处理
再由实现IoFilter接口的实现类来处理消息 基本上就结束了。
IoFilter有编解码,日志,线程池 这个有很多大家可以看下API。
private int removeSessions() {
int removedSessions = 0;
for (S session = removingSessions.poll(); session != null; session = removingSessions.poll()) {
SessionState state = getState(session);
// Now deal with the removal accordingly to the session's state
switch (state) {
case OPENED:
// Try to remove this session
if (removeNow(session)) {
removedSessions++;
}
break;
case CLOSING:
// Skip if channel is already closed
break;
case OPENING:
// Remove session from the newSessions queue and
// remove it
newSessions.remove(session);
if (removeNow(session)) {
removedSessions++;
}
break;
default:
throw new IllegalStateException(String.valueOf(state));
}
}
return removedSessions;
}
如果在IoSession真正关闭时,有数据尚未写入到系统缓冲区,将会有异常抛出。
AbstractPollingIoProcessor<S extends AbstractIoSession>.removeNow(S session)-->AbstractPollingIoProcessor<S extends AbstractIoSession>.clearWriteRequestQueue()
private void clearWriteRequestQueue(S session) {
WriteRequestQueue writeRequestQueue = session.getWriteRequestQueue();
WriteRequest req;
List<WriteRequest> failedRequests = new ArrayList<WriteRequest>();
if ((req = writeRequestQueue.poll(session)) != null) {
Object message = req.getMessage();
if (message instanceof IoBuffer) {
IoBuffer buf = (IoBuffer) message;
// The first unwritten empty buffer must be
// forwarded to the filter chain.
if (buf.hasRemaining()) {
buf.reset();
failedRequests.add(req);
} else {
IoFilterChain filterChain = session.getFilterChain();
filterChain.fireMessageSent(req);
}
} else {
failedRequests.add(req);
}
// Discard others.
while ((req = writeRequestQueue.poll(session)) != null) {
failedRequests.add(req);
}
}
// Create an exception and notify.
if (!failedRequests.isEmpty()) {
WriteToClosedSessionException cause = new WriteToClosedSessionException(failedRequests);
for (WriteRequest r : failedRequests) {
session.decreaseScheduledBytesAndMessages(r);
r.getFuture().setException(cause);
}
IoFilterChain filterChain = session.getFilterChain();
filterChain.fireExceptionCaught(cause);
}
}
参考:
http://blog.csdn.net/smart_k/article/details/6617334
http://blog.csdn.net/wzm112358/article/details/46409181
mina写入数据的过程的更多相关文章
- Elasticsearch写入数据的过程是什么样的?以及是如何快速更新索引数据的?
前言 最近面试过程中遇到问Elasticsearch的问题不少,这次总结一下,然后顺便也了解一下Elasticsearch内部是一个什么样的结构,毕竟总不能就只了解个倒排索引吧.本文标题就是我遇到过的 ...
- ES 18 - (底层原理) Elasticsearch写入索引数据的过程 以及优化写入过程
目录 1 Lucene操作document的流程 1.1 添加document的流程 1.2 删除document的流程 2 优化写入流程 - 实现近实时搜索 2.1 流程的改进思路 2.2 设置re ...
- Python中,添加写入数据到已经存在的Excel的xls文件,即打开excel文件,写入新数据
背景 Python中,想要打开已经存在的excel的xls文件,然后在最后新的一行的数据. 折腾过程 1.找到了参考资料: writing to existing workbook using xlw ...
- 转载-python学习笔记之输入输出功能读取和写入数据
读取.写入和 Python 在 “探索 Python” 系列以前的文章中,学习了基本的 Python 数据类型和一些容器数据类型,例如tuple.string 和 list.其他文章讨论了 Pytho ...
- 通过I2C总线向EEPROM中写入数据,记录开机次数
没买板子之前,用protues画过电路图,实现了通过i2c总线向EEPROM中写入和读出数据. 今天,在自己买的板子上面写关于i2c总线的程序,有个地方忘了延时,调程序的时候很蛋疼.下面说说我对I2c ...
- HBase BulkLoad批量写入数据实战
1.概述 在进行数据传输中,批量加载数据到HBase集群有多种方式,比如通过HBase API进行批量写入数据.使用Sqoop工具批量导数到HBase集群.使用MapReduce批量导入等.这些方式, ...
- ElasticSearch写入数据的工作原理是什么?
面试题 es 写入数据的工作原理是什么啊?es 查询数据的工作原理是什么啊?底层的 lucene 介绍一下呗?倒排索引了解吗? 面试官心理分析 问这个,其实面试官就是要看看你了解不了解 es 的一些基 ...
- Kafka权威指南 读书笔记之(三)Kafka 生产者一一向 Kafka 写入数据
不管是把 Kafka 作为消息队列.消息总线还是数据存储平台来使用 ,总是需要有一个可以往 Kafka 写入数据的生产者和一个从 Kafka 读取数据的消费者,或者一个兼具两种角色的应用程序. 开发者 ...
- Mysql数据库写入数据速度优化
Mysql数据库写入数据速度优化 1)innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit 默认值为1:设置为0,可以提高写入速度. 值为0:提升写入速度,但是安全方面较差,mysql服务器 ...
随机推荐
- 深入理解Node.js中的垃圾回收和内存泄漏的捕获
深入理解Node.js中的垃圾回收和内存泄漏的捕获 文章来自:http://wwsun.github.io/posts/understanding-nodejs-gc.html Jan 5, 2016 ...
- 异常:没有找到本地方法库,java.lang.UnsatisfiedLinkError: no trsbean in java.library.path
1.问题描述 迁移环境中遇到这个问题 : Fri Apr 20 15:22:31 CST 2018, Exception:500004___-500004,没有找到本地方法库,java.lang.Un ...
- 生产环境中,通过域名映射ip切换工具SwitchHosts
项目中,经常需要配置host.将某个域名指向某个ip.手动配置C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts,非常不方便.这里分享一个可以高效切换host工具:Switch ...
- linux 查看各目录(文件夹)下文件大小
# 显示总大小(/下全部文件占用大小) du -sh /* | sort -nr # 显示各文件夹的大小(当前文件夹下各文件夹的大小) du --max-depth=1
- 最全面的linux信号量解析
信号量 一.什么是信号量 信号量的使用主要是用来保护共享资源,使得资源在一个时刻只有一个进程(线程) 所拥有. 信号量的值为正的时候,说明它空闲.所测试的线程可以锁定而使用它.若为0,说明 它被占用, ...
- 【转】java中静态方法和非静态方法的存储
将某 class 产生出一个 instance 之后,此 class 所有的 instance field 都会新增一份,那么所有的 instance method 是否也会新增一份?答案是不会,我们 ...
- 表单验证-JS实现
//获取下一个span,可以通过这个对象给状态 function gspan(cobj){ while(true){ if(cobj.nextSibling.nodeName!="SPAN& ...
- R语言基础入门之二:数据导入和描述统计
by 写长城的诗 • October 30, 2011 • Comments Off This post was kindly contributed by 数据科学与R语言 - go there t ...
- java:system根据输入的内容,然后输出(字节流)
把输入的内容输出来:根据system.in的内容System.out.println输出出来 都是字节流,的形式: //限制读取的字符长度 //字节流 InputStream ips = System ...
- 使用PathfindingProject Pro 4.0.10实现2D自动寻路
昨天由于策划的要求,要在项目的最后加个自动寻路的功能,跑去研究了下自动寻路的插件.不多说,上操作 首先在寻路的游戏物体上加上seeker.AI Lerp这两个脚本,注意要给target赋值. 之后给目 ...