漫谈可视化Prefuse(二)---一分钟学会Prefuse
前篇《漫谈可视化Prefuse(一)---从SQL Server数据库读取数据》主要介绍了prefuse如何连接数据库sql server并读取数据进行可视化展现。
回头想想还是应该好好捋一捋prefuse框架中各个主要接口的职责以及如何有序使用它们构建一个prefuse应用。首先看图:
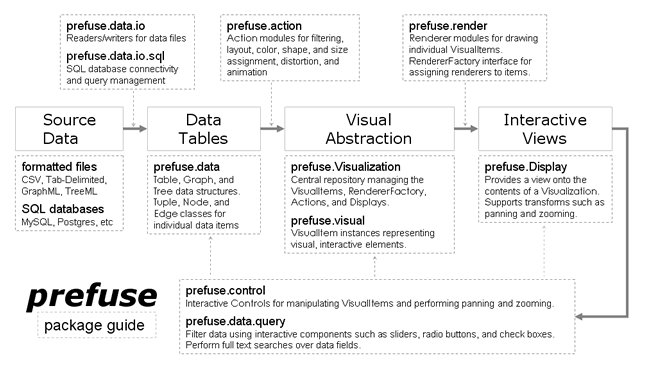
从图中可以发现一个prefuse程序的编写需要经历以下步骤:
- 准备好原始数据(文件或是数据库数据);
- 通过prefuse.data.io以及prefuse.data.io.sql包将数据读入prefuse,实现原始数据与内置丰富的数据结构如Table、Graph、Tree等之间的映射;
- 为数据添加各种Action,执行布局、着色、设置形状等操作;
- 将上面处理好的数据存入数据存储中心Visuallization中;
- 为可视化组件添加渲染器Renderer,并将渲染器注册到Visualization上;
- 通过Display将Visualization中的可视化组件显示到屏幕上;
- 通过上图发现是个闭环图,当执行控制器以及过滤操作后又会得到更新后的Visualization,之后依次执行3、4、5、6步骤。
下面我们通过一个例子具体了解如何创建一个prefuse应用。
1. 加载数据:
首先是加载图数据到Prefuse的图实例中,这里用的是socialnet.xml数据集。代码中使用GraphMLReader类读取数据集。
在方法readGraph中关于能读取“/socialnet.xml”文件的说明:通过读源码发现首先会检查这个字符串是不是一个URL链接,如果是的话则直接打开这个链接,如果不是则检查其是否是一个Java Runtime 内的classpath资源链接,如果还不是,则会将该字符串视为一个文件或是文件系统。
Graph graph = null;
try {
graph = new GraphMLReader().readGraph("/socialnet.xml");
} catch ( DataIOException e ) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.err.println("Error loading graph. Exiting...");
System.exit(1);
}
2 .创建数据存储中心Visualization实例:
创建一个抽象的视觉图形。在此之前,需要创建一个Visualization实例并添加图形数据,同时在代码中可以看到还要赋给一个名称(group name)。当图或树的实例添加到Visualization对象上的时候,另外两个子组名(subgroups)也会自动被创建:一个是节点(以“.nodes”为后缀),一个是边(以“.edges”为后缀)
// add the graph to the visualization as the data group "graph"
// nodes and edges are accessible as "graph.nodes" and "graph.edges"
Visualization vis = new Visualization();
vis.add("graph", graph);
3.渲染和渲染工厂的创建:
使用Renderers渲染器绘制Visualization对象中的VisualItems。默认情况下,Visualization类中包含了DefaultRendererFactory,其使用EdgeRenderer(默认绘制直连边)、ShapeRenderer绘制图形(比如正方形或三角形)。当希望看到节点上标签值是,可以创建一个LabelRenderers并为标签数据域赋值。
// draw the "name" label for NodeItems
LabelRenderer r = new LabelRenderer("name");
r.setRoundedCorner(8, 8); // round the corners
// create a new default renderer factory
// return our name label renderer as the default for all non-EdgeItems
// includes straight line edges for EdgeItems by default
vis.setRendererFactory(new DefaultRendererFactory(r));
4.添加处理的动作Actions:
添加所需的视觉效果。通过创建不同的Action模块处理Visualization上的VisualItems。比如可以创建一个颜色动作事件(ColorActions),该VisualItem默认支持三种颜色赋值:描边颜色、填充颜色以及文本颜色。描边的颜色是线条和轮廓的颜色;填充颜色是VisualItem的内部颜色;文本颜色是文本或是标签的颜色。默认情况下,所有颜色都是纯透明的。ColorLib类提供了很多颜色赋值的方法。
通过以下代码可以看出通过创建DataColorAction完成颜色分配工作。DataColorAction构造器的参数如下:
(1)要运行的数据组名(这里是graph.nodes)
(2)数据域的名称(这里是gender)
(3)数据域的数据类型,有三种:NOMINAL(适用于类别标签集),ORDINAL(适用于有序集合),以及NUMERICAL(适用于数字)。
(4)颜色域的设置,有描边、填充和文本三种。
(5)可选的调色板
注意:这里DataColorAction对于赋值颜色的选取也是有排序的,一般是自然排序的顺序,比如对于文本来说是按照字母表的先后顺序来的。这就是为什么这里的粉红色排在前面,因为按照字母顺序,“F”排在“M”的前面。
// create our nominal color palette
// pink for females, baby blue for males
int[] palette = new int[] {
ColorLib.rgb(255,180,180), ColorLib.rgb(190,190,255)
};
// map nominal data values to colors using our provided palette
DataColorAction fill = new DataColorAction("graph.nodes", "gender", Constants.NOMINAL, VisualItem.FILLCOLOR, palette);
// use black for node text
ColorAction text = new ColorAction("graph.nodes", VisualItem.TEXTCOLOR, ColorLib.gray(0));
// use light grey for edges
ColorAction edges = new ColorAction("graph.edges",
VisualItem.STROKECOLOR, ColorLib.gray(200));
// create an action list containing all color assignments
ActionList color = new ActionList();
color.add(fill);
color.add(text);
color.add(edges);
接着再创建关于动画布局的ActionList。所有的Action都可以进行参数控制的指定运行多少次(默认情况下是一次),也可以限定指定间隔时间运行,或者指定间隔时间无限制运行。代码中通过添加ForceDirectedLayout布局来进行图中节点的位置更新。添加RepaintAction()来实现当布局重新计算后就进行图形重绘的功能。
// create an action list with an animated layout
// the INFINITY parameter tells the action list to run indefinitely
ActionList layout = new ActionList(Activity.INFINITY);
layout.add(new ForceDirectedLayout("graph"));
layout.add(new RepaintAction());
然后将这两个ActionLists添加到Visualization上,每个注册的Action都有唯一标示以方便调用。
// add the actions to the visualization
vis.putAction("color", color);
vis.putAction("layout", layout);
5.展现和交互控制:
创建Display实现数据可视化。这里创建一个Display实例将Visualization中的Visualitems进行参数配置。可以设置想要展现的Display的大小、像素。这里,我们添加三个交互控制器:
(1) 拖拽控制
(2) 平移控制
(3) 缩放控制
// create a new Display that pull from our Visualization Display display = new Display(vis); display.setSize(720, 500); // set display size display.addControlListener(new DragControl()); // drag items around display.addControlListener(new PanControl()); // pan with background left-drag display.addControlListener(new ZoomControl()); // zoom with vertical right-drag
6.可视化呈现:
剩下要做的就是添加Display显示到一个应用程序窗口并让程序运行。该例中,创建Java Swing编程中的顶级类JFrame,设置标题。“pack”可以使得窗口合适的布局并确保窗口可见。
// create a new window to hold the visualization
JFrame frame = new JFrame("prefuse example");
// ensure application exits when window is closed
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.add(display);
frame.pack(); // layout components in window
frame.setVisible(true); // show the window
vis.run("color"); // assign the colors
vis.run("layout"); // start up the animated layout
执行结果如下:
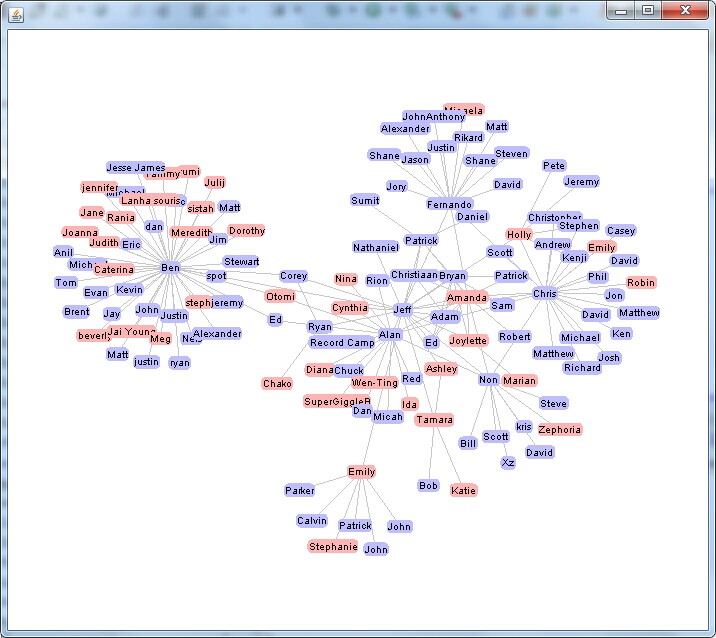
另外,在《可视化工具solo show-----Prefuse自带例子GraphView讲解》篇中,对GraphView.java进行了阅读并注释,这里再贴出RadialGraphView.java和TreeView.java的部分注释。
RadialGraphView.java
public class RadialGraphView extends Display {
public static final String DATA_FILE = "socialnet.xml";
private static final String tree = "tree";
private static final String treeNodes = "tree.nodes";
private static final String treeEdges = "tree.edges";
private static final String linear = "linear";
private LabelRenderer m_nodeRenderer;
private EdgeRenderer m_edgeRenderer;
private String m_label = "label";
public RadialGraphView(Graph g, String label) {
super(new Visualization());
m_label = label;
// -- set up visualization --
m_vis.add(tree, g);//将graph对象添加到m_vis对象上
m_vis.setInteractive(treeEdges, null, false);
// -- set up renderers -- 设置点和边的渲染器
m_nodeRenderer = new LabelRenderer(m_label);
m_nodeRenderer.setRenderType(AbstractShapeRenderer.RENDER_TYPE_FILL);
m_nodeRenderer.setHorizontalAlignment(Constants.CENTER);
m_nodeRenderer.setRoundedCorner(8,8);
m_edgeRenderer = new EdgeRenderer();
DefaultRendererFactory rf = new DefaultRendererFactory(m_nodeRenderer);
rf.add(new InGroupPredicate(treeEdges), m_edgeRenderer);
m_vis.setRendererFactory(rf);
// -- set up processing actions --
// colors
ItemAction nodeColor = new NodeColorAction(treeNodes);
ItemAction textColor = new TextColorAction(treeNodes);
m_vis.putAction("textColor", textColor);
ItemAction edgeColor = new ColorAction(treeEdges,
VisualItem.STROKECOLOR, ColorLib.rgb(200,200,200));//新建边颜色Action
FontAction fonts = new FontAction(treeNodes,
FontLib.getFont("Tahoma", 10));//设置节点大小以及字体
fonts.add("ingroup('_focus_')", FontLib.getFont("Tahoma", 11));
// recolor 新建重新着色ActionList,并添加上面的节点和边Action
ActionList recolor = new ActionList();
recolor.add(nodeColor);
recolor.add(textColor);
m_vis.putAction("recolor", recolor);
// repaint 新建重绘ActionList,并加入recolor以及RepaintAction
ActionList repaint = new ActionList();
repaint.add(recolor);
repaint.add(new RepaintAction());
m_vis.putAction("repaint", repaint);
// animate paint change
ActionList animatePaint = new ActionList(400);
animatePaint.add(new ColorAnimator(treeNodes));
animatePaint.add(new RepaintAction());
m_vis.putAction("animatePaint", animatePaint);
// create the tree layout action 采用径向树布局
RadialTreeLayout treeLayout = new RadialTreeLayout(tree);
//treeLayout.setAngularBounds(-Math.PI/2, Math.PI);
m_vis.putAction("treeLayout", treeLayout);
CollapsedSubtreeLayout subLayout = new CollapsedSubtreeLayout(tree);//折叠子树布局
m_vis.putAction("subLayout", subLayout);
// create the filtering and layout 创建过滤器和布局 在图形呈现之前,做好过滤filter工作
ActionList filter = new ActionList();
filter.add(new TreeRootAction(tree));
filter.add(fonts);
filter.add(treeLayout);
filter.add(subLayout);
filter.add(textColor);
filter.add(nodeColor);
filter.add(edgeColor);
m_vis.putAction("filter", filter);
// animated transition 动画过渡
ActionList animate = new ActionList(1250);
animate.setPacingFunction(new SlowInSlowOutPacer());//起搏功能,提供渐入渐出效果
animate.add(new QualityControlAnimator());//可以平滑切换动画的动画控制器
animate.add(new VisibilityAnimator(tree));
animate.add(new PolarLocationAnimator(treeNodes, linear));
animate.add(new ColorAnimator(treeNodes));
animate.add(new RepaintAction());
m_vis.putAction("animate", animate);
m_vis.alwaysRunAfter("filter", "animate");
// initialize the display
setSize(600,600);//初始化JFrame大小 注意:这里没有像GraphView一样创建Display对象,是因为该类RadialGraphView继承 了Display,可以直接调用方法
setItemSorter(new TreeDepthItemSorter());//为树状深度设置排序分类器
addControlListener(new DragControl());//一下都是设置监听类,包括拖拽、缩放至适合显示、平移、聚焦、悬停
addControlListener(new ZoomToFitControl());
addControlListener(new ZoomControl());
addControlListener(new PanControl());
addControlListener(new FocusControl(1, "filter"));
addControlListener(new HoverActionControl("repaint"));
// filter graph and perform layout
m_vis.run("filter");
// maintain a set of items that should be interpolated linearly
// this isn't absolutely necessary, but makes the animations nicer
// the PolarLocationAnimator should read this set and act accordingly
m_vis.addFocusGroup(linear, new DefaultTupleSet());
m_vis.getGroup(Visualization.FOCUS_ITEMS).addTupleSetListener(//添加数据集监听器,监听数据变化
new TupleSetListener() {
public void tupleSetChanged(TupleSet t, Tuple[] add, Tuple[] rem) {
TupleSet linearInterp = m_vis.getGroup(linear);
if ( add.length < 1 ) return; linearInterp.clear();
for ( Node n = (Node)add[0]; n!=null; n=n.getParent() )
linearInterp.addTuple(n);
}
}
);
SearchTupleSet search = new PrefixSearchTupleSet();//监听搜索栏数据
m_vis.addFocusGroup(Visualization.SEARCH_ITEMS, search);
search.addTupleSetListener(new TupleSetListener() {
public void tupleSetChanged(TupleSet t, Tuple[] add, Tuple[] rem) {
m_vis.cancel("animatePaint");
m_vis.run("recolor");
m_vis.run("animatePaint");
}
});
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------
public static void main(String argv[]) {
String infile = DATA_FILE;
String label = "name";
if ( argv.length > 1 ) {
infile = argv[0];
label = argv[1];
}
UILib.setPlatformLookAndFeel();
JFrame frame = new JFrame("p r e f u s e | r a d i a l g r a p h v i e w");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setContentPane(demo(infile, label));
frame.pack();
frame.setVisible(true);
}
public static JPanel demo() {
return demo(DATA_FILE, "name");
}
public static JPanel demo(String datafile, final String label) {
Graph g = null;
try {
g = new GraphMLReader().readGraph(datafile);
} catch ( Exception e ) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
return demo(g, label);
}
public static JPanel demo(Graph g, final String label) {
// create a new radial tree view //创建一个径向树形布局
final RadialGraphView gview = new RadialGraphView(g, label);
Visualization vis = gview.getVisualization();
// create a search panel for the tree map
SearchQueryBinding sq = new SearchQueryBinding(
(Table)vis.getGroup(treeNodes), label,
(SearchTupleSet)vis.getGroup(Visualization.SEARCH_ITEMS));
JSearchPanel search = sq.createSearchPanel();
search.setShowResultCount(true);
search.setBorder(BorderFactory.createEmptyBorder(5,5,4,0));
search.setFont(FontLib.getFont("Tahoma", Font.PLAIN, 11));
final JFastLabel title = new JFastLabel(" ");
title.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(350, 20));
title.setVerticalAlignment(SwingConstants.BOTTOM);
title.setBorder(BorderFactory.createEmptyBorder(3,0,0,0));
title.setFont(FontLib.getFont("Tahoma", Font.PLAIN, 16));
gview.addControlListener(new ControlAdapter() {//为搜索框添加监听事件
public void itemEntered(VisualItem item, MouseEvent e) {
if ( item.canGetString(label) )//如果搜索框文本发生变化,则将最新文本值赋给搜索文本框
title.setText(item.getString(label));
}
public void itemExited(VisualItem item, MouseEvent e) {//如果搜索框失去焦点,则置搜索文本框值为空
title.setText(null);
}
});
Box box = new Box(BoxLayout.X_AXIS);//创建盒子容器,装在上面的搜索面板和搜索文本框(安装水平方向布局)
box.add(Box.createHorizontalStrut(10));
box.add(title);
box.add(Box.createHorizontalGlue());
box.add(search);
box.add(Box.createHorizontalStrut(3));
JPanel panel = new JPanel(new BorderLayout());//按照组件级别从小到大,先创建JPanel对象,并将上面的RadialGraphView和Box注册到JPanel上
panel.add(gview, BorderLayout.CENTER);//RadialGraphView对象放到面板中间位置
panel.add(box, BorderLayout.SOUTH);//Box对象放到面板南边位置
Color BACKGROUND = Color.WHITE;
Color FOREGROUND = Color.DARK_GRAY;
UILib.setColor(panel, BACKGROUND, FOREGROUND);//设置整个panel面板的前景和背景颜色
return panel;
}
/**
* Switch the root of the tree by requesting a new spanning tree
* at the desired root
*/
public static class TreeRootAction extends GroupAction {
public TreeRootAction(String graphGroup) {
super(graphGroup);
}
public void run(double frac) {
TupleSet focus = m_vis.getGroup(Visualization.FOCUS_ITEMS);//如果没有点被选中或选中为空则跳出run函数
if ( focus==null || focus.getTupleCount() == 0 ) return;
Graph g = (Graph)m_vis.getGroup(m_group);
Node f = null;
Iterator tuples = focus.tuples();
while (tuples.hasNext() && !g.containsTuple(f=(Node)tuples.next()))//迭代选中的焦点,如果选中焦点不是上次的焦点,则置f为空,并跳出run函数
{
f = null;
}
if ( f == null ) return;
g.getSpanningTree(f);//返回一个生成树
}
}
/**
* Set node fill colors 设置点的填充色
*/
public static class NodeColorAction extends ColorAction {
public NodeColorAction(String group) {
super(group, VisualItem.FILLCOLOR, ColorLib.rgba(255,255,255,0));
add("_hover", ColorLib.gray(220,230));
add("ingroup('_search_')", ColorLib.rgb(255,190,190));
add("ingroup('_focus_')", ColorLib.rgb(198,229,229));
}
} // end of inner class NodeColorAction
/**
* Set node text colors 设置点内文本颜色
*/
public static class TextColorAction extends ColorAction {
public TextColorAction(String group) {
super(group, VisualItem.TEXTCOLOR, ColorLib.gray(0));
add("_hover", ColorLib.rgb(255,0,0));
}
} // end of inner class TextColorAction
} // end of class RadialGraphView
TreeView.java
public class TreeView extends Display {
public static final String TREE_CHI = "chi-ontology.xml.gz";
private static final String tree = "tree";
private static final String treeNodes = "tree.nodes";
private static final String treeEdges = "tree.edges";
private LabelRenderer m_nodeRenderer;
private EdgeRenderer m_edgeRenderer;
private String m_label = "label";
private int m_orientation = Constants.ORIENT_LEFT_RIGHT;//设置树的布局方式,有left->right,right->left,top->bottom,bottom->top共四种方式
public TreeView(Tree t, String label) {
super(new Visualization());
m_label = label;
m_vis.add(tree, t);//将tree注册到m_vis对象上
m_nodeRenderer = new LabelRenderer(m_label);//新建节点和边的渲染器
m_nodeRenderer.setRenderType(AbstractShapeRenderer.RENDER_TYPE_FILL);
m_nodeRenderer.setHorizontalAlignment(Constants.LEFT);
m_nodeRenderer.setRoundedCorner(8,8);
m_edgeRenderer = new EdgeRenderer(Constants.EDGE_TYPE_CURVE);
DefaultRendererFactory rf = new DefaultRendererFactory(m_nodeRenderer);
rf.add(new InGroupPredicate(treeEdges), m_edgeRenderer);
m_vis.setRendererFactory(rf);//将上面的点和边的渲染器注册到DefaultRendererFactory,再添加到m_vis对象上
// colors
ItemAction nodeColor = new NodeColorAction(treeNodes);
ItemAction textColor = new ColorAction(treeNodes,
VisualItem.TEXTCOLOR, ColorLib.rgb(0,0,0));
m_vis.putAction("textColor", textColor);
ItemAction edgeColor = new ColorAction(treeEdges,
VisualItem.STROKECOLOR, ColorLib.rgb(200,200,200));
// quick repaint
ActionList repaint = new ActionList();
repaint.add(nodeColor);
repaint.add(new RepaintAction());
m_vis.putAction("repaint", repaint);
// full paint
ActionList fullPaint = new ActionList();
fullPaint.add(nodeColor);
m_vis.putAction("fullPaint", fullPaint);
// animate paint change
ActionList animatePaint = new ActionList(400);
animatePaint.add(new ColorAnimator(treeNodes));
animatePaint.add(new RepaintAction());
m_vis.putAction("animatePaint", animatePaint);
// create the tree layout action
NodeLinkTreeLayout treeLayout = new NodeLinkTreeLayout(tree,
m_orientation, 50, 0, 8);//50代表树深度之间的距离 0代表兄弟节点之间的距离 8代表相邻子树之间的距离
treeLayout.setLayoutAnchor(new Point2D.Double(25,300));
m_vis.putAction("treeLayout", treeLayout);
CollapsedSubtreeLayout subLayout =
new CollapsedSubtreeLayout(tree, m_orientation);
m_vis.putAction("subLayout", subLayout);
AutoPanAction autoPan = new AutoPanAction();
// create the filtering and layout 在图形呈现之前,做好过滤filter工作,包括默认显示几层树,采用什么布局,节点和边如何展示等等
ActionList filter = new ActionList();
filter.add(new FisheyeTreeFilter(tree, 2));//添加一个鱼眼树形过滤器 设置初始界面显示几层节点
filter.add(new FontAction(treeNodes, FontLib.getFont("Tahoma", 16)));
filter.add(treeLayout);
filter.add(subLayout);
filter.add(textColor);
filter.add(nodeColor);
filter.add(edgeColor);
m_vis.putAction("filter", filter);
// animated transition 动画过渡
ActionList animate = new ActionList(1000);
animate.setPacingFunction(new SlowInSlowOutPacer());//使用SlowInSlowOutPacer可以实现一开始速度缓慢,中途加速,即将停止之前变慢的效果
animate.add(autoPan);
animate.add(new QualityControlAnimator());
animate.add(new VisibilityAnimator(tree));
animate.add(new LocationAnimator(treeNodes));
animate.add(new ColorAnimator(treeNodes));
animate.add(new RepaintAction());//从RepaintAction的构造函数可以看出每次执行RepaintAction时都会执行m_vis,即刷新执行一个上面的m_vis,所以就不需要add上面的sublayout、treelayout、filter等,因为这些已经被putAction进入m_vis了
m_vis.putAction("animate", animate);
m_vis.alwaysRunAfter("filter", "animate");//第一个参数:等待的Action名称 第二个参数:第一个Action运行完再运行的Action
// create animator for orientation changes 针对图形布局方向改变时进行的操作
ActionList orient = new ActionList(2000);
orient.setPacingFunction(new SlowInSlowOutPacer());
orient.add(autoPan);
orient.add(new QualityControlAnimator());
orient.add(new LocationAnimator(treeNodes));
orient.add(new RepaintAction());
m_vis.putAction("orient", orient);
// initialize the display
setSize(700,600);
setItemSorter(new TreeDepthItemSorter());
addControlListener(new ZoomToFitControl());
addControlListener(new ZoomControl());
addControlListener(new WheelZoomControl());
addControlListener(new PanControl());
addControlListener(new FocusControl(1, "filter"));//其中1代表鼠标聚焦点击的次数
registerKeyboardAction(//注册快捷键响应事件 ctrl+1、ctrl+2、ctrl+3、ctrl+4分别对应不同的布局方式
new OrientAction(Constants.ORIENT_LEFT_RIGHT),
"left-to-right", KeyStroke.getKeyStroke("ctrl 1"), WHEN_FOCUSED);
registerKeyboardAction(
new OrientAction(Constants.ORIENT_TOP_BOTTOM),
"top-to-bottom", KeyStroke.getKeyStroke("ctrl 2"), WHEN_FOCUSED);
registerKeyboardAction(
new OrientAction(Constants.ORIENT_RIGHT_LEFT),
"right-to-left", KeyStroke.getKeyStroke("ctrl 3"), WHEN_FOCUSED);
registerKeyboardAction(
new OrientAction(Constants.ORIENT_BOTTOM_TOP),
"bottom-to-top", KeyStroke.getKeyStroke("ctrl 4"), WHEN_FOCUSED);
// ------------------------------------------------
// filter graph and perform layout
setOrientation(m_orientation);
m_vis.run("filter");
TupleSet search = new PrefixSearchTupleSet();
m_vis.addFocusGroup(Visualization.SEARCH_ITEMS, search);
search.addTupleSetListener(new TupleSetListener() {
public void tupleSetChanged(TupleSet t, Tuple[] add, Tuple[] rem) {
m_vis.cancel("animatePaint");
m_vis.run("fullPaint");
m_vis.run("animatePaint");
}
});
}
public void setOrientation(int orientation) {
NodeLinkTreeLayout rtl
= (NodeLinkTreeLayout)m_vis.getAction("treeLayout");
CollapsedSubtreeLayout stl
= (CollapsedSubtreeLayout)m_vis.getAction("subLayout");
switch ( orientation ) {
case Constants.ORIENT_LEFT_RIGHT:
m_nodeRenderer.setHorizontalAlignment(Constants.LEFT);
m_edgeRenderer.setHorizontalAlignment1(Constants.RIGHT);
m_edgeRenderer.setHorizontalAlignment2(Constants.LEFT);
m_edgeRenderer.setVerticalAlignment1(Constants.CENTER);
m_edgeRenderer.setVerticalAlignment2(Constants.CENTER);
break;
case Constants.ORIENT_RIGHT_LEFT:
m_nodeRenderer.setHorizontalAlignment(Constants.RIGHT);
m_edgeRenderer.setHorizontalAlignment1(Constants.LEFT);
m_edgeRenderer.setHorizontalAlignment2(Constants.RIGHT);
m_edgeRenderer.setVerticalAlignment1(Constants.CENTER);
m_edgeRenderer.setVerticalAlignment2(Constants.CENTER);
break;
case Constants.ORIENT_TOP_BOTTOM:
m_nodeRenderer.setHorizontalAlignment(Constants.CENTER);
m_edgeRenderer.setHorizontalAlignment1(Constants.CENTER);
m_edgeRenderer.setHorizontalAlignment2(Constants.CENTER);
m_edgeRenderer.setVerticalAlignment1(Constants.BOTTOM);
m_edgeRenderer.setVerticalAlignment2(Constants.TOP);
break;
case Constants.ORIENT_BOTTOM_TOP:
m_nodeRenderer.setHorizontalAlignment(Constants.CENTER);
m_edgeRenderer.setHorizontalAlignment1(Constants.CENTER);
m_edgeRenderer.setHorizontalAlignment2(Constants.CENTER);
m_edgeRenderer.setVerticalAlignment1(Constants.TOP);
m_edgeRenderer.setVerticalAlignment2(Constants.BOTTOM);
break;
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Unrecognized orientation value: "+orientation);
}
m_orientation = orientation;
rtl.setOrientation(orientation);
stl.setOrientation(orientation);
}
public int getOrientation() {
return m_orientation;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------
public static void main(String argv[]) {
String infile = TREE_CHI;
String label = "name";
if ( argv.length > 1 ) {
infile = argv[0];
label = argv[1];
}
JComponent treeview = demo(infile, label);
JFrame frame = new JFrame("p r e f u s e | t r e e v i e w");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setContentPane(treeview);
frame.pack();
frame.setVisible(true);
}
public static JComponent demo() {
return demo(TREE_CHI, "name");
}
public static JComponent demo(String datafile, final String label) {
Color BACKGROUND = Color.WHITE;
Color FOREGROUND = Color.BLACK;
Tree t = null;
try {
t = (Tree)new TreeMLReader().readGraph(datafile);
} catch ( Exception e ) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
// create a new treemap 创建一个树状图并设置前景背景颜色
final TreeView tview = new TreeView(t, label);
tview.setBackground(BACKGROUND);
tview.setForeground(FOREGROUND);
// create a search panel for the tree map 为树状图添加一个搜索文本标签
JSearchPanel search = new JSearchPanel(tview.getVisualization(),
treeNodes, Visualization.SEARCH_ITEMS, label, true, true);
search.setShowResultCount(true);//显示搜索符合条件的节点个数
search.setBorder(BorderFactory.createEmptyBorder(5,5,4,0));
search.setFont(FontLib.getFont("Tahoma", Font.PLAIN, 11));
search.setBackground(BACKGROUND);
search.setForeground(FOREGROUND);
final JFastLabel title = new JFastLabel(" ");//为树状图添加一个搜索面板
title.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(350, 20));//长350 宽20
title.setVerticalAlignment(SwingConstants.BOTTOM);
title.setBorder(BorderFactory.createEmptyBorder(3,0,0,0));
title.setFont(FontLib.getFont("Tahoma", Font.PLAIN, 16));
title.setBackground(BACKGROUND);
title.setForeground(FOREGROUND);
tview.addControlListener(new ControlAdapter() {
public void itemEntered(VisualItem item, MouseEvent e) {
if ( item.canGetString(label) )
title.setText(item.getString(label));
}
public void itemExited(VisualItem item, MouseEvent e) {
title.setText(null);
}
});
Box box = new Box(BoxLayout.X_AXIS);
box.add(Box.createHorizontalStrut(10));
box.add(title);
box.add(Box.createHorizontalGlue());
box.add(search);
box.add(Box.createHorizontalStrut(3));
box.setBackground(BACKGROUND);
JPanel panel = new JPanel(new BorderLayout());
panel.setBackground(BACKGROUND);
panel.setForeground(FOREGROUND);
panel.add(tview, BorderLayout.CENTER);
panel.add(box, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
return panel;
}
public class OrientAction extends AbstractAction {//方向Action,针对界面中变换布局方式所做的响应
private int orientation;
public OrientAction(int orientation) {
this.orientation = orientation;
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent evt) {
setOrientation(orientation);
getVisualization().cancel("orient");
getVisualization().run("treeLayout");
getVisualization().run("orient");//通过进入getVisualization方法可以发现该方法返回的是m_vis对象,getVisualization().run("orient");等价于m_vis.run("orient");
}
}
public class AutoPanAction extends Action {
private Point2D m_start = new Point2D.Double();
private Point2D m_end = new Point2D.Double();
private Point2D m_cur = new Point2D.Double();
private int m_bias = 150;
public void run(double frac) {
TupleSet ts = m_vis.getFocusGroup(Visualization.FOCUS_ITEMS);
if ( ts.getTupleCount() == 0 )
return;
if ( frac == 0.0 ) {
int xbias=0, ybias=0;
switch ( m_orientation ) {
case Constants.ORIENT_LEFT_RIGHT:
xbias = m_bias;
break;
case Constants.ORIENT_RIGHT_LEFT:
xbias = -m_bias;
break;
case Constants.ORIENT_TOP_BOTTOM:
ybias = m_bias;
break;
case Constants.ORIENT_BOTTOM_TOP:
ybias = -m_bias;
break;
}
VisualItem vi = (VisualItem)ts.tuples().next();
m_cur.setLocation(getWidth()/2, getHeight()/2);
getAbsoluteCoordinate(m_cur, m_start);
m_end.setLocation(vi.getX()+xbias, vi.getY()+ybias);
} else {
m_cur.setLocation(m_start.getX() + frac*(m_end.getX()-m_start.getX()),
m_start.getY() + frac*(m_end.getY()-m_start.getY()));
panToAbs(m_cur);
}
}
}
public static class NodeColorAction extends ColorAction {
public NodeColorAction(String group) {
super(group, VisualItem.FILLCOLOR);
}
public int getColor(VisualItem item) {
if ( m_vis.isInGroup(item, Visualization.SEARCH_ITEMS) )
return ColorLib.rgb(255,190,190);
else if ( m_vis.isInGroup(item, Visualization.FOCUS_ITEMS) )
return ColorLib.rgb(198,229,229);
else if ( item.getDOI() > -1 )
return ColorLib.rgb(164,193,193);
else
return ColorLib.rgba(255,255,255,0);
}
} // end of inner class TreeMapColorAction
} // end of class TreeMap
原文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/bigdataZJ/p/VisualizationPrefuse2.html
画外音:1.prefuse真的很全面、很强大,不知道为什么后面一直没有更新,是转为商业化运营了么???
2.感觉研究可视化的小伙伴不是很多啊。。。
友情赞助
如果你觉得博主的文章对你那么一点小帮助,恰巧你又有想打赏博主的小冲动,那么事不宜迟,赶紧扫一扫,小额地赞助下,攒个奶粉钱,也是让博主有动力继续努力,写出更好的文章^^。
1. 支付宝 2. 微信


漫谈可视化Prefuse(二)---一分钟学会Prefuse的更多相关文章
- 漫谈可视化Prefuse(三)---Prefuse API数据结构阅读有感
前篇回顾:上篇<漫谈可视化Prefuse(二)---一分钟学会Prefuse>主要通过一个Prefuse的具体实例了解了构建一个Prefuse application的具体步骤.一个Pre ...
- 漫谈可视化Prefuse(五)---一款属于我自己的可视化工具
伴随着前期的基础积累,翻过API,读过一些Demo,总觉得自己已经摸透了Prefuse,小打小闹似乎已经无法满足内心膨胀的自己.还记得儿时看的<武状元苏乞儿>中降龙十八掌最后一张居然是空白 ...
- 漫谈可视化Prefuse(五)
伴随着前期的基础积累,翻过API,读过一些Demo,总觉得自己已经摸透了Prefuse,小打小闹似乎已经无法满足内心膨胀的自己.还记得儿时看的<武状元苏乞儿>中降龙十八掌最后一张居然是空白 ...
- Gephi可视化(二)——Gephi Toolkit叫板Prefuse
继在园子里写的<Gephi可视化(一)——使用Gephi Toolkit创建Gephi应用>介绍了如何使用Gephi Toolkit工具集进行可视化编程后,本篇对Gephi Toolkit ...
- 漫谈可视化Prefuse(六)---改动源码定制边粗细
可视化一路走来,体会很多:博客一路写来,收获颇丰:代码一路码来,思路越来越清晰.终究还是明白了一句古话:纸上得来终觉浅,绝知此事要躬行. 跌跌撞撞整合了个可视化小tool,零零碎碎结交了众多的志同道合 ...
- 漫谈可视化Prefuse(四)---被玩坏的Prefuse API
这个双12,别人都在抢红包.逛淘宝.上京东,我选择再续我的“漫谈可视化”系列(好了,不装了,其实是郎中羞涩...) 上篇<漫谈可视化Prefuse(三)---Prefuse API数据结构阅读有 ...
- 漫谈可视化Prefuse(六)
可视化一路走来,体会很多:博客一路写来,收获颇丰:代码一路码来,思路越来越清晰.终究还是明白了一句古话:纸上得来终觉浅,绝知此事要躬行. 跌跌撞撞整合了个可视化小tool,零零碎碎结交了众多的志同道合 ...
- Gephi可视化(二)
继在园子里写的<Gephi可视化(一)——使用Gephi Toolkit创建Gephi应用>介绍了如何使用Gephi Toolkit工具集进行可视化编程后,本篇对Gephi Toolkit ...
- 《量化投资:以MATLAB为工具》连载(2)基础篇-N分钟学会MATLAB(中)
http://www.matlabsky.com/thread-43937-1-1.html <量化投资:以MATLAB为工具>连载(3)基础篇-N分钟学会MATLAB(下) ...
随机推荐
- 【原创】--linux平台下opencv安装
1.到opencv官网下载源码 也可以下载此链接http://pan.baidu.com/s/1mgId5ZM 2.解压到任意目录 可以使用右键-提取到此处,也可以在命令行中使用指令解压(linux中 ...
- Linux文件目录权限总结
代表字符 权限 对文件含义 对目录含义 r 读权限 允许查看文件内容 允许列出目录中内容 w 写权限 允许修改文件内容 允许在目录中创建或删除文件 x 执行权限 允许执行文件 允许进入目录
- linux-10 基本命令之查看内存使用情况- free,history,who,last
free 命令 显示当前系统中内存的使用量情况 格式如下:free[-m/-g] 以m为单位显示当前内存的使用情况 [root@localhost /]# free -m 内存总量 已用量 可用量 ...
- Java多线程2:Thread中的实例方法
Thread类中的方法调用方式: 学习Thread类中的方法是学习多线程的第一步.在学习多线程之前特别提出一点,调用Thread中的方法的时候,在线程类中,有两种方式,一定要理解这两种方式的区别: 1 ...
- Unity3D音乐音效研究-MIDI与波表
其实音乐音效这个命题本身没什么好研究的. Unity3D提供了丰富的结构和使用方式,足够使用了. 但是我有一些小小的想法和需求,一般的Unity资料并没有给我答案. 一个是容量要小.MP3.OGG的高 ...
- 5、CC2541芯片中级教程-OSAL操作系统(PWM+看门狗)
本文根据一周CC2541笔记汇总得来—— 适合概览和知识快速索引—— 全部链接: 中级教程-OSAL操作系统\OSAL操作系统-实验01 OSAL初探 [插入]SourceInsight-工程建立方法 ...
- [ACM_动态规划] 数字三角形(数塔)
递归方法解决数塔问题 状态转移方程:d[i][j]=a[i][j]+max{d[i+1][j],d[i+1][j+1]} 注意:1\d[i][j]表示从i,j出发的最大总和;2\变界值设为0;3\递归 ...
- Yii CModel中rules验证 获取错误信息
在model中定义 public function rules(){ return array( array('Name,Email','required'), array('Email','uniq ...
- java内存管理总结
编译好的java程序需要运行在jvm中. 程序,无论是代码还是数据,都需要存储在内存中.JVM为java提供并管理所需要的内存空间. JVM内存分为堆.栈.方法区. 对象存储在堆中. This liv ...
- 翻译:AKKA笔记 - 介绍Actors
任何以前做过多线程的人都不会否认管理多线程程序是困难并且痛苦的. 我说管理是因为它开始很容易而且当你看到性能提升时会很兴奋.但是,当你看到你没法从子线程的错误中恢复 或者 这些僵尸bug很难重现 或者 ...
