SDWebImage源码解读之SDWebImageCache(下)
第六篇
前言
我们在SDWebImageCache(上)中了解了这个缓存类大概的功能是什么?那么接下来就要看看这些功能是如何实现的? 再次强调,不管是图片的缓存还是其他各种不同形式的缓存,在原理上都极其相似,我们通过SDWebImageCache,来看看作者是如何实现这个功能的。
在业务中,经常要缓存数据,通过本篇的学习,我们写出的缓存管理者这个管理者对象,就能够有所进步。
NSCache
对于很多开发者来说,NSCache是一个陌生人,因为大家往往对NSMutableDictionary情有独钟。可怜的 NSCache 一直处于 NSMutableDictionary 的阴影之下。就好像没有人知道它提供了垃圾处理的功能,而开发者们却费劲力气地去自己实现它。
没错,NSCache 基本上就是一个会自动移除对象来释放内存的 NSMutableDictionary。无需响应内存警告或者使用计时器来清除缓存。唯一的不同之处是键对象不会像 NSMutableDictionary 中那样被复制,这实际上是它的一个优点(键不需要实现 NSCopying 协议)。
当有缓存数据到内存的业务的时候,就应该考虑NSCache了,有缓存就有清楚缓存。
NSCache 每个方法和属性的具体作用,请参考这篇文章NSCache
AutoPurgeCache
NSCache在收到内存警告的时候会释放自身的一部分资源,设计AutoPurgeCache的目的是在收到警告时,释放缓存的所有资源。
通过继承自NSCache,监听UIApplicationDidReceiveMemoryWarningNotification来实现。
@interface AutoPurgeCache : NSCache
@end
@implementation AutoPurgeCache
- (nonnull instancetype)init {
self = [super init];
if (self) {
#if SD_UIKIT
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] addObserver:self selector:@selector(removeAllObjects) name:UIApplicationDidReceiveMemoryWarningNotification object:nil];
#endif
}
return self;
}
- (void)dealloc {
#if SD_UIKIT
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] removeObserver:self name:UIApplicationDidReceiveMemoryWarningNotification object:nil];
#endif
}
@end
计算一个UIImage的SDCacheCost
图片在该缓存中的大小是通过像素来衡量的。
FOUNDATION_STATIC_INLINE NSUInteger SDCacheCostForImage(UIImage *image) {
#if SD_MAC
return image.size.height * image.size.width;
#elif SD_UIKIT || SD_WATCH
return image.size.height * image.size.width * image.scale * image.scale;
#endif
}
** 注意:FOUNDATION_STATIC_INLINE表示该函数是一个具有文件内部访问权限的内联函数,所谓的内联函数就是建议编译器在调用时将函数展开。建议的意思就是说编译器不一定会按照你的建议做。因此内联函数尽量不要写的太复杂。**
Properties
SDWebImageCache实现部分有下边几个属性:
#pragma mark - Properties
@property (strong, nonatomic, nonnull) NSCache *memCache;
@property (strong, nonatomic, nonnull) NSString *diskCachePath;
@property (strong, nonatomic, nullable) NSMutableArray<NSString *> *customPaths;
@property (SDDispatchQueueSetterSementics, nonatomic, nullable) dispatch_queue_t ioQueue;
@end
@implementation SDImageCache {
NSFileManager *_fileManager;
}
memCache内存容器diskCachePath硬盘缓存路径customPaths自定义的读取路径,这是一个数组,我们可以通过addReadOnlyCachePath:这个方法往里边添加路径。当我们读取读片的时候,这个数组的路径也会作为数据源ioQueue称作输入输出队列,队列往往可以当做一种“锁”来使用,我们把某些任务按照顺利一步一步的进行,必须考虑线程是否安全_fileManager文件管理者,这个就不多说了,大家都知道怎么用
初始化
这一部分关系到Singleton, init, dealloc这三个方面的代码,初始化有四个方法,我们重点讲解最后一个初始化方法(这也是作者建议的方法,其他方法通过该方法实现):
+ (nonnull instancetype)sharedImageCache
- (instancetype)init
- (nonnull instancetype)initWithNamespace:(nonnull NSString *)ns
- (nonnull instancetype)initWithNamespace:(nonnull NSString *)ns
diskCacheDirectory:(nonnull NSString *)directory
- (nonnull instancetype)initWithNamespace:(nonnull NSString *)ns
diskCacheDirectory:(nonnull NSString *)directory {
if ((self = [super init])) {
NSString *fullNamespace = [@"com.hackemist.SDWebImageCache." stringByAppendingString:ns];
// Create IO serial queue
_ioQueue = dispatch_queue_create("com.hackemist.SDWebImageCache", DISPATCH_QUEUE_SERIAL);
_config = [[SDImageCacheConfig alloc] init];
// Init the memory cache
_memCache = [[AutoPurgeCache alloc] init];
_memCache.name = fullNamespace;
// Init the disk cache
if (directory != nil) {
_diskCachePath = [directory stringByAppendingPathComponent:fullNamespace];
} else {
NSString *path = [self makeDiskCachePath:ns];
_diskCachePath = path;
}
dispatch_sync(_ioQueue, ^{
_fileManager = [NSFileManager new];
});
#if SD_UIKIT
// Subscribe to app events
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] addObserver:self
selector:@selector(clearMemory)
name:UIApplicationDidReceiveMemoryWarningNotification
object:nil];
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] addObserver:self
selector:@selector(deleteOldFiles)
name:UIApplicationWillTerminateNotification
object:nil];
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] addObserver:self
selector:@selector(backgroundDeleteOldFiles)
name:UIApplicationDidEnterBackgroundNotification
object:nil];
#endif
}
return self;
}
这个方法其实就做了两件事:1.初始化自身的属性 2.添加通知监听。其他的初始化代码在这里就不写了。
Cache paths
1.添加自定义路径
- (void)addReadOnlyCachePath:(nonnull NSString *)path {
if (!self.customPaths) {
self.customPaths = [NSMutableArray new];
}
if (![self.customPaths containsObject:path]) {
[self.customPaths addObject:path];
}
}
2.文件名(MD5)
- (nullable NSString *)cachedFileNameForKey:(nullable NSString *)key {
const char *str = key.UTF8String;
if (str == NULL) {
str = "";
}
unsigned char r[CC_MD5_DIGEST_LENGTH];
CC_MD5(str, (CC_LONG)strlen(str), r);
NSString *filename = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%@",
r[0], r[1], r[2], r[3], r[4], r[5], r[6], r[7], r[8], r[9], r[10],
r[11], r[12], r[13], r[14], r[15], [key.pathExtension isEqualToString:@""] ? @"" : [NSString stringWithFormat:@".%@", key.pathExtension]];
return filename;
}
3.默认的某个图片的路径
- (nullable NSString *)defaultCachePathForKey:(nullable NSString *)key {
return [self cachePathForKey:key inPath:self.diskCachePath];
}
4.根据名称和路径拼接路径
- (nullable NSString *)cachePathForKey:(nullable NSString *)key inPath:(nonnull NSString *)path {
NSString *filename = [self cachedFileNameForKey:key];
return [path stringByAppendingPathComponent:filename];
}
Store Image
保存图片也有四个方法,我们按照顺序来看:
1.保存数据到Disk
- (void)storeImageDataToDisk:(nullable NSData *)imageData forKey:(nullable NSString *)key {
if (!imageData || !key) {
return;
}
[self checkIfQueueIsIOQueue];
if (![_fileManager fileExistsAtPath:_diskCachePath]) {
[_fileManager createDirectoryAtPath:_diskCachePath withIntermediateDirectories:YES attributes:nil error:NULL];
}
// get cache Path for image key
NSString *cachePathForKey = [self defaultCachePathForKey:key];
// transform to NSUrl
NSURL *fileURL = [NSURL fileURLWithPath:cachePathForKey];
[_fileManager createFileAtPath:cachePathForKey contents:imageData attributes:nil];
// disable iCloud backup
if (self.config.shouldDisableiCloud) {
[fileURL setResourceValue:@YES forKey:NSURLIsExcludedFromBackupKey error:nil];
}
}
- 检查imageData或者key是否为nil
- 检查是否在自身的队列中进行的操作
- 创建Disk缓存文件夹
- 根据key获取默认的缓存路径
- 将数据写入到上边获取的路径中
- 根据配置文件设置是否禁用iCloud的备份功能
2.参数最多的保存图片的方法
- (void)storeImage:(nullable UIImage *)image
imageData:(nullable NSData *)imageData
forKey:(nullable NSString *)key
toDisk:(BOOL)toDisk
completion:(nullable SDWebImageNoParamsBlock)completionBlock {
if (!image || !key) {
if (completionBlock) {
completionBlock();
}
return;
}
// if memory cache is enabled
if (self.config.shouldCacheImagesInMemory) {
NSUInteger cost = SDCacheCostForImage(image);
[self.memCache setObject:image forKey:key cost:cost];
}
if (toDisk) {
dispatch_async(self.ioQueue, ^{
NSData *data = imageData;
if (!data && image) {
SDImageFormat imageFormatFromData = [NSData sd_imageFormatForImageData:data];
data = [image sd_imageDataAsFormat:imageFormatFromData];
}
[self storeImageDataToDisk:data forKey:key];
if (completionBlock) {
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
completionBlock();
});
}
});
} else {
if (completionBlock) {
completionBlock();
}
}
}
- 检查image或者key是否为nil
- 根据配置文件中是否设置了缓存到内存,保存image到缓存中,这个过程是非常快的,因此不用考虑线程
- 如果保存到Disk,创建异步串行队列 我们把数据保存到Disk,其实保存的应该是数据的二进制文件
- 保存二进制数据到Disk,如果不存在,需要把image转换成NSData
- 调用Block
3.其他两个保存的方法
- (void)storeImage:(nullable UIImage *)image
forKey:(nullable NSString *)key
completion:(nullable SDWebImageNoParamsBlock)completionBlock {
[self storeImage:image imageData:nil forKey:key toDisk:YES completion:completionBlock];
}
- (void)storeImage:(nullable UIImage *)image
forKey:(nullable NSString *)key
toDisk:(BOOL)toDisk
completion:(nullable SDWebImageNoParamsBlock)completionBlock {
[self storeImage:image imageData:nil forKey:key toDisk:toDisk completion:completionBlock];
}
Query and Retrieve 数据
1.根据key判断Disk中的数据是否存在
- (void)diskImageExistsWithKey:(nullable NSString *)key completion:(nullable SDWebImageCheckCacheCompletionBlock)completionBlock {
dispatch_async(_ioQueue, ^{
BOOL exists = [_fileManager fileExistsAtPath:[self defaultCachePathForKey:key]];
// fallback because of https://github.com/rs/SDWebImage/pull/976 that added the extension to the disk file name
// checking the key with and without the extension
if (!exists) {
exists = [_fileManager fileExistsAtPath:[self defaultCachePathForKey:key].stringByDeletingPathExtension];
}
if (completionBlock) {
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
completionBlock(exists);
});
}
});
}
2.获取缓存到内存中的数据
- (nullable UIImage *)imageFromMemoryCacheForKey:(nullable NSString *)key {
return [self.memCache objectForKey:key];
}
3.获取Disk中的数据
在Disk中获取数据跟在内存中获取不一样,内存中直接保存的是UIImage,而Disk中保存的是NSData,因此肯定需要一个NSData -> UIImage 的转换过程。接下来我们看看这个转换过程:
根据key获取Disk中的NSData数据,总体思路就是先从默认的路径获取,如果没有获取到,再从自定义的路径获取,值得注意的是,要考虑没有pathExtention的情况
- (nullable NSData *)diskImageDataBySearchingAllPathsForKey:(nullable NSString *)key {
NSString *defaultPath = [self defaultCachePathForKey:key];
NSData *data = [NSData dataWithContentsOfFile:defaultPath];
if (data) {
return data;
} // fallback because of https://github.com/rs/SDWebImage/pull/976 that added the extension to the disk file name
// checking the key with and without the extension
data = [NSData dataWithContentsOfFile:defaultPath.stringByDeletingPathExtension];
if (data) {
return data;
} NSArray<NSString *> *customPaths = [self.customPaths copy];
for (NSString *path in customPaths) {
NSString *filePath = [self cachePathForKey:key inPath:path];
NSData *imageData = [NSData dataWithContentsOfFile:filePath];
if (imageData) {
return imageData;
} // fallback because of https://github.com/rs/SDWebImage/pull/976 that added the extension to the disk file name
// checking the key with and without the extension
imageData = [NSData dataWithContentsOfFile:filePath.stringByDeletingPathExtension];
if (imageData) {
return imageData;
}
} return nil;
}
根据NSData 获取 UIImage,需要scaled图片,根据配置文件的设置,是否解压图片
- (nullable UIImage *)diskImageForKey:(nullable NSString *)key {
NSData *data = [self diskImageDataBySearchingAllPathsForKey:key];
if (data) {
UIImage *image = [UIImage sd_imageWithData:data];
image = [self scaledImageForKey:key image:image];
if (self.config.shouldDecompressImages) {
image = [UIImage decodedImageWithImage:image];
}
return image;
}
else {
return nil;
}
}
将UIImage 放入内存,返回图片
- (nullable UIImage *)imageFromDiskCacheForKey:(nullable NSString *)key {
UIImage *diskImage = [self diskImageForKey:key];
if (diskImage && self.config.shouldCacheImagesInMemory) {
NSUInteger cost = SDCacheCostForImage(diskImage);
[self.memCache setObject:diskImage forKey:key cost:cost];
} return diskImage;
}
4.先获取内存的数据,如果没有,在获取Disk的数据
- (nullable UIImage *)imageFromCacheForKey:(nullable NSString *)key {
// First check the in-memory cache...
UIImage *image = [self imageFromMemoryCacheForKey:key];
if (image) {
return image;
}
// Second check the disk cache...
image = [self imageFromDiskCacheForKey:key];
return image;
}
5.异步获取数据
上边1.2.3.4 中获取数据的方法都不是异步获取的,在SDWebImageCache中,涉及到异步获取的,都会通过Block来回调的。
这个异步获取值得说的有两点:
- 如果在内存中获取到的图片是GIF,那么要去Disk中获取
- 为什么要返回一个NSOperation对象呢? 其实我们可以通过这个NSOperation对象取消获取任务
代码:
- (nullable NSOperation *)queryCacheOperationForKey:(nullable NSString *)key done:(nullable SDCacheQueryCompletedBlock)doneBlock {
if (!key) {
if (doneBlock) {
doneBlock(nil, nil, SDImageCacheTypeNone);
}
return nil;
}
// First check the in-memory cache...
UIImage *image = [self imageFromMemoryCacheForKey:key];
if (image) {
NSData *diskData = nil;
if ([image isGIF]) {
diskData = [self diskImageDataBySearchingAllPathsForKey:key];
}
if (doneBlock) {
doneBlock(image, diskData, SDImageCacheTypeMemory);
}
return nil;
}
NSOperation *operation = [NSOperation new];
dispatch_async(self.ioQueue, ^{
if (operation.isCancelled) {
// do not call the completion if cancelled
return;
}
@autoreleasepool {
NSData *diskData = [self diskImageDataBySearchingAllPathsForKey:key];
UIImage *diskImage = [self diskImageForKey:key];
if (diskImage && self.config.shouldCacheImagesInMemory) {
NSUInteger cost = SDCacheCostForImage(diskImage);
[self.memCache setObject:diskImage forKey:key cost:cost];
}
if (doneBlock) {
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
doneBlock(diskImage, diskData, SDImageCacheTypeDisk);
});
}
}
});
return operation;
}
Remove 数据
- (void)removeImageForKey:(nullable NSString *)key withCompletion:(nullable SDWebImageNoParamsBlock)completion {
[self removeImageForKey:key fromDisk:YES withCompletion:completion];
}
- (void)removeImageForKey:(nullable NSString *)key fromDisk:(BOOL)fromDisk withCompletion:(nullable SDWebImageNoParamsBlock)completion {
if (key == nil) {
return;
}
if (self.config.shouldCacheImagesInMemory) {
[self.memCache removeObjectForKey:key];
}
if (fromDisk) {
dispatch_async(self.ioQueue, ^{
[_fileManager removeItemAtPath:[self defaultCachePathForKey:key] error:nil];
if (completion) {
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
completion();
});
}
});
} else if (completion){
completion();
}
}
Mem Cache settings
- (void)setMaxMemoryCost:(NSUInteger)maxMemoryCost {
self.memCache.totalCostLimit = maxMemoryCost;
}
- (NSUInteger)maxMemoryCost {
return self.memCache.totalCostLimit;
}
- (NSUInteger)maxMemoryCountLimit {
return self.memCache.countLimit;
}
- (void)setMaxMemoryCountLimit:(NSUInteger)maxCountLimit {
self.memCache.countLimit = maxCountLimit;
}
清空数据
清空数据有值得我们注意的地方,我们一个一个方法的看:
1.清空内存缓存数据
- (void)clearMemory {
[self.memCache removeAllObjects];
}
2.清空Disk数据
- (void)clearDiskOnCompletion:(nullable SDWebImageNoParamsBlock)completion {
dispatch_async(self.ioQueue, ^{
[_fileManager removeItemAtPath:self.diskCachePath error:nil];
[_fileManager createDirectoryAtPath:self.diskCachePath
withIntermediateDirectories:YES
attributes:nil
error:NULL];
if (completion) {
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
completion();
});
}
});
}
3.清空旧数据
对于清空旧数据而言,我们需要考虑两个方面:
- 首先要清空掉所有的过期的数据
- 过期的数据清空后,缓存的数据比我们设置的最大缓存量还大,我们要继续清空数据,直到满足我们的需求为止
这里边大概用到的思路就是上边说的两点,关键是如何实现上边所说的内容。有一些我们平时可能不太接触的知识点,在这里做一些简要的讲解
首先我们需要遍历Disk缓存路径下的所有文件,那么我们怎么遍历呢?NSFileManager有一个很好地方法:
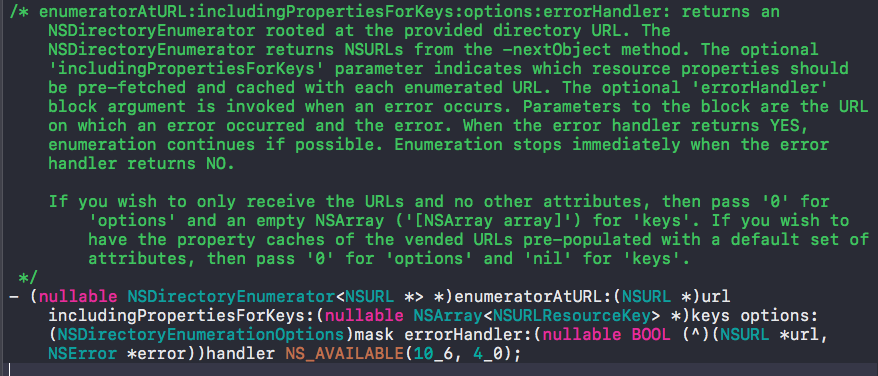
返回一个
NSDirectoryEnumerator<NSURL *> *这个对象中存放的是NSURLsurl 需要遍历的路径
(nullable NSArray<NSURLResourceKey> \*)keys这个需要传入一个数组,表示想获取的NSURLResourceKeys,我们来看看这个NSURLResourceKey: 点进去看了下。太长了,在这里就不copy了。有兴趣的同学,自己去看看,太长了。我们就说说着这个清空方法中用到的把:- NSURLIsDirectoryKey 是否是文件夹
- NSURLContentModificationDateKey 最后修改时间
- NSURLTotalFileAllocatedSizeKey 分配的尺寸
options:(NSDirectoryEnumerationOptions)mask 传入过滤参数,这里NSDirectoryEnumerationSkipsHiddenFiles 是指忽略隐藏文件
其次,我们有了这些参数了。在根据最后修改日期是否过期,删除掉过期的数据就行了。还有一个值得我们注意的就是如何对一个字典进行排序:
NSArray<NSURL *> *sortedFiles = [cacheFiles keysSortedByValueWithOptions:NSSortConcurrent
usingComparator:^NSComparisonResult(id obj1, id obj2) {
return [obj1[NSURLContentModificationDateKey] compare:obj2[NSURLContentModificationDateKey]];
}];
这个会返回排好序的字典的所有的key。NSSortConcurrent是并发排序,效率高,但可能不稳定,NSSortStable 稳定,但可能效率不如NSSortConcurrent高。排序的规则通过Block指定。
好了,基本要注意的就这些。这个函数的实现也是基于这种思路。
- (void)deleteOldFiles {
[self deleteOldFilesWithCompletionBlock:nil];
}
- (void)deleteOldFilesWithCompletionBlock:(nullable SDWebImageNoParamsBlock)completionBlock {
dispatch_async(self.ioQueue, ^{
NSURL *diskCacheURL = [NSURL fileURLWithPath:self.diskCachePath isDirectory:YES];
NSArray<NSString *> *resourceKeys = @[NSURLIsDirectoryKey, NSURLContentModificationDateKey, NSURLTotalFileAllocatedSizeKey];
// This enumerator prefetches useful properties for our cache files.
NSDirectoryEnumerator *fileEnumerator = [_fileManager enumeratorAtURL:diskCacheURL
includingPropertiesForKeys:resourceKeys
options:NSDirectoryEnumerationSkipsHiddenFiles
errorHandler:NULL];
NSDate *expirationDate = [NSDate dateWithTimeIntervalSinceNow:-self.config.maxCacheAge];
NSMutableDictionary<NSURL *, NSDictionary<NSString *, id> *> *cacheFiles = [NSMutableDictionary dictionary];
NSUInteger currentCacheSize = 0;
// Enumerate all of the files in the cache directory. This loop has two purposes:
//
// 1. Removing files that are older than the expiration date.
// 2. Storing file attributes for the size-based cleanup pass.
NSMutableArray<NSURL *> *urlsToDelete = [[NSMutableArray alloc] init];
for (NSURL *fileURL in fileEnumerator) {
NSError *error;
NSDictionary<NSString *, id> *resourceValues = [fileURL resourceValuesForKeys:resourceKeys error:&error];
// Skip directories and errors.
if (error || !resourceValues || [resourceValues[NSURLIsDirectoryKey] boolValue]) {
continue;
}
// Remove files that are older than the expiration date;
NSDate *modificationDate = resourceValues[NSURLContentModificationDateKey];
if ([[modificationDate laterDate:expirationDate] isEqualToDate:expirationDate]) {
[urlsToDelete addObject:fileURL];
continue;
}
// Store a reference to this file and account for its total size.
NSNumber *totalAllocatedSize = resourceValues[NSURLTotalFileAllocatedSizeKey];
currentCacheSize += totalAllocatedSize.unsignedIntegerValue;
cacheFiles[fileURL] = resourceValues;
}
for (NSURL *fileURL in urlsToDelete) {
[_fileManager removeItemAtURL:fileURL error:nil];
}
// If our remaining disk cache exceeds a configured maximum size, perform a second
// size-based cleanup pass. We delete the oldest files first.
if (self.config.maxCacheSize > 0 && currentCacheSize > self.config.maxCacheSize) {
// Target half of our maximum cache size for this cleanup pass.
const NSUInteger desiredCacheSize = self.config.maxCacheSize / 2;
// Sort the remaining cache files by their last modification time (oldest first).
NSArray<NSURL *> *sortedFiles = [cacheFiles keysSortedByValueWithOptions:NSSortConcurrent
usingComparator:^NSComparisonResult(id obj1, id obj2) {
return [obj1[NSURLContentModificationDateKey] compare:obj2[NSURLContentModificationDateKey]];
}];
// Delete files until we fall below our desired cache size.
for (NSURL *fileURL in sortedFiles) {
if ([_fileManager removeItemAtURL:fileURL error:nil]) {
NSDictionary<NSString *, id> *resourceValues = cacheFiles[fileURL];
NSNumber *totalAllocatedSize = resourceValues[NSURLTotalFileAllocatedSizeKey];
currentCacheSize -= totalAllocatedSize.unsignedIntegerValue;
if (currentCacheSize < desiredCacheSize) {
break;
}
}
}
}
if (completionBlock) {
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
completionBlock();
});
}
});
}
申请一段时间在后台删除旧数据
- (void)backgroundDeleteOldFiles {
Class UIApplicationClass = NSClassFromString(@"UIApplication");
if(!UIApplicationClass || ![UIApplicationClass respondsToSelector:@selector(sharedApplication)]) {
return;
}
UIApplication *application = [UIApplication performSelector:@selector(sharedApplication)];
__block UIBackgroundTaskIdentifier bgTask = [application beginBackgroundTaskWithExpirationHandler:^{
// Clean up any unfinished task business by marking where you
// stopped or ending the task outright.
[application endBackgroundTask:bgTask];
bgTask = UIBackgroundTaskInvalid;
}];
// Start the long-running task and return immediately.
[self deleteOldFilesWithCompletionBlock:^{
[application endBackgroundTask:bgTask];
bgTask = UIBackgroundTaskInvalid;
}];
}
Cache Info
- (NSUInteger)getSize {
__block NSUInteger size = 0;
dispatch_sync(self.ioQueue, ^{
NSDirectoryEnumerator *fileEnumerator = [_fileManager enumeratorAtPath:self.diskCachePath];
for (NSString *fileName in fileEnumerator) {
NSString *filePath = [self.diskCachePath stringByAppendingPathComponent:fileName];
NSDictionary<NSString *, id> *attrs = [[NSFileManager defaultManager] attributesOfItemAtPath:filePath error:nil];
size += [attrs fileSize];
}
});
return size;
}
- (NSUInteger)getDiskCount {
__block NSUInteger count = 0;
dispatch_sync(self.ioQueue, ^{
NSDirectoryEnumerator *fileEnumerator = [_fileManager enumeratorAtPath:self.diskCachePath];
count = fileEnumerator.allObjects.count;
});
return count;
}
- (void)calculateSizeWithCompletionBlock:(nullable SDWebImageCalculateSizeBlock)completionBlock {
NSURL *diskCacheURL = [NSURL fileURLWithPath:self.diskCachePath isDirectory:YES];
dispatch_async(self.ioQueue, ^{
NSUInteger fileCount = 0;
NSUInteger totalSize = 0;
NSDirectoryEnumerator *fileEnumerator = [_fileManager enumeratorAtURL:diskCacheURL
includingPropertiesForKeys:@[NSFileSize]
options:NSDirectoryEnumerationSkipsHiddenFiles
errorHandler:NULL];
for (NSURL *fileURL in fileEnumerator) {
NSNumber *fileSize;
[fileURL getResourceValue:&fileSize forKey:NSURLFileSizeKey error:NULL];
totalSize += fileSize.unsignedIntegerValue;
fileCount += 1;
}
if (completionBlock) {
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
completionBlock(fileCount, totalSize);
});
}
});
}
总结
SDWebImageCache 就写完了,本篇算是长文了,对于那种图片比较多的app,实现一个自己的缓存类还是很有必要的。
由于个人知识有限,如有错误之处,还望各路大侠给予指出啊
- SDWebImage源码解读 之 NSData+ImageContentType 简书 博客园
- SDWebImage源码解读 之 UIImage+GIF 简书 博客园
- SDWebImage源码解读 之 SDWebImageCompat 简书 博客园
- SDWebImage源码解读 之SDWebImageDecoder 简书 博客园
- SDWebImage源码解读 之SDWebImageCache(上) 简书 博客园
SDWebImage源码解读之SDWebImageCache(下)的更多相关文章
- SDWebImage源码解读之SDWebImageCache(上)
第五篇 前言 本篇主要讲解图片缓存类的知识,虽然只涉及了图片方面的缓存的设计,但思想同样适用于别的方面的设计.在架构上来说,缓存算是存储设计的一部分.我们把各种不同的存储内容按照功能进行切割后,图片缓 ...
- SDWebImage源码解读之SDWebImageDownloaderOperation
第七篇 前言 本篇文章主要讲解下载操作的相关知识,SDWebImageDownloaderOperation的主要任务是把一张图片从服务器下载到内存中.下载数据并不难,如何对下载这一系列的任务进行设计 ...
- SDWebImage源码解读之SDWebImageDownloader
SDWebImage源码解读之SDWebImageDownloader 第八篇 前言 SDWebImageDownloader这个类非常简单,作者的设计思路也很清晰,但是我想在这说点题外话. 如果有人 ...
- SDWebImage源码解读之SDWebImageManager
第九篇 前言 SDWebImageManager是SDWebImage中最核心的类了,但是源代码确是非常简单的.之所以能做到这一点,都归功于功能的良好分类. 有了SDWebImageManager这个 ...
- SDWebImage源码解读之SDWebImagePrefetcher
> 第十篇 ## 前言 我们先看看`SDWebImage`主文件的组成模块: sd_animatedGIFNamed:(NSString *)name ----- 根据名 ...
随机推荐
- iOS可视化动态绘制八种排序过程
前面几篇博客都是关于排序的,在之前陆陆续续发布的博客中,我们先后介绍了冒泡排序.选择排序.插入排序.希尔排序.堆排序.归并排序以及快速排序.俗话说的好,做事儿要善始善终,本篇博客就算是对之前那几篇博客 ...
- PHP 5.6 编译安装选项说明
`configure' configures this package to adapt to many kinds of systems. Usage: ./configure [OPTION].. ...
- 零OCR基础6行代码实现C#验证码识别
这两天因为工作需要,要到某个网站采集信息,一是要模拟登陆,二是要破解验证码,本想用第三方付费打码,但是想想网上免费的代码也挺多的,于是乎准备从网上撸点代码下来,谁知道,撸了好多个都不行,本人以前也没接 ...
- 普通程序员如何转向AI方向
眼下,人工智能已经成为越来越火的一个方向.普通程序员,如何转向人工智能方向,是知乎上的一个问题.本文是我对此问题的一个回答的归档版.相比原回答有所内容增加. 一. 目的 本文的目的是给出一个简单的,平 ...
- 【知识必备】一文让你搞懂design设计的CoordinatorLayout和AppbarLayout联动,让Design设计更简单~
一.写在前面 其实博主在之前已经对design包的各个控件都做了博文说明,无奈个人觉得理解不够深入,所以有了这篇更加深入的介绍,希望各位看官拍砖~ 二.从是什么开始 1.首先我们得知道Coordina ...
- Postman - 功能强大的 API 接口请求调试和管理工具
Postman 是一款功能强大的的 Chrome 应用,可以便捷的调试接口.前端开发人员在开发或者调试 Web 程序的时候是需要一些方法来跟踪网页请求的,用户可以使用一些网络的监视工具比如著名的 Fi ...
- Xamarin.iOS开发初体验
aaarticlea/png;base64,iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUgAAAKwAAAA+CAIAAAA5/WfHAAAJrklEQVR4nO2c/VdTRxrH+wfdU84pW0
- On cloud, be cloud native
本来不想起一个英文名,但是想来想去都没能想出一个简洁地表述该意思的中文释义,所以就用了一个英文名称,望见谅. Cloud Native是一个刚刚由VMware所提出一年左右的名词.其表示在设计并实现一 ...
- MyBatis3:SQL映射
前言 前面学习了config.xml,下面就要进入MyBatis的核心SQL映射了,第一篇文章的时候,student.xml里面是这么写的: <?xml version="1.0&qu ...
- 白板编程浅谈——Why, What, How
作者:Lucida 微博:@peng_gong 豆瓣:@figure9 原文链接:http://lucida.me/blog/whiteboard-coding-demystified/ 这篇文章节选 ...
