数据结构 - 静态单链表的实行(C语言)
一、什么是循环链表?
将单链表中终端结点的指针端自空指针改为指向头结点,就使整个单链表形成一个环,这种头尾相接的单链表称为单循环链表,简称循环链表(circular linked
list)。
相比单链表,循环链表解决了一个很麻烦的问题。 即可以从任意一个结点出发,而不一定是要从头结点出发,就可访问到链表的全部结点。
为了使空链表与非空链表处理一致,我们通常设一个头结点,当然, 这并不是说,循环链表一定要头结点,这需要注意。 循环链表带有头结点的空链表如下图所示:
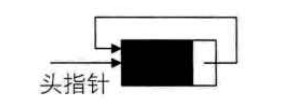
对于非空的循环链表就如下图所示:
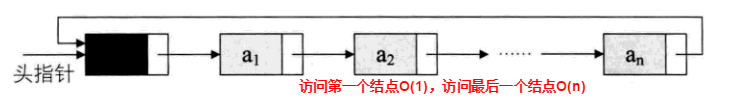
其实循环链表和单链表的主要差异就在于循环的判断条件上,原本是判断 p->next 是否为空,现在则是 p-> next 不等于头结点,则循环未结束。
二、循环链表的基本操作
2.1 初始化链表操作
// 初始化链表操作
void initList(LinkList **pList) // 必须使用双重指针,一重指针申请会出错
{
*pList = (LinkList *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if (!pList)
{
printf("malloc error!\n");
return;
}
(*pList)->data = 0;
// 因为是循环链表,所以尾指针指向头节点
(*pList)->next = *pList;
}
循环链表的所有操作程序与单链表大致相同,只是修改了链表的结束判断条件,因为尾结点的 next 不再指向 NULL,而是指向头结点。
2.2 插入元素操作
// 插入元素操作
Status insertList(LinkList *pList, int i, const ElemType e)
{
Node *front; // 指向位置i所在的前一个结点
int j; // 计数器
// 判断链表是否存在
if (!pList)
{
printf("list not exist!\n");
return FALSE;
}
// 只能在位置1以及后面插入,所以i至少为1
if (i < 1)
{
printf("i is invalid!\n");
return FALSE;
}
// 找到i位置所在的前一个结点
front = pList;
if (i != 1) // 对i=1的情况特殊处理
{
front = pList->next; // 指向第2个结点的前一个结点,与j对应
for (int j = 2; j < i; j++) // j为计数器,赋值为2,对应front指向的下一个结点
{
front = front->next;
if (front == pList)
{
printf("dont find front!\n");
return false;
}
}
}
// 创建一个空节点,存放要插入的新元素
Node *temp = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if (!temp)
{
printf("malloc error!\n");
return FALSE;
}
temp->data = e;
// 插入结点
temp->next = front->next;
front->next = temp;
return TRUE;
}
与单链表相比,找到 i 位置的前一个结点的结束判断更难处理,这里可以进一步改进。
2.3 删除元素操作
// 删除元素操作
Status deleteList(LinkList *pList, int i, ElemType *e)
{
Node *front; // 指向位置i所在的前一个结点
int j; // 计数器
// 判断链表是否存在
if (!pList)
{
printf("list not exist!\n");
return FALSE;
}
// 只能删除位置1以及以后的结点
if (i < 1)
{
printf("i is invalid!\n");
return FALSE;
}
// 找到i位置所在的前一个结点
front = pList;
if (i != 1) // 对i=1的情况特殊处理
{
front = pList->next; // 指向第2个结点的前一个结点,与j对应
for (int j = 2; j < i; j++) // j为计数器,赋值为2,对应front指向的下一个结点
{
front = front->next;
if (front->next == pList)
{
printf("dont find front!\n");
return false;
}
}
}
// 提前保存要删除的结点
Node *temp = front->next;
*e = temp->data; // 将要删除结点的数据赋给e
// 删除结点
front->next = front->next->next;
// 销毁结点
free(temp);
temp = NULL;
return TRUE;
}
三、完整程序
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
typedef int Status; // Status是函数结果状态,成功返回TRUE,失败返回FALSE
typedef int ElemType;
/* 线性表的循环链表存储结构 */
typedef struct node
{
ElemType data;
struct node *next;
}Node, LinkList;
void initList(LinkList **pList); // 初始化链表操作
Status insertList(LinkList *pList, int i, const ElemType e); // 插入元素操作
Status deleteList(LinkList *pList, int i, ElemType *e); // 删除元素操作
Status getElem(LinkList *pList, int i, ElemType *e); // 获取元素操作
Status insertListHead(LinkList *pList, const ElemType e); // 头部后插入元素操作
Status insertListTail(LinkList *pList, const ElemType e); // 尾部后插入元素操作
Status clearList(LinkList *pList); // 清空链表操作
void traverseList(LinkList *pList); // 遍历链表操作
int getLength(LinkList *pList); // 获取链表长度操作
// 初始化链表操作
void initList(LinkList **pList) // 必须使用双重指针,一重指针申请会出错
{
*pList = (LinkList *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if (!pList)
{
printf("malloc error!\n");
return;
}
(*pList)->data = 0;
// 因为是循环链表,所以尾指针指向头节点
(*pList)->next = *pList;
}
// 插入元素操作
Status insertList(LinkList *pList, int i, const ElemType e)
{
Node *front; // 指向位置i所在的前一个结点
int j; // 计数器
// 判断链表是否存在
if (!pList)
{
printf("list not exist!\n");
return FALSE;
}
// 只能在位置1以及后面插入,所以i至少为1
if (i < 1)
{
printf("i is invalid!\n");
return FALSE;
}
// 找到i位置所在的前一个结点
front = pList;
if (i != 1) // 对i=1的情况特殊处理
{
front = pList->next; // 指向第2个结点的前一个结点,与j对应
for (int j = 2; j < i; j++) // j为计数器,赋值为2,对应front指向的下一个结点
{
front = front->next;
if (front == pList)
{
printf("dont find front!\n");
return false;
}
}
}
// 创建一个空节点,存放要插入的新元素
Node *temp = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if (!temp)
{
printf("malloc error!\n");
return FALSE;
}
temp->data = e;
// 插入结点
temp->next = front->next;
front->next = temp;
return TRUE;
}
// 删除元素操作
Status deleteList(LinkList *pList, int i, ElemType *e)
{
Node *front; // 指向位置i所在的前一个结点
int j; // 计数器
// 判断链表是否存在
if (!pList)
{
printf("list not exist!\n");
return FALSE;
}
// 只能删除位置1以及以后的结点
if (i < 1)
{
printf("i is invalid!\n");
return FALSE;
}
// 找到i位置所在的前一个结点
front = pList;
if (i != 1) // 对i=1的情况特殊处理
{
front = pList->next; // 指向第2个结点的前一个结点,与j对应
for (int j = 2; j < i; j++) // j为计数器,赋值为2,对应front指向的下一个结点
{
front = front->next;
if (front->next == pList)
{
printf("dont find front!\n");
return false;
}
}
}
// 提前保存要删除的结点
Node *temp = front->next;
*e = temp->data; // 将要删除结点的数据赋给e
// 删除结点
front->next = front->next->next;
// 销毁结点
free(temp);
temp = NULL;
return TRUE;
}
// 获取元素操作
Status getElem(LinkList *pList, int i, ElemType *e)
{
Node *cur;
// 判断链表是否存在
if (!pList)
{
printf("list not exist!\n");
return FALSE;
}
// 只能获取位置1以及以后的元素
if (i < 1)
{
printf("i is invalid!\n");
return FALSE;
}
// 找到i位置所在的结点
cur = pList->next; // 这里是让cur指向链表的第1个结点
int j = 1; // j为计数器,赋值为1,对应cur指向结点
while (cur != pList && j < i)
{
cur = cur->next;
j++;
}
// 未找到i位置所在的前一个结点
if (cur == pList)
{
printf("dont find front!\n");
return FALSE;
}
// 取第i个结点的数据
*e = cur->data;
return TRUE;
}
// 头部后插入元素操作
Status insertListHead(LinkList *pList, const ElemType e)
{
Node *head;
Node *temp;
// 判断链表是否存在
if (!pList)
{
printf("list not exist!\n");
return FALSE;
}
// 让head指向链表的头结点
head = pList;
// 创建存放插入元素的结点
temp = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if (!temp)
{
printf("malloc error!\n");
return FALSE;
}
temp->data = e;
// 头结点后插入结点
temp->next = head->next;
head->next = temp;
return TRUE;
}
// 尾部后插入元素操作
Status insertListTail(LinkList *pList, const ElemType e)
{
Node *cur;
Node *temp;
// 判断链表是否存在
if (!pList)
{
printf("list not exist!\n");
return FALSE;
}
// 找到链表尾节点
cur = pList;
while (cur->next != pList)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
// 创建存放插入元素的结点
temp = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if (!temp)
{
printf("malloc error!\n");
return -1;
}
temp->data = e;
// 尾结点后插入结点
temp->next = cur->next;
cur->next = temp;
return TRUE;
}
// 清空链表操作
Status clearList(LinkList *pList)
{
Node *cur; // 当前结点
Node *temp; // 事先保存下一结点,防止释放当前结点后导致“掉链”
// 判断链表是否存在
if (!pList)
{
printf("list not exist!\n");
return FALSE;
}
cur = pList->next; // 指向头结点后的第一个结点
while (cur != pList)
{
temp = cur->next; // 事先保存下一结点,防止释放当前结点后导致“掉链”
free(cur); // 释放当前结点
cur = NULL;
cur = temp; // 将下一结点赋给当前结点p
}
pList->next = NULL; // 头结点指针域指向空
return TRUE;
}
// 遍历链表操作
void traverseList(LinkList *pList)
{
// 判断链表是否存在
if (!pList)
{
printf("list not exist!\n");
return;
}
Node *cur = pList->next;
while (cur != pList)
{
printf("%d ", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
// 获取链表长度操作
int getLength(LinkList *pList)
{
Node *cur = pList;
int length = 0;
while (cur->next != pList)
{
cur = cur->next;
length++;
}
return length;
}
int main()
{
LinkList *pList;
// 初始化链表
initList(&pList);
printf("初始化链表!\n\n");
// 尾部后插入结点
insertListTail(pList, 1);
printf("尾部后插入元素1\n");
insertListTail(pList, 2);
printf("尾部后插入元素2\n\n");
// 插入结点
insertList(pList, 1, 4);
printf("位置1插入元素4\n\n");
// 删除结点
int val;
deleteList(pList, 3, &val);
printf("删除位置3的结点,删除结点的数据为: %d\n", val);
printf("\n");
// 遍历链表并显示元素操作
printf("遍历链表:");
traverseList(pList);
printf("\n");
// 获得链表长度
printf("链表长度: %d\n\n", getLength(pList));
// 销毁链表
clearList(pList);
printf("销毁链表\n\n");
return 0;
}
参考:
《大话数据结构 - 第3章》 线性表
数据结构 - 静态单链表的实行(C语言)的更多相关文章
- 数据结构 - 动态单链表的实行(C语言)
动态单链表的实现 1 单链表存储结构代码描述 若链表没有头结点,则头指针是指向第一个结点的指针. 若链表有头结点,则头指针是指向头结点的指针. 空链表的示意图: 带有头结点的单链表: 不带头结点的单链 ...
- 【数据结构】单链表&&静态链表详解和代码实例
喜欢的话可以扫码关注我们的公众号哦,更多精彩尽在微信公众号[程序猿声] 01 单链表(Singly Linked List ) 1.1 什么是单链表? 单链表是一种链式存储的结构.它动态的为节点分配存 ...
- javascript实现数据结构与算法系列:线性表的静态单链表存储结构
有时可借用一维数组来描述线性链表,这就是线性表的静态单链表存储结构. 在静态链表中,数组的一个分量表示一个结点,同时用游标(cur)代替指针指示结点在数组中的相对位置.数组的第0分量可看成头结点,其指 ...
- Python数据结构之单链表
Python数据结构之单链表 单链表有后继结点,无前继结点. 以下实现: 创建单链表 打印单链表 获取单链表的长度 判断单链表是否为空 在单链表后插入数据 获取单链表指定位置的数据 获取单链表指定元素 ...
- javascript数据结构之单链表
下面是用javascript实现的单链表,但是在输出的时候insert方法中存在问题,chrome的console报错说不能读取空的属性,调试了很久都没有通过,先在这里存着,以后再来修改一下. //数 ...
- 数据结构之单链表的实现-java
一.单链表基本概念 单链表是一种链式存取的数据结构,用一组地址任意的存储单元(一般是非连续存储单元)存放线性表中的数据元素.链表中的数据是以结点来表示的,每个结点的构成:元素data + 指针next ...
- 数据结构—单链表(类C语言描写叙述)
单链表 1.链接存储方法 链接方式存储的线性表简称为链表(Linked List). 链表的详细存储表示为: ① 用一组随意的存储单元来存放线性表的结点(这组存储单元既能够是连续的.也能够是不连续的) ...
- 数据结构(一) 单链表的实现-JAVA
数据结构还是很重要的,就算不是那种很牛逼的,但起码得知道基础的东西,这一系列就算是复习一下以前学过的数据结构和填补自己在这一块的知识的空缺.加油.珍惜校园中自由学习的时光.按照链表.栈.队列.排序.数 ...
- python 数据结构之单链表的实现
链表的定义: 链表(linked list)是由一组被称为结点的数据元素组成的数据结构,每个结点都包含结点本身的信息和指向下一个结点的地址.由于每个结点都包含了可以链接起来的地址信息,所以用一个变量就 ...
随机推荐
- 进程(WINAPI),遍历并查找树状的进程信息,实现控制系统进程
#include <TlHelp32.h> //检索系统全部进程 void showall() { PROCESSENTRY32 pe32 = {0}; pe32.dwSize = siz ...
- 【APUE】信号量、互斥体和自旋锁
http://www.cnblogs.com/biyeymyhjob/archive/2012/07/21/2602015.html http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-205 ...
- CentOS 6.x ELK(Elasticsearch+Logstash+Kibana)
CentOS 6.x ELK(Elasticsearch+Logstash+Kibana) 前言 Elasticsearch + Logstash + Kibana(ELK)是一套开源的日志管理方案, ...
- POJ 1679 The Unique MST 推断最小生成树是否唯一
The Unique MST Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 22715 Accepted: 8055 D ...
- The sandbox is not sync with the Podfile.lock
github下载的Demo,很多时候使用到CocoaPods,有的时候因为依赖关系或者版本问题不能编译运行. 出现 以下错误 The sandbox is not sync with the Podf ...
- 积跬步,聚小流------Bootstrap学习记录(3)
响应式作为Bootstrap的一大特色.栅格系统可谓是功不可没,既然如此,那我们就来看一下栅格系统是怎样帮助bootstrap实现响应式布局的呢? 1.什么是栅格系统 我们能够从Bootstrap的官 ...
- 发现个delphi调用vc写的Dll中包括pchar參数报错奇怪现象
发现个delphi调用vc写的Dll中包括pchar參数奇怪现象 procedure中的第一行语句不能直接调用DLL的函数,否则会执行报错,在之前随意加上条语句就不报错了奇怪! vc的DLL源代码地址 ...
- Thinkpad升级Window10无法安装expresscache
本人有一台Thinkpad T440s,自从看了这篇帖子12秒开机!ExpressCache SSD缓存加速,就给自己的小黑加持了一块固态硬盘.使用后效果确实很明显. 问题 自从系统自动升级到wind ...
- Java使用三种不同循环结构对1+2+3+...+100 求和
▷//第一种求法,使用while结构 /** * @author 9527 * @since 19/6/20 */ public class Gaosi { public static void ma ...
- android 怎样将主菜单图标改成按安装时间排序
1. 在 LauncherModel.java 中增加例如以下代码, 假设是KK Launcher3 ApplicationInfo要替换为AppInfo public static final Co ...
