CF581C Developing Skills 模拟
Petya loves computer games. Finally a game that he's been waiting for so long came out!
The main character of this game has n different skills, each of which is characterized by an integer ai from 0 to 100. The higher the number ai is, the higher is the i-th skill of the character. The total rating of the character is calculated as the sum of the values of 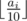 for all i from 1 to n. The expression ⌊ x⌋ denotes the result of rounding the number x down to the nearest integer.
for all i from 1 to n. The expression ⌊ x⌋ denotes the result of rounding the number x down to the nearest integer.
At the beginning of the game Petya got k improvement units as a bonus that he can use to increase the skills of his character and his total rating. One improvement unit can increase any skill of Petya's character by exactly one. For example, if a4 = 46, after using one imporvement unit to this skill, it becomes equal to 47. A hero's skill cannot rise higher more than 100. Thus, it is permissible that some of the units will remain unused.
Your task is to determine the optimal way of using the improvement units so as to maximize the overall rating of the character. It is not necessary to use all the improvement units.
The first line of the input contains two positive integers n and k (1 ≤ n ≤ 105, 0 ≤ k ≤ 107) — the number of skills of the character and the number of units of improvements at Petya's disposal.
The second line of the input contains a sequence of n integers ai (0 ≤ ai ≤ 100), where ai characterizes the level of the i-th skill of the character.
The first line of the output should contain a single non-negative integer — the maximum total rating of the character that Petya can get using k or less improvement units.
2 4
7 9
2
3 8
17 15 19
5
2 2
99 100
20
In the first test case the optimal strategy is as follows. Petya has to improve the first skill to 10 by spending 3 improvement units, and the second skill to 10, by spending one improvement unit. Thus, Petya spends all his improvement units and the total rating of the character becomes equal to lfloor frac{100}{10} rfloor + lfloor frac{100}{10} rfloor = 10 + 10 = 20.
In the second test the optimal strategy for Petya is to improve the first skill to 20 (by spending 3 improvement units) and to improve the third skill to 20 (in this case by spending 1 improvement units). Thus, Petya is left with 4 improvement units and he will be able to increase the second skill to 19 (which does not change the overall rating, so Petya does not necessarily have to do it). Therefore, the highest possible total rating in this example is 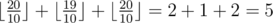 .
.
In the third test case the optimal strategy for Petya is to increase the first skill to 100 by spending 1 improvement unit. Thereafter, both skills of the character will be equal to 100, so Petya will not be able to spend the remaining improvement unit. So the answer is equal to 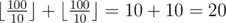 .
.
注意一些坑点即可;
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<string>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<bitset>
#include<ctime>
#include<deque>
#include<stack>
#include<functional>
#include<sstream>
//#include<cctype>
//#pragma GCC optimize(2)
using namespace std;
#define maxn 1000005
#define inf 0x7fffffff
//#define INF 1e18
#define rdint(x) scanf("%d",&x)
#define rdllt(x) scanf("%lld",&x)
#define rdult(x) scanf("%lu",&x)
#define rdlf(x) scanf("%lf",&x)
#define rdstr(x) scanf("%s",x)
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef unsigned int U;
#define ms(x) memset((x),0,sizeof(x))
const long long int mod = 1e9 + 7;
#define Mod 1000000000
#define sq(x) (x)*(x)
#define eps 1e-4
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
#define pi acos(-1.0)
//const int N = 1005;
#define REP(i,n) for(int i=0;i<(n);i++)
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
inline ll rd() {
ll x = 0;
char c = getchar();
bool f = false;
while (!isdigit(c)) {
if (c == '-') f = true;
c = getchar();
}
while (isdigit(c)) {
x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c ^ 48);
c = getchar();
}
return f ? -x : x;
} ll gcd(ll a, ll b) {
return b == 0 ? a : gcd(b, a%b);
}
int sqr(int x) { return x * x; } /*ll ans;
ll exgcd(ll a, ll b, ll &x, ll &y) {
if (!b) {
x = 1; y = 0; return a;
}
ans = exgcd(b, a%b, x, y);
ll t = x; x = y; y = t - a / b * y;
return ans;
}
*/ int n, k;
int a[maxn];
struct node {
int dt;
int org;
}d[maxn];
bool cmp(node a, node b) {
return a.dt < b.dt;
}
int main() {
//ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin >> n >> k;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)rdint(a[i]), d[i].org = a[i];
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (d[i].org % 10 != 0) {
int tp = (d[i].org / 10 + 1) * 10;
d[i].dt = tp - d[i].org;
}
else if (d[i].org != 0 && d[i].org % 10 == 0)d[i].dt = 0;
else if (d[i].org == 0)d[i].dt = 10;
} sort(d + 1, d + 1 + n, cmp);
int cnt = 1;
int sy = 0;
while (k > 0) {
if (cnt == 1) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (k >= d[i].dt) {
k -= d[i].dt;
d[i].org += d[i].dt;
ans += (d[i].org / 10);
if (d[i].org <= 100) {
sy += 100 - (d[i].org);
}
}
else {
ans += (d[i].org / 10);
}
}
cnt++;
if (k <= 0)break;
}
else {
ans += (min(sy, k)) / 10;
k = 0;
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
CF581C Developing Skills 模拟的更多相关文章
- cf581C Developing Skills
Petya loves computer games. Finally a game that he's been waiting for so long came out! The main cha ...
- Codeforces Round #322 (Div. 2) C. Developing Skills 优先队列
C. Developing Skills Time Limit: 1 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/contest/581/p ...
- codeforces 581C. Developing Skills 解题报告
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/581/C 题目意思:给出 n 个数:a1, a2, ..., an (0 ≤ ai ≤ 100).给出值 ...
- Developing Skills
题目传送门:点击打开链接 #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstdlib> #include < ...
- 【Henu ACM Round#19 C】 Developing Skills
[链接] 我是链接,点我呀:) [题意] 在这里输入题意 [题解] 优先把不是10的倍数的变成10的倍数. (优先%10比较大的数字增加 如果k还有剩余. 剩下的数字都是10的倍数了. 那么先加哪一个 ...
- Codeforces Round #322 (Div. 2)
水 A - Vasya the Hipster /************************************************ * Author :Running_Time * C ...
- codeforces581C
Developing Skills CodeForces - 581C 你在玩一个游戏.你操作的角色有n个技能,每个技能都有一个等级ai.现在你有k次提升技能的机会(将其中某个技能提升一个等级,可以重 ...
- How do I learn mathematics for machine learning?
https://www.quora.com/How-do-I-learn-mathematics-for-machine-learning How do I learn mathematics f ...
- 每日英语:A Better Way To Treat Anxiety
Getting up the nerve to order in a coffee shop used to be difficult for 16-year-old Georgiann Steely ...
随机推荐
- navicat for mysql ,mysql版本是8.0的版本,连接数据库报错1251,解决办法。
我的mysql版本是8.0的版本,因为毕竟新的mysql采用新的保密方式,所以就的似乎不能用,改密码方式: 用管理员身份打开cmd mysql -uroot -p(输入密码) 进 ...
- 第二章 深入分析Java I/O的工作机制(待续)
Java的I/O类库的基本架构 磁盘I/O工作机制 网络I/O工作机制 NIO的工作方式 I/O调优 设计模式解析之适配器模式 设计模式解析之装饰器模式 适配器模式与装饰器模式的区别
- Java中Object.hashCode contract
面试时在这个问题上犯了个错误,只重写了equals方法,而没有覆盖hashCode()方法. 回来重读了Effective Java的Item 9,里面提到Object.hashCode contra ...
- 问题:oracle 不等于;结果:Oracle中的不等于号
Oracle中的不等于号 今天碰到一个Oracle不等于的问题,最后搜索了一下,发现下面资料,拿来跟大家分享一下 关于Oracle中的不等于号: 在Oracle中, <> != ~= ...
- 百度Apollo解析——0.使用VSCode编译Apollo项目
1.安装微软Visual Studio Code 1.1 方法一 开始之前,首先需要安装Ubuntu Make.虽然Ubuntu Make存在Ubuntu15.04官方库中,但是需要Ubuntu Ma ...
- Freemarker 使用注意事项
上次借助 Freemaker 模板引擎来动态构造 Kylin 访问的 SQL,在使用过程中,遇到了一些坑. ${} 输出变量时需要注意: 示例 WHERE shop_id = ${val} 里的 v ...
- iBase4J项目笔记
目录: 1 数据库密码加密 2 service层概述 3 web层概述 4 后端CRUD 4.1 READ 4.2 UPDATE 4.3 CREATE 4.4 DELETE 5 facade层概述 1 ...
- ZBar开发详解
博客转载自:https://blog.csdn.net/skillcollege/article/details/38855023 什么是ZBar? ZBar是一个开源库,用于扫描.读取二维码和条形码 ...
- 51NOD1052 最大M字段和
传送门 分析 一眼看去我们自然会想到dp[i][j][k]表示区间[i,j]中选k个子段的最大值.然后我们考虑降去一维.我们设dp[i][j]表示考虑了前i个数,在选了a[i]的情况下共有j个子段的最 ...
- Luogu 2322 [HNOI2006]最短母串问题
唔,太菜了,弄了好几个小时. 状压dp,设$f_{s, i}$表示选了集合$s$,以$i$结尾的最短长度,设$g_{i, j}$表示串$i$的后缀和串$j$的前缀的最长匹配长度. $f_{s, i} ...
