python基础之元组、文件操作、编码、函数、变量
1、集合set
集合是无序的,不重复的,主要作用:
去重,把一个列表变成集合,就可以自动去重
关系测试,测试两组数据的交集,差集,并集等关系
操作例子如下:
list_1 = [1,4,5,7,3,6,7,9]
list_1=set(list_1) list_2 = set([2,6,0,66,22,8,4]) print(list_1,list_2) print(list_1,type(list_1))
运行结果如下:
D:\python35\python.exe D:/python培训/s14/day3/set集合.py
{1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9} {0, 2, 66, 4, 6, 8, 22}
{1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9} <class 'set'> Process finished with exit code 0
关于集合的功能及操作
关于就集合的交集intersection:
print(list_1.intersection(list_2))
print(list_1 & list_2)
运行结果如下:
D:\python35\python.exe D:/python培训/s14/day3/set集合.py
{1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9} {0, 2, 66, 4, 6, 8, 22}
{4, 6}
{4, 6}
#并集union
print(list_1.union(list_2))
print(list_1 | list_2)
运行结果如下:
D:\python35\python.exe D:/python培训/s14/day3/set集合.py
{1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9} {0, 2, 66, 4, 6, 8, 22}
{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 66, 9, 8, 22}
{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 66, 9, 8, 22} Process finished with exit code 0
#差集difference
print(list_1.difference(list_2))
print(list_2.difference(list_1))
print(list_1-list_2)
运行结果如下:
D:\python35\python.exe D:/python培训/s14/day3/set集合.py
{1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9} {0, 2, 66, 4, 6, 8, 22}
{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 66, 9, 8, 22}
{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 66, 9, 8, 22} Process finished with exit code 0
#子集issubset
list_3=set([1,3,7])
print(list_3.issubset(list_1))
print(list_1.issubset(list_2))
#父集issuperset
print(list_1.issuperset(list_2))
运行结果如下:
D:\python35\python.exe D:/python培训/s14/day3/set集合.py
{1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9} {0, 2, 66, 4, 6, 8, 22}
True
False
False Process finished with exit code 0
#对称差集
print(list_1.symmetric_difference(list_2))
print(list_1 ^ list_2)
运行结果如下:
D:\python35\python.exe D:/python培训/s14/day3/set集合.py
{1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9} {0, 2, 66, 4, 6, 8, 22}
{0, 1, 2, 66, 3, 5, 7, 8, 9, 22}
{0, 1, 2, 66, 3, 5, 7, 8, 9, 22} Process finished with exit code 0
#判断是否有交集,如果没有返回True
list_4 = set([5,6,8])
print(list_4.isdisjoint(list_3))
运行结果如下:
D:\python35\python.exe D:/python培训/s14/day3/set集合.py
{1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9} {0, 2, 66, 4, 6, 8, 22}
True Process finished with exit code 0
#增加add
list_1.add(999)
print(list_1)
#更新
list_1.update([888,777,555])
print(list_1)
#删除
list_1.remove(4334)
print(list_1)
#随机删除
list_1.pop()
print(list_1)
#如果没有存在不会报错,如果是remove的时候会报错
list_1.discard()
#集合的长度
len(list_1)
# x in s 判断x是否是s的成员
2、关于文件操作
f = open("file.txt","r",encoding="utf-8") #文件句柄,即文件内存对象
写操作w,这个会将文件清空,即将文件重新写一遍,并且如果没有这个文件会创建
既读又写a----append 只能向文件中追加内容,也是不能读
读写r+
写读w+
追加写a+
#循环读这个文件
f=open("file.txt","r",encoding="utf-8")
for i in f.readlines():
print(i.strip())
f=open("file.txt","r",encoding="utf-8")
for index,line in enumerate(f.readlines()):
if index==2:
print("分割线".center(10,"-"))
continue
print(line.strip())
但是上面的效率比较低
下面这种方式更好
f=open("file.txt","r",encoding="utf-8")
count =0
for line in f:
count +=1
if count == 3:
print("分割线".center(10, "-"))
print(line.strip()) f.tell()打印当前的位置
f.seek()返回某个位置
f=open("file.txt","r",encoding="utf-8")
print(f.tell())
print(f.readline())
print(f.readline())
print(f.readline())
f.seek(0)
print(f.tell())
print(f.readline()) 对于上面打开文件的时候用的方式,后面都需要加f.close(),有一种方式可以省却这个步骤
with open(“file.txt”,‘r’) as f:
3、 Unicode不管是中文和因为都是占两个字符,16位
ASCII 不存在中文,8位
UTF-8可变长字符编码
在utf-8中所有的银根字符用ascii存放,
所有的中文字符都是3个字节
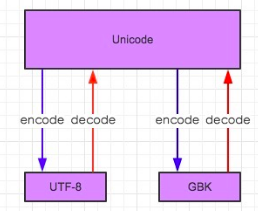
通过上图解释关于不同字符编码之间的转换
GBK转换成UTF-8
需要先通过decode解码转换为Unicode编码格式
再通过encode转换为UTF-8编码格式
4、 函数
函数是指将一组语句的集合通过一个名字封装起来,要想执行这个函数,只需调用其函数名字即可
函数的特性:
减少重复代码
是程序易于扩展
使程序变得容易维护
编程语言中函数定义:函数是逻辑结构化和过程化的一种变成方法
一个函数的定义方法:
def test(x):
"the function definitions"
x+=1
return x
print(test(2))
运行结果如下:
D:\python35\python.exe D:/python培训/s14/day3/func.py
3 Process finished with exit code 0
其中:
def:定义函数的关键字
test:函数名
():可以定义参数
“”:文档描述
return:定义返回值 一个函数的例子:
import time def logger_test():
time_format="%Y-%m-%d %X"
time_current = time.strftime(time_format)
with open("a.txt","a+") as f:
f.write('time %s end action\n' %time_current) def test1():
print("test1 starting action...")
logger_test() def test2():
print("test2 starting action...")
logger_test() def test3():
print("test3 starting action...")
logger_test() test1()
test2()
test3()
运行结果如下:
D:\python35\python.exe D:/python培训/s14/day3/def函数.py
test1 starting action...
test2 starting action...
test3 starting action...
并生成a.txt文件内容如下:
time 2016-08-10 10:52:49 end action
time 2016-08-10 10:52:49 end action
time 2016-08-10 10:52:49 end action
从这里也可以看出,通过定义函数,可以让程序更易于扩展
5、 函数和过程
过程定义:就是没有返回值的函数,在一个函数中没有使用return显示定义返回值时,python解释器会隐式的返回None,所以在python中即便是过程也算做函数
6、关于函数的返回值
代码如下:
def test01():
pass def test02():
return 0 def test03():
return 3,2,"hello","zf",["zhaofan","name"],{"name":"dean","age":23}
t1 = test01()
t2=test02()
t3=test03() print("from test01 return is %s:" %type(t1),t1)
print("from test01 return is %s:" %type(t2),t2)
print("from test01 return is %s:" %type(t3),t3)
运行结果如下:
D:\python35\python.exe D:/python培训/s14/day3/函数2.py
from test01 return is <class 'NoneType'>: None
from test01 return is <class 'int'>: 0
from test01 return is <class 'tuple'>: (3, 2, 'hello', 'zf', ['zhaofan', 'name'], {'name': 'dean', 'age': 23}) Process finished with exit code 0
从上面可以看出:
返回值=0:返回None
返回值的个数为1返回object
返回值的个数大于1:返回tuple
7、 函数的调用:
调用函数的时候()里可以有参数也可以没有
参数:
形参和实参
形参:形式参数,不是实际存在的,是虚拟变量,在定义函数和函数体的时候使用形参,目的是在函数调用时接收实参
位置参数和关键字参数(标准调用:实参与形参的位置一一对应;关键字参数调用:位置无序固定)
默认参数
参数组
注意:关键参数不能再位置参数前面
关于参数的列子:
#AUTHOR:FAN
#接收N个位置参数,转换成元组的形式
def test1(x,*args):
print(x)
print(args) test1(1,2,3,4,5,6,7) #**kwargs:把N个关键字参数,转换成字典的方式
def test2(**kwargs):
print(kwargs)
print(kwargs["name"])
print(kwargs["age"])
print(kwargs["sex"])
#
#
test2(name="zhaofan",age=22,sex="男")
test2(**{"name":"zhaofan","age":22,"sex":"男"}) def test3(name,**kwargs):
print(name)
print(kwargs) test3("alex",age=12,sex="mm") def test4(name,age=18,**kwargs):
print(name)
print(age)
print(kwargs) test4("zhaofan",sex="zz",age=12,hobby="tsl") def test5(name,age=12,*args,**kwargs):
print(name)
print(age)
print(args)
print(kwargs) test5("zhaofan",age=34,sex="m",hobby="tsla")
8、变量
局部变量只在函数里生效
字符串、整数等在函数里更改不会影响全局变量
列表和字典,集合,类等可以在函数里进行更改
例子演示:
#AUTHOR:FAN
name = "zhaofan"
def change_name(name):
print("before change:",name)
name = "dean"
print("after change:",name) change_name(name)
print("-----",name)
程序运行结果: D:\python35\python.exe D:/python培训/s14/day3/局部变量2.py
before change: zhaofan
after change: dean
----- zhaofan Process finished with exit code 0
9、 递归
def calc(n):
print(n)
if int(n/2) >0:
return calc(int(n/2))
print("----->",n) calc(10)
运行结果:
D:\python35\python.exe D:/python培训/s14/day3/递归.py
10
5
2
1
-----> 1 Process finished with exit code 0
递归的特性:
必须有一个明确的结束条件
每次进入更深一层时,问题规模要比上次减少
递归效率不高
递归循环只能循环999层
python基础之元组、文件操作、编码、函数、变量的更多相关文章
- Python基础-week03 集合 , 文件操作 和 函数详解
一.集合及其运算 1.集合的概念 集合是一个无序的,不重复的数据组合,它的主要作用如下 *去重,把一个列表变成集合,就自动去重了 *关系测试,测试两组数据之前的交集.并集.差集.子集.父级.对称差集, ...
- Python自动化 【第三篇】:Python基础-集合、文件操作、字符编码与转码、函数
1. 集合 1.1 特性 集合是一个无序的,不重复的数据组合,主要作用如下: 去重,把一个列表变成集合实现自动去重. set可以看成数学意义上的无序和无重复元素的集合,因此,两 ...
- python基础3之文件操作、字符编码解码、函数介绍
内容概要: 一.文件操作 二.字符编码解码 三.函数介绍 一.文件操作 文件操作流程: 打开文件,得到文件句柄并赋值给一个变量 通过句柄对文件进行操作 关闭文件 基本操作: #/usr/bin/env ...
- python学习笔记-(七)python基础--集合、文件操作&函数
本节内容 1.集合操作 2.文件操作 3.字符编码与转码 4.函数操作 1.集合操作 集合是一个无序的.不重复的数据组合: 1.1 常用操作 它的作用是: 1)自动去重:列表变成集合,自动去重: &g ...
- python基础知识-day7(文件操作)
1.文件IO操作: 1)操作文件使用的函数是open() 2)操作文件的模式: a.r:读取文件 b.w:往文件里边写内容(先删除文件里边已有的内容) c.a:是追加(在文件基础上写入新的内容) d. ...
- Python基础7:文件操作
[ 文件操作] 1 对文件操作流程 打开文件,得到文件句柄并赋值给一个变量 通过句柄对文件进行操作 关闭文件 现有文件如下: 昨夜寒蛩不住鸣. 惊回千里梦,已三更. 起来独自绕阶行. 人悄悄,帘外月胧 ...
- python基础学习笔记——文件操作
文件操作 初始文件操作 使用Python来读写文件是非常简单的操作,我们使用open()函数来打开一个文件,获取到文件句柄,然后通过文件句柄就可以进行各种各样的操作了 根据打开方式的不同能够执行的操作 ...
- Python基础知识(八)----文件操作
文件操作 一丶文件操作初识 ###f=open('文件名','模式',编码): #open() # 调用操作系统打开文件 #mode #对文件的操作方式 #encoding # 文件的编码格式 存储编 ...
- python基础八之文件操作
python的文件操作 1,打开文件 编码方式要和文件的编码方式相同! #open('路径','打开方式','指定编码方式') f = open(r'E:\pycharm\学习\day8\test', ...
- Python基础之 一 文件操作
文件操作 流程: 1:打开文件,得到文件句柄并赋值给一个变量 2:通过句柄对文件进行操作 3:关闭文件 模式解释 r(读) , w(写) ,a(附加)r+(读写的读), w+(读写的写),a+(读附加 ...
随机推荐
- sql表和字段的别名
1. sql表和字段的别名通过关键字 AS 来指定. 2.通常,定义字段别名的 AS 关键字可以省略,但我们建议不要省略 AS 关键字.别名(alias)是 SQL 的标准语法,几乎所有的数据库系统都 ...
- winform listview控件、容器控件
ListVies控件主要用于展示数据 常用属性: FullRowSelect:设置是否行选择模式.(默认为false) (开启之后一下选中一行数据) GridLines:设置行和列之间是否显示网格线. ...
- 解决rand()伪随机数
利用time改变种子 例: #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <time.h>//使用当前时钟做种子 ...
- wenbenfenlei
ICTCLAS: 该分词系统的主要思想是先通过CHMM(层叠形马尔可夫模型)进行分词,通过分层,既增加了分词的准确性,又保证了分词的效率.基本思路是:先进行原子切分,然后在此基础上进行N-最短路径粗切 ...
- 2016 Multi-University Training Contest 2
8/13 2016 Multi-University Training Contest 2官方题解 数学 A Acperience(CYD)题意: 给定一个向量,求他减去一个 α(>=0)乘以 ...
- IE8+兼容经验小结
最近一段时间,我都使用Flask+Bootstrap3的框架组合进行开发.本文就是在这种技术组合下,分享IE8+兼容性问题的解决方法.根据我的实践经验,如果你在写HTML/CSS时候是按照W3C推荐的 ...
- Unity Standard Assets 简介之 Characters
这篇介绍Characters资源包.包含三个文件夹:FirstPersonCharacter.RollerBall.ThirdPersonCharacter. FirstPersonCharacter ...
- SQLite 粗劣内容
SQLite 的官网 http://addons.mozillan.org/firefox/addon/sqlite-manager/ http://www.sqlite.org sqlite3 *s ...
- 你应该在开始API开发之前知道的事(上)(翻译)
这篇文章的源地址:http://dev.dota2.com/showthread.php?t=58317 由于文章内容较多,英语水平有限,准备尝试着以中英混搭的形式翻译,免得曲解一些不懂内容的意思.以 ...
- 转:Maven常用命令
转:Maven常用命令 Maven库: http://repo2.maven.org/maven2/ Maven依赖查询: http://mvnrepository.com/ Maven常用命令: 1 ...
