JDBC示例(增删查改)
前提:
1、项目中引入MySQL的JAR包,POM参考如下配置:
<!-- mysql-connector-java -->
<!-- http://mvnrepository.com/artifact/mysql/mysql-connector-java -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.38</version>
</dependency>
示例:
一、创建数据库
//STEP 1. Import required packages
import java.sql.*; public class JDBCExample {
// JDBC driver name and database URL
static final String JDBC_DRIVER = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/"; // Database credentials
static final String USER = "root";
static final String PASS = "root"; public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try {
// STEP 2: Register JDBC driver
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); // STEP 3: Open a connection
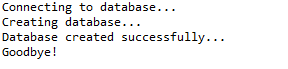
System.out.println("Connecting to database...");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL, USER, PASS); // STEP 4: Execute a query
System.out.println("Creating database...");
stmt = conn.createStatement(); String sql = "CREATE DATABASE STUDENTS";
stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
System.out.println("Database created successfully...");
} catch (SQLException se) {
// Handle errors for JDBC
se.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
// Handle errors for Class.forName
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// finally block used to close resources
try {
if (stmt != null)
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException se2) {
} // nothing we can do
try {
if (conn != null)
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException se) {
se.printStackTrace();
} // end finally try
} // end try
System.out.println("Goodbye!");
}// end main
}// end JDBCExample
这将产生如下所示结果:
二、选择数据库
//STEP 1. Import required packages
import java.sql.*; public class JDBCExample2 {
// JDBC driver name and database URL
static final String JDBC_DRIVER = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/STUDENTS?serverTimezone=UTC"; // Database credentials
static final String USER = "root";
static final String PASS = "root"; public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
try {
// STEP 2: Register JDBC driver
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); // STEP 3: Open a connection
System.out.println("Connecting to a selected database...");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL, USER, PASS);
System.out.println("Connected database successfully...");
} catch (SQLException se) {
// Handle errors for JDBC
se.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
// Handle errors for Class.forName
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// finally block used to close resources
try {
if (conn != null)
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException se) {
se.printStackTrace();
} // end finally try
} // end try
System.out.println("Goodbye!");
}// end main
}// end JDBCExample
这将产生如下所示结果:

三、删除数据库
//STEP 1. Import required packages
import java.sql.*; public class JDBCExample3 {
// JDBC driver name and database URL
static final String JDBC_DRIVER = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/"; // Database credentials
static final String USER = "root";
static final String PASS = "root"; public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try {
// STEP 2: Register JDBC driver
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); // STEP 3: Open a connection
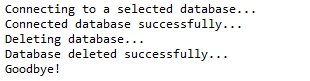
System.out.println("Connecting to a selected database...");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL, USER, PASS);
System.out.println("Connected database successfully..."); // STEP 4: Execute a query
System.out.println("Deleting database...");
stmt = conn.createStatement(); String sql = "DROP DATABASE STUDENTS";
stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
System.out.println("Database deleted successfully...");
} catch (SQLException se) {
// Handle errors for JDBC
se.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
// Handle errors for Class.forName
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// finally block used to close resources
try {
if (stmt != null)
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException se) {
} // do nothing
try {
if (conn != null)
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException se) {
se.printStackTrace();
} // end finally try
} // end try
System.out.println("Goodbye!");
}// end main
}// end JDBCExample
这将产生如下所示结果:
四、创建表
//STEP 1. Import required packages
import java.sql.*; public class JDBCExample4 {
// JDBC driver name and database URL
static final String JDBC_DRIVER = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/STUDENTS?serverTimezone=UTC"; // Database credentials
static final String USER = "root";
static final String PASS = "root"; public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try {
// STEP 2: Register JDBC driver
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); // STEP 3: Open a connection
System.out.println("Connecting to a selected database...");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL, USER, PASS);
System.out.println("Connected database successfully..."); // STEP 4: Execute a query
System.out.println("Creating table in given database...");
stmt = conn.createStatement(); String sql = "CREATE TABLE REGISTRATION " + "(id INTEGER not NULL, " + " first VARCHAR(255), "
+ " last VARCHAR(255), " + " age INTEGER, " + " PRIMARY KEY ( id ))"; stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
System.out.println("Created table in given database...");
} catch (SQLException se) {
// Handle errors for JDBC
se.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
// Handle errors for Class.forName
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// finally block used to close resources
try {
if (stmt != null)
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException se) {
} // do nothing
try {
if (conn != null)
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException se) {
se.printStackTrace();
} // end finally try
} // end try
System.out.println("Goodbye!");
}// end main
}// end JDBCExample
这将产生如下所示结果:

五、删除表
//STEP 1. Import required packages
import java.sql.*; public class JDBCExample5 {
// JDBC driver name and database URL
static final String JDBC_DRIVER = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/STUDENTS?serverTimezone=UTC"; // Database credentials
static final String USER = "root";
static final String PASS = "root"; public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try {
// STEP 2: Register JDBC driver
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); // STEP 3: Open a connection
System.out.println("Connecting to a selected database...");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL, USER, PASS);
System.out.println("Connected database successfully..."); // STEP 4: Execute a query
System.out.println("Deleting table in given database...");
stmt = conn.createStatement(); String sql = "DROP TABLE REGISTRATION "; stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
System.out.println("Table deleted in given database...");
} catch (SQLException se) {
// Handle errors for JDBC
se.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
// Handle errors for Class.forName
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// finally block used to close resources
try {
if (stmt != null)
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException se) {
} // do nothing
try {
if (conn != null)
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException se) {
se.printStackTrace();
} // end finally try
} // end try
System.out.println("Goodbye!");
}// end main
}// end JDBCExample
这将产生如下所示结果:

六、插入记录
//STEP 1. Import required packages
import java.sql.*; public class JDBCExample6 {
// JDBC driver name and database URL
static final String JDBC_DRIVER = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/STUDENTS?serverTimezone=UTC"; // Database credentials
static final String USER = "root";
static final String PASS = "root"; public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try {
// STEP 2: Register JDBC driver
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); // STEP 3: Open a connection
System.out.println("Connecting to a selected database...");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL, USER, PASS);
System.out.println("Connected database successfully..."); // STEP 4: Execute a query
System.out.println("Inserting records into the table...");
stmt = conn.createStatement(); String sql = "INSERT INTO Registration " + "VALUES (100, 'Zara', 'Ali', 18)";
stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
sql = "INSERT INTO Registration " + "VALUES (101, 'Mahnaz', 'Fatma', 25)";
stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
sql = "INSERT INTO Registration " + "VALUES (102, 'Zaid', 'Khan', 30)";
stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
sql = "INSERT INTO Registration " + "VALUES(103, 'Sumit', 'Mittal', 28)";
stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
System.out.println("Inserted records into the table..."); } catch (SQLException se) {
// Handle errors for JDBC
se.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
// Handle errors for Class.forName
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// finally block used to close resources
try {
if (stmt != null)
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException se) {
} // do nothing
try {
if (conn != null)
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException se) {
se.printStackTrace();
} // end finally try
} // end try
System.out.println("Goodbye!");
}// end main
}// end JDBCExample
这将产生如下所示结果:

七、查询表记录
//STEP 1. Import required packages
import java.sql.*; public class JDBCExample7 {
// JDBC driver name and database URL
static final String JDBC_DRIVER = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/STUDENTS?serverTimezone=UTC"; // Database credentials
static final String USER = "root";
static final String PASS = "root"; public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try {
// STEP 2: Register JDBC driver
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); // STEP 3: Open a connection
System.out.println("Connecting to a selected database...");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL, USER, PASS);
System.out.println("Connected database successfully..."); // STEP 4: Execute a query
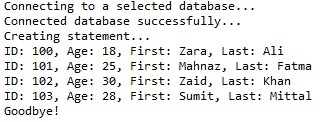
System.out.println("Creating statement...");
stmt = conn.createStatement(); String sql = "SELECT id, first, last, age FROM Registration";
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
// STEP 5: Extract data from result set
while (rs.next()) {
// Retrieve by column name
int id = rs.getInt("id");
int age = rs.getInt("age");
String first = rs.getString("first");
String last = rs.getString("last"); // Display values
System.out.print("ID: " + id);
System.out.print(", Age: " + age);
System.out.print(", First: " + first);
System.out.println(", Last: " + last);
}
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException se) {
// Handle errors for JDBC
se.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
// Handle errors for Class.forName
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// finally block used to close resources
try {
if (stmt != null)
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException se) {
} // do nothing
try {
if (conn != null)
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException se) {
se.printStackTrace();
} // end finally try
} // end try
System.out.println("Goodbye!");
}// end main
}// end JDBCExample
这将产生如下所示结果:
八、更新表记录
//STEP 1. Import required packages
import java.sql.*; public class JDBCExample8 {
// JDBC driver name and database URL
static final String JDBC_DRIVER = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/STUDENTS?serverTimezone=UTC"; // Database credentials
static final String USER = "root";
static final String PASS = "root"; public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try {
// STEP 2: Register JDBC driver
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); // STEP 3: Open a connection
System.out.println("Connecting to a selected database...");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL, USER, PASS);
System.out.println("Connected database successfully..."); // STEP 4: Execute a query
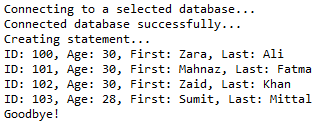
System.out.println("Creating statement...");
stmt = conn.createStatement();
String sql = "UPDATE Registration " + "SET age = 30 WHERE id in (100, 101)";
stmt.executeUpdate(sql); // Now you can extract all the records
// to see the updated records
sql = "SELECT id, first, last, age FROM Registration";
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql); while (rs.next()) {
// Retrieve by column name
int id = rs.getInt("id");
int age = rs.getInt("age");
String first = rs.getString("first");
String last = rs.getString("last"); // Display values
System.out.print("ID: " + id);
System.out.print(", Age: " + age);
System.out.print(", First: " + first);
System.out.println(", Last: " + last);
}
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException se) {
// Handle errors for JDBC
se.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
// Handle errors for Class.forName
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// finally block used to close resources
try {
if (stmt != null)
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException se) {
} // do nothing
try {
if (conn != null)
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException se) {
se.printStackTrace();
} // end finally try
} // end try
System.out.println("Goodbye!");
}// end main
}// end JDBCExample
这将产生如下所示结果:
九、删除记录
//STEP 1. Import required packages
import java.sql.*; public class JDBCExample9 {
// JDBC driver name and database URL
static final String JDBC_DRIVER = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/STUDENTS?serverTimezone=UTC"; // Database credentials
static final String USER = "root";
static final String PASS = "root"; public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try {
// STEP 2: Register JDBC driver
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); // STEP 3: Open a connection
System.out.println("Connecting to a selected database...");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL, USER, PASS);
System.out.println("Connected database successfully..."); // STEP 4: Execute a query
System.out.println("Creating statement...");
stmt = conn.createStatement();
String sql = "DELETE FROM Registration " + "WHERE id = 101";
stmt.executeUpdate(sql); // Now you can extract all the records
// to see the remaining records
sql = "SELECT id, first, last, age FROM Registration";
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql); while (rs.next()) {
// Retrieve by column name
int id = rs.getInt("id");
int age = rs.getInt("age");
String first = rs.getString("first");
String last = rs.getString("last"); // Display values
System.out.print("ID: " + id);
System.out.print(", Age: " + age);
System.out.print(", First: " + first);
System.out.println(", Last: " + last);
}
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException se) {
// Handle errors for JDBC
se.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
// Handle errors for Class.forName
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// finally block used to close resources
try {
if (stmt != null)
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException se) {
} // do nothing
try {
if (conn != null)
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException se) {
se.printStackTrace();
} // end finally try
} // end try
System.out.println("Goodbye!");
}// end main
}// end JDBCExample
这将产生如下所示结果:
十、Where子句
//STEP 1. Import required packages
import java.sql.*; public class JDBCExample10 {
// JDBC driver name and database URL
static final String JDBC_DRIVER = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/STUDENTS?serverTimezone=UTC"; // Database credentials
static final String USER = "root";
static final String PASS = "root"; public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try {
// STEP 2: Register JDBC driver
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); // STEP 3: Open a connection
System.out.println("Connecting to a selected database...");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL, USER, PASS);
System.out.println("Connected database successfully..."); // STEP 4: Execute a query
System.out.println("Creating statement...");
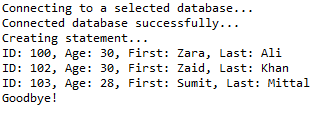
stmt = conn.createStatement(); // Extract records without any condition.
System.out.println("Fetching records without condition...");
String sql = "SELECT id, first, last, age FROM Registration";
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql); while (rs.next()) {
// Retrieve by column name
int id = rs.getInt("id");
int age = rs.getInt("age");
String first = rs.getString("first");
String last = rs.getString("last"); // Display values
System.out.print("ID: " + id);
System.out.print(", Age: " + age);
System.out.print(", First: " + first);
System.out.println(", Last: " + last);
} // Select all records having ID equal or greater than 101
System.out.println("Fetching records with condition...");
sql = "SELECT id, first, last, age FROM Registration" + " WHERE id >= 101 ";
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql); while (rs.next()) {
// Retrieve by column name
int id = rs.getInt("id");
int age = rs.getInt("age");
String first = rs.getString("first");
String last = rs.getString("last"); // Display values
System.out.print("ID: " + id);
System.out.print(", Age: " + age);
System.out.print(", First: " + first);
System.out.println(", Last: " + last);
}
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException se) {
// Handle errors for JDBC
se.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
// Handle errors for Class.forName
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// finally block used to close resources
try {
if (stmt != null)
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException se) {
} // do nothing
try {
if (conn != null)
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException se) {
se.printStackTrace();
} // end finally try
} // end try
System.out.println("Goodbye!");
}// end main
}// end JDBCExample
这将产生如下所示结果:
十一、Like子句
//STEP 1. Import required packages
import java.sql.*; public class JDBCExample11 {
// JDBC driver name and database URL
static final String JDBC_DRIVER = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/STUDENTS?serverTimezone=UTC"; // Database credentials
static final String USER = "root";
static final String PASS = "root"; public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try {
// STEP 2: Register JDBC driver
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); // STEP 3: Open a connection
System.out.println("Connecting to a selected database...");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL, USER, PASS);
System.out.println("Connected database successfully..."); // STEP 4: Execute a query
System.out.println("Creating statement...");
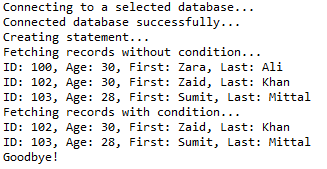
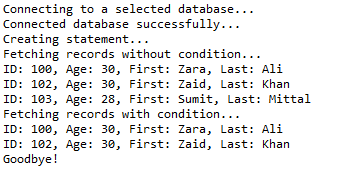
stmt = conn.createStatement(); // Extract records without any condition.
System.out.println("Fetching records without condition...");
String sql = "SELECT id, first, last, age FROM Registration";
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql); while (rs.next()) {
// Retrieve by column name
int id = rs.getInt("id");
int age = rs.getInt("age");
String first = rs.getString("first");
String last = rs.getString("last"); // Display values
System.out.print("ID: " + id);
System.out.print(", Age: " + age);
System.out.print(", First: " + first);
System.out.println(", Last: " + last);
} // Select all records having ID equal or greater than 101
System.out.println("Fetching records with condition...");
sql = "SELECT id, first, last, age FROM Registration" + " WHERE first LIKE '%za%' ";
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql); while (rs.next()) {
// Retrieve by column name
int id = rs.getInt("id");
int age = rs.getInt("age");
String first = rs.getString("first");
String last = rs.getString("last"); // Display values
System.out.print("ID: " + id);
System.out.print(", Age: " + age);
System.out.print(", First: " + first);
System.out.println(", Last: " + last);
}
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException se) {
// Handle errors for JDBC
se.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
// Handle errors for Class.forName
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// finally block used to close resources
try {
if (stmt != null)
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException se) {
} // do nothing
try {
if (conn != null)
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException se) {
se.printStackTrace();
} // end finally try
} // end try
System.out.println("Goodbye!");
}// end main
}// end JDBCExample
这将产生如下所示结果:
十二、排序
//STEP 1. Import required packages
import java.sql.*; public class JDBCExample12 {
// JDBC driver name and database URL
static final String JDBC_DRIVER = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/STUDENTS?serverTimezone=UTC"; // Database credentials
static final String USER = "root";
static final String PASS = "root"; public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try {
// STEP 2: Register JDBC driver
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); // STEP 3: Open a connection
System.out.println("Connecting to a selected database...");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL, USER, PASS);
System.out.println("Connected database successfully..."); // STEP 4: Execute a query
System.out.println("Creating statement...");
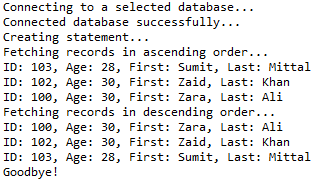
stmt = conn.createStatement(); // Extract records in ascending order by first name.
System.out.println("Fetching records in ascending order...");
String sql = "SELECT id, first, last, age FROM Registration" + " ORDER BY first ASC";
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql); while (rs.next()) {
// Retrieve by column name
int id = rs.getInt("id");
int age = rs.getInt("age");
String first = rs.getString("first");
String last = rs.getString("last"); // Display values
System.out.print("ID: " + id);
System.out.print(", Age: " + age);
System.out.print(", First: " + first);
System.out.println(", Last: " + last);
} // Extract records in descending order by first name.
System.out.println("Fetching records in descending order...");
sql = "SELECT id, first, last, age FROM Registration" + " ORDER BY first DESC";
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql); while (rs.next()) {
// Retrieve by column name
int id = rs.getInt("id");
int age = rs.getInt("age");
String first = rs.getString("first");
String last = rs.getString("last"); // Display values
System.out.print("ID: " + id);
System.out.print(", Age: " + age);
System.out.print(", First: " + first);
System.out.println(", Last: " + last);
}
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException se) {
// Handle errors for JDBC
se.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
// Handle errors for Class.forName
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// finally block used to close resources
try {
if (stmt != null)
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException se) {
} // do nothing
try {
if (conn != null)
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException se) {
se.printStackTrace();
} // end finally try
} // end try
System.out.println("Goodbye!");
}// end main
}// end JDBCExample
这将产生如下所示结果:
测试工程:https://github.com/easonjim/5_java_example/tree/master/jdbcbasics/test10/
JDBC示例(增删查改)的更多相关文章
- SSH框架的多表查询和增删查改 (方法一)上
原创作品,允许转载,转载时请务必标明作者信息和声明本文章==> http://www.cnblogs.com/zhu520/p/7772823.html 因为最近在做Android 练习的 ...
- jdbc的实例应用:增删查改实现
//在jdbc中进行增删查改 //查看所有 public static void findAll() { String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ ...
- 2015.8.2 jdbc实现商品类的增删查改
在惠普济宁基地进行了两周sql和java的学习,学到很多东西 刚才实现了用jdbc访问数据库对数据库进行操作,是用eclipse写的,过几天移植到NetBeans上,个人还是比较习惯看图形化界面 前几 ...
- JDBC+Servlet+jsp(增删查改)
先在mysql新增数据库和表先,把下面的几句代码复制去到mysql运行就可以创建成功了! 创建数据库 create database jdbc01 character set utf8 collat ...
- JDBC终章- 使用 DBUtils实现增删查改- C3P0Utils数据源/QueryRunner runner连接数据源并执行sql
JDBC终章- 使用 DBUtils实现增删查改 1.数据库结构 Create Table CREATE TABLE `user` ( `id` ) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, ...
- [课本]JDBC课程6--使用JDBC的DAO模块化--完成数据库的增删查改_工具类JDBCTools四个(Preparedstatement)功能模块的敲定版
(课本P273-任务九) /**DAO: Data Access Object * 为什么用: 实现功能的模块化,更有利于代码的维护和升级 * 是什么: 访问数据信息的类,包含对数据的CRUD(cre ...
- 在Eclipse上实现简单的JDBC增删查改操作
在Javaweb的学习里,学到了如何完成简单的增删查改操作,在这里撰写一篇文章以便自己整理回忆. 首先要建立一些包和导入一些文件.建一些类.具体框架如图 编写Product类 public clas ...
- hibernate基础增删查改简单实例
hibernate 基础理论知识网上很多,可以百度和google.这里不做多的介绍,以一个User表来开展例子 建一个web-project 我这里用了junit单元测试环境来进行增删查改的测试,别的 ...
- 利用dbutils工具实现数据的增删查改操作(dbutis入门)
一.前期准备 1.安装数据库(如:mysql5.5) 2.安装Eclipse(如:3.4) 3.下载数据库驱动包 4.下载dbutis工具包 5.在Eclipse创建名为 dbutils 的工程并在工 ...
- 极极极极极简的的增删查改(CRUD)解决方案
去年这个时候写过一篇全自动数据表格的文章http://www.cnblogs.com/liuyh/p/5747331.html.文章对自己写的一个js组件做了个概述,很多人把它当作了一款功能相似的纯前 ...
随机推荐
- IIS 安装了.net framework 4.0/4.5 却找不到相应应用程序池
通常情况下是因为没注册造成的,有些安装包会自己帮你注册上有些不会,感觉略坑. 注册方法:在计算机中点击 开始菜单–>运行 拷贝以下内容运行一下即可. C:\WINDOWS\Microsoft.N ...
- win7打开网络看不到局域网的其他电脑
双击打开桌面上的“网络”,在打开的窗口中看不到局域网的其他电脑/计算机.以前都可以看到的.可能是没有开启网络发现的原因,可是我并没有关闭网络发现.不知,怎么回事? Windows7查看网络邻居要开启g ...
- 掌握Spark机器学习库-07-回归分析概述
1)回归与分类算法的区别 回归的预测结果是连续的,分类的预测结果是离散的. 2)spark实现的回归算法有: 3)通过相关系数衡量线性关系的程度
- vscode增加xdebug扩展
首先确保php增加了xdebug扩展,方法很多,可参考 https://www.cnblogs.com/wanghaokun/p/9084188.html.可通过phpinfo()查看是否已开启支持. ...
- php简单实用的调试工具类
<?php /* * 调试类 */ class Common_Debug { //打开错误报告 public static function showError($debug = true) { ...
- apt-get update 报错 W: Unknown Multi-Arch type 'no' for package 'compiz-core'
源 #deb包 deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ xenial main restricted universe multiverse deb http:// ...
- bin/hadoop checknative
bin/hadoop checknative #检查是否支持本地库 [root@node01 ~]# hadoop checknative19/05/28 23:12:46 INFO bzip2.Bz ...
- mysql图形化工具获取表的源码
打开数据库,选择要查看的表,点击右键>对象信息>DDL:
- Spring boot 控制台打印sql
在application.ym中加入: logging: level: com.wechat.cwbt.dao : debug 发现无效 在log4j.properties中加入: log4j.log ...
- mybatis中<![CDATA[]]>的作用
此篇文章引自QH_JAVA的文章 在使用mybatis 时我们sql是写在xml 映射文件中,如果写的sql中有一些特殊的字符的话,在解析xml文件的时候会被转义,但我们不希望他被转义,所以我们要使用 ...
