c++实验3类和对象
实 验 3:
part 1:验证

part 2:graph
#include <iostream>
#include "graph.h"
using namespace std; int main() {
Graph graph1('*',);
graph1.draw(); system("pause");
system("cls"); Graph graph2('$',);
graph2.draw();
system("pause"); return ;
}
main.cpp
// 类graph的实现 #include "graph.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; // 带参数的构造函数的实现
Graph::Graph(char ch, int n): symbol(ch), size(n) {
} // 成员函数draw()的实现
// 功能:绘制size行,显示字符为symbol的指定图形样式
void Graph::draw() {
for(int i=;i<=size;i++)
{for(int j=;j<=size-i;j++)
cout<<" ";
for(int k=;k<*i-;k++)
cout<<symbol;
cout<<endl;
}
}
graph.cpp
#ifndef GRAPH_H
#define GRAPH_H // 类Graph的声明
class Graph {
public:
Graph(char ch, int n); // 带有参数的构造函数
void draw(); // 绘制图形
private:
char symbol;
int size;
}; #endif
graph.h
运行结果:
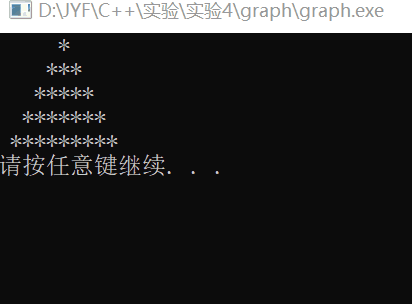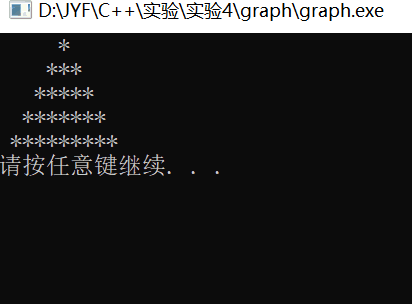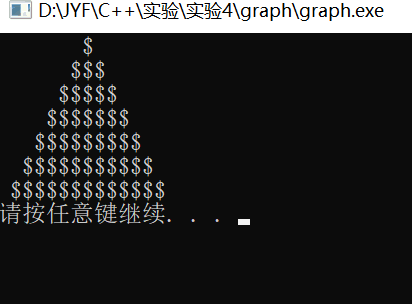
part 3:分数的加减乘除
#ifndef Fraction_H
#define Fraction_H
// 类Fraction的声明
class Fraction {
public:
Fraction(int t=, int b=):top(t),bottom(b){
}// 带有参数的构造函数
void add(Fraction a, Fraction b);
void sub(Fraction a, Fraction b);
void mul(Fraction a, Fraction b);
void div(Fraction a, Fraction b);
void compare(Fraction a, Fraction b);
void show();
private:
int top;
int bottom;
}; #endif
fraction.h
#include <iostream>
#include "fraction.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{int x,y,m,n;
Fraction a;
a.show();
Fraction b(,);
b.show();
Fraction c();
c.show();
cout<<"Input two score: "<<endl;
cin>>x>>y;
cin>>m>>n;
while(y==||n==)
{cout<<"ERROR!Please try again!"<<endl;
cin>>x>>y;
cin>>m>>n;
}
Fraction d(x,y);
Fraction e(m,n);
a.add(d,e);
a.sub(d,e);
a.mul(d,e);
a.div(d,e);
a.compare(d,e);
return ;
}
main.cpp
#include"fraction.h"
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void Fraction::show(){
if (top == ) cout << <<endl;
else if (bottom == ) cout << top << endl;
else cout << top << "/" << bottom << endl;
}
void Fraction::add(Fraction a, Fraction b){
int gbs,m=a.bottom,n=b.bottom,t,r,fz,fm;
if(m<n)
{t=m;m=n;n=t;}
r=m%n;
while(r!=)
{m=n;n=r;r=m%n;}
gbs=a.bottom*b.bottom/n;
fz=a.top*(gbs/a.bottom)+b.top*(gbs/b.bottom);
fm=gbs;
cout<<"add: "<<fz<<"/"<<fm<<endl;
}
void Fraction::sub(Fraction a, Fraction b){
int gbs,m=a.bottom,n=b.bottom,t,r,fz,fm;
if(m<n)
{t=m;m=n;n=t;}
r=m%n;
while(r!=)
{m=n;n=r;r=m%n;}
gbs=a.bottom*b.bottom/n;
fz=a.top*(gbs/a.bottom)-b.top*(gbs/b.bottom);
fm=gbs;
cout<<"sub: "<<fz<<"/"<<fm<<endl;
}
void Fraction::mul(Fraction a, Fraction b){
int fz,fm;
fz=a.top*b.top;
fm=a.bottom*b.bottom;
cout<<"mul: "<<fz<<"/"<<fm<<endl;
}
void Fraction::div(Fraction a, Fraction b){
int fz,fm;
fz=a.top*b.bottom;
fm=b.top*a.bottom;
cout<<"div: "<<fz<<"/"<<fm<<endl;
} void Fraction::compare(Fraction a, Fraction b){
int gbs,m=a.bottom,n=b.bottom,t,r,fz,fm;
if(m<n)
{t=m;m=n;n=t;}
r=m%n;
while(r!=)
{m=n;n=r;r=m%n;}
gbs=a.bottom*b.bottom/n;
fz=a.top*(gbs/a.bottom)-b.top*(gbs/b.bottom);
if(fz<)
cout<<"compare: "<<a.top<<"/"<<a.bottom<<"<"<<b.top<<"/"<<b.bottom<<endl;
else if(fz>)
cout<<"compare: "<<a.top<<"/"<<a.bottom<<">"<<b.top<<"/"<<b.bottom<<endl;
else
cout<<"compare: "<<a.top<<"/"<<a.bottom<<"="<<b.top<<"/"<<b.bottom<<endl;
}
fraction.cpp
运行结果:
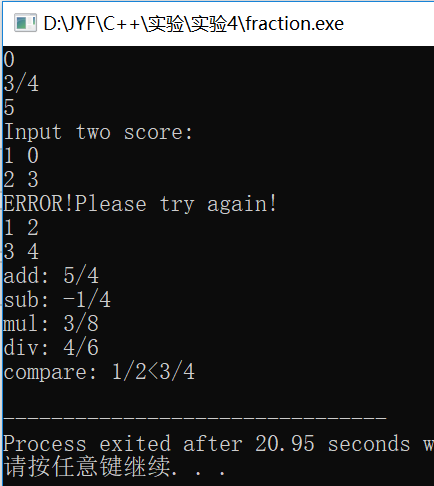
总结:
1、part3中有许多代码是重复的,目前还想不到好的解决方案。
2、在做题时,还是会翻阅书,参考样例,不够熟练。
3、学习了用项目。
评论:
1、https://www.cnblogs.com/shenqidetao/p/10742384.html
2、https://www.cnblogs.com/qsxsc/p/10742704.html
3、https://www.cnblogs.com/csc13813017371/p/10743961.html
c++实验3类和对象的更多相关文章
- 【C++ 实验5 类和对象】
1. #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <string> using namespace std; // ...
- C++ 实验3 类和对象
Part 2 #ifndef GRAPH_H #define GRAPH_H class Graph { public: Graph(char ch, int n); void draw(); pri ...
- 【C++/实验三】类和对象
1.定义一个矩形类,有长,宽两个属性,有成员函数计算矩形的面积. 在该矩形类中,我做了5个主要的测试. 构造函数带默认值参数,利用默认值参数计算矩形面积:rectangle(double x=2.0, ...
- 第四周总结和实验二Java简单类与对象
实验目的 掌握类的定义,熟悉属性.构造函数.方法的使用,掌握用类作为类型声明变量和方法返回值: 理解类和对象的区别,掌握构造函数的使用,熟悉通过对象名引用实列的方法和属性: 理解static修饰对类. ...
- C++ Daily 《6》---- 类静态对象与函数静态对象
C++ 的一个哲学基础是,你不应该为你使用的东西付出代价. class 拥有一个 static 成员,即使从未被用到,它也会被构造和析构: 而 函数拥有一个 static 成员, 如果这个函数从未被调 ...
- iOS RunTime运行时(1):类与对象
Objective-C语言是一门动态语言,他将很多静态语言在编译和链接期做的事放到了运行时来处理.这种动态语言的优势在于:我们写代码更具有灵活性,如我们可以把消息转发给我们想要的对象,或者随意交换一下 ...
- JAVA入门第二季 第一章 类和对象
面向对象编程 Object Oriented Programming OOP 第一.什么是类和对象 在具体说明类和对象之前,先说说别的. 眼睛在人类身体上最为有用的器官.如果一个没有了眼睛,这个人与世 ...
- php学习小记2 类与对象
php类的一些特性: 1. 伪变量$this.$this是一个到主叫对象的引用.取值:该方法所从属的对象,可能是另外的对象(前提,当该方法被静态调用时).$this变量存在于一个类的非静态方法中,在静 ...
- 非常易于理解‘类'与'对象’ 间 属性 引用关系,暨《Python 中的引用和类属性的初步理解》读后感
关键字:名称,名称空间,引用,指针,指针类型的指针(即指向指针的指针) 我读完后的理解总结: 1. 我们知道,python中的变量的赋值操作,变量其实就是一个名称name,赋值就是将name引用到一个 ...
随机推荐
- IT人们给个建议
开篇声明:我本身是中学老师,师范类大学计算机专业毕业,现在马上研究生学位就要拿上了,平时在学校搞网络维护什么的,事少,业余时间充足,也不想拘泥于做老师拿点工资,觉得白学计算机了,所以也搞些业余开发,如 ...
- windows下makefile命令详解
转自https://blog.csdn.net/xiexievv/article/details/45775005 1. 如果已经有vc6的dsp工程,可直接导出nmake脚本文件(.mak) “Pr ...
- [18/12/05]接口(interface)
一.定义(类之上的公共标准) 一个特殊的类,用interface关键字来表示.只有全局变量和抽象方法.解决Java中子类只能单继承的问题 [语法] [访问修饰符:public 或 default] ...
- context.RewritePath
context.RewritePath原理修改HttpRequest类中的Path属性
- (转)HTML5之渐变
<!DOCTYPE> <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"> <head> <meta h ...
- HDU 1071 The area(求三个点确定的抛物线的面积,其中一个点是顶点)
传送门: http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1071 The area Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) ...
- js箭头函数
ES6标准新增了一种新的函数:Arrow Function(箭头函数). 为什么叫Arrow Function?因为它的定义用的就是一个箭头 x =>x*x 相当于: function(x) { ...
- 浅谈箭头函数和setTimeout中的this
箭头函数会改变this的指向,这个大家看文档都看到过,可是有没有具体理解呢?我发现自己应该可能大概是......emmmm,然后我整理了一遍,加强一下概念吧顺带再讲一下setTimeout这个函数改写 ...
- CPU运行的流程
- pycharm中配置pyspark
1 下载官网spark-2.1.1-bin-hadoop2.7.tgz(版本自己选择),解压将文件放在了指定路径下,这个文件夹里面有python文件,python文件下还有两个压缩包py4j-some ...
